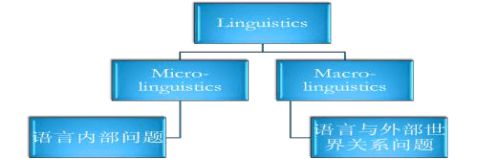
We can study Linguistics from three parts: introduction to Linguistics, main branches of Linguistics, main theories about Linguistics.
The introduction to Linguistics is made up of design feature of language, language families, important distinctions in Linguistics and scope of Linguistics.
Design features refer to the defining properties of human language that distinguish it from any animal system of communication. The following are the most distinguished properties: creativity, arbitrariness, displacement, cultural transmission and duality.
Creativity, in other words, language can be used to create new meanings because of its duality.
Arbitrariness is the forms of human language demonstrate a property.
Displacement. Language can refer to contexts removed from the immediate situations of the language user. This property of human language is called displacement.
Cultural transmission is the process whereby language is passed on and on from one generation to the next.
Duality is the property of having two levels of structures, such that units of the primary level are composed of elements of the secondary level. For example: Sounds > syllables > words > phrases > clauses > sentences> texts/discourses
There are some important distinctions in Linguistics: descriptive & prescriptive, synchronic & diachronic, langue & parole, competence & performance.
Descriptive is describing how things are. Prescriptive is prescribing how things ought to be.
For example: Don't say X. People don't say X. The first is a prescriptive command, while the second is a descriptive statement.
Synchronic is to take a fixed instant as its point of observation. Diachronic is the study of a language through the course of its history.
Langue refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all members of a speech community. Parole refers to realization of language in actual use. It is one of the most important distinctions in linguistics introduced by Sassure (father of modern linguistics) in his Course in General Linguistics.
Competence is user's knowledge of rules about the linguistic system. Performance is the actual realization of this knowledge in concrete situations. It is introduced by Chomsky between general linguistic ability and individual language use, which is connected to de Sassure’s distinction langue vs. parole.
In terms of the number of individual speakers and individual languages, four language families are considered to be the most important, namely, the Indo-European Family, the Sino-Tibetan Family, the Austronesian Family, and the Afroasiatic Family.
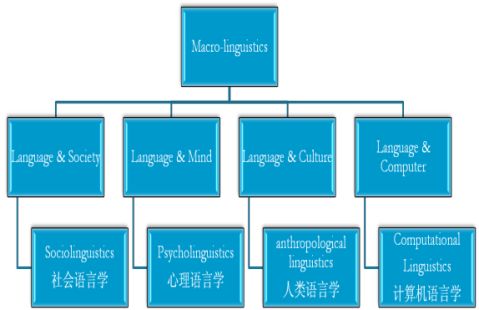
There are several kinds of classifications of Linguistics.
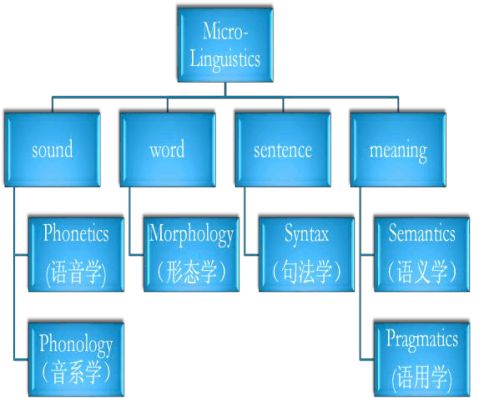
Phonetics studies all speech sounds in human languages: how they are produced, transmitted and how they are received.
Phonology aims to discover how speech sounds in a language form patterns and how these sounds are used to convey meaning in linguistic communication.
Classification of Phonetics: articulatory phonetics(发音语音学)--speaker’s production, acoustic phonetics(声学语音学)--transmission’s medium, auditory phonetics(听觉语音学)--receiver’s reception.
How speech sounds are made? This is a picture about the speech organs.
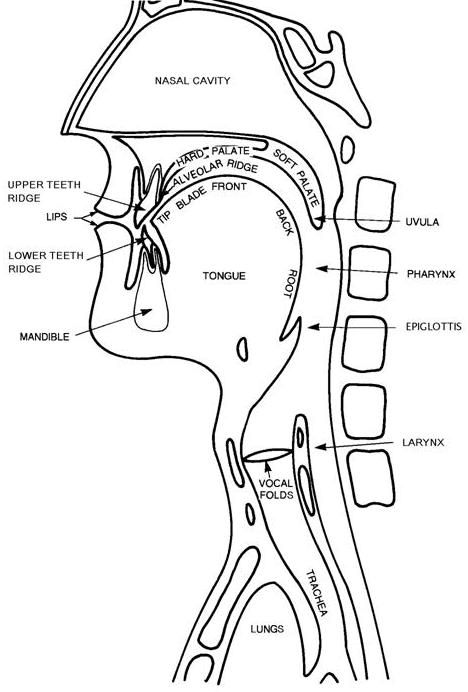
Position of the vocal folds(声带) connects with: voicing(浊音) and voiceless (清音)
Voiceless(清音):vocal cords are drawn wide apart, letting the air stream go through without causing obstruction. Eg.:[p,s,t]
Voicing/Voiced(浊音):vocal cords held together, letting the air stream vibrates. Eg.: [b,z,d]
The distinction between vowels and consonants lies in the obstruction of airstream. As there is no obstruction of air in the production of vowels, the description of the consonants and vowels cannot be done along the same lines.
Phonology is the study of how speech sounds in a language form patterns and how these sounds are used to convey meaning in linguistic communication. There are some important definitions in phonology: phone音子,phoneme音位 (音系研究的基本单位), supra-segmental features超音段特征.
Phone(音子):a phonetic unit; the speech sounds we hear and produce during communication are all phones. For example: too 和 tea 中的 /t/. 发too中的/t/时, 舌位更靠近口腔前部.发tea中的/t/时,舌位更靠近口腔后部. 所以too 和 tea 中的 /t/两个不同的音子.
Phoneme(音位): phonological and abstract unit, a unit of distinctive value; the smallest unit of sound in a language which can distinguish two words. For example: tea 和 sea, /t/和/s/是两个不同的音位morpheme
Suprasegmental features (超音段特征) :phonemic features that occur above the level of the segments . The principal suprasegmentals are: syllable, stress, tone, intonation.
Morphology focuses on the study of the internl structure of words and ways to form words.
morpheme(语素)is the most basic element of meaning in language,an element that cannot be further divided into smaller units without altering its meaning.

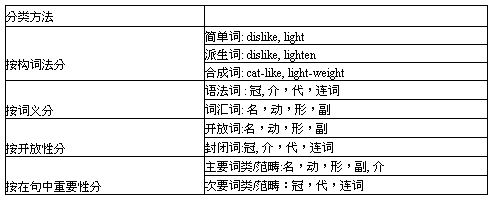
Morpheme may be classified in more than one dimension. Firstly, morphemes are bound morphemes are free morphemes. Free morphemes(自由语素) are those that may constitute words by themselves, eg boy, girl, table, nation. Bound morphemes(黏着)are those that cannot occur alone, eg -s, -ed, dis-, un-. Inflectional morpheme (屈折语素)=inflectional affix(屈折词缀):change the grammatical meaning (number, aspect, case, tense). Derivational morpheme(派生语素)=inflectional affix (派生词缀): change the lexical meaning.

Syntax is the study of how words combine to form sentences and the rules which govern the rules which govern the formation of sentences. Category(范畴): a group of linguistic items which fulfill the same or similar functions in a particular language such as sentence, a noun phrase or a verb (起相同作用的一类语言单位). Syntactical category(句法范畴): a group of linguistic items which fulfill the same or similar functions in sentence-formation. (在句子构成中起相同作用的一类语言单位)Word--lexical category. Phrase--phrasal category. Clause--clausal category.
Semantics can be classified into four kinds by different studies, namely, Linguistic Semantics, Logical Semantics, Philosophical Semantics and General Semantics.
The sense relation of words falls into five aspects: polysemy, homonymy, synonymy, antonymy and hyponymy. Polysemy refers to the phenomenon that the same word may have a set of different meanings. Homonyms are generally defined as words different in meaning but either identical in sound and spelling or identical only in sound or spelling. Synonymy is one of the basic features of any natural language. Antonymy can be defined as words which are opposite in meaning. Hyponymy refers to the hierarchical relationship between meanings of general and specific lexical items.
Pragmatics can be identified by this formula: Pragmatics=meaning-semantics.
Speech Act Theory: John Austin (1911-1960). How to Do Things with Words (1962). Main Idea: things can be done with words.
Constatives(叙事句)are utterances which roughly serves to state a fact, report that something is the case, or describe what something is, eg: I go to the park every Sunday.
Performatives(施为句)are utterances which are used to perform acts, do not describe or report anything at all; the uttering of the sentence is the doing of an action; they cannot be said to be true or false. Performative verbs: name, bet, etc.
Three Speech Acts (三种言语行为): A locutionary act (言内行为): the act of uttering words, phrase, sentences. It is an act of conveying literal meaning by means of syntax, lexicon and phonology. An illocutionary act(言外行为): an act of expression speaker’s intention; it is an act performed in saying something. A perlocutionary act(言后行为): the act preformed by or as a result of saying, the effects on the hearer. For example: 老师对学生说: You have left the door open. Locutionary act(言内行为): the act of uttering the words of “you”, “have”, “left”, “the”, “door”, “open” Illocutinary act(言外行为): the act of expressing the teacher’s intention of asking the student to close the door. Perlocutionary act(言后行为): the effect of the utterance: student goes to close the door.
The Cooperative Principle (CP,合作原则): Maxim of Quality(数量准则). Maxim of Quantity(质量准则). Maxim of Relation(关系准则). Maxim of Manner(方式准则)
