The Mobile Internet industry has been booming over the past few years and a continuing growth is expected. With the growing penetration rate of smart phones and the more intense use of Mobile Internet, the whole industry is estimated to reach the revenue of $402.8 billion in 2018. To become a market leader of Mobile Internet, one should start off with a decided advantage. Pukou, a district of high-tech industrial parks in Nanjing, China, will give you the competitive edge of convenient transportation, support from the government, qualified personnel and most important of all, access to the local and global market.
The industrial parks in Pukou are established with the purpose to integrate resources from Universities, R&D Institutions and corporations. Under the guidance of the State Council, Nanjing is determined to make Pukou a strong industrial area with intensive development.
Location & Transportation
Pukou is located at the north shore of the Changjiang River, a river across from the urban areas of Nanjing. With four bridges and a tunnel connecting Pukou with the city area and two metro lines, transportation from Pukou to elsewhere has been facilitated. It only takes 40 minutes by metro to get to the city central from Pukou.
Access to the local Market and global market
The need for Mobile Internet products in developing countries is rising. By the end of 2013, Mobile Internet users in China have reached 500 million with an increasing rate of 19% comparing to last year. Being located in Pukou gives you the opportunity to be
close to the local market and reach the largest customer base in the world. It is also very easy to reach the overseas market from Pukou as Nanjing has established trade relations with over 200 countries. For the first two months of 2014, Nanjing has exported $1.04 billion high-tech products.
Infrastructure & Surrounding Environment
The local government has great expectation in Pukou. The plan is to further improve the infrastructure of Pukou to make it more convenient and efficient by providing a best living environment and public services.
Human Resources
Nanjing is a city with some of the China’s top universities. These institutions provide competent stuff to enterprises. Along with local graduates, Nanjing has also attracted lots of overseas R&D personnel with its ‘introduction of overseas talents’ policy.
Support from the government.
To facilitate the high-tech industrial parks in Pukou, the local government has established several promoting policies. Mobile Internet is one of the areas the government is determined to improve. Last year, 104 million Yuan was spent on supporting high-tech corporations by the local government. Other than direct funding, the government also offers preferential policies such as tax deduction.
Overall, with the advantages in location, finance and the market, Pukou is a desired
place to start a Mobile Internet business.
第二篇:中国移动年度分析报告英文版
CONTENTS
China Mobile (Hong Kong) Ltd CONTENTS
CHINA MOBILE KEY CONTACT INFORMATION...........................................................................1
CHINA MOBILE SUMMARY............................................................................................................2
CHINA MOBILE FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE..............................................................................3
China Mobile Quarterly Results, March 2004-March 2005.................................................................3
China Mobile Audited Annual Results, 2000-2004.............................................................................3
China Mobile Revenue and Operating Income, 2000-2004................................................................4
China Mobile Breakdown of Revenues by Business Area, 2002-2004..............................................4
CHINA MOBILE CORPORATE STRUCTURE.................................................................................5
Subsidiaries.....................................................................................................................................................6
Principal Subsidiaries................................................................................................................................6
CHINA MOBILE CORPORATE STRATEGY...................................................................................7
CHINA MOBILE RECENT DEVELOPMENTS.................................................................................8
CHINA MOBILE TIMELINE OF SIGNIFICANT EVENTS...............................................................11
China Mobile Corporate Timeline, 1994-2005..................................................................................11
CHINA MOBILE OPERATING STATISTICS..................................................................................14
China Mobile Quarterly Operating Statistics, 2004-2005..................................................................14
China Mobile Annual Operating Statistics, 2001-2004.....................................................................14
CHINA MOBILE SWOT ANALYSIS...............................................................................................15
CHINA MOBILE NETWORKS AND SERVICES............................................................................16
Networks.........................................................................................................................................................16
China Mobile GSM Network Statistics, 2000-2004...........................................................................16
Services..........................................................................................................................................................17
Strategic Alliance with Vodafone.................................................................................................................17
Research and Development.........................................................................................................................18
China Mobile Recent Equipment Supply Contracts, 2004-2005.......................................................18
June 2005 ? Espicom Business Intelligence
CONTENTS
INDEX OF TABLES
China Mobile Quarterly Results, March 2004-March 2005.................................................................3
China Mobile Audited Annual Results, 2000-2004..............................................................................3
China Mobile Revenue and Operating Income, 2000-2004................................................................4
China Mobile Breakdown of Revenues by Business Area, 2002-2004...............................................4
China Mobile Corporate Timeline, 1994-2005..................................................................................11
China Mobile Quarterly Operating Statistics, 2004-2005..................................................................14
China Mobile Annual Operating Statistics, 2001-2004......................................................................14
China Mobile GSM Network Statistics, 2000-2004...........................................................................16
China Mobile Recent Equipment Supply Contracts, 2004-2005.......................................................18
INDEX OF CHARTS
Ownership Structure and Operating Companies (as of December 2004)..........................................5
China Mobile Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats Analysis...................................15
June 2005 ? Espicom Business Intelligence
CHINA MOBILE KEY CONTACT INFORMATION
China Mobile (Hong Kong) Ltd
CHINA MOBILE KEY CONTACT INFORMATION
Head Office
China Mobile (Hong Kong) Ltd
60/F, The Center
99 Queen's Road Central
Hong Kong
Tel: 00 852 3121 8888
Fax: 00 852 2511 9092
Web: Key Executives Mr Wang Jianzhou – Executive Director, Chairman, & Chief Executive Officer Mr Li Yue - Executive Director and Vice President, Network & Planning Mr Lu Xiangdong - Executive Director and Vice President, Marketing & Operations Mr Xue Taohai - Executive Director, Vice President, and Chief Financial Officer, Corporate Finance Mr Zhang Chenshuang - Executive Director and Vice President, Corporate Affairs & Development Strategy Madam Li Mofang - Executive Director, Vice President and Chief Engineer, Research & Development Mr He Ning - Executive Director and Vice President, Administration & Media Relations
Mr Li Gang - Executive Director, and Chairman and President of Guangdong Mobile
Mr Xu Long - Executive Director, and Chairman and President of Zhejiang Mobile
Ms Grace Wong Wai Lan – Company Secretary
June 2005 ? Espicom Business Intelligence 1
CHINA MOBILE SUMMARY
CHINA MOBILE SUMMARY
China Mobile (Hong Kong) Ltd, together with its subsidiaries, was incorporated in Hong Kong on September 3, 1997 and listed on the Hong Kong and New York Stock Exchanges in October 1997. The company operates mobile networks in all the 31 provinces, municipalities, and autonomous regions of China through 31 wholly-owned subsidiaries.
China Mobile (Hong Kong) is the leading mobile services provider in mainland China and boasts the world’s largest unified, contiguous all-digital mobile network and the world’s largest mobile subscriber base. As of May 31, 2005, the company had a subscriber base of 220.51 million, consisting of 60.51 million contract and 160 million pre-paid customers.
China Mobile (Hong Kong) provides mobile telecommunication services primarily through the GSM platform. The company also provides voice and data services including wireless data and Internet access.
China Mobile (Hong Kong) Ltd’s majority shareholder is China Mobile (Hong Kong) Group Ltd, which, as of December 31, 2004 indirectly held an equity interest of approximately 75.6% of the company through a wholly-owned subsidiary, China Mobile Hong Kong (BVI) Ltd. China Mobile Hong Kong (BVI), in turn, is wholly-owned by China Mobile
Communications Corporation (CMCC), the ultimate parent company. The remaining 24.4% of the shares were held by public investors, including Vodafone Group of the UK, with an approximate 3.26% interest. No other persons own 5% or more of China Mobile’s shares.
As of May 31, 2005, approximately 75.5% of China Mobile’s shares were held by China Mobile (Hong Kong) Group.
Note: This profile is about China Mobile (Hong Kong) Ltd, which is referred to as China Mobile from this point on. It should also be noted that CMCC often places contracts with equipment suppliers that cover China Mobile companies.
2 ? Espicom Business Intelligence June 2005
CHINA MOBILE FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE
CHINA MOBILE FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE
China Mobile Quarterly Results, March 2004-March 2005
Quarter ended
Revenues
Operating Income (PTOP) EBITDA Net Income Capital Expenditure Total Assets
Note: The above financial data recognises the impact of new and revised Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standards and Hong Kong Accounting Standards (New HKFRSs) which became effective for accounting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2005.
March 05(Yn m)
%chg
30.2NC22.019.8
NANCNA
NA
NC
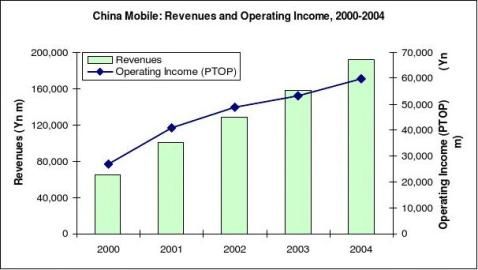
China Mobile Audited Annual Results, 2000-2004
Year ended December 31
2000(Yn m)
Operating Income (PTOP)
26,826
2001(Yn m)
100,33141,01260,27027,95539,500174,953
2002(Yn m)
128,56148,79677,30932,60140,083286,021
%chg
28.119.028.316.63.863.5
% chg
23.4 9.0 19.4 9.1
2004(Yn m)
192,38159,734107,22142,004
%chg
21.312.316.218.122.820.0
Net Income Capital Expenditure Total Assets
Cellular Subscribers (000)
Cellular Subs/Employee Revenues/Employee (Yn 000) PTOP/Employee (Yn 000)
Revenues/Cellular Sub (Yn) PTOP/Cellular Sub (Yn) CAPEX/Cellular Sub (Yn)
PTOP: Revenues (%)
41.31,140.0594.4496.61,177.01,694.0699.645,13418,24021,964157,702
38,74869,643
59,633117,676
53.969.0
38.044.3
1,797.32,589.31,058.4
1,973.32,155.9818.3
-9.8-16.7-22.7
4.4-12.1-18.6
1,440.7588.9567.2
1,092.5414.7340.6
-24.2-30.0-38.6
-15.8-22.1NC
40.938.0--
June 2005 ? Espicom Business Intelligence 3
CHINA MOBILE FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE
China Mobile Revenue and Operating Income, 2000-2004
China Mobile Breakdown of Revenues by Business Area, 2002-2004
Year ended December 31
Usage fees Monthly fees
Other operating revenue Total
2002(Yn m)
93,27216,90118,388128,561
2003 (Yn m)
2004(Yn m)
%chg
15.819.845.221.3
26,911
39,087
4 ? Espicom Business Intelligence June 2005
CHINA MOBILE CORPORATE STRUCTURE
CHINA MOBILE CORPORATE STRUCTURE
China Mobile (Hong Kong) Group Ltd holds its stake in China Mobile Ltd through a wholly-owned intermediate holding company called China Mobile Hong Kong (BVI) Ltd. China Mobile Communications Corporation (CMCC), a state-owned company, holds all of the voting shares and economic interest in China Mobile (Hong Kong) Group Ltd. The majority of the mobile network operating companies are held via separate wholly-owned intermediate holding companies which are registered in the British Virgin Islands (BVI). For example, Fuijan Mobile Communication Company Ltd (Fuijan Mobile), which operates a network in the province of Fuijan, is held through Fuijan Mobile (BVI) Ltd. The exceptions to this are Zhejiang Mobile and Guangdong Mobile. The operating companies are registered in China as wholly-owned foreign enterprises.
China Mobile operates mobile networks in 31 provinces, municipalities, and autonomous regions in China through 31 wholly-owned subsidiaries. These subsidiaries are represented in the following diagram, along with the ownership structure of the China Mobile group.
Ownership Structure and Operating Companies (as of December 2004)

Note: The diagram above does not include intermediate holding companies.
As of May 31, 2005, approximately 75.5% of China Mobile’s shares were held by China Mobile (Hong Kong) Group. No other persons own 5% or more of China Mobile’s shares.
June 2005 ? Espicom Business Intelligence 5
CHINA MOBILE CORPORATE STRUCTURE
Subsidiaries
All the subsidiaries represented in the diagram above, except two, are mobile network operating companies, of which there are 31. The subsidiaries which are not mobile network operators are:
? China Mobile (Shenzhen) Ltd - established in June 2000 and functions as the corporate operation controller.
China Mobile (Shenzhen) was established to improve profit monitoring and financial management of the
company’s operating subsidiaries in mainland China, to handle roaming and interconnection clearing and
settlement among the subsidiaries and other enterprises of China Mobile Communications Corporation
(CMCC), and to conduct research and development relating to wireless data communications.
Aspire Holdings Ltd - registered in the Cayman Islands and owned 66.41% by China Mobile, 9.99% by
Vodafone Jersey (a subsidiary of Vodafone Group), and 7% by Hewlett-Packard (HP). Aspire Holdings Ltd owns 100% of Aspire (BVI) Ltd, which in turn owns Aspire Technologies (Shenzhen) Ltd (technology
platform development and maintenance), Aspire Information Network (Shenzhen) Ltd (provision of mobile data solutions, system integration, and development), and, Aspire Information Technologies (Beijing) Ltd (technology platform development and maintenance). Under platform development agreements with CMCC, services offered by Aspire include gateway and system integration, software, system and hardware
development, overhaul services for data centres, and technical support. Both are registered in China as wholly-owned foreign enterprises. Aspire is a joint-venture company which has become the research and
development arm of China Mobile. It is engaged in the provision of wireless data and Internet enabling
technologies, applications and service platforms including the unified Mobile Information Service Center (MISC) platform through which China Mobile and CMCC provide Monternet and other wireless data services to their subscribers. Aspire also operates China Mobile's mobile R&D centre in Shenzhen. ?
Aspire has formed business alliances with HP and Vodafone Group. The companies work together to develop, implement, and support mobile data services in China. Aspire has also formed a strategic investment alliance with global investment bank, Merrill Lynch. In addition, it has formed business partnerships with domestic and international software and technology companies, including: Microsoft, Oracle, Cisco Systems, Ericsson, Nokia, Alcatel, Intel, BEA, 724 Solutions, Liming Network Group, TSSX, Any8, tencent.com, and Digital China.
Principal Subsidiaries
China Mobile also owns stakes in the following companies:
?
?
?
?
? Zhongjing Design Institute BVI (100%) – an investment holding company established in March 2004. Jingyi Design Institute (100) – involved in the provision of telecommunications network planning design and consulting services. The company was established in March 2004. CMC BVI (100%) – formed in March 2004, CMC is an investment holding company. CMC (100%) – a network and business coordination centre formed in February 2004. Fujian FUNO Mobile Communication Technology Co Ltd (formerly known as Fuijan Nokia Mobile
Communication Technology Company Ltd) was a 50:50 joint venture with Nokia, formed in 1997 and
involved in network planning, optimising, testing, and supervising, technology support, development, and
training for Nokia GSM 900 and 1800 equipment. During 2004, China Mobile raised its equity interest in Fujian FUNO to 51%.
6 ? Espicom Business Intelligence June 2005
CHINA MOBILE CORPORATE STRATEGY
CHINA MOBILE CORPORATE STRATEGY
As the market leader in the world’s largest mobile telecommunications market, China Mobile intends to focus on its core mobile telecommunications business, enhance its core competitiveness through economies of scale, continue to
implement a differentiated sales strategy, develop new businesses, enhance its network management, establish a world class telecommunications and IT supporting network, and further consolidate the company’s position as the market leader in the mobile telecommunications industry in mainland China.
China Mobile believes the mobile telecommunications market in mainland China will continue to expand, and has
designed its business strategy to achieve sustainable growth. The company’s business strategy includes the following key elements:
?
?
?
?
?
implement a differentiated sales and marketing strategy; continue to improve customer services and satisfaction; refine and optimise its telecommunications and IT supporting networks; emphasise innovation in developing new businesses; and, continue to utilise its existing competitive advantages in terms of network, technology, and resources, market experience and market leading position to actively prepare for the construction and development of 3G.
June 2005 ? Espicom Business Intelligence 7
CHINA MOBILE RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
CHINA MOBILE RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
? June 2005 - AsiaInfo Holdings Inc signed a contract with Shanghai Mobile to provide its IN-BOSS billing
software solution to support the carrier's real-time monitoring of prepaid calling charges. Faced with an increasing number of overdue and unpaid subscriber bills, Shanghai Mobile will implement AsiaInfo's IN-BOSS billing software solution in order to reduce its billing costs and further improve its network management
efficiency. The software will also provide the carrier with a number of real-time services including monitoring, billing, rebating, accounting, and information inquiry processing and management. As a means of preparing for the imminent implementation of 3G systems, Shanghai Mobile will begin the gradual transfer of all prepaid services over to the BOSS system.
June 2005 – China Mobile lost out to Emirates Telecommunications Corp (ETISALAT) in the bidding contest for a 26% stake in Pakistan Telecommunication Co Ltd (PTCL). ETISALAT submitted the highest offer of US$2.59 billion for the stake, somewhat higher than the second highest bid from China Mobile of US$1.409 billion.
June 2005 - Amdocs and HP China, a subsidiary of Hewlett-Packard, announced a joint project to provide integrated billing for Beijing Mobile.
May 2005 - Telestone Technologies Corporation was awarded a one-year US$2.5 million contract from China Mobile to boost residential wireless coverage across Xinjiang Province. According to the contract, Telestone will install a series of its repeater and indoor distribution systems throughout China Mobile's GSM network in Urumqi City, the capital of Xinjiang, as well as in other regional cities including Yi Ning, Yi Li and Ka Shi. Telestone will also provide China Mobile with ongoing engineering service and system maintenance for the length of the contract.
May 2005 - Telcordia, a provider of telecommunications software and services, announced that
Liaoning Mobile had selected the cornerstone of the Telcordia Granite Service Resource Management Portfolio, Granite Inventory Management. The Granite solution enables China Mobile to intelligently manage network and service-related assets across the organisation in a consolidated, flexible, service-centric manner. April 2005 - It was announced that China Mobile was deploying a switching solution from Nortel
Networks to provide secure 'anywhere, anytime' mobile Internet data capabilities to its 210 million subscribers. The solution would also enhance China Mobile's network management to ensure high levels of security are maintained as the company meets increased demand for new services.
March 2005 – China Mobile announced changes in the company’s board. Sir Julian Michael Horn-Smith, deputy chief executive officer of Vodafone Group Plc, was appointed as the company’s new non-executive director.
March 2005 - Alcatel signed contracts worth a total of €17 million to expand the GSM networks of Jilin Mobile Communications Company (Jilin MCC) and Shanxi Mobile Communications Co Ltd (Shanxi MCC.
January 2005 – Sichuan Mobile deployed the Comverse Intelligent Short Message Service Center (ISMSC) to handle its increased SMS text messaging needs. The high capacity Comverse ISMSC
processes over 2,200 short messages per second via a single point code, making it one of the largest single SMS platforms deployed in China at that time. Comverse ISMSC provides the additional capacity required to support the growing demand for text messaging services used by Sichuan Mobile’s customers. The ISMSC’s open standards-based platform and extensive database capabilities enable full support of and easy integration with the hundreds of third-party SMS-based content services available on the Sichuan Mobile network.
January 2005 - Nokia signed a contract with Jiangxi Mobile (Jiangxi MCC) for the expansion of its GSM network. Financial details were not disclosed. Under the agreement, Nokia supplied its GSM core and radio-access network infrastructure. The project was completed during the first quarter of 2005.
January 2005 – China Mobile’s subscriber base crossed the 204 million mark. The customer base of the company grew 38.2 million to 204.3 million in December 2004. There were 59.9 million contract GSM
subscribers and 144.4 million prepaid GSM subscribers during the period. ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
8 ? Espicom Business Intelligence June 2005
? CHINA MOBILE RECENT DEVELOPMENTS January 2005 – China Mobile signed agreements with China Mobile Communications Corp. The
company signed telecommunications services agreement and property leasing agreement with China Mobile Communications Corp (CMCC), under a continued connected transaction agreement. As per the telecom services agreement, China Mobile would procure certain communications equipment and other services such as project planning and network maintenance services from CMCC. Through the property leasing agreement, China Mobile is entitled to use certain CMCC’s premises such as retail outlets, warehouses and office spaces. ·December 2004 – China Mobile formed a strategy-making Consulting Committee. The committee, comprising economists, telecom experts, government officials, and lawyers, was formed in response to
anticipated heavy competition from overseas and incumbent rivals in the mobile market. With the formation of the committee, China Mobile aims to sustain market leadership position in the some of the saturated markets and also to fully prepare the company for the 3G market.
December 2004 - AsiaInfo Holdings signed contracts with Shanghai Mobile and Gansu Mobile to
upgrade the carriers' business operation support systems (BOSS) to its latest OpenBOSS version 1.5. Gansu Mobile's upgraded OpenBOSS system will offer 24-hour online support to its over 2.4 million
subscribers and will facilitate online bill inquiry, payment and real-time remote services. The system will feature advanced customer authentication capabilities to ensure security. Initially constructed by AsiaInfo in 2001, Shanghai Mobile's new OpenBOSS system will significantly enhance services for its enterprise customers through improved channel management, marketing, sales, and mobile data business platforms while ensuring system security.
December 2004 – AsiaInfo Holdings signed a contract with Beijing Mobile to implement phase II upgrades to the carrier's Operational Customer Relationship Management (OCRM) system. Beijing
Mobile's new OCRM system will improve customer satisfaction through enhancements in handling and tracking of sales orders, customer requests, quotations, credit checks and other related data. Following the upgrades, Beijing Mobile's OCRM system will link with its business operation support system (BOSS) while continuing to use the carrier's existing decision support system (DSS). The phase II upgrades will significantly enhance the carrier's marketing activities through expansion of the system's ability to collect and interpret information. December 2004 - Ericsson signed a US$50 million GSM/GPRS network expansion contract with Hebei Mobile
December 2004 - Ericsson was awarded a US$805 million contract by Guangdong Mobile
Communication Co (GMCC) to expand its GSM network in Guangdong Province. The project was expected to be completed by the end of March 2005. After this expansion, the capacity of GMCC's GSM network will reach 54 million subscribers.
December 2004 – China Mobile certified two Panasonic GSM mobile phones. The company has certified the M-ZONE A500 and X200 mobile phones supporting China Mobile’s wireless web access service, M-ZONE. December 2004 – China Mobile initiated operations of 3G mobile communications network in Beijing. The company’s subsidiary, Beijing Mobile, commenced the ground work for offering 3G mobile services in China in the wake of the impending 3G licence grant in 2005.
December 2004 - Huawei Technologies announced that it had built what it claimed was the world's largest Softswitch network in China for China Mobile Communications Corporation. The project was completed on November 27, 2004 with the aim of reducing operating costs and increasing network flexibility. According to Huawei, this implementation is of great significance in the industry because this is the first time a Chinese operator has engaged in Softswitch-based network construction and service cut-over of such a large scale. This network is expected to carry '17951' provincial inter-network traffic across 31 provinces in China, with the total traffic equivalent to one-third of the traditional provincial network traffic.
November 2004 - Anhui Mobile commissioned the Siemens Communications Group to expand the GSM and GPRS mobile network in the province of Anhui.
November 2004 - Siemens Communications Group has announced contracts worth US$100 million in total to expand the GSM/GPRS networks of China's two mobile operators, China Mobile
Communications Corporation and China United Telecommunications (China Unicom). The projects were carried out in a number of provinces and autonomous regions, including Tibet, Xinjiang, Beijing, and Shanghai. November 2004 – China Mobile deployed Vyyo solutions in Heilongjiang Province. Vyyo, a leading data connections and telephony broadband solutions provider, supplied solutions for cellular backhaul with Wuhan Research Institute (WRI) as system integrator. ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
June 2005 ? Espicom Business Intelligence 9
CHINA MOBILE RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
? November 2004 - China Mobile chose to expand its deployment of Vyyo Inc's solution for cellular and
Wi-Fi backhaul in eight cities in Jiangsu province, including: Su Zhou, Wu Xi, Chang Zhou, Zhen Jiang, Yang Zhou, Nan Tong, Tai An, and Huan An. Situated north of Shanghai on China's southeast coast, the densely populated Jiangsu province covers 100,000 square kilometres with a population of over 70 million. October 2004 - UTStarcom signed a contract with China Mobile to provide its NetRing multiservice optical transport solutions. The NetRing platform delivers high-density, high-speed aggregation and transport of voice, data, and video services in metropolitan networks. Under the contract, UTStarcom will deploy nearly 200 NetRing nodes to expand the metropolitan area network of China Mobile in Tianjin in northeastern China.
November 2004 - Henan Mobile selected Nokia to provide phase 9 of its GSM network build out in a deal valued at US$200 million. The phase 9 expansion, which will be the biggest increase in Henan MCC's network capacity since Nokia's co-operation began with the Chinese operator in 1995, will greatly enhance network coverage in rural regions, scenic spots, and city areas in Henan province. ? ?
10 ? Espicom Business Intelligence June 2005
CHINA MOBILE TIMELINE OF SIGNIFICANT EVENTSCHINA MOBILE TIMELINE OF SIGNIFICANT EVENTS
China Mobile Corporate Timeline, 1994-2005
1994
1997 China Telecommunications Corporation (China Telecom) was formed out of the Directorate General of Telecommunications (DGT) of the Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications (MPT). In March, China Telecom (Hong Kong) Ltd (CTHK) was established as a joint venture between China Telecom (49%) and
Tianbo Telecommunications Holding (51%) to develop telecommunications activities in Hong Kong and mainland China.
In September, CTHK was incorporated in Hong Kong. On formation, CTHK's initial mobile telecom operations included those in Guangdong province conducted by Guangdong Mobile Communication Company Ltd and in Zhejiang province conducted by Zhejiang Mobile Communication Company Ltd. As part of the restructuring in preparation for the initial public offering (IPO), the former Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications transferred to CTHK a 100% equity interest in Guangdong Mobile and a 99.63% equity interest in Zhejiang Mobile.
In October, CTHK conducted an IPO, with its shares listed on the New York Stock Exchange and the Stock Exchange of Hong Kong. CTHK raised US$4,200 million from its IPO.
1998
1999 In June, CTHK acquired Jiangsu Mobile from the parent company for HK$22,475 million. The acquisition was financed by internal cash and proceeds from the IPO. China Telecom was corporatised, following which it adopted the China Telecommunications Corporation identity. The
company was split into four discrete companies with common ownership: China Telecom (fixed-line services), China Mobile Communications Corporation (CMCC) (cellular services), Guoxin Paging Corporation (paging services - later transferred to China Unicom), and China Telecommunications Broadcast Satellite Corporation (ChinaSat) (satellite services).
CMCC was established in July 1999 as a state-owned company to hold and operate the mobile telecommunications business nationwide resulting from the separation. As part of this separation, in July 1999, CMCC obtained an approximately 57% holding of voting shares and economic interest in China Mobile (Hong Kong) Group Ltd, previously held by Telpo
Communications (Group) Ltd, an entity 100% controlled by the former Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications.
In November, CTHK completed an equity offering of around US$2,000 million and an offering of notes due 2004 of US$600 million.
Also in November, CTHK acquired Fujian Mobile, Henan Mobile, and Hainan Mobile from CMCC for a total of HK$49,715 million (approx. US$32,840 million). The acquisition was made with HK$19,031 million in cash and HK$30,684 million in the form of new shares issued to China Mobile Hong Kong (BVI) Ltd (CMHK (BVI)).
2000 In May, the remaining 43% interest in China Mobile (Hong Kong) Group Ltd was transferred to CMCC; it was previously held
by the Directorate General of Telecommunications (now part of the Ministry of Information Industry). As a result, CMCC became the owner of all voting shares and economic interest in China Mobile (Hong Kong) Group Ltd and thus all of the Chinese government’s interest in China Mobile.
In June, CTHK established Aspire Holdings Ltd for the research and development of mobile data businesses.
Also in June, CTHK changed its name to China Mobile (Hong Kong) Ltd to better reflect its core cellular telephony businesses.
In October, Vodafone Group agreed to acquire new shares in China Mobile for US$2,500 million, which represented
approximately 2.1% of China Mobile’s capital. The two companies also entered into a co-operation agreement, and the investment was the beginning of a long-term strategic alliance between them.
June 2005 ? Espicom Business Intelligence 11
CHINA MOBILE TIMELINE OF SIGNIFICANT EVENTS
In November, China Mobile completed an equity offering of approximately US$6,865 million and an offering of convertible notes due 2005 of US$690 million. It also raised Yn12,500 million by way of syndicated loans.
Also in November, China Mobile acquired seven mobile operators from its parent company for HK$256,021 million
(approximately US$32,840 million). The companies were: Beijing Mobile, Tianjin Mobile, Shanghai Mobile, Hebei Mobile, Liaoning Mobile, Shandong Mobile, and Guangxi Mobile. The acquisition was financed by HK$74,609 million in cash and HK$181,412 million in the form of new shares issued to CMHK (BVI) Ltd.
2001 In January, Hewlett-Packard (HP) formed an alliance with China Mobile's Aspire Holdings subsidiary. HP paid an initial
US$8.5 million in cash for a 1.7% stake in Aspire and agreed to acquire additional shares of up to 7%, up to a maximum value of US$35 million, within a year of the initial purchase.
In February, China Mobile and Vodafone formed a strategic alliance providing for co-operation in the exchange and sharing of corporate management, technical and operational expertise and resources, joint research and development, the introduction of products and services, and the development and implementation of standards and protocols for mobile services. Vodafone Chief Executive, Sir Chris Gent, was appointed as an independent non-executive director of China Mobile.
In June, China Mobile, through its wholly-owned subsidiary, Guangdong Mobile Communications Company, issued Yn5,000 million of corporate bonds in China, which were listed on the Shanghai Securities Exchange in October 2001.
In December, China officially joined the WTO. In the same month, the State Council, the highest state administrative body in China, formally approved the restructuring of the former China Telecommunications Corp, China Netcom Corporation Ltd, and Jitong Network Communications Company Ltd. After the restructuring, China Netcom Group would consist of 10 provincial telecom companies originally owned by the former China Telecommunications Corporation in Beijing, nine other provinces, one directly-administered municipality, China Netcom Corporation Ltd, and Jitong Network Communications Company Ltd. China Telecommunications Corporation would retain the telecom companies originally owned by the former China
Telecommunications Corporation in the remaining provinces, directly administered municipalities, and autonomous regions. As a result, apart from CMCC, principal participants in the telecom industry in mainland China also included China
Telecommunications Corporation, China Netcom Group, China United Teleco1mmunications Corporation (China Unicom), China Satellite Communications Corporation, and China Railcom. Among those six participants, CMCC (including China Mobile), and China Unicom are the two operators that provide mobile telecom services in mainland China.
2002 In January, Vodafone Holding, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Vodafone Group, agreed to invest US$34.965 million in Aspire.
Vodafone Americas Asia, another Vodafone subsidiary, entered into a business alliance agreement with Aspire. At the same time, HP, through its indirect wholly-owned subsidiary, Hanover Asia Pacific Investments, agreed to subscribe to additional shares in Aspire. As a result, Aspire became 66.41%-owned by China Mobile, 9.99% by Vodafone Jersey, 7% by HP, and 16.6% by ASP. The companies agreed to work together to develop, implement, and support mobile data services in China.
In May, the Ministry of Information Industry officially broke up China Telecommunications Corporation into two companies.
In July, China Mobile acquired the entire equity interest of Anhui Mobile, Jiangxi Mobile, Chongqing Mobile, Sichuan Mobile, Hubei Mobile, Hunan Mobile, Shaanxi Mobile, and Shanxi Mobile for a total of US$8,573 million from its parent company, CMCC. In order to fund the acquisition, China Mobile issued new shares to Vodafone in July 2002, taking Vodafone's stake in China Mobile to 3.27%. The deal was financed by using existing internal cash resources of US$2,400 million, representing 76.19% of the cash portion of the initial consideration, and the entire proceeds of the issue and allotment of shares totalling HK$5,850 million to Vodafone. China Mobile assumed the entire net debt of the eight companies, which totalled Yn13,467 million at December 31, 2001. The acquisition increased the number of provinces/regions in which China Mobile operated at that time from 13 to 21 and the number of subscribers from around 69.64 million before the acquisition, or approximately 48% of all subscribers in mainland China as of December 31, 2001, to around 90.57 million after the acquisition, or 63% of all subscribers in mainland China as of such date. The acquisition increased the population in the areas where China Mobile operated from approximately 632.8 million to 1.05 billion people, or 82.3% of mainland China’s total population as of December 31, 2001. This equated to a penetration rate of 8.6%.
12 ? Espicom Business Intelligence June 2005
CHINA MOBILE TIMELINE OF SIGNIFICANT EVENTSIn October, China Mobile, through its subsidiary Guangdong Mobile Communications Company, issued Yn3,000 million
(approximately HK$2,830 million) five-year guaranteed bonds and Yn5,000 million (approximately HK$4,720 million) 15-year guaranteed bonds. The bonds were listed on the Shanghai Stock Exchange in January 2003.
2004 In April, China Mobile Hong Kong (CMHK) signed a conditional sale and purchase agreement to acquire 100% equity interests
in 10 provincial GSM mobile communications operators and other assets from its state-owned parent company, China Mobile Hong Kong (BVI), for US$3,650 million. Upon completion of the acquisition, CMHK would have 166 million subscribers and its service areas would expand to all 31 provinces in mainland China with a combined population of around 1.3 billion. The
companies to be acquired by CMHK included: Neimenggu Mobile (Inner Mongolia), Jilin Mobile, Heilongjiang Mobile, Guizhou Mobile, Yunnan Mobile, Xizang Mobile (Tibet), Gansu Mobile, Qinghai Mobile, Ningxia Mobile, and Xinjiang Mobile
Communication Co Ltd, China Mobile Communication Co (CMC), and Jingyi Design Institute. Of the total purchase price, CMHK would pay US$2,000 million in cash to the parent upon the completion of the acquisition. The balance, amounting to US$1,650 million, will be structured as a deferred consideration. CMHK intended to finance the initial consideration from its existing internal cash resources. The deferred consideration is payable 15 years after completion of the acquisition. China Mobile completed the acquisition in July 2004.
June 2005 ? Espicom Business Intelligence 13
CHINA MOBILE OPERATING STATISTICS
CHINA MOBILE OPERATING STATISTICS
China Mobile Quarterly Operating Statistics, 2004-2005
Quarter ended
Total subscribers (000) - Contract - Prepaid
Mobile data services subscribers (000)
Total usage minutes (million)
Average minutes of use (MOU) per subscriber per month (mins) Average revenue per minute (Yn) SMS usage volume (million) Network capacity (users) (million) Network utilisation rate (%)
Mar 04
150,25651,56898,688110,700
97119,530
2750.35332,40017685.4
Jun 04
158,63751,977106,660 139,730
Sep 04
194,382 59,466 134,916 147,090
204,292 59,887 144,405 156,830
Mar 05
213,87460,268153,606174,000
182,740
287* 0.324* 37,400 21785.4
170,370
297 0.302 40,000 226 86.0
188,270
313 0.290 62,800 244 83.6
196,480
3180.27959,10025484.2
84,06190,771
Note: The above operational data includes figures referring to all 31 provincial mobile operators. * Average for the period January to June 2004.
China Mobile Annual Operating Statistics, 2001-2004
Year ended December 31
Total subscribers (million) - Contract - Prepaid
Net additional subscribers (million) Total usage (billion minutes) - Contract - Prepaid
Average minutes of usage (MOU) per subscriber per month - Contract - Prepaid
Average revenue per user (ARPU) per month (Yn) - Contract - Prepaid
SMS usage volume (billion messages) Average monthly churn rate (%)
2001
69.634.035.632.6161.3130.830.52xxxxxxxxxxxx9727.30.55
2002
117.7
141.6
2004
204.3
144.427.1 260.1
23.9 373.2
38.2660.9
207
240
297
115
102
92
5640.4 0.69
93.5 1.05
172.61.31
14 ? Espicom Business Intelligence June 2005
CHINA MOBILE SWOT ANALYSIS
CHINA MOBILE SWOT ANALYSIS
China Mobile Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats Analysis
?
China Mobile is a market leader in China with a 64.3% market share as of December 2004. The company’s presence spans 31 Chinese provinces/regions. ?
The Chinese government has granted various concessions to companies like China Mobile, allowing it to lower its GSM mobile tariffs by up to 10% below government standard rates, which has helped it gain significant market share. ? ? ? ?
China Mobile is the first overseas-listed Chinese telecom service provider operating in all 31 provinces in mainland China. Large connectivity with a number of overseas operators linking 184 countries helps to fight competition
The company has been posting steady revenue growth, with 2004 revenues reaching Yn192,381 million, up 21.3% over 2003. For 2004, the company reported a robust (free) cash flow of Yn42,381 million due to positive business growth with corresponding benefits from cost controls and economies of scale. The company’s policies have helped enhance management and operational efficiency, which in turn has reduced operational and management costs. ?
China Mobile has a strategic alliance with Vodafone Group, the world’s largest mobile operator.
? ? ? ?
The take-up of wireless data services may be slow. Increase in prepaid subscriber base and downward price pressures have resulted in decreases in ARPU.
China Mobile is subject to extensive government regulation but there is no comprehensive telecommunications law in China.
China Mobile is controlled by CMCC, a state-owned enterprise, which may not act in the interests of minor shareholders.
?
China is a growing economy and a developing market, and its accession to the WTO has eliminated current restrictions on foreign ownership in the telecom industry. Furthermore, this has led to a new regulatory regime aligned with international practice. ? This may enable China Mobile to raise additional funding from foreign establishments in the near future. ?
China Mobile is expected to receive a 3G mobile licence, although ? the timing of when these licences will be awarded keeps being deferred. ? ?
Low penetration rate in China and high growth rate for mobile services promise steady revenues in the future.
The Chinese economy is moving towards a more transparent and open regulatory environment, which would boost demand and purchasing power. ?
The potential for wireless services as an alternative to fixed-line services is sound; the number of mobile subscribers has exceeded fixed-line subscribers in China.
? ? ?
The company faces strong competition from China Unicom which is expanding its code division multiple access (CDMA)-based network.
Regulatory changes may negatively affect China Mobile’s position, particularly if there is increased competition in the future from new entrants, perhaps from new 3G licensees. China Mobile has sufficient spectrum allocation for anticipated subscriber growth in the near term, but it may require additional spectrum to accommodate future subscriber growth or to develop mobile services using new technologies. Network expansion plans may be affected if the company is able to obtain additional spectrum.
Changing of restrictions on foreign ownership may increase competition in the mobile communications service sector. Increasing competition from personal handyphone system (PHS)-type (Xiaolingtong) services offered by fixed-line operators, which are cheaper than GSM services but have limited mobility, may threaten China Telecom’s offerings.
June 2005 ? Espicom Business Intelligence 15
CHINA MOBILE NETWORKS AND SERVICES
CHINA MOBILE NETWORKS AND SERVICES
Networks
China Mobile operates GSM mobile communications networks in mainland China via its 31 wholly-owned operating subsidiaries. The company operates in all 31 provinces, autonomous regions, and directly-administered municipalities throughout mainland China.
The Ministry of Information Industry allocated a total of 24MHz of spectrum in the 900MHz frequency band and 10MHz in the 1800MHz frequency band to China Mobile’s parent company, CMCC. Under the existing agreement between CMCC and China Mobile, China Mobile has the exclusive right to use this frequency spectrum in mainland China.
China Mobile terminated analogue mobile services on December 31, 2001 and, as of January 1, 2002, all of the company’s subscribers had migrated to the GSM system.
China Mobile’s networks currently reach virtually all cities and counties and major roads and highways throughout mainland China. The company intends to continue its network expansion and optimisation with an emphasis on improving network utilisation and operating efficiency as well as expanding the coverage and capacity of its GSM networks. The company’s network expansion and optimisation plans depend to a large extent upon the availability of sufficient spectrum. In addition, in order to improve the capacity of its mobile telecommunications networks in certain major urban centres, GSM-compatible 1800MHz digital cellular system technology has been introduced.
China Mobile GSM Network Statistics, 2000-2004
Year ended December 31
Subscribers (000) Voice Channels (000)
2000
43,1851,860
2001
69,6432,7875991,48043,223
2002
117,6764,7121,0202,49384,824
2003
141,616 5,734
2004
204,290
NA
Base Stations
31,593
NA
NA104,000
NA
The statistics for 2000 and 2001 do not include the eight operating companies acquired by China Mobile in July 2002 (see Timeline of Significant Events section for details of the acquisition). As of December 31, 2001, these eight operating companies had a combined total of 20.93 million subscribers, their networks reached all cities, counties, and major roads and highways within their respective geographic regions, and the average population coverage rate was approximately 90%. Their combined networks had an aggregate of 257 mobile switching centres, 22,688 base stations, an aggregate wireless network capacity of 32.18 million subscribers, and an aggregate average utilisation rate of approximately 65%.
Capital expenditures incurred during 2002, 2003, and 2004 were Yn40,083 million, Yn50,005 million, and Yn61,398
million (US$7,418 million), respectively. This was principally invested in the construction of GSM networks, support
systems, transmission facilities, infrastructure buildings, and the development of new technologies and new businesses. The increase in capital expenditures was primarily due to the inclusion of capital expenditures of the eight regional mobile telecommunications companies China Mobile acquired in July 2002 and the 10 regional mobile
telecommunications companies and other telecommunications assets acquired in July 2004, as well as as a result of the organic growth of the company’s business.
China Mobile estimates that it will spend approximately Yn64.6 billion (US$7.8 billion) in 2005, Yn53.8 billion (US$6.5 billion) in 2006, and Yn45.5 billion (US$5.5 billion) in 2007 in capital expenditures. Such capital expenditure plan does not include investment of 3G network construction.
16 ? Espicom Business Intelligence June 2005
CHINA MOBILE NETWORKS AND SERVICES
China Mobile selects its principal equipment suppliers from among international and domestic manufacturers of mobile equipment. In 2004, the company purchased its GSM infrastructure primarily from Ericsson, Huawei Technologies, Nokia, Motorola, and Alcatel.
Services
China Mobile primarily divides its business into “voice business” and ”new businesses” and mainly uses three brands, each with a different focus. “GoTone” targets high to middle-end subscribers, “Shenzhouxing” targets the mass market, and the “M-Zone” brand targets the young user group through the integration of voice and data services. The company also provides virtual private mobile network (VPMN) services to its corporate customers.
The company’s voice business services include local calls, domestic long-distance calls, international long-distance calls, intra-provincial roaming, inter-provincial roaming, and international roaming. The company’s new businesses include voice value-added services and data businesses. Value-added services mainly include short message services (SMS), WAP, Color Ring, multimedia messaging service (MMS), and Java Applications services. China Mobile has also developed other data products, such as M-commerce, “Mobile Mailbox”, “12586 mobile chat services”, “Mobile Secretary”, and “12590 voice-SMS information”.
China Mobile conducts various data businesses under the “Monternet” platform. As a carrier of data businesses,
“Monternet” enables service providers to realise their creative and competitive advantages, and to commercially launch their products quickly and efficiently. As of the end of 2004, China Mobile had entered into broad co-operation arrangements with over 1,000 service providers. In addition, over 100,000 SMS applications, over 10,000 MMS applications, over 10,000 WAP applications and over 2,000 JAVA applications were supported by the “Monternet” platform as of the end of 2004.
The company provides wireless Internet access by utilising general packet radio service (GPRS) and wireless local area network (WLAN) technologies to access WAP websites and Internet websites. China Mobile has begun providing WLAN services at “hot spots”, such as airports, hotels, conference and exhibition centres and office buildings, within certain major cities.
As of December 31, 2004, China Mobile’s GSM global roaming services covered 184 countries and regions, while its GPRS global roaming services coverage was extended to 73 countries and regions.
Strategic Alliance with Vodafone
China Mobile has a strategic alliance agreement with Vodafone, which provides for a number of co-operation arrangements between the two companies, including:
?
?
?
?
Under the agreement, Vodafone is China Mobile’s preferred partner in the above mentioned areas, and China Mobile is Vodafone’s sole strategic partner in China for all areas of potential co-operation within the scope of the strategic alliance. As part of the alliance, as of May 31, 2005, Vodafone held approximately 3.26% of China Mobile’s outstanding shares. the exchange and sharing of corporate management, technical and operational expertise and resources; joint research and development; the introduction of global products and services for the mobile community; and, the development and implementation of standards and protocols relevant to mobile telecommunications.
June 2005 ? Espicom Business Intelligence 17
CHINA MOBILE NETWORKS AND SERVICES
Research and Development
China Mobile’s research and development (R&D) efforts focus on:
?
?
The principal business focuses of Aspire, China Mobile’s majority-owned subsidiary with operations based in Shenzhen, China, include systems integration, product development, and technical support for mobile data systems and related applications in mainland China. Aspire also operates China Mobile’s wireless data R&D centre in Shenzhen, China.
Aspire has a business alliance with each of Hewlett-Packard and Vodafone Americas Asia Inc, a subsidiary of Vodafone, to develop wireless data and Internet and related applications. As of May 31, 2005, Hanover Asia-Pacific Investments Ltd, an indirectly wholly-owned subsidiary of Hewlett-Packard, and Vodafone Holdings (Jersey) Ltd, a subsidiary of Vodafone, hold a 7% and a 9.99% equity interest in Aspire, respectively.
Aspire has also entered into a master agreement with China Mobile for the development of its mobile information service centre platform. Under this master agreement, Aspire provides system and gateway integration services, hardware, software, and system development, technical support and major overhaul services of data centres to China Mobile.
developing advanced data application solutions suitable for the particulars of the consumer markets in mainland China; and, monitoring technological trends, including advancement in 3G, which may have an impact on the development of the company’s current business and the implementation of its wireless data strategy.
China Mobile Recent Equipment Supply Contracts, 2004-2005
Details
March, Nokia supplied its WAP Gateway solution to Guangdong Mobile Communication Co (GMCC) to provide WAP
service to the majority of Guangdong Province. The system provided by Nokia was one of the largest implementations of the Nokia WAP Gateway to date, able to handle a "massive number" of simultaneous WAP sessions.
In May, China Mobile selected Huawei Technologies’ global system for mobile communications(GSM) softswitch MSC to build its TMSC plane network. The TMSC network would cover the entire network of China Mobile in 31 provinces and
branches, and also deal with all long-distance mobile calls between the two branches. The GSM softswitch MSC is based on packet-switched technology and can be shared by GSM and WCDMA. It will also support smooth evolution from GSM to
WCDMA.
Also in May, BOCO Inter-Telecom, CMCC’s largest network management system (NMS) vendor in mainland China, selected ADC's Metrica for CMCC's GSM and general packet radio service (GPRS) networks. BOCO said it would integrate Metrica software into its own NMS to provide a total solution to China Mobile, including professional performance management and analysis of China Mobile's GSM and GPRS network.
In July, China Mobile subsidiary Hubei Mobile selected Ericsson to supply infrastructure equipment to expand its network, including MSC AXE 10s, and services, including turnkey deployment and integration, network performance improvement, and technical support. The expansion was to increase the capacity of Hubei Mobile's GSM network, as well as enable the
provision of high-speed data applications and services.
Also in July, CMCC selected Siemens to upgrade its networks in mainland China under a US$41 million contract. Siemens agreed to expand the GSM/GPRS network in Anhui Province with additional base stations and switching technology. The
expansion was expected to increase the capacity of the network by one million subscribers.
18 ? Espicom Business Intelligence June 2005
Details CHINA MOBILE NETWORKS AND SERVICESIn August, China Mobile subsidiary Chongqing Mobile awarded a US$27 million GSM expansion contract to Ericsson. Ericsson agreed to supply equipment and services, including switching platforms, base stations, network deployment, network support, and an operation support system (OSS) upgrade. Following the expansion, the network would have EDGE capability, providing the foundation for Chongqing's network to migrate smoothly to 3G in the future. Post deployment, the total capacity of Chongqing Mobile's GSM network would reach six million subscribers.
In August, AsiaInfo Holdings Inc, a provider of software, solutions, and services to telecommunications operators and enterprises in China, signed a network solutions contract with China Mobile to carry out phase II of its IP backbone (CMNet) upgrade and optimisation. Under the agreement, AsiaInfo will provide integration services to support the upgrade of phase II of China Mobile's CMNet system. The high-capacity enhanced system will incorporate leading edge Internet technology to deliver China Mobile's expanded data-related applications, including multimedia and IP, VoIP, VPN, and WAP services. AsiaInfo has been a technology partner of China Mobile since 2000, when it first built and managed the network integration of China Mobile's CMNet national IP backbone to connect China's 31 provincial capitals. AsiaInfo co-operates with China Mobile in a number of areas, including IP network infrastructure, billing, SMS software solutions, and CRM solutions, and claims to be the largest supplier of business operation support systems (BOSS) to the China Mobile market.
In September, Jiangxi Mobile, selected Nokia for the next phase of its GSM network expansion. Under the US$60 million agreement, Nokia would supply its GSM core and radio access network equipment, as well as implementation, optimisation, and care services, to Jiangxi Mobile.
In September, Shandong Mobile selected Ericsson for a US$150 million GSM network expansion contract. Ericsson agreed to supply equipment and services to support the upgrade and expansion of Shandong Mobile's network. It also agreed to introduce the latest AXE810 switching platform and software to the GSM network to provide a foundation for future migration to a 3G mobile communications system. The upgrade and expansion project was expected to help Shandong Mobile to achieve a total network capacity of 18 million users by December 2004.
In September, China Mobile selected Dilithium Networks’ Dilithium Networks Analyzer (DNA), a 3G protocol analysis and test tool, which allows 3G operators to identify and address service issues for interoperability testing and standards compliance with equipment manufacturers.
In September, AsiaInfo Holdings signed a contract with Liaoning Mobile to construct an electronic business system. Under a separate contract, AsiaInfo will also help the carrier to upgrade its customer service centre. AsiaInfo will develop a
comprehensive e-business system for Liaoning Mobile which is capable of processing both voice and data business and will allow mobile users to conduct on-line interactive business transactions. The new platform will be accessible via WAP, short messaging and the Internet and will provide users with an individualised on-line interface to view and manage relevant information. In related news, AsiaInfo was also awarded a contract by Liaoning Mobile to upgrade the carrier's customer service center. The upgraded system will have enhanced analytical processing capabilities with added functions including quality checking and outbound calling. Liaoning Mobile initially contracted AsiaInfo to establish its BOSS network at the end of 2002. In 2003, the carrier selected AsiaInfo to deploy its Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software solution. The carrier's upgraded customer service platform is an external interface of BOSS and will work closely with the system.
In September, China Mobile Communications Corporation (CMCC) selected Ericsson to supply equipment for its CMNet Phase Two IP backbone network expansion in all 31 Chinese provinces and autonomous regions. Under the contract, Ericsson would provide AXI 580-3 and AXI 520-8 IP backbone routers, while expanding the existing AXI 520-4 routers. The Phase Two expansion is expected to increase backbone bandwidth, reliability, and the range of mobile Internet applications available to China Mobile subscribers. It will also improve overall scalability in China Mobile's network and facilitate more efficient use of bandwidth through MPLS traffic engineering. Ericsson was the sole equipment supplier of China Mobile's Phase One IP backbone networks in 2000.
In October, UTStarcom signed a contract with China Mobile to provide its NetRing multiservice optical transport solutions. The NetRing platform delivers high-density, high-speed aggregation and transport of voice, data, and video services in
June 2005 ? Espicom Business Intelligence 19
CHINA MOBILE NETWORKS AND SERVICES
Details
metropolitan networks. UTStarcom will deploy nearly 200 NetRing nodes to expand the metropolitan area network of China Mobile in Tianjin in northeastern China. UTStarcom's NetRing product line provides aggregation, grooming, cross-connect, and transport functionality to deliver high-density, highly efficient STM-1 to STM-64, PDH (E1/DS1, E3/DS3), Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, and ATM services in SDH-based carrier networks. All systems support full redundancy, multiple protection options, and in-service upgrades. The NetRing product family combines Add-Drop Multiplexing (ADM), Digital Cross-Connect System (DCS), Ethernet switching, ATM multiplexing, and RPR functionality into an integrated multi-service system.
In November, China Mobile deployed Vyyo solutions in Heilongjiang Province. Vyyo, a leading data connections and
telephony broadband solutions provider, supplied solutions for cellular backhaul with Wuhan Research Institute (WRI) as
system integrator.
In November, China Mobile chose to expand its deployment of Vyyo Inc's solution for cellular and Wi-Fi backhaul in eight cities in Jiangsu province, including: Su Zhou, Wu Xi, Chang Zhou, Zhen Jiang, Yang Zhou, Nan Tong, Tai An, and Huan An. Situated north of Shanghai on China's southeast coast, the densely populated Jiangsu province covers 100,000 square
kilometres with a population of over 70 million.
In November, Henan Mobile selected Nokia to provide phase 9 of its GSM network build out in a deal valued at US$200
million. The phase 9 expansion, which will be the biggest increase in Henan MCC's network capacity since Nokia's co-
operation began with the Chinese operator in 1995, will greatly enhance network coverage in rural regions, scenic spots, and city areas in Henan province. Under the agreement, Nokia is providing GSM core and radio access network equipment and services for operators. In addition to care services, Nokia will provide a range of radio and core GPRS optimisation services, software maintenance services, and consultative support, as well as implementation services. Deliveries have begun and the network expansion is expected to be fully operational in the first half of 2005.
In November, Anhui Mobile commissioned the Siemens Communications Group to expand the GSM and GPRS mobile network in the province of Anhui. The order involved Siemens enhancing the network's capacity, providing Power CPs - high-performance processors for the switching systems - and expanding the base stations. Anhui Mobile's customers will be able to benefit from the enhanced network performance as early as January 2005. The new order was worth US$60 million.
In December, Ericsson signed a US$50 million GSM/GPRS network expansion contract with Hebei Mobile.
In December, Ericsson was awarded a US$805 million contract by Guangdong Mobile Communication Co (GMCC) to expand its GSM network in Guangdong Province. The project was expected to be completed by the end of March 2005. After this expansion, the capacity of GMCC's GSM network will reach 54 million subscribers.
In December, Huawei Technologies announced that it had built what it claimed was the world's largest Softswitch network in China for China Mobile Communications Corporation. The project was completed on November 27, 2004 with the aim of
reducing operating costs and increasing network flexibility. According to Huawei, this implementation is of great significance in the industry because this is the first time a Chinese operator has engaged in Softswitch-based network construction and
service cut-over of such a large scale. This network is expected to carry '17951' provincial inter-network traffic across 31
provinces in China, with the total traffic equivalent to one-third of the traditional provincial network traffic.
January, Sichuan Mobile deployed Comverse’s Intelligent Short Message Service Center (ISMSC), a SMS solution. Under
the contract, Comverse, a premier network-based multimedia-enabled systems and software communication services provider, supplied the ISMSC to meet the growing SMS traffic. The Comverse ISMSC’s main function is to process more than 2,200 messages per second through a single point code. The ISMSC features database capabilities and an open standards-based platform to support Sichuan Mobile network-based third-party SMS-based content services.
Also in January, Nokia signed a contract with Jiangxi Mobile for the expansion of its GSM network. Financial details were not disclosed. Under the agreement, Nokia supplied its GSM core and radio-access network infrastructure. The project was
completed during the first quarter of 2005.
20 ? Espicom Business Intelligence June 2005
Details CHINA MOBILE NETWORKS AND SERVICESIn March, Alcatel signed contracts worth a total of €17 million to expand the GSM networks of Jilin Mobile and Shanxi
Mobile. Under the terms of these contracts, Alcatel provided its Evolium solution, including base stations (BTS), base station controllers (BSC), operation and maintenance controller (OMC-R), and a personalised ring back tone (PRBT) platform, to enable the operators to meet the enhanced requirements of high-quality voice, GPRS, and value-added services. This
expansion project for Jilin MCC covered seven cities across Jilin Province, including Changchun, Siping, Liaoyuan, Songyuan, Tonghua, Baishan, and Baicheng. The project was expected to be completed in late-March 2005, and increase the capacity of Jilin MCC's GSM network to around six million subscribers. Alcatel also helped upgrade the operator's network software which has enabled Jilin MCC's subscriber base to take advantage of GPRS and personalised ring back tone services. The Shanxi MCC project, the operator's ninth GSM expansion, further improved its GSM network capability and reliability. Upon completion, the capacity of Shanxi MCC's GPRS core network accommodated up to 600,000 subscribers.
In April, it was announced that China Mobile was deploying a switching solution from Nortel Networks to provide secure 'anywhere, anytime' mobile Internet data capabilities to its 210 million subscribers. The solution would also enhance China Mobile's network management to ensure high levels of security are maintained as the company meets increased demand for new services. China Mobile is deploying 40 Nortel intelligent Layer 4-7 switches at its Mobile Information Service Centre (MISC) headquarters in Beijing and across 13 provincial and municipal branches, including Guangdong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Fujian, Henan, Hebei, Liaoning, Sichuan, Hunan, Hubei, Yunnan, and Anhui Provinces and Chongqing city. The MISC serves as the platform for all value-added GSM and GPRS mobile Internet services. China Mobile provides its customers WAP, SMS, MMS, and KJAVA services. MISC also supplies a uniformed data interface to provide mobile data roaming capabilities for mobile subscribers, regulate Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) services and deliver billing information to third party service providers.
In May, Telcordia, a provider of telecommunications software and services, announced that Liaoning Mobile had selected the cornerstone of the Telcordia Granite Service Resource Management Portfolio, Granite Inventory Management. The Granite solution enables China Mobile to intelligently manage network and service-related assets across the organisation in a
consolidated, flexible, service-centric manner. The Telcordia Granite Inventory Management will provide Liaoning Mobile with the necessary operations environment to introduce new services quickly and efficiently across its multi-technology based network.
In May, Telestone Technologies Corporation was awarded a one-year US$2.5 million contract from China Mobile to boost residential wireless coverage across Xinjiang, the largest provincial administrative region in the Peoples Republic of China. According to the contract, Telestone will install a series of its repeater and indoor distribution systems throughout China
Mobile's GSM network in Urumqi City, the capital of Xinjiang, as well as in other regional cities including Yi Ning, Yi Li and Ka Shi. Telestone will also provide China Mobile with ongoing engineering service and system maintenance for the length of the contract.
In June, Amdocs and HP China, a subsidiary of Hewlett-Packard, announced a joint project to provide integrated billing for Beijing Mobile. HP China will prime the project and work in conjunction with Amdocs to integrate Amdocs Billing 6 in order to support pre-and post-paid customers for voice, data, and advanced services. In addition, Amdocs Billing 6 will be fully
integrated into BMCC's CRM systems to reduce operating costs, provide faster response time to market, deliver more flexible business and promotions plan, and online charging schemes. HP China and Amdocs will also provide ongoing technical support and maintenance services to BMCC once the implementation is completed.
In June, AsiaInfo Holdings Inc signed a contract with Shanghai Mobile to provide its IN-BOSS billing software solution to support the carrier's real-time monitoring of prepaid calling charges. Faced with an increasing number of overdue and unpaid subscriber bills, Shanghai Mobile will implement AsiaInfo's IN-BOSS billing software solution in order to reduce its billing costs and further improve its network management efficiency. The software will also provide the carrier with a number of real-time services including monitoring, billing, rebating, accounting, and information inquiry processing and management. As a means of preparing for the imminent implementation of 3G systems, Shanghai Mobile will begin the gradual transfer of all prepaid services over to the BOSS system.
June 2005 ? Espicom Business Intelligence 21
CHINA MOBILE NETWORKS AND SERVICES
[This page left intentionally blank]
22 ? Espicom Business Intelligence June 2005
