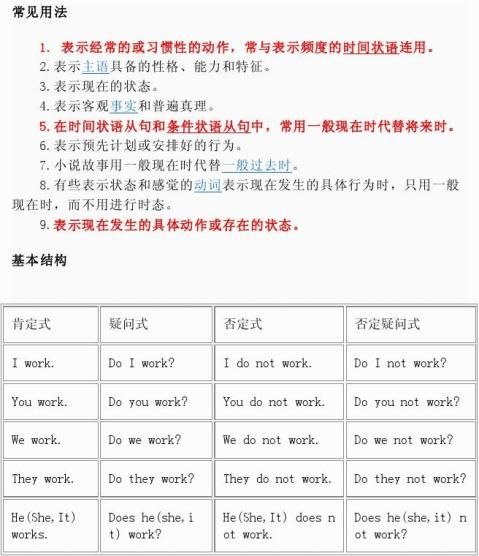
常见用法
1. 表示经常的或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用。
2.表示主语具备的性格、能力和特征。 3.表示现在的状态。
4.表示客观事实和普遍真理。 5.在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中,常用一般现在时代替将来时。
6.表示预先计划或安排好的行为。 7.小说故事用一般现在时代替一般过去时。
8.有些表示状态和感觉的动词表示现在发生的具体行为时,只用一般现在时,而不用进行时态。
9.表示现在发生的具体动作或存在的状态。
基本结构
肯定式 疑问式 否定式 否定疑问式
I work. Do I work? I do not work. Do I not work?
You work. Do you work? You do not work. Do you not work?
We work. Do we work? We do not work. Do we not work?
They work. Do they work? They do not work. Do they not work?
He(She,It) works. Does he(she,it) work? He(She,It) does not work. Does he(she,it) not work?
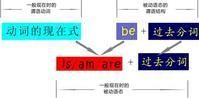
口诀
当主语是第三人称单数时 :
肯定句 主语+动词单三+其他 否定句 主语+doesn't+动词原形+其他
一般疑问句 Does+主语+动词原形+其他 肯定回答 Yes,主语+does 否定回答 No,主语+doesn't
特殊疑问句 特殊疑问词+一般疑问句
当主语不是第三人称单数时
肯定句 主语+动词原形+其他 否定句 主语+don't+动词原形+其他 一般疑问句 Do+主语+动词原形+其他
1.表示经常的或习惯性的动作,常与表示频率的时间状语连用。
时间状语: always, usually,regularly,every morning/night/evening/day/week/year,often,sometimes,occasionally,from time to time, twice a week,rarely,seldom,once a month, hardly, ever, never.
e.g. I leave home for school at 7:00 every morning.
2.表示主语具备的性格、能力、特征和状态。
e.g. I don't want so much.
Ann Wang writes good English but does not speak well.
3.表示客观事实和普遍真理。
e.g The earth moves around the sun.
Shanghai lies in the east of China.
4.在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中,常用一般现在时代替将来时。
5.表示预先计划或安排好的行为。
6.小说故事用一般现在时代替一般过去时。新闻报道类的内容,为了体现其“新鲜”性,也用一般现在时来表示过去发生的事情。
7.有些表示状态和感觉的动词表示现在发生的具体行为时,只用一般现在时,而不用进行时态。
8.表示现在发生的具体动作或存在的状态
9表示格言或警句中。 e.g Pride goes before a fall. 骄者必败。
☆注意★:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。
例:Columbus proved that the earth is round.. 第一句用一般现在时
4.现在一般时常用的时间词语
常用于现在一般时的词语有 sometimes/usally/often, every day[week, year], now , always 等。请记住:这些时间词语只是辅助作用,这些词语也可用于其它的时态,所以谓语动词变化才是最关键的。
疑问句型
表示将来
在一些情况下,一般现在时能用来表示将来时。
1. 谓语动词是:come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return,live,fly 等,可以表示将来发生的动作。
The train leaves at six tomorrow morning.
When does the bus start? It starts in ten minutes.
2. 在时间或条件从句中,一般要用一般现在时表示将来,而不用一般将来时。
When Bill comes , ask him to wait for me.
I'll write to you as soon as I arrive there.
3. 谓语动词是 hope, take care that, make sure that 等后的宾语从句中,用一般现在时表示将来。
I hope they have a nice time next week.
Make sure that the windows are closed before you leave the room.
4.这种时态可以和一个时间短语连用以表示已确定的、对将来的安排:
如:The boys start school on Monday.男孩们星期一开学。
I leave tonight.我今天晚上动身。
5.这一用法代替了较常用的现在进行时态:
如:The bys are starting school on Monday.男孩儿们星期一就要开学了。
I’m leaving tonight.我今天晚上就动身。
6.这两种时态之间的差别是:
(1)一般现在时比现在进行时具有的个人色彩更少: I’m leaving tonight通常可能含有我决定离开的意思,但I leave tonight可指这是计划的一部分,但计划不一定是我订的。
(2)一般现在时要比现在进行时听起来更为正式。计划开办一个新分店的百货商店很可能说Our new branch opens next week(本店新设分店下周开业),而不说Our new branch is opening next week。
(3)现在进行时显得累赘的地方就用一般现在时,例如在谈到像旅程安排那样的一系列预定的将来的动作时,可以这样说:
We leave at six,arrive in Dublin at ten and take the plane on?
我们6点出发,10点到达都柏林,并在??乘飞机??
而不说:
We are leaving at six,arriving in Dublin at ten and taking the plane on然而要注意,在像My train leaves at six(我常乘坐的火车6点开)这样的句子中,用一般现在时表示习惯性动作,这里就不能用现在进行时来代替。
编辑本段表示过去
1.用于某些动词(tell, say, hear, learn, gather等)表示不确定的过去时间:
John tells me you will leave tomorrow. 约翰告诉我你明天离开。
I hear that he got married again last month. 我听说他上个月结婚了。
Mary says that you told her to come over here. 玛丽说是你让她到这儿来的。
2. 当要陈述一个客观事实时,有时即使有过去时间状语也可用一般现在时:
The story is set in the summer of 1937. 故事的背景是19xx年夏天。
The story begins in the year 1937. 故事开始于19xx年。
编辑本段句型区别
一般现在时与现在进行时的区别
准确理解两种时态的主要含义:
一般现在时 1.表示事物的本质特性或客观存在,没有时限性。 The table ____ soft。 (feels) 表特性特征。 Japan ___ to the east of China。 (lies) 表客观事实 2.现阶段经常性、习惯性的行为,可带频率时间。 The shop closes at 7:30 p.m. Father doesn’t smoke. (习惯) 3.表说话时的状态,感觉或结果,一般用状态动词,如:It doesn’t matter. Does it hurt? (感觉结果) 4.特殊用法: -在条件、时间、让步从句中用现在时代替将来。 -If you go there, I’ll help you. —用在begin ,come ,go ,leave ,return ,open ,close 等短暂位移动词表规定计划。 The plane takes off at 11:30. (不受主观支配的计划) -在剧本、解说、标题或there (here)开头的句中表进行 There goes the bell/Here comes Mr.Wang. I declare the meeting opens.(正在宣布) He meets the ball and hits back to No.2 (正在发生) 现在进行时 1.说话时正在发生,进行的动作 Look! Dark clouds are gathering . (正在发生) 2.表现阶段正在进行,但此刻不一定正在进行的事。 He usually gets up at 6:00 , but this week he is getting up at 7:00. (现阶段正在进行,但说话时不一定在起床) 3.现在进行时的特殊意义 -表示主观打算常用于 go , come , leave , start , begin 等,位移、趋向动词。 How long are you staying here ? (准备停留) -表示眼前刚过去的语意即“话音刚落”,适用于tell , say , talk , discuss ?. You don’t believe it ? You know I’m telling the truth. -表示安慰、关心、喜欢、讨厌??感情色彩。 He is always making noises in class. (讨厌) -在条件、时间、让步状语从句中表示将来正在进行。 Don’t bother him if he is reading this time tomorrow. 严格区分进行时与一般时的语义 1. 持续动词的一般时表持续情况,经常性,习惯性行为或客观存在的事实,进行时表暂时性或有限时刻的持续。 2.短暂动词的一般时叙述事实,特征,能力而短暂动作进行时描述反复发生,即将发生或刚开始行为。 3.短暂动词和静态动词一般时表示实际情况客观状态、结果、特征、特性,进行时表未完成含开始或渐进之意。 The bus stops. (车停了-事实) The bus is stopping. (渐渐停下来) I love the job. (静态事实) I am loving the job. ( 渐渐爱上了) 4.come ,go ,leave ,start ,return ,move ,reach ,sail ,fall 等一般时态表客观规定计划,进行时表主观打算推测。 Flight 254 leaves at 5:30. (表主观打算) The plane is taking off an hour later.(主观判断) 5.现在进行时带always ,often ,usually ,sometimes ,等频率副词表感情色彩,一般现在时则没有此用法。
第二篇:一般现在时常见用法
口诀
当主语是第三人称单数时
一般现在时
肯定句 主语+动词单三+其他
1.表示经常的或习惯性的动作,常与表示频率的时间状语连用。 时间状语: always, usually,regularly,every
morning/night/evening/day/week/year,often,sometimes,occasionally,from time to time,twice a week,rarely,seldom,once a month, hardly, ever,never.
e.g. I leave home for school at 7:00 every morning.
.表示主语具备的性格、能力、特征和状态。
e.g. I don't want so much.
Ann Wang writes good English but does not speak well.
比较:Now I put the sugar in the cup.
I am doing my homework now.
3.表示客观事实和普遍真理。
e.g The earth moves around the sun.
Shanghai lies in the east of China.
4.在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中,常用一般现在时代替将来时。
5.表示预先计划或安排好的行为。
6.小说故事用一般现在时代替一般过去时。新闻报道类的内容,为了体现其“新鲜”性,也用一般现在时来表示过去发生的事情。
7.有些表示状态和感觉的动词表示现在发生的具体行为时,只用一般现在时,而不用进行时态。
8.表示现在发生的具体动作或存在的状态
9表示格言或警句中。 e.g Pride goes before a fall. 骄者必败。 ☆注意★:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。
例:Columbus proved that the earth is round.. 第一句用一般现在时,用于操作演示或指导说明的示范性动作,表示言行的瞬间动作。再如:Now watch me, I switch on the current and stand back. 第二句中的now是进行时的标志,表示正在进行的动作的客观状况,所以后句用一般现在时。
编辑本段表达方法
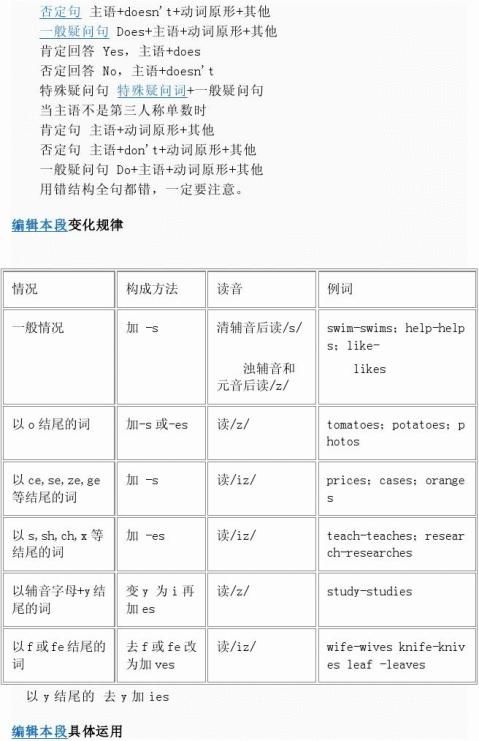
主要通过谓语动词的变化和用时间词语来表示,其中最主要的是谓语动词的变化。现在一般时动词变化的规则是:
1.如果主语是名词复数和第一人称I、 we ,谓语动词不用做任何变化,即仍然用动词原型表示:
We usually go to school at 7:30. 我们通常7:30上学去。[go] My parents give ten yuan to my sister every week.我父母每星期给我妹妹十元钱。[give]
2.主语是任何一个单数名词或者是第三人称单数,谓语动词要进行必要的变化。特别提一点:不可数名词也算作单数处理。
3.谓语动词的变化规律是:
(1) 在动词后加-s,-es
read - reads,write - writes,say - says
(2) 以s,x,ch,sh 结尾的词加-es
一般现在时
teach - teaches,wash - washes,guess - guesses
(3) 以辅音字母+y结尾的词变y为i再加-es
try - tries,carry - carries
(4) 特殊变化的词
be (是) - am, is, are
I am
she/he/it, 名词单数都用 is
we, you, they, 名词复数都用are
have (有) - have, has
I, we, you, they, 名词复数都用have
she/he/it is, 名词单数都用 has
(5) 助动词,不论单复数、不论什么人称都没有变化,都用 can, may, must, need, ought to 等。而且,句子中有了助动词,谓语动词就不需要有任何变化了,即用动词原形表示。
请看下面的例子:
Lucy is at home now. 露茜现在在家。
We have six classes every day. 我们每天上六节课。
I often get up at 6:30. 我经常6:30起床。
Jack likes Chinese food very much. 杰克很喜欢中国饮食。 We can see some pictures on the wall. 我们能看到墙上的画。
4.现在一般时常用的时间词语
常用于现在一般时的词语有 sometimes/usally/often, every
day[week, year], now , always 等。请记住:这些时间词语只是辅助作用,这些词语也可用于其它的时态,所以谓语动词变化才是最关键的。
编辑本段疑问句型
1.对于谓语动词或助动词是 be、have、can/may/must 等,将这些词移到主语前面。
Are you students?Yes, we are. / No, we aren't.
Is Jane in the classroom? Yes, he is. / No, he isn't.
Does the house have two rooms? Yes,it does / No, it doesn't. Is there any water in the glass? Yes, there is. / No, there isn't. Can you swim? Yes, I can. / No, I can't.
2.谓语动词是实义动词,方法是在主语前加助动词do或does构成,句中动词要改用原型动词。do 用于第一人称和名词复数,does 用于第三人称单数和名词单数或不可数名词。
Do you know it?Yes, I do. / No, I don't.
Does she have a pen?Yes, she does. / No, she hasn't.[have 这里是实义动词]
Do they play basketball after school? Yes, they do. / No, they don't.
编辑本段否定句型
1.谓语动词或助动词是 be、have、can/may/must 等,在将助动词后加not.
I am not at college.
Mr. Wang isn't 50 years old.
The Jacksons doesn't have two sons.
You may not go now.
2.谓语动词是实义动词,是在谓语动词前加do not 或does not,谓语动词改用动词原型。
I don't have luch at home.
They don't play basketball on the sportsground.
Mr.Jimmy doesn't know French.
编辑本段表示将来
在一些情况下,一般现在时能用来表示将来时。
1. 谓语动词是:come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return,live,fly 等,可以表示将来发生的动作。
The train leaves at six tomorrow morning.
When does the bus start? It starts in ten minutes.
2. 在时间或条件从句中,一般要用一般现在时表示将来,而不用一般将来时。
When Bill comes , ask him to wait for me.
I'll write to you as soon as I arrive there.
3. 谓语动词是 hope, take care that, make sure that 等后的宾语从句中,用一般现在时表示将来。
I hope they have a nice time next week.
Make sure that the windows are closed before you leave the room.
4.这种时态可以和一个时间短语连用以表示已确定的、对将来的安排: 如:The boys start school on Monday.男孩们星期一开学。 I leave tonight.我今天晚上动身。
5.这一用法代替了较常用的现在进行时态:
如:The bys are starting school on Monday.男孩儿们星期一就要开学了。
I’m leaving tonight.我今天晚上就动身。
6.这两种时态之间的差别是:
(1)一般现在时比现在进行时具有的个人色彩更少: I’m leaving tonight通常可能含有我决定离开的意思,但I leave tonight可指这是计划的一部分,但计划不一定是我订的。
(2)一般现在时要比现在进行时听起来更为正式。计划开办一个新分店的百货商店很可能说Our new branch opens next week(本店新设分店下周开业),而不说Our new branch is opening next week。
(3)现在进行时显得累赘的地方就用一般现在时,例如在谈到像旅程安排那样的一系列预定的将来的动作时,可以这样说:
We leave at six,arrive in Dublin at ten and take the plane on? 我们6点出发,10点到达都柏林,并在??乘飞机??
而不说:
We are leaving at six,arriving in Dublin at ten and taking the plane on然而要注意,在像My train leaves at six(我常乘坐的火车6点开)这样的句子中,用一般现在时表示习惯性动作,这里就不能用现在进行时来代替。
编辑本段表示过去
1.用于某些动词(tell, say, hear, learn, gather等)表示不确定的过去时间:
John tells me you will leave tomorrow. 约翰告诉我你明天离开。 I hear that he got married again last month. 我听说他上个月结婚了。
Mary says that you told her to come over here. 玛丽说是你让她到这儿来的。
2. 当要陈述一个客观事实时,有时即使有过去时间状语也可用一般现在时:
The story is set in the summer of 1937. 故事的背景是19xx年夏天。
The story begins in the year 1937. 故事开始于19xx年。 编辑本段句型区别
一般现在时与现在进行时的区别
准确理解两种时态的主要含义:
一般现在时
1.表示事物的本质特性或客观存在,没有时限性。
The table ____ soft。 (feels) 表特性特征。
Japan ___ to the east of China。 (lies) 表客观事实
2.现阶段经常性、习惯性的行为,可带频率时间。
The shop closes at 7:30 p.m.
Father doesn’t smoke. (习惯)
3.表说话时的状态,感觉或结果,一般用状态动词,如:It doesn’t matter. Does it hurt? (感觉结果)
4.特殊用法:
-在条件、时间、让步从句中用现在时代替将来。
-If you go there, I’ll help you.
—用在begin ,come ,go ,leave ,return ,open ,close 等短暂位移动词表规定计划。
The plane takes off at 11:30. (不受主观支配的计划) -在剧本、解说、标题或there (here)开头的句中表进行 There goes the bell/Here comes Mr.Wang.
I declare the meeting opens.(正在宣布)
He meets the ball and hits back to No.2 (正在发生)
现在进行时
1.说话时正在发生,进行的动作
Look! Dark clouds are gathering . (正在发生)
2.表现阶段正在进行,但此刻不一定正在进行的事。
He usually gets up at 6:00 , but this week he is getting up at 7:00. (现阶段正在进行,但说话时不一定在起床)
3.现在进行时的特殊意义
-表示主观打算常用于 go , come , leave , start , begin 等,位移、趋向动词。
How long are you staying here ? (准备停留)
-表示眼前刚过去的语意即“话音刚落”,适用于tell , say , talk , discuss ?.
You don’t believe it ? You know I’m telling the truth. -表示安慰、关心、喜欢、讨厌??感情色彩。
He is always making noises in class. (讨厌)
-在条件、时间、让步状语从句中表示将来正在进行。
Don’t bother him if he is reading this time tomorrow. 严格区分进行时与一般时的语义
1. 持续动词的一般时表持续情况,经常性,习惯性行为或客观存在的事实,进行时表暂时性或有限时刻的持续。
2.短暂动词的一般时叙述事实,特征,能力而短暂动作进行时描述反复发生,即将发生或刚开始行为。
3.短暂动词和静态动词一般时表示实际情况客观状态、结果、特征、特性,进行时表未完成含开始或渐进之意。
The bus stops. (车停了-事实)
The bus is stopping. (渐渐停下来)
I love the job. (静态事实)
I am loving the job. ( 渐渐爱上了)
4.come ,go ,leave ,start ,return ,move ,reach ,sail ,fall 等一般时态表客观规定计划,进行时表主观打算推测。
Flight 254 leaves at 5:30. (表主观打算)
The plane is taking off an hour later.(主观判断)
5.现在进行时带always ,often ,usually ,sometimes ,等频率副词表感情色彩,一般现在时则没有此用法。
