课题一 电火花技术简要介绍
一、电火花简介
电火花技术,又称放电加工,日本叫法是Electrical Discharge Machining,简称EDM,苏联称电蚀加工,Electroerosion Machining,指利用两极间的脉冲放电产生的电腐蚀现象,对材料进行加工的方法。
电火花与机械加工的区别:机械加工是通过机床部件的相对运动,用比工件硬的刀具切除工件上多余的部分,来得到成品零件的;而电火花加工,工具与工件并不接触,靠工具和工件之间不断的脉冲性火花放电,产生局部的瞬间高温,把金属材料蚀除掉。
电火花腐蚀的主要原因是什么?火花放电时火花通道中瞬间产生大量的热,达到很高的温度,足以使任何金属材料局部熔化、气化而蚀除,形成放电凹坑,从而将金属材料腐蚀掉。
二、电火花的历史
在插头或电器开关触点开、闭时,往往会产生火花而把接触表面烧毛,腐蚀成粗糙不平的凹坑而逐渐损坏,人们不断地避免这种有害的电腐蚀。1940年,苏联学者拉扎连科夫妇开始研究发明电火花加工,之后随着脉冲电源和控制系统的改进,而迅速发展起来。
最初使用的脉冲电源是简单的电阻-电容回路。50年代初,改进为电阻-电感-电容等回路。同时,还采用脉冲发电机之类的所谓长脉冲电源,使蚀除效率提高,工具电极相对损耗降低。
随后又出现了大功率电子管、闸流管等高频脉冲电源,使在同样表面粗糙度条件下的生产率得以提高。60年代中期,出现了晶体管和可控硅脉冲电源,提高了能源利用效率和降低了工具电极损耗,并扩大了粗精加工的可调范围。
到70年代,出现了高低压复合脉冲、多回路脉冲、等幅脉冲和可调波形脉冲等电源,在加工表面粗糙度、加工精度和降低工具电极损耗等方面又有了新的进展。在控制系统方面,从最初简单地保持放电间隙,控制工具电极的进退,逐步发展到利用微型计算机,对电参数和非电参数等各种因素进行适时控制。
三、有害的火花放电转化为有用的加工技术的条件
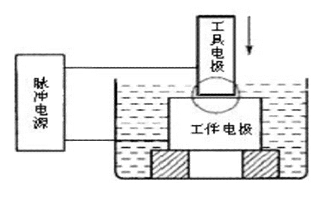
图1 电加工的示意图
1、使工具电极和工件被加工表面之间保持一定的放电间隙,几微米-几百微米,不能间隙太小或太大,应具备工具电极的自动进给和调节装置。
2、必须采用脉冲电源,使火花放电为瞬时的脉冲性放电,并在延续一段时间后,停歇一段时间,(放电持续时间10 -7-10-3 s)。
3、火花放电要在有一定绝缘性能的液体介质中进行,如煤油,皂化油,去离子水,液体介质又称工作液,具有较高的绝缘强度,同时可以将碳墨、金属悬浮物排除,具有冷却作用。
煤油导电吗?是不导电的。煤油可应用在清洁剂与燃料:煤油在煤油灯中稳定地燃烧,但是会散发油腻的黑烟。一些模型飞机也使用煤油或者使用掺有煤油的燃料。航空煤油则是搀有其它物质的煤油,不仅用于涡轮发动机,也是火箭发动机的燃料;做为清洁剂出售的煤油纯度高,不含重分子,因此可以去除金属表面强力附着的油腻和污物。如煤油与汽油相比,煤油的危险性较低。包括变压器里的油也是起到绝缘和散热的作用的。
四、电火花的加工的基本原理
进行电火花加工时,工具电极和工件分别接脉冲电源的两极,并浸入工作液中,或将工作液充入放电间隙。通过间隙自动控制系统控制工具电极向工件进给,当两电极间的间隙达到一定距离时,两电极上施加的脉冲电压将工作液击穿,产生火花放电。
在放电的微细通道中瞬时集中大量的热能,温度可高达一万摄氏度以上,压力也有急剧变化,从而使这一点工作表面局部微量的金属材料立刻熔化、气化,并爆炸式地飞溅到工作液中,迅速冷凝,形成固体的金属微粒,被工作液带走。这时在工件表面上便留下一个微小的凹坑痕迹,放电短暂停歇,两电极间工作液恢复绝缘状态。
紧接着,下一个脉冲电压又在两电极相对接近的另一点处击穿,产生火花放电,重复上述过程。这样,虽然每个脉冲放电蚀除的金属量极少,但因每秒有成千上万次脉冲放电作用,就能蚀除较多的金属,具有一定的生产率。
在保持工具电极与工件之间恒定放电间隙的条件下,一边蚀除工件金属,一边使工具电极不断地向工件进给,最后便加工出与工具电极形状相对应的形状来。因此,只要改变工具电极的形状和工具电极与工件之间的相对运动方式,就能加工出各种复杂的型面。
工具电极常用导电性良好、熔点较高、易加工的耐电蚀材料,如铜、石墨、铜钨合金和钼等。在加工过程中,工具电极也有损耗,但小于工件金属的蚀除量,甚至接近于无损耗。
工作液作为放电介质,在加工过程中还起着冷却、排屑等作用。常用的工作液是粘度较低、闪点较高、性能稳定的介质,如煤油、去离子水和乳化液等。
五、电火花加工的微观过程
这一过程大致分为以下几个阶段:
(1)极间介质的电离、击穿,形成放电通道。
放电通道是有大量带正电和负电的粒子以及中型粒子组成,带电粒子高速运动,相互碰撞,产生大量热能,使通道温度升高,通道中心温度可达到10000摄氏度以上。由于放电开始阶段通道截面很小,而通道内有高温热膨胀形成的压力高达几万帕,高温高压的放电通道急速扩展,产生一个强烈的冲击波向四周传播。在放电的同时还伴随着光效应和声效应,这就形成了肉眼所能看到的电火花。
(2)电极材料的融化,汽化热膨胀。
液体介质被电离、击穿,形成放电通道后,通道间带负电的粒子奔向正极,带正电的粒子奔向负极,粒子间相互撞击,产生大量的热能,使通道瞬间达到很高的温度。通道高温首先使工作液汽化,进而气化,然后高温向四周扩散,使两电极表面的金属材料开始融化直至沸腾气化。气化后的工作液和金属蒸汽瞬间体积猛增,形成了爆炸的特性。所以在观察电火花加工时,可以看到工件与工具电极间有冒烟现象并听到轻微的爆炸声。

图2 电加工的微观物理过程
(3)电极材料的抛出。
正负电极间产生的电火花现象,使放电通道产生高温高压。通道中心的压力最高,工作液和金属汽化后不断向外膨胀,形成内外瞬间压力差,高压力处的熔融金属液体和蒸汽被排挤,抛出放电通道,大部分被抛入到工作液中。加工中看到的桔红色火花就是被抛出的高温金属熔滴和碎屑。
(4)极间介质的消电离。
在电火花放电加工过程中产生的电蚀产物如果来不及排除和扩散,那么产生的热量将不能及时传出,使该处介质局部过热,局部过热的工作液高温分解,结碳,使加工无法进行,并烧坏电极。因此为了保证电火花加工过程的正常进行,在两次放电之间必须有足够的时间间隔让电蚀产物充分排除,恢复放电通道的绝缘性,使工作液介质消电离实际上,电火花加工的过程远比上述复杂,它是电力、磁力、热力、流体动力、电化学和胶体化学等综合作用的过程。到目前为止,人们对电火花加工过程的了解还有限,需要进一步研究。
总结一下,放电加工时,金属材料蚀除的微观过程分为以下四个连续的阶段:
1.极间介质的击穿与放电,形成放电通道;
2.介质的热分解,电极材料融化气化,热膨胀并冒出气泡,工作液变黑;
3.电极材料的抛出;
4.极间介质的消电离,恢复绝缘。
六、主要名词术语
1、工具电极:电火花加工用的工具,工具或电极。
2、放电间隙:指加工时工具和工件之间产生的火花放电的一层距离间隙。
3、脉冲电源:给放电间隙提供一定能量的电脉冲。
4、伺服进给系统:用作使工具电极伺服进给,自动调节。
5、工作液介质:电火花加工时,工具和工件之间的放电间隙必须浸泡在有一定绝缘性能的液体介质中,此液体介质称工作液。
6、电蚀产物:金属微粒小屑和煤油在高温下分解出来的碳黑。
7、电参数电规准:电加工过程中的电压、电流、脉宽、脉间、功率和能量等电参数。
8、脉冲宽度ti:加到工具和工件上放电间隙两端的电压脉冲的持续时间。粗加工用大脉宽大于100us,精加工时用小脉宽小于50us。
9、脉冲间隔to:是指两个电压脉冲之间的时间,利用放电间隙进行消电离和恢复绝缘。
10、击穿延时td:是从间隙两端加上电压脉冲到介质击穿之前的一段时间。
11、停歇时间teo:即放电间隔,是指相邻两次放电之间的时间间隔。teo=to+td。
12、脉冲周期tp:从一个电压脉冲开始到下一个电压脉冲开始之间的时间。
13、放电时间te:是指介质击穿后,间隙中通过放电电流的时间,称电流脉宽。

图3 电脉冲加工过程各段时间示意图
(其中Ti-脉宽、Td-击穿延时、To-脉间、Te-放电时间、Tp-脉冲周期、Teo-停歇时间)
14、开路电压:间隙击穿之前的极间峰值电压。
15、加工电压:是指正常加工时,间隙两端的电压即电压表的读数。
16、加工电流:通过加工间隙电流算术平均值。精加工时小,粗加工时大。
17、二次放电:是指在已加工面上,由于加工屑的介入,进行再次放电的现象。
18、极性效应:由于正负极性不同而彼此电蚀量不一样的现象,即工件为正,正极性加工;工件为负,负极性加工。
19、吸附效应:碳粒带负电荷,向正极移动,正的电极表面吸附了分解游离出来的碳微粒,减小电极损耗,保护了正极。
20、粗加工:用一个电极加工掉很大的余量而电极尺寸形状基本不变。
21、精加工:脉宽窄,正极工具表面吸附的碳黑很少,挡不住负电子对正极的强烈冲击,因此损耗比会增大,但此时余量小,绝对损耗量也不大。
22、电加工金属:由难至易,钨-铜-银-钼-铝-钽-铂-铁-镍-钢-钛。一般成型机电极材料用铜,线切割电极用钼。
七、电火花加工的优点及局限性
1.电火花加工的优点:
(1)可以加工难以用金属切削方法加工的零件,不受材料硬度影响。
(2)由于工具电极与工件电极不直接接触,没有机械切削力。所以在制作工具电极时不必考虑其受力特性,工具电极可以做的十分微细,能进行微细加工和复杂型面加工。
(3)电火花加工是通过脉冲放电来蚀除金属材料的,而脉冲电源的参数随时可调,因此在同一情况下,只需调整电参数即可切换粗、半精、精、超精加工。
2、电火花加工的局限性
(1)加工速度比较慢,需先切削掉大部分余量,再进行电火花加工。
(2)被加工的工件只能是金属等导体材料。
(3)存在电极损耗,由于电火花靠热、电来进行蚀除金属,电极也会有所损耗。多在尖角或底面,影响了成型精度。
(4) 加工过程必须在工作液中进行。电火花加工时放电部位必须在工作液中,否则将引起异常放电。
八、电火花加工的分类与发展概况
1、根据目前电火花设备使用情况来分,可分为3大类:
(1)电火花穿孔成型加工
采用成型工具电极进行仿形电火花加工的方法。
(2)电火花线切割加工
利用金属线作为电极对工件进行切割的方法。
(3)其他类型电火花加工
如电火花磨削加工、电火花回转加工、电火花研磨、珩磨以及金属电火花表面强化、刻字等。
2、我国电火花加工的发展
20世纪50年代初期,我国开始研究和试制电火花镀敷设备,即把硬质合金用电火花工艺镀敷在高速钢金属切削刀具和冷冲模刃口上,提高金属切削刀具和模具的使用寿命。同时我国还成功研制了电火花穿孔机,并广泛应用于柴油机喷嘴小孔的加工。
60年代初,上海科学院电工研究所成功研制了我国第一台靠模仿形电火花线切割机床。随后又出现了具有我国特色的冷冲模工艺,即直接采用凸模打凹模的方法,使凸凹模配合的均匀性得到了保证,大大简化了工艺过程。
60年代末,上海电表厂张维良工程师在阳极切割的基础上发明了我国独有的高速走丝线切割机床。上海复旦大学研制出电火花线切割数控系统。
70年代随着电火花工艺装备的不断进步,电火花型腔模具成型加工工艺已经成熟。线切割工艺也从加工小型冷冲模发展到可以加工中型和较大型模具。切割厚度不断增加,加工精度也不断提高。
80年代以来计算机技术飞速发展,电火花加工也引进了数控技术和电脑编程技术,数控系统的普及,使人们从繁重、琐碎的编程工作中解放出来,极大的提高了效率。
九、型号知识
例:DB703的含义
D-类代号:电;
B-宝玛;
7-电火花成型机;电火花线切割机床;
0-穿孔机;
3-折算系数:最大穿孔直径。
例:DK77的含义
D-类代号:电;
K-数控;
7-电火花成型机;电火花线切割机床;
7-往复走丝电火花切割机。
第二篇:工程技术介绍
Appropriate Technology
Introduction to Engineering
Tech Adoption Worldwide?For the past 3 years, China has been the world’s largest importer of ICT
?In India, 50% of all urban dwellers have mobile or fixed telephones; however, only 6% of rural Indians have phones
Tech Diffusion?Technology is spreading to emerging markets faster than ever before
?The technology lag is decreasing
?New technologies are entering developing countries and “leapfrogging” over older technologies (i.e., cell phones)
Rates of Tech Diffusion
?Tech diffusion is lowest in Latin American countries
?Less than 2% of the business workforce in Chile and Brazil are in ICT, Why?
–
–
–
–Inward-looking economic policiesImport restrictions on technologyProblems in the educational systemsLess money is spent on R&D: Developed countries spend 2.3% GDP on R&D, East Asian, 1.4%. But, Latin America spends only 0.6%
What is appropriate technology?
?Appropriate technology has been used to cover a wide range of both technologies and lifestyles including sustainable living, alternative fuels, and ethical technology transfers.
?A technology is considered appropriate if it solves a social problem without many adverse negative effects.
?Every new technology has consequences for society. A technology is appropriate when its intended positive consequences outweigh its unintended negative consequences
How do we evaluate appropriateness??There are three ways of evaluating appropriateness: technical, cultural, and economic.
–Technical--considering the technical knowledge and background of the people who will be using this technology.
–Cultural—the relationship of the technology to the critical social systems in the society including family systems, religious beliefs, division of labor in a society, and levels of education and training. –Economic--a technology's effect on income levels and income distribution in a society and income disparity between different socio-economic
Factorsfor the assessment of an appropriate technology
?Various factors for assessment of appropriateness would include the following1:
–What is the need?
–Is there an adequate business environment in place for this technology?
–What is the best technical option for the transfer? (Some issues include the requirements for operating the technology, repair facilities for the technology, scope of the technology)–What are the possible unintended negative effects of the technology?
–What are the broader cultural, political and/or social effects of the technology?
Everts, S. (1998). Gender and technology. Empowering women, engendering development. New York: Zed Books, p 34.
Examples of appropriate technologies???Please click on the topic above to read more about each of these appropriate technologies

Renewable Energy
?Renewable energy industries produce energy using resources such as sunlight, wind, water current, and organic waste
?Renewable sources of energy are diffuse (spread thin) and intermittent. One example of the diffuseness feature is that a 1000-megawatt solar farm might occupy about 5000 acres of land, while a nuclear power station with the same generating capacity only requires around 150 acres.
Examples of Renewable Energy--Biomass?Many developing countries depend on wood and agricultural waste for energy.
?Almost half of India's and nearly 90 percent of total energy consumption in several small countries in Africa is provided by wood.
?Sweden has increased its use of biomass dramatically in the last ten years and presently uses fast-growing willow trees and other organics to supply 20 percent of its total energy supply.
Billion KilowatthoursExamples of Hydropower450400350300250Modern large hydropower
plants are very expensive to build; however, hydropower is not distributed equally around the world. 200150501000
Top Hydroelectric Generating Countries. Source: Energy Information Administration, US Department of Energy.
In the US, about 10 percent of the total electricity is generated from hydropower. It has dropped since the 1940s when 40 percent of the electricity in the US was hydropower.Disruption of the environment is the major reason why there are fewer hydropower plants being built today.
Examples of Renewable Energy--Geothermal Energy
?The Philippines has the highest percentage of power generated from geothermal sources; 22 percent of its electricity is generated with geothermal steam. ?The percentage of geothermal is high (at least 10-20 percent of the total) in four other countries: Costa Rica, El Salvador, Kenya, and Nicaragua.
?Central America, parts of Southeast Asia, and the western United States have the greatest potential for major reliance on geothermal energy. Promising sites also exist in parts of southern Europe and East Africa.
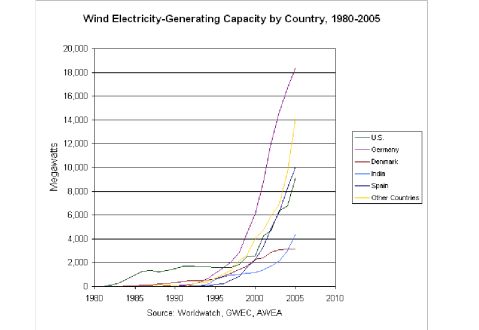
Examples of Renewable Energy--WindExperts in the field of alternative energy feel wind energy is the most auspicious (favorable) of the renewables. Windmills mechanically turn turbines without an intermediate stage of heating water. In the early 1980s, more than 8000 wind machines were installed in California. One of the largest wind farms is presently found in the rolling, windswept hills of the Altamont Pass, east of San Francisco.
Attempts to reap economies of scale by building larger windmills capable of generating more than one megawatt of power have been suppressed by
Click on graph to see an enlarged viewtechnical problems. Capital costs have remained prohibitive.
Examples of Renewable Energy—The Ocean
?Three methods for extracting energy from the sea have been reviewed seriously: wave power, ocean thermal energy conversion, and tidal power.
–Wave Power aims to harness the motion of the waves using a variety of devices.
–Ocean thermal energy conversion seeks to exploit the temperature differences between the warm surface layer and the colder deep waters of the world's oceans.
–Tidal power is similar to hydroelectric power in the sense it is severely restricted by geography. It requires long, tapering bays that drive the tide into a large bore as it moves along the channel. The incoming tide can then be trapped behind a barrier of some sort and ultimately used to drive turbines on its way out again.
Examples of Renewable Energy--Photovoltaic Cells
A conference room covered in photovoltaic cells at the Bewag power plant in Berlin. ? Wolfgang Hoffmann
/stories/2003/feb03/energy.htm
?Semi-conductors have the unique property of being able to turn sunlight directly into electric current. This application is surfacing in a variety of items such as solar-powered calculators, refrigerators, and satellites. ?According to some energy forecasters, solar cells installed on rooftops may allow for a much greater decentralization of electricity than other technologies.
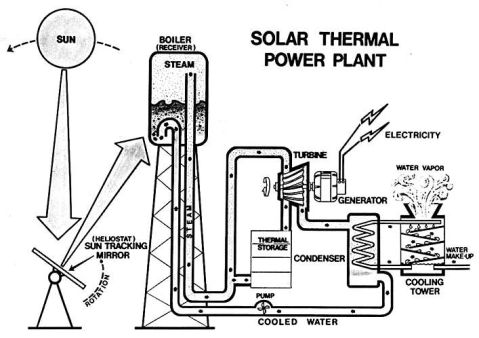
Examples of Renewable Energy--Thermal Solar Power
Solar thermal power technologies and solar ponds are projected to have competitive generating costs by the end of the century. The capital cost for expensive items like polished mirrors to track the path of the sun is presently exorbitant.http://www.sandiego.edu/weather/images/N/solar_thermal_power_plant.jpg
Click on diagram to see enlarged picture
Solar Two
Example: Solar Two—the solar energy was collected through a field of individually guided mirrors, called heliostats. The sunlight heats salt to 1,050 degrees Fahrenheit, which turns the salt into a liquid (or molten salt). The liquid and hot salt was then piped away, stored, and used to power a steam turbine.
?
Smart Growth
?Smart growth is development that accommodates the needs of a community without sacrificing the environment.
?Smart growth aims to balance development and environmental protection by creating new developments that are:
–centered more in the towns and cities
–include alternative transit options (trains, bike paths, and safe walkways)
–have mixed use development.
?Mixed use development moves away from the post-WWII ideal of single-home-only suburbs to a model that includes housing, commercial, and retail space in the same development.
Types of Smart Growth
?Smart growth means that less land can accommodate new development: this development is sometimes called compact development. There are three common techniques to achieve compact development: infill development, brownfields redevelopment, and cluster development.
Infill development
Infill development is development that attempts to add additional housing or business facilities inside an existing development. This way, a city can fill up unused space in a particular area. An example of a recent mixed use development is the Paseo Colorado complex in Pasadena, California. The new complex was built in center of town and includes a two-level shopping center with four stories of apartments above the shopping areas.
Cluster development
Cluster development allows for similar dwellings as does “regular” developments; however, the individual lot sizes are
reduced and room is left for open spaces in the development
Brownfields redevelopment
Brownfields redevelopment is development that targets the empty factories inside the city and develops them into new living and/or retail space. One of these former DelMonte canneries, Plant 51, is the site of a brownfield development to convert the

cannery into lofts.
?
Green Buildings
?Buildings are a major source of air pollution in the US. According to the US Department of Energy?Buildings emit
–52 percent of all sulfur dioxide
–19 percent of all nitrous oxide
–38 percent of carbon dioxide
–5 percent of particulate emissions
?Considering the number of homes and businesses in the US—over 76 million residential and 5 million commercial buildings at last count—this problem is considerable.
Techniques used in Green Construction?Designing energy efficient buildings. Energy efficiency is the most important factor in green construction.
The Solectrogen House is an off-grid PV-powered residence in Nicasio, CA. It was designed to use active and passive solar energy, serve as a live-in laboratory for energy conservation and alternative energy products, and be a comfortable, traditionally attractive home with all the conveniences of modern living. Source:
Techniques used in Green Construction
?Reducing material use in construction. Smaller is better for the environment; using less materials is always preferable from an environmental point of view.
?However, the trend today is for houses to get larger and larger.
?Using low-impact materials during construction.
–Many construction and building materials contain toxins. Many types of carpeting, for example, emit gases as they age.
–Research has found, particularly in houses that are tightly sealed, that their exposures to dangerous chemicals and pesticides is much higher inside the house rather than outside the house.
?
Sustainable Agriculture
?Sustainability is built upon three broad goals: farm profitability, improvement of the environment, and increased quality of life for farmers and their communities.
Practices used in sustainable agriculture
?Integrated pest management (IPM) is a system for managing pests to keep them at levels where they cause minimal damage to crops.
?Conservation tillage--any plowing system that leaves at least 30 percent of the soil surface covered with residue from the year’s plantings. This is done so that there will be enough soil coverage to decrease soil erosion.
Rows of soybean plants emerge from a field covered with old corn stalks from the previous harvest. These soybeans were planted in narrower (15-inch) rows because as they mature their big leaves will quickly shade the ground, making it harder for the sun to warm weed seeds that may lie between the rows. This natural canopy from the growing soybean plants can help farmers reduce the need for herbicides (weed killers). (CTIC/Towery photo) Source: http://www.ctic.purdue.edu/Core4/CT/images/cornsoytt.jpg[2002, February 4].
Practices used in sustainable agriculture
?Enhanced nutrient management includes testing of the soil before using any fertilizer. The goal of nutrient management is to minimize unused nutrients.
?Precision agriculture is the newest and the most technology-intensive technique in sustainable agriculture. Precision agriculture uses information technologies including global positioning systems (GPS) and remote sensing to achieve optimal farming outputs.
?
Click on graph to return to presentation
Click on diagram to return to presentation
