数据结构实验报告
实验一:栈和队列
实验目的:
掌握栈和队列特点、逻辑结构和存储结构
熟悉对栈和队列的一些基本操作和具体的函数定义。
利用栈和队列的基本操作完成一定功能的程序。
实验任务
1.给出顺序栈的类定义和函数实现,利用栈的基本操作完成十进制数N与其它d进制数的转换。(如N=1357,d=8)
实验原理:将十进制数N转换为八进制时,采用的是“除取余数法”,即每次用8除N所得的余数作为八进制数的当前个位,将相除所得的商的整数部分作为新的N值重复上述计算,直到N为0为止。此时,将前面所得到的各余数反过来连接便得到最后的转换结果。
程序清单
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
typedef int DATA_TYPE;
const int MAXLEN=100;
enum error_code
{
success,overflow,underflow
};
class stack
{
public:
stack();
bool empty()const;
error_code get_top(DATA_TYPE &x)const;
error_code push(const DATA_TYPE x);
error_code pop();
bool full()const;
private:
DATA_TYPE data[MAXLEN];
int count;
};
stack::stack()
{
count=0;
}
bool stack::empty()const
{
return count==0;
}
error_code stack::get_top(DATA_TYPE &x)const
{
if(empty())
return underflow;
else
{
x=data[count-1];
return success;
}
}
error_code stack::push(const DATA_TYPE x)
{
if(full())
return overflow;
else
{
data[count]=x;
count++;
}
}
error_code stack::pop()
{
if(empty())
return underflow;
else
{
count--;
return success;
}
}
bool stack::full()const
{
return count==MAXLEN;
}
void main()
{
stack S;
int N,d;
cout<<"请输入一个十进制数N和所需转换的进制d"<<endl;
cin>>N>>d;
if(N==0)
{
cout<<"输出转换结果:"<<N<<endl;
}
while(N)
{
S.push(N%d);
N=N/d;
}
cout<<"输出转换结果:"<<endl;
while(!S.empty())
{
S.get_top(N);
cout<<N;
S.pop();
}
cout<<endl;
}
while(!S.empty())
{
S.get_top(x);
cout<<x;
S.pop();
}
}
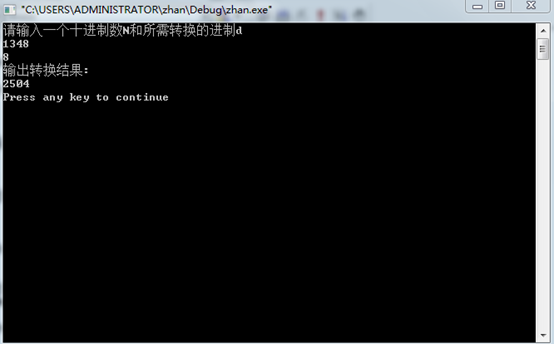
测试数据:N=1348 d=8
运行结果:
2.给出顺序队列的类定义和函数实现,并利用队列计算并打印杨辉三角的前n行的内容。(n=8)
实验原理:杨辉三角的规律是每行的第一和最后一个数是1,从第三行开始的其余的数是上一行对应位置的左右两个数之和。因此,可用上一行的数来求出对应位置的下一行内容。为此,需要用队列来保存上一行的内容。每当由上一行的两个数求出下一行的一个数时,其中的前一个便需要删除,而新求出的数就要入队。
程序清单:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
typedef int DATA_TYPE;
const int MAXLEN=100;
enum error_code
{
success,underflow,overflow
};
class queue
{
public:
queue();
bool empty()const;
error_code get_front(DATA_TYPE &x)const;
error_code append(const DATA_TYPE x);
error_code serve();
bool full()const;
private:
int front,rear;
DATA_TYPE data[MAXLEN];
};
queue::queue()
{
rear=0;
front=0;
}
bool queue::empty()const
{
return (front%MAXLEN==rear%MAXLEN);
}
error_code queue::get_front(DATA_TYPE &x)const
{
if(empty())
return underflow;
else
{
x=data[front%MAXLEN];
return success;
}
}
error_code queue::append(const DATA_TYPE x)
{
if(full())
return overflow;
else
{
data[rear%MAXLEN]=x;
rear++;
}
}
error_code queue::serve()
{
if(empty())
return underflow;
else
{
front++;
return success;
}
}
bool queue::full()const
{
return((rear+1)%MAXLEN==front);
}
void main()
{
queue Q;
int num1,num2;
int i=0;
cout<<1<<endl;
Q.append(1);
num1=0;
num2=1;
for(i=0;i<=7;i++)
{
int j=0;
int k=0;
num1=0;
for(j=0;j<=i;j++)
{
Q.get_front(num2);
Q.serve();
cout<<num1+num2<<" ";
Q.append(num1+num2);
num1=num2;
}
cout<<1<<endl;
Q.append(1);
}
}
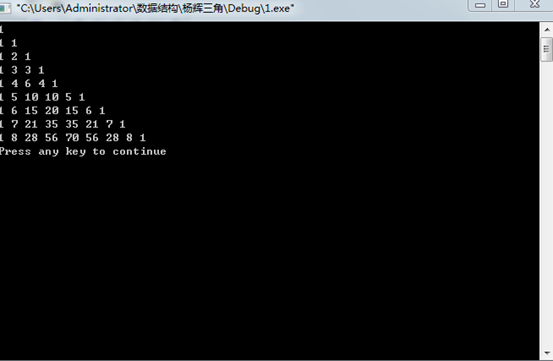
运行结果:
3.给出链栈的类定义和函数实现,并设计程序完成如下功能:读入一个有限大小的整数n,并读入n个数,然后按照与输入次序相反的次序输出各元素的值。
实验原理:依次将栈中的元素出栈,因为栈的一个特点就是先进后出,。这样,当将原栈为空时,输出与输入次序相反,从而实现了本题的要求。
程序清单:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
typedef int DATA_TYPE;
typedef struct LNode
{
DATA_TYPE data;
LNode *next;
}LNode;
enum error_code
{
range_error,success,underflow
};
class linkstack
{
public:
linkstack();
~linkstack();
bool empty()const;
error_code push(const DATA_TYPE x);
error_code get_top(DATA_TYPE &x)const;
error_code pop();
private:
LNode *top;
int count;
DATA_TYPE data;
};
linkstack::linkstack()
{
top=NULL;
count=0;
}
bool linkstack::empty()const
{
return (count==0);
}
error_code linkstack::push(const DATA_TYPE x)
{
LNode *s=new LNode;
s->data=x;
s->next=top;
top=s;
count++;
return success;
}
error_code linkstack::get_top(DATA_TYPE &x)const
{
if(empty())
return underflow;
else
{
x=top->data;
return success;
}
}
error_code linkstack::pop()
{
if(empty())
return underflow;
else
{
LNode *u=new LNode;
u=top;
top=top->next;
delete u;
count--;
return success;
}
}
linkstack::~linkstack()
{
while(!empty())
{
pop();
}
}
void main()
{
linkstack L;
int n;
cout<<"请任意输入一个整数n:"<<endl;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
L.push(i);
}
while(!L.empty())
{
L.get_top(i);
cout<<i<<" ";
L.pop();
}
}
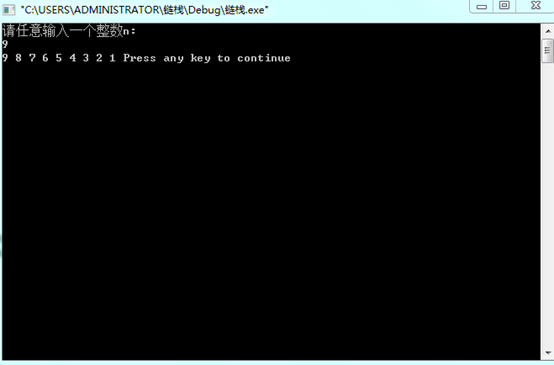
测试数据:n=9 i=1
运行结果:
实验二:单链表
实验目的:
理解线性表的链式存储结构。
熟练掌握动态链表结构及有关算法的设计。
根据具体问题的需要,设计出合理的表示数据的链表结构,并设计相关算法。
实验任务:
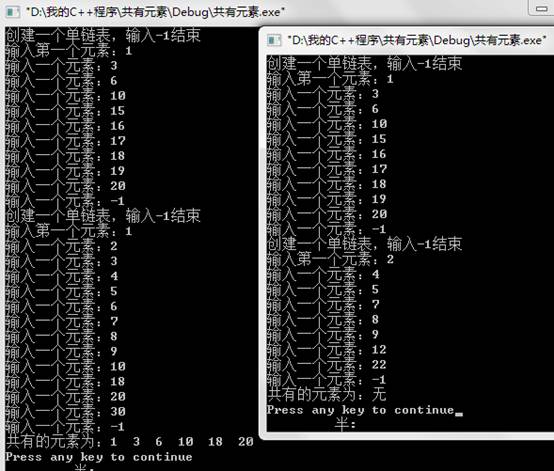
在一个递增有序的链表L中插入一个值为x的元素,并保持其递增有序特性。
1.实验数据:链表元素为(10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100),x分别为25,85,110和8。
实验原理:给出了要插入的条件,但没有给定插入位置。因此,需要搜索满足这一条件的插入位置的前驱结点而不是序号。
程序清单:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
typedef struct snode
{
int data;
struct snode *next;
}node;
enum error_code{arrange_error,success};
class list
{
public:
list();
void create2();
int length() const;
error_code get_element(const int i,int &x) const;
error_code insert(const int &x);
error_code delete_element(const int i);
node *locate(const int x) const;
node *get_head(){return head;}
void print();
private:
int count;
node *head;
};
list::list()
{
head=new node; head->next=NULL;
count=0;
}
void list::create2()
{
int x; node *p=head;
node *s; cout<<"输入一个值:";
cin>>x;
while(x!=-1)
{
s=new node; s->data=x;
s->next=NULL; p->next=s;
p=s; cout<<"输入一个值:";
cin>>x;
}
}
int list::length() const
{
return count;
}
error_code list::get_element(const int i,int &x) const
{
int j=1; node *p=head->next;
while(p!=NULL&&j!=i)
{
p=p->next; j++;
}
if(p==NULL)
return arrange_error;
x=p->data;
return success;
}
node *list::locate(const int x) const
{
node *p=head->next;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->data==x)
return p;
p=p->next;
}
return NULL;
}
error_code list::insert(const int &x)
{
node *s; node *q=head; node *p=head->next;
while(p!=NULL&&p->data<x)
{
q=p; p=p->next;
}
if(p==NULL)
{
s=new node; s->data=x;
s->next=NULL; q->next=s; count++;
}
else{
s=new node; s->data=x; s->next=q->next;
q->next=s; count++;
}
return success;
}
error_code list::delete_element(const int i)
{
node *u; node *p=head; int j=0;
while(j!=i-1&&p!=NULL)
{
p=p->next; j++;
}
if(i<1||i>count)
return arrange_error;
u=p->next; p->next=u->next;
delete u; count--;
return success;
}
void list::print()
{
node *p=head->next;
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
void main()
{
list l;
int x;
cout<<"创建一个链表(输入‘-1’结束):"<<endl;
l.create2();
cout<<"输入要插入的数(输入‘-1’结束):"<<endl;
cout<<"输入一个数:";
cin>>x;
while(x!=-1)
{
l.insert(x);
cout<<"输入一个数:";
cin>>x;
}
l.print();
}
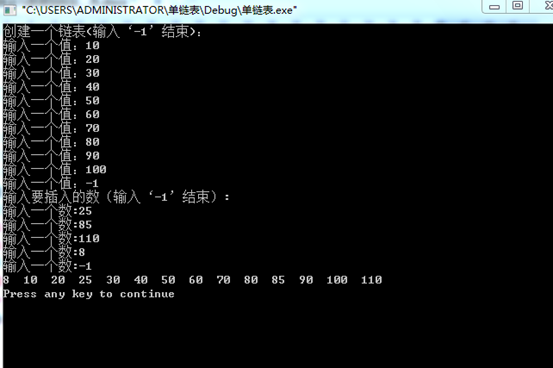
测试数据:链表元素为(10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100),x分别为25,85,110和8。
运行结果:
2.将单链表L中的奇数项和偶数项结点分解开,并分别连成一个带头结点的单链表,然后再将这两个新链表同时输出在屏幕上,并保留原链表的显示结果,以便对照求解结果。
实验原理:依据题目的要求,需要再创建两个新链表来存储分离后的奇偶项,而奇偶项可以根据数字来控制,把他们取出来并重新连起来。
程序清单:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
typedef struct snode
{
int data;
struct snode *next;
}node;
enum error_code{arrange_error,success};
class list
{
public:
list();
void create2();
int length() const;
error_code get_element(const int i,int &x) const;
error_code insert(const int &x);
error_code delete_element(const int i);
node *locate(const int x) const;
node *get_head(){return head;}
divide(list &B,list &C);
void print();
private:
int count;
node *head;
};
list::list()
{
head=new node; head->next=NULL;
count=0;
}
void list::create2()
{
int x; node *p=head;
node *s; cout<<"输入一个值:";
cin>>x;
while(x!=-1)
{
s=new node; s->data=x;
s->next=NULL; p->next=s;
p=s; cout<<"输入一个值:";
cin>>x;
}
}
int list::length() const
{
return count;
}
error_code list::get_element(const int i,int &x) const
{
int j=1; node *p=head->next;
while(p!=NULL&&j!=i)
{
p=p->next; j++;
}
if(p==NULL)
return arrange_error;
x=p->data;
return success;
}
node *list::locate(const int x) const
{
node *p=head->next;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->data==x)
return p;
p=p->next;
}
return NULL;
}
void list::divide(list &B,list &C)
{
node *u; node *pa=head->next;
node *pb=B.get_head(); node *pc=C.get_head();
for(int i=0;pa!=NULL;i++,pa=pa->next)
{
u=new node; u->data=pa->data;
if(i%2==0)
{
pb->next=u; pb=pb->next;
}
else
{
pc->next=u; pc=pc->next;
}
pb->next=NULL; pc->next=NULL;
}
}
error_code list::insert(const int &x)
{
node *s; node *q=head; node *p=head->next;
while(p!=NULL&&p->data<x)
{
q=p; p=p->next;
}
if(p==NULL)
{
s=new node; s->data=x;
s->next=NULL; q->next=s; count++;
}
else{
s=new node; s->data=x; s->next=q->next;
q->next=s; count++;
}
return success;
}
error_code list::delete_element(const int i)
{
node *u; node *p=head; int j=0;
while(j!=i-1&&p!=NULL)
{
p=p->next; j++;
}
if(i<1||i>count)
return arrange_error;
u=p->next; p->next=u->next;
delete u; count--;
return success;
}
void list::print()
{
node *p=head->next;
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
void main()
{
list A,B,C; int x,y,z;
A.create_R(); A.divide(B,C);
cout<<"原表:"; A.output();
cout<<"奇数表:"; B.output();
cout<<"偶数表:"; C.output();
}
测试数据:第一组数据:链表元素为 (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,20,30,40,50,60)
第二组数据:链表元素为 (10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100)
运行结果:

3.求两个递增有序链表L1和L2中的公共元素,并以同样方式连接成链表L3。
实验原理:设置两个指针怕,pa,pb分别依次指示A,B表中的元素,其初始值分别为A.head->next和B.head->next。在pa,pb均非空时,根据其值的大小关系可能有如下三种情况。
(1).pa->data==pb->data:搜索到公共元素,应在C表表尾插入一个结点,其值为pa->data,然后继续A表中下一个元素的搜索,即pa=pa->next,同时pb也往后移。
(2). pa->data>pb->data:表明A表中这一元素可能在B表当前元素的后面,因此要往B表的后面搜索,故而执行pb=pb->next,然后继续搜索。
(3). pa->data<pb->data:表明A中这一元素在B中不存在,因而执行pa=pa->next以继续对A表中下一个元素的判断。
反复执行上述比较,直到pa,pb至少有一个为空为止。此时,剩余的非空部分没有所需要的公共元素,因而搜索结束。
程序清单:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
typedef struct snode
{
int data;
struct snode *next;
}node;
enum error_code{arrange_error,success};
class list
{
public:
list();
void create2();
int length() const;
error_code get_element(const int i,int &x) const;
error_code insert(const int &x);
error_code delete_element(const int i);
node *locate(const int x) const;
node *get_head(){return head;}
void list::gongyou(list &L1,list &L2)
void print();
private:
int count;
node *head;
};
list::list()
{
head=new node; head->next=NULL;
count=0;
}
void list::create2()
{
int x; node *p=head;
node *s; cout<<"输入一个值:";
cin>>x;
while(x!=-1)
{
s=new node; s->data=x;
s->next=NULL; p->next=s;
p=s; cout<<"输入一个值:";
cin>>x;
}
}
int list::length() const
{
return count;
}
error_code list::get_element(const int i,int &x) const
{
int j=1; node *p=head->next;
while(p!=NULL&&j!=i)
{
p=p->next; j++;
}
if(p==NULL)
return arrange_error;
x=p->data;
return success;
}
void list::gongyou(list &L1,list &L2)
{
node *p1=L1.head->next; node *p2=L2.head->next;
node *p3=head; node *u;
while(p1!=NULL&&p2!=NULL)
{
if(p1->data==p2->data)
{
u=new node; u->data=p1->data; p3->next=u;
p1=p1->next; p2=p2->next; p3=p3->next;
}
else{
if(p1->data<p2->data)
p1=p1->next;
else
p2=p2->next;
}
}
p3->next=NULL;
}
node *list::locate(const int x) const
{
node *p=head->next;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->data==x)
return p;
p=p->next;
}
return NULL;
}
void list::divide(list &B,list &C)
{
node *u; node *pa=head->next;
node *pb=B.get_head(); node *pc=C.get_head();
for(int i=0;pa!=NULL;i++,pa=pa->next)
{
u=new node; u->data=pa->data;
if(i%2==0)
{
pb->next=u; pb=pb->next;
}
else
{
pc->next=u; pc=pc->next;
}
pb->next=NULL; pc->next=NULL;
}
}
error_code list::insert(const int &x)
{
node *s; node *q=head; node *p=head->next;
while(p!=NULL&&p->data<x)
{
q=p; p=p->next;
}
if(p==NULL)
{
s=new node; s->data=x;
s->next=NULL; q->next=s; count++;
}
else{
s=new node; s->data=x; s->next=q->next;
q->next=s; count++;
}
return success;
}
error_code list::delete_element(const int i)
{
node *u; node *p=head; int j=0;
while(j!=i-1&&p!=NULL)
{
p=p->next; j++;
}
if(i<1||i>count)
return arrange_error;
u=p->next; p->next=u->next;
delete u; count--;
return success;
}
void list::print()
{
node *p=head->next;
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
void main()
{
list L1,L2,L3;
L1.create_R(); L2.create_R(); L3.gongyou(L1,L2);
cout<<"共有的元素为:"; L3.output();
}
测试数据:第一组数据:
第一个链表元素为 (1,3,6,10,15,16,17,18,19,20)
第二个链表元素为 (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,18,20,30)
第二组数据:
第一个链表元素为 (1,3,6,10,15,16,17,18,19,20)
第二个链表元素为 (2,4,5,7,8,9,12,22)
运行结果:
实验三:二叉树
一、 实验目的
1. 掌握二叉树的动态链表存储结构及表示。
2. 掌握二叉树的三种遍历算法(递归和非递归两类)。
3. 运用二叉树三种遍历的方法求解有关问题。
二、实验任务
1. 建立一棵采用二叉链表结构存储的二叉树。
2. 分别采用递归和非递归两种方式对该二叉树进行先序、中序和后序遍历。
3. 求二叉树的高度以及二叉树中叶子结点的数目。
实验原理:在二叉链表存储结构中,每个结点应包括存储结点值的数据部分及指向两个孩子结点的指针,不妨设为data,lchild和rchild。对二叉树的遍历是在对各子树分别遍历的基础之上进行的。由于各子树的遍历和整个二叉树的遍历方式相同,因此,可借助对整个二叉树的遍历算法来实现对左、右子树的遍历。
程序清单:
#include<iostream.h>
#define maxlen 200
enum tagtype{L1,L2};
typedef struct node
{
char data; struct node *lchild,*rchild;
}bnode;
typedef struct{
bnode *ptr; tagtype tag;
}stacknode;
enum error_code{success,underflow,overflow};
class stack
{
public:
stack();
bool empty()const;
bool full()const;
error_code get_top(stacknode &x);
error_code get_top(bnode* &x);
error_code push(stacknode x);
error_code push(bnode* x);
error_code pop();
private:
int count; bnode* data_xian[maxlen];
stacknode data_hou[maxlen];
};
stack::stack()
{
count=0;
}
bool stack::empty()const
{
if(count==0)
return true;
return false;
}
bool stack::full()const
{
if(count==maxlen)
return true;
return false;
}
error_code stack::get_top(stacknode &x)
{
if(empty())
return underflow;
x=data_hou[count-1];
return success;
}
error_code stack::get_top(bnode* &x)
{
if(empty())
return underflow;
x=data_xian[count-1];
return success;
}
error_code stack::push(stacknode x)
{
if(full())
return overflow;
data_hou[count]=x; count++;
return success;
}
error_code stack::push(bnode* x)
{
if(full())
return overflow;
data_xian[count]=x; count++;
return success;
}
error_code stack::pop()
{
if(empty())
return underflow; count--;
return success;
}
bitree.h
#include"stack.h"
class bitree
{
public:
bitree();
bnode *create();
bnode *get_root(){return root;}
int max(int a,int b);
void preorder1(){preorder1(root);}
void inorder1(){inorder1(root);}
void postorder1(){postorder1(root);}
void preorder2(){preorder2(root);}
void inorder2(){inorder2(root);}
void postorder2(){postorder2(root);}
int high(bnode *T);
int leaf(bnode *T);
private:
bnode *root;
void visite(bnode *T);
void preorder1(bnode *T);
void inorder1(bnode *T);
void postorder1(bnode *T);
void preorder2(bnode *T);
void inorder2(bnode *T);
void postorder2(bnode *T);
};
bitree::bitree()
{
root=NULL;
}
bnode* bitree::create()
{
char ch; bnode *p;
cout<<"输入二叉树的值:"; cin>>ch;
if(ch=='#')
return NULL;
p=new bnode; p->data=ch;
if(root==NULL)
root=p;
p->lchild=create(); p->rchild=create();
return p;
}
int bitree::max(int a,int b)
{
if(a>=b)
return a;
return b;
}
void bitree::preorder1(bnode *T)
{
if(T!=NULL)
{
visite(T); preorder1(T->lchild); preorder1(T->rchild);
}
}
void bitree::inorder1(bnode *T)
{
if(T!=NULL)
{
preorder1(T->lchild); visite(T); preorder1(T->rchild);
}
}
void bitree::postorder1(bnode *T)
{
if(T!=NULL)
{
preorder1(T->lchild); preorder1(T->rchild); visite(T);
}
}
void bitree::preorder2(bnode *T)
{
stack s;
if(T!=NULL)
{
s.push(T);
while(!s.empty())
{
s.get_top(T); s.pop(); visite(T);
if(T->rchild!=NULL)
s.push(T->rchild);
if(T->lchild!=NULL)
s.push(T->lchild);
}cout<<endl;
}
}
void bitree::inorder2(bnode *T)
{
stack s;
if(T!=NULL)
{
while(T!=NULL||!s.empty())
{
while(T!=NULL)
{
s.push(T); T=T->lchild;
}
if(!s.empty())
{
s.get_top(T); s.pop();
visite(T); T=T->rchild;
}
}cout<<endl;
}
}
void bitree::postorder2(bnode *T)
{
stack s;
stacknode x;
do{
while(T!=NULL)
{
x.ptr=T; x.tag=L1;
s.push(x); T=T->lchild;
}
int continue1=1;
while(!s.empty()&&continue1)
{
s.get_top(x); s.pop(); T=x.ptr;
switch(x.tag)
{
case L1: x.tag=L2;
s.push(x); T=T->rchild; continue1=0;
break;
case L2:visite(T);
break;
}
}
}while(!s.empty());
cout<<endl;
}
int bitree::high(bnode *T)
{
if(T==NULL)
return 0;
else
return max(high(T->lchild),high(T->rchild))+1;
}
int bitree::leaf(bnode *T)
{
if(T==NULL)
return 0;
if(T->lchild==NULL&&T->rchild==NULL)
return 1;
return leaf(T->lchild)+leaf(T->rchild);
}
void bitree::visite(bnode *T)
{
cout<<T->data<<" ";
}
void main()
{
bitree b; int x;
cout<<"创建一个先序二叉树(输入‘#’为空):"<<endl; b.create();
cout<<"1.递归遍历"<<" "<<"2.非递归遍历"<<endl;
cout<<"输入你的选择(输入-1退出):"; cin>>x;
while(x!=-1)
{
switch(x){
case 1:
cout<<"先序遍历为:"; b.preorder1(); cout<<endl;
cout<<"中序遍历为:"; b.inorder1(); cout<<endl;
cout<<"后序遍历为:"; b.postorder1(); cout<<endl;
cout<<"树的高度为:"; cout<<b.high(b.get_root())<<endl;
cout<<"叶子结点数为:"; cout<<b.leaf(b.get_root())<<endl;
break;
case 2:
cout<<"先序遍历为:"; b.preorder2();
cout<<"中序遍历为:"; b.inorder2();
cout<<"后序遍历为:"; b.postorder2();
cout<<"树的高度为:"; cout<<b.high(b.get_root())<<endl;
cout<<"叶子结点数为:"; cout<<b.leaf(b.get_root())<<endl;
break;
}cout<<endl;
cout<<"1.递归遍历"<<" "<<"2.非递归遍历"<<endl;
cout<<"输入你的选择(输入-1退出):"; cin>>x;
}
}
运行结果:

实验四:图
一、 实验目的
1. 掌握图的基本概念。
2. 掌握图的存储结构的设计与实现,基本运算的实现。
3. 掌握图的两种遍历算法,以及遍历算法的应用。
二、实验任务
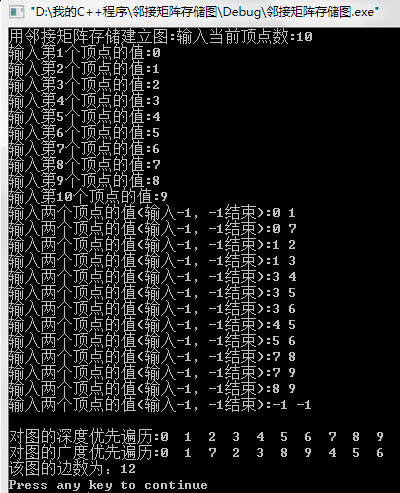
1.分别以邻接矩阵和邻接表的存储结构建立图。
2.分别对图进行深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历。
3.求图中边的数目。
实验原理:邻接矩阵是表示图中顶点之间邻接关系的矩阵,即表示各顶点之间是否有边关系的矩阵。因此,对有n个顶点的图来说,其邻接矩阵A为n*n阶的,其中Aij表示顶点vi到vj之间是否有边或弧:若存在,则Aij为1,否则为0。邻接表的表示方式是将每个顶点的邻接点连成链表,并将各链表的表头指针合在一起,其中每个头指针与该结点的信息合为一个整体结点。在执行遍历dfs(v)时,搜索下一个访问顶点是从当前访问顶点v的邻接表中搜索的,因此,每搜索到一个邻接点即意味着搜索到一条以v为一个端点的边或弧,故应在dfs算法中计数。
程序清单:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
const int maxvertex=100;
class graph
{
public:
graph();
void createadj();
void trave_dfs();
void trave_bfs();
void dfs(int v);
void bfs(int v);
int firstadj(int v);
int nextadj(int v,int m);
void visit(int v);
void edgenum();
void dijkstra(int v0);
private:
int vertex[maxvertex];
int edge[maxvertex][maxvertex];
int currentvertex;
bool visited[maxvertex];
};
graph::graph()
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<maxvertex;i++) vertex[i]=0;
for(i=0;i<maxvertex;i++)
for(j=0;j<maxvertex;j++)
edge[i][j]=0;
}
void graph::createadj()
{
int i,j,k;
cout<<"输入当前顶点数:"; cin>>currentvertex;
for(k=0;k<currentvertex;k++)
{
cout<<"输入第"<<k+1<<"个顶点的值:";
cin>>vertex[k];
}
cout<<"输入两个顶点的值(输入-1,-1结束):"; cin>>i>>j;
while(i!=-1&&j!=-1)
{
edge[i][j]=edge[j][i]=1;
cout<<"输入两个顶点的值(输入-1,-1结束):"; cin>>i>>j;
}
}
void graph::trave_dfs()
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<currentvertex;i++) visited[i]=false;
for(i=0;i<currentvertex;i++)
if(!visited[i])
dfs(vertex[i]);
}
void graph::trave_bfs()
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<currentvertex;i++) visited[i]=false;
for(i=0;i<currentvertex;i++)
if(!visited[i])
bfs(vertex[i]);
}
void graph::dfs(int v)
{
int w; visit(v);
visited[v]=true; w=firstadj(v);
while(w!=-1)
{
if(!visited[w]) dfs(w);
w=nextadj(v,w);
}
}
void graph::bfs(int v)
{
queue Q;
int w,x; visit(v);
visited[v]=true; Q.append(v);
while(!Q.empty())
{
Q.get_front(x); v=x;
Q.serve(); w=firstadj(v);
while(w!=-1)
{
if(!visited[w])
{
visit(w); visited[w]=true;
Q.append(w);
}w=nextadj(v,w);
}
}
}
int graph::firstadj(int v)
{
if(v!=-1)
{
for(int i=0;i<currentvertex;i++)
if(edge[v][i]>0)
return i;
}return -1;
}
int graph::nextadj(int v,int m)
{
if(v!=-1&&m!=-1)
{
for(int i=m+1;i<currentvertex;i++)
if(edge[v][i]>0)
return i;
}return -1;
}
void graph::visit(int v)
{
cout<<v<<" ";
}
void graph::edgenum()
{
int num=0,i,j;
for(i=0;i<currentvertex;i++)
for(j=0;j<currentvertex;j++)
if(edge[i][j]>0)
num++;
cout<<num/2<<endl;
}
void main()
{
graph G;
cout<<"用邻接矩阵存储建立图:"; G.createadj(); cout<<endl;
cout<<"对图的深度优先遍历:"; G.trave_dfs(); cout<<endl;
cout<<"对图的广度优先遍历:"; G.trave_bfs(); cout<<endl;
cout<<"该图的边数为:"; G.edgenum();
}
实验五:查找
一、 实验目的
1. 掌握顺序表的查找方法,尤其是二分查找方法。
2. 掌握二叉排序树的建立与查找。
二、实验任务
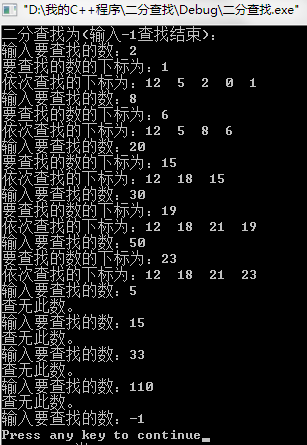
1. 对下列数据表,分别采用二分查找算法实现查找,给出查找过程依次所比较的元素(的下标),并以二分查找的判定树来解释。
实验原理:设查找区域的首尾下标分别用变量low和high表示,将待查关键字x和该区域的中间元素的关键字进行比较。
程序清单:
#include<iostream.h>
int bin_search(int a[],int n,int x);
int bin[25]; int i=0;
void main()
{
int a[]={1,2,3,4,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,17,18,19,20,24,25,26,30,35,40,45,50,100};
int x,n,num; n=sizeof(a)/4;
cout<<"二分查找为(输入-1查找结束):"<<endl;
cout<<"输入要查找的数:"; cin>>x;
while(x!=-1)
{
num=bin_search(a,n,x);
if(num==-1)
cout<<"查无此数。"<<endl;
else{
cout<<"要查找的数的下标为:"<<num<<endl;
cout<<"依次查找的下标为:";
for(int j=0;j<i;j++)
cout<<bin[j]<<" ";
i=0; cout<<endl;
}
cout<<"输入要查找的数:"; cin>>x;
}
}
int bin_search(int a[],int n,int x)
{
int mid,low=0,high=n-1;
while(low<=high)
{
mid=(low+high)/2; bin[i]=mid; i++;
if(a[mid]==x) return mid;
else if(a[mid]<x) low=mid+1;
else high=mid-1;
}return -1;
}
测试数据:
数据表为 (1,2,3,4,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,17,18,19,20,24,25,26,30,35,40,45,50,100)
查找的元素分别为: 2,8,20, 30,50,5,15,33,110
运行结果:
实验六:排序
一、 实验目的
1. 掌握各种内部排序算法。
2. 理解各种内部排序算法的特性、时间性能和空间性能,在此基础上能根据具体情况选择合适的排序算法。
二、实验任务
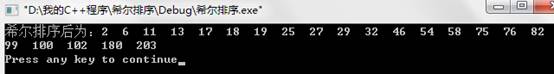
1. 实现希尔排序算法,并观察在采用不同的步长选取方法对排序过程中数据的比较和移动次数的影响。
实验原理:将待排序列划分为若干组,在每组内进行直接插入排序,以使整个序列基本有序,然后再对整个序列进行直接插入排序。
程序清单:
#include<iostream.h>
void shell_sort(int a[],int n);
void main()
{
int n;
int a[]={180,203,32,46,25,76,17,58,99,100,11,102,13,54,75,6,27,18,19,29,2,82};
n=sizeof(a)/4; shell_sort(a,n);
cout<<"希尔排序后为:";
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
void shell_sort(int a[],int n)
{
int i,j,temp,d=n/2;
while(d>0)
{
for(i=d;i<n;i++)
{
temp=a[i]; j=i-d;
while(j>=0&&a[j]>temp)
{
a[j+d]=a[j]; j=j-d;
}a[j+d]=temp;
}d=d/2;
}
}
运行结果:
2. 实现堆排序算法,给出排序结果。
实验原理:首先,由无序序列建堆可通过反复调用筛选操作来实现。为此,需满足筛选的条件,即左、右子树必须为堆。因此,建堆过程要从下往上逐棵子树的进行筛选。从易于编程的角度出发,根的下标自然是按从大到小,即按照根的下标从n/2到1的次序调整各子树为堆。排序可通过反复执行如下操做而最终得到一个有序序列:输出根:即将根与当前子序列中的最后一个元素交换;调整根:将输出根之后的子序列调整为堆。
程序清单:
#include<iostream.h>
void sift(int a[],int k,int m);
void heap_sort(int a[],int n);
void main()
{
int i,n;
int a[]={106,213,325,446,579,654,721,870,917,510,21,632,73,14,815,316,412,18,619,720,21,808,923,25,26};
n=sizeof(a)/4;
cout<<"堆排序的结果为:"; heap_sort(a,n); cout<<endl;
}
void sift(int a[],int k,int m)
{
int i,j,x; bool finished=false;
x=a[k]; i=k; j=k*2;
while(j<m&&!finished)
{
if(j<m&&a[j]<a[j+1]) j=j+1;
if(x>=a[j]) finished=true;
else{
a[i]=a[j]; i=j; j=j*2;
}
}a[i]=x;
}
void heap_sort(int a[],int n)
{
int i;
for(i=(n-1)/2;i>=0;i--) sift(a,i,n-1);
for(i=n-1;i>=1;i--)
{
cout<<a[0]<<" ";
a[0]=a[i]; sift(a,0,i-1);
}
}
测试数据:
(106,213,325,446,579,654,721,870,917,510,21,632,73,14,815,316,412 ,18,619,720,21,808,923,
25,26)
运行结果:

