初二上几何知识点总结
命题和证明
1、判断一件事情的句子,叫做命题。判断为正确的命题叫做真命题;判断为错误的命题叫做假命题。
2、数学命题通常由题设、结论两部分组成。题设是已知事项,结论是由已知事项推出的事项。因此命题可以写成“如果〃〃〃〃〃〃,那么〃〃〃〃〃〃”的形式。 3、人们从长期实践中总结出来的真命题叫做公理,它们可以作为判断其他命题真假的原始数据。
4、有些命题是从公理或其他真命题出发,用推理的方法证明为正确的,并进一步作为判断其他命题真假的依据,这样的真命题叫做定理。
证明举例
1、由题设、定义以及已被确定的公理、定理等,经过逻辑推理,来判断一个命题是否正确,这样的推理过程叫做证明。
2、真命题的证明一般包括“画图、写已知求证、证明”三个基本步骤。“画图和已知求证”通常是告诉大家的,因此不必书写。
3、几何证明没有固定的方法可循,因此只能在训练的过程中,积累一般分析方法和思维方法。例如:证明线段、角相等的一般途径有哪些?证明两直线平行、垂直的一般途径有哪些?常用的添加辅助线的方法有哪几种?等等。
逆命题和逆定理
1、在两个命题中,如果第一个命题的题设是第二个命题的结论,而第一个命题
的结论又是第二个命题的题设,那么这两个命题叫做互逆命题。如果把其中一个命题叫做原命题,那么另一个命题叫做它的逆命题。
2、如果一个定理的逆命题经过证明也是定理,那么这两个定理叫做互逆定理,其中一个叫做另一个的逆定理。
3、每个命题都有逆命题,但每个定理不一定都有逆定理。
线段的垂直平分线
1、定理:线段垂直平分线上任意一点到这条线段两个端点的距离相等。 2、逆定理:和一条线段两个端点距离相等的点,在这条线段的垂直平分线上。 3、线段垂直平分线可以看作和一条线段两个端点距离相等的点的集合。 角的平分线
1、角的平分线的概念:从角的顶点出发,等分这个角的射线,叫做这个角的平分线。
2、角是轴对称图形,它的对称轴是这个角的平分线所在的直线。 3、角的平分线性质:在角的平分线上的点到这个角的两边的距离相等。 4、角的平分线性质的逆定理:在一个角的内部(包括顶点)且到角的两边距离相等的点在这个角的平分线上。
3、角的平分线可以看作这个角的内部(包括顶点)到角的两边距离相等的点的集合。
轨迹
1、点的轨迹:符合某些条件的所有的点的集合叫做点的轨迹。 2、基本轨迹
(1)和线段两个端点距离相等的点的轨迹是这条线段的垂直平分线。 (2)在一个角的内部(包括顶点)且到角两边距离相等的点的轨迹是这个角的平分线。
(3)到定点的距离等于定长的点的轨迹是以这个定点为圆心、定长为半径的圆。 3、交轨法:先找出符合一部分作图要求的点的轨迹,再找出符合另一部分作图要求的点的轨迹,然后得出这两个轨迹的交点。这种利用轨迹相交进行作图的方法叫做交轨法。
直角三角形全等的判定
1、直角三角形是特殊的三角形,对于一般三角形全等的判定方法,直角三角形都适用。
2、直角三角形全等的判定定理
定理:如果两个直角三角形的斜边和一条直角边对应相等,那么这两个直角三角形全等(简记为H.L.)。
直角三角形的性质
直角三角形的性质,可以从它的角、边以及特殊线段之间构成的各种关系的特征去理解。
1、 定理1:直角三角形的两个锐角互余。
2、 定理2:在直角三角形中,斜边上的中线等于斜边的一半。
推论1
斜边的一半。 30,那么它所对的直角边等于
推论2:在直角三角形中,如果一条直角边等于斜边的一半,那么这条直角边所对的角等于30度。
勾股定理
1、在直角三角形中,斜边大于直角边。
2、勾股定理:直角三角形两条直角边的平方和,等于斜边的平方。
3、勾股定理的逆定理:如果三角形的一条边的平方等于其他两条边的平方和,那么这个三角形是直角三角形。
4、勾股定理及其逆定理在实际生活中有着广泛的应用。
第二篇:初二上知识点总结
Unit 1 what did you go on vacation?
一、Vocabulary:p 121-122
Important words:
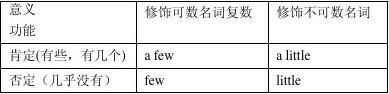
1. few/a few/ little/a little:
There?s little rice in the bowl. I can speak a little French.
Eg : there are a few eggs in the fridge, so I needn?t buy any at once.
There are few eggs in the fridge, so I must buy some.
quite a few&quiet a little :
quite a few:相当多,不少 修饰可数名词复数 He will stay here for quiet a few.
quiet a little:许多,相当多 修饰不可数名词 There is quite a little water in the bottle.
2. vacation&holiday&leave:
vacation:名词,假期,通常指一次性休假,无论假期有多长,尤其用于学校的假期。任何节假日,休假日,单复数皆可,是美式用法。The summer vacation 暑假 spend/take a vacation 去度假 on vocation/holiday 在度假
holiday:指规定的不工作的日子,表示“假期”时常用复数,是英式用法。Holiday; 假日,节日,休假 winter holidays 寒假 school holidays 学校的假期
leave:工作中的请假,休假。 A sick leave of three days 三天病假
3.most :前不加冠词,做代词时,表示“大多数”,后面常接表示范围的of短语; most的单复式概念取决于of后面的名词,谓语动词根据of后面的名词来决定。
most of the students in our school are from the country. Most of the time= most time 大部分时间
4. seem: 作不及物动词,“好像,似乎,看来”常用于以下结构:
①seem+(to be)+形容词/名词“看起来.....”: You seem(to do) happy today.
②seem + to do sth. “似乎好像做某事”: I seem to have a cold.
③It seems/seemed that +从句“看起来....,似乎....”:It seems that mo one believes you. ④seem like......“好像,似乎....”:It seems like a good idea.
5. bored&boring: bored: 厌倦的,烦闷的,以-ed结尾的形容词,如:interested,excited等,一般在句中修饰人,作表语; I?m bored with what he said.
boring:无趣的,令人厌烦的,以-ing结尾的形容词,如:interesting,exciting等,一般在句中修饰事或物,可作表语和定语. I find the story is very boring.
6. decide:动词:决定,选定 decide =make up one?s mind
①decide to do sth. 决定做某事=decide+ 从句: I decide to buy a car.=I decide that I would buy a car. ②decide后接“疑问词+动词不定式): He can not decide wen to leave.
decision:名词:决定 make a decision 做一个决定 make a decision to do sth
7. try:及物动词:尝试,试图,努力 try/do one?s best to do sth try on 试穿 try to do sth; 尽力,设法去做某事,强调付出一定的努力 设法去完成;
try doing sth: 尝试着做某事,表示一种尝试,做做看的想法,不一定付出很多努力。 名词:“尝试? have to try 试一试
8. Feel like:①“感觉像是”:My legs feel like cotton wool(棉花);
②“想要....?:I don?t feel like cooking.
9. because of&because:
because:作连词,用于引导原因状语从句或作why开头问句的答语。后跟句子; because of :为介词短语,后接名词、名词短语或代词等,不能接句子。
He is absent today because he is ill. He stayed in hospital because of his illness.
10. enough:①形容词:足够的,充分的,常与for或不定式连用通常修饰复数名词后不可数名词,可作表语和定语,作定语置于被修饰的名词的前后均可。
He has enough money to buy a car. Five men will be quite enough.
②副词:足够地,充分地,用来修饰形容词或副词,一般置于被修饰词之后。 He runs quickly enough. He is old enough to go to school.
11. as的用法:①副词“像...一样”用来表示程度:She sings as well as singer.
②用作介词“当作,作为”: He worked as a teacher for 10 years.
③用作连词“像,按照”: You must do everything as I told you.
④用作连词“当....时候”:As the students were talking, Mr. Wang came in.
As we can see...... As we all know, It is known to us that........
12. too many/too much/much too:
too many:后接可数名词复数,意为“太多”Mother bought too many eggs yesterday. too much:后接不可数名词,意为“太多”;还可修饰动词作状语:
We have too much work to do. Don?t talk too much.
much too:修饰形容词或副词,意为“太”The hat is much too big for me.
13. forget to do sth/forget doing sth:
forget so do sth:忘记要做某事(事情还没有做):Don?t forget to close the window.
forget doing sth:忘记做过某事 (事情已经做过了): I forget closing the window.
14.stop to do sth/stop doing sth:
Stop to do sth:停下来去做另一件事:We stopped to eat.
Stop doing sth: 停止做某事: We stopped eating
15.bring/take :take:“带走,拿走”指从说话者所在地带到别处去:
Bring:“带来,拿来”指从别处带到说话者所在地:
We?ll take the students to the museum. Don?t forget to bring your homework here tomorrow.
16. ith:①介词,带有,具有: He?s a tall kid with short hair.
②介词,和.....在一起:I often go to school with my friends
③介词,以(手段,材料),用(工具): Cut the apple with a knife.
17. 与jump 相关的短语: jump into 跳入 jump off 跳离 jump over 跳过jump out of 跳出 Jump up and down 上蹿下跳
二、Phrases:
1.go on vacation/summer camp 11.of course
2.go out 12.feel /sound /taste /look like
3.go to the mountains 13.go shopping
4.visit museums 14.in the past
5.quite a few/little 15.walk around
6.study for..... 16.too many/much
7.stay at home 17.because of
8.most of the time 18.one bowl/spoonful of .......
9.taste good 19.the next day
10.have a good/great time 20.drink tea
23.find out 27.up and down 24.go on (with).... 28.enough money/old enough 25.take photos 29.the top of the hill 26.something important 30.come up/out/on/about/across 三、用法集荟:
1.buy sth for sb/buy sb sth 10.look/seem(to be)/taste+adj. 2.nothing.....but do sth 11.dislike/hate doing sth
12.why not/why don?t you +do sth 3arrive in+大地方 / arrive at +小地方
4.decide to do sth/make a decision to do sth 13.how/what about +Ving sth 5.try doing sth/try to do sth 14.so+adj.+that+从句
6.enjoy/finish/mind/feel like+doing sth 15.tell sb (not) to do sth 7.want to do sth 16.keep /go on doing sth 8.start/begin doing sth 17.forget to do sth /forget doing sth 9.stop doing/to do sth
四、单元语法:不定代词和一般过去时态 代词:
一、定义与分类
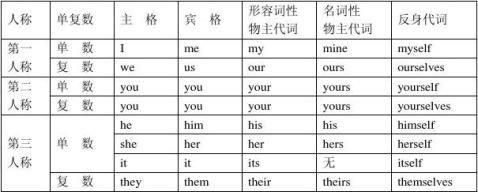
代词是代替名词及起名词作用的短语或句子的词。代词根据其意思和用法可分为人称代词、物主代词、反身代词、指示代词、相互代词、疑问代词、连接代词、关系代词、不定代词等。 二、人称代词,物主代词,反身代词用法概述
这三种代词都有人称(一、二、三人称)的变化、数(单、复数)的变化,以及性(阴性、阳性、中性)的变化。其中,人称代词除了这三种变化外,还有格(主格、宾格)的变化。 物主代词又包括两种形式:形容词性物主代词和名词性物主代词。特别注意:形容词性物主代词its没有相应的名词性物主代词。
不定代词的用法
1)定义:不定代词是不指明代替任何特定名词或形容词的代词。
2)种类:英语中不定代词有:some(something,somebody,someone,somewhere),any(anything,anybody,anyone,anywhere), no(nothing,nobody,no one), every(everything,everybody,everyone,everywhere),all,each,both,much,many,(a)little,(a)few,other(s),another,none,one,either, neither等。 3)不定代词的句法功能
1)作主语,例: Both(of us) are right. Is everybody here?
2)作宾语,例: There is room for all of us. He gave two to each(of them).
3)作表语,例:That’s nothing.Is that all you want to know?
4)作定语,例: You may take either road. Every room is clean and tidy.
5)作同位语,例: They both agreed to stay here. We are all for him.
☆不定代词是英语所有代词中最重要的一类,也是中考英语中最常考的一类,复习时应注意以下几点:
1. some和 any的比较:
不定代词some,any都是“一些”的意思,都可和可数名词或不可数名词连用。some一般用于肯定句中;而any则用于否定句、疑问句或条件从句中.
例:Tom has some picture-books.I have waited some time.
Have you any questions? There aren?t any pictures on the wall.
☆注意:在表示请求、邀请或征求意见的句子中,通常要用 some 而不用any。 如:Will you lend me some money? Why don?t you bring some flowers?
2. 指两者和三者的不定代词。有些不定代词用于指两者(如both, either, neither),有的不定代词用于指三者(如all, any, none, every),具体使用时要根据一定的上下文正确选用。 如:He is blind in both eyes. 他双目失明。
Were they all college students? 他们都是大学生吗?
注:each 可用于两者、三者或三者以上,而 every 只用于三者或三者以上,因此用于两者时只能用 each,不能用 every。如:
There are trees on each side of the road. There are tress on both sides of the road.
3. (a) few 与 (a) little。few和a few 后接复数名词,而little和a little后接不可数名词。其中不带不定冠词的 few 和 little表示数量很少或几乎没有,强调“少”,含有否定意义;而带有不定冠词的a few 和 a little 则表示数量虽然少但毕竟还有,强调“有”,含有肯定意义。如:He knew few of them. He sold only a few of the papers.
He knew little about it. There is still a little left.
4. all, every, each的用法。从强调重点上看:all强调整体地考虑总体,every 强调考虑总体中的所有成员(与all很接近),each则强调逐个逐个地考虑总体;从用法上看:all和each既可单独使用,也可后接名词,还可后接of短语;而every 后必须接名词,既不能单独使用也不能后接 of 短语;从含义上看,each 指两者或两者以上的“每个”,every指三者或三者以上“每个”,因此指两者时只能用 each
如:All was destroyed in the big fire. All are present.=Everyone is present.
There is room for all of us.Each of us has a book.
注:1)在表示“每个”、“全体”意思时,every的意思与all很接近。但一般情况下every和单数名词搭配,all和复数名词搭配,例:
Every child enjoys Christmas. All children enjoy Christmas.
2)Each也是“每一个”的意思,但与every不同,each用于指两个或两个以上的人或物,着重于个别概念,例:Two men came into the room. Each carried an umbrella.
Each/Every book on this desk is worth reading.
5. other, the other, another, others的用法。指单数时,若泛指用another,若特指用the other;指复数时,若泛指用other(后接复数名词)或others(其后不接名词),若特指用the other (后接
复数名词)或the others(其后不接名词)。
如:Show me some others. 再拿一些给我看。Show me another. 另拿一个给我看。
We should think of others. 我们应该多为别人着想。Where are the other students?
注:another后一般要单数可数名词,但若其后的名词有数词或 few 修饰,则也可接复数名词。如:I've got another five minutes. 我还有5分钟。
6. no one, nobody, none 的用法。no one 与nobody 用法相似,均只用于指人不用于指物,且其后不能接of短语,用作主语时谓语单数;而none 既可用于指人也可用于指物,其后通常接of短语,用作主语时,若指不可数名词,谓语只能用单数,若指复数名词,则谓语可用单数(较正式)也可用复数(用于非正式文体)。
如:No one [Nobody] has read it. None of this milk can be used. 这牛奶一点都不能用了。 None of the films is [are] worth seeing. 没有一部电影值得看。
7. 复合不定代词的用法:
复合不定代词主要包括 something, somebody, someone, anything, anybody, anyone, nothing, nobody, no one, everything, everybody, everyone 等,它们在句中可用作主语、宾语或表语,但不能用作定语。
其中something, someone 等和 anything, anyone等的区别与 some 和 any 的区别一样,前者一般用于肯定句,后者一般用于否定句、疑问句或条件句。使用时应请注意以下几点:
(1)形容词修饰不定代词,应置于其后。
如:Tell us something interesting. There was nobody tired.
(2) 指人的复合不定代词若用作主语,其谓语动词一般用单数,相应的人称代词和物主代词也用单数 。如:If anybody [anyone] comes, ask him to wait. 要是有人来,让他等着。
(3) anyone, everyone 等只能指人,不能指物,且其后一般不接of 短语。若是指物或后接 of 短语,可用 any one, every one (即分开写)。
一般过去时:
一、巧记一般过去时
动词一般过去时,表示过去发生的事;be用was或用were; have,has变had;
谓语动词过去式,过去时间作标志;一般动词加-ed,若是特殊得硬记。
否定句很简单,主语之后didn?t添;
疑问句也不难,did放在主语前;
不含be动词时,如果谓语之前有did,谓语动词需还原;
动词若是was,were,否定就把not添。
含be动词时疑问句也不难,要把was,were放在主语前。
二、be的一般过去时:学习动词be的一般过去时,下面有一口诀,它可以帮你们更好地掌 握动词be的一般过去时。 be的过去时有四巧:
一是时间状语巧, 表示过去的短语要记牢;
二是形式巧,单数was,复数were;
三巧是否定句结构,not紧跟was/were;
四是疑问句式巧,was/were向前跑(提前)。
【一巧】时间状语(即标志词)巧。一般过去时表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态,恰巧
与表示过去的一些时间状语连用。
【二巧】形式巧。它与一般现在时一样,形式多样:当主语是第一人称单数或第三人称单数时,谓语动词用was;主语是第二人称或其他人称复数时,谓语动词用were。 例如: I was in the classroom yesterday morning. 昨天早上我在教室里。
He was at school last Tuesday. 上周二他在学校。
They were over there a moment ago. 刚才他们在那边。
【三巧】否定句结构巧。与动词be的一般现在时一样,它在动词后面加not即可变成否定句,并且was, were与not可以缩写成wasn't, weren't。即:主语 + wasn't/ weren't + 表语 + 其他。例如:I was not (=wasn't) here yesterday. 昨天我不在这儿。
My parents were not (=weren't) at home last Sunday. 上周日我父母不在家
【四巧】 疑问句式巧。把was, were提到句首,句末用问号即可变为一般疑问句。即: Was(Were) + 主语 +表语 + 其他?这恰巧与动词be的一般现在时的疑问句式相似。 例如: Were you at home the day before yesterday﹖ 前天你在家吗?
Was she late this morning﹖今天早上她迟到了吗?
更巧的是疑问句的答语也相似,肯定回答用“Yes, 主语+was/were.”;
否定回答用“No,主语+wasn't/weren't.”。
例如:—Were Wei Hua and Han Mei here just now﹖ 刚才魏华和韩梅在这儿吗? —Yes, they were. (No, they weren't.) 是的,她们在。(不,她们不在。)
Unit2 how often do you exercise?
一、Vocabulary:p122-123
Important words:
1. exercise: 作动词讲,运动,锻炼:We often exercise twice a week.
作不可数名词讲,运动,锻炼:We should do more exercise.
作可数名词讲,练习:We do more exercises every day.
2.help: help with sth. 帮助做某事 help sb with sth= help sb (to) do sth 帮助某人做某事
3.some time/sometime/some times/sometimes:
some time:名词短语,一段时间,句中谓语动词常为延续性动词,对它提问用how long; some times:名词短语,几次;几倍,time是可数名词,对它提问用how many times; sometimes:频率副词,有时,表示动作发生的不经常性,对它提问用how often; sometime:副词,某个时候,表示某个不确切或不具体的时间,对它提问用when. 巧记:分开“一段时间”(some time),相聚为“某时”(sometime)
“有时”相聚加-s (sometimes)“几次”分开带-s (some times)
4. hard/hardly: hard:副词,努力地,位于动词之后:He works hard.
hardly:频率副词,几乎不,一般位于实意动词之前:He hardly works .
5.use/with:with介词,在句中作状语,表示方式:I write with a pen.
use:动词,在句中作位于,表示用途:I use the pen to write. Use sth to do sth
6. maybe;副词,做状语,意为“或许,大概,可能”:Maybe you are right.
May be:属于“情态动词+be动词”的结构,意为“可能是”:

You may be right.
7.stay up late:指“熬夜到很晚,迟睡” Don?t stay up late next time.
stay up: 指“熬夜,不睡觉”He stayed up all night to write his story.
8. go to bed:强调上床睡觉的动作及过程,但人不一定睡着:I went to bed at 7 o?clock last night. go to sleep:强调入睡,睡着,进入梦乡:She was so tired that she went to sleep.
9. want: 动词,想要 ①want to do sth ②want sth ③want sb (not) to do sth
10. be good for/with/to /at:
be good at: 擅长,后接名词、代词或动词ing,相当于 do well in...;
be good with: 和.......相处得好;相当于get on(well) with/get along with
be good for: 对....有益;Exercise is good for our health.
be good to 对.....好(和善,慈爱) We should be good with the old.
11.find: 动词,发现,发觉常用于以下结构:
①find+宾语(to do) +名词: We find him( to be) a good boy.
②find +宾语+形容词:He find the room dirty.
③find +宾语+现在分词:He find her standing at the door.
④find +that 从句:We find that he is a good boy.
12. precent: 名词,百分之.....构成: 基数词+percent:percent没有复数形式,作主语时,根据他所修饰的名词来判定谓语的单复数。
13. not.... at all: 一点儿也不 相当于 not in the lightest
not at all: 不客气,相当于 you?re welcome.
14. However/but:可是
But:“可是”一般作连词,可连接前后两个分局,意义上表示的一种转折关系; It began to rain. However, we went out to look for her.
However:“然而,可是”,既可作副词,也可作连词,不能直接连接两个分句,必须另起新句,用逗号隔开,表示的是一种补充的关系。 It is a sunny morning, but very cold.
15.afraid:形容词,害怕的,担心的,常用于以下结构:
①be afraid to do sth, 害怕去做某事:I ?m afraid to trave by plane.
②be afraid of sth/sb,害怕某人、某事:Some children are afraid of the dark. ③be afraid of doing sth, 害怕做某事:Don?t be afraid of asking question.
④be afraid +从句,恐怕,担心: I?m afraid that I have to go now.
16. spend/cost/take/pay: 花费,付账
spend:主语为人,常用结构:sb spends time/money on sth/(in) doing sth
pay: 主语为人,常用结构: sb pays money for sth.
cost: 主语为物,常用结构: sth costs sb money
take: it作形式主语,常用结构: it takes sb time/money to do sth.
二、Phrases:
1.help with homework 10.surf the internet/go online
2.go shopping 11.be free
3.on weekends/on the weekend 12.have dance and piano lessons
4.how often/far/soon 13.swing dance
5.hardly ever/almost not 14.play tennis/basketball
6.once/twice a week/month 15.stay up late/stay up
7.go to the movies/see a film 16.at least/most
8.everyday/every day 17.go to bed early
9.use the internet 18.be good at/for/to/with
19.in one?s free time 23.old habits die hard
20.not....at all/not at all 24.go to the dentist
21.the most popular 25.more/less than
22.such as/for example 26.junk/fast food
三、用法集荟:
6.It?s+形容词+to do sth 三、help sb with sth
2.how/what about....? 7.spend time with sb
3.want sb to do sth. 8.ask sb about sth.
9.by doing sth. 4.How many可数名词复数+一般疑问句?
10. What?s your favorite ....?/ How much 不可数名词+一般疑问句?
What +n.do you like best? 5.主语+find +that 从句
11.the best way to do sth.
12. 以how引导的特殊疑问词的归纳:
①how often: 多久一次,用来提问动作发生的频率;
②how long:多长,用来询问多长时间,也可询问某物有多长;
③how far: 多远,用来询问距离,指路程的远近;
④how are you? 用来提问最近的身体状况;
⑤how old are you? 用来询问年龄
⑥how much: 多少,提问数量,后接可数名词复数
⑦how many:多少,提问数量后接不可数名词;多少钱,提问价格
四、单元语法:频率副词的用法
常用的频度副词按频率发生的高低依次为:
Always>usually>often>sometimes>seldom>rarely>hardly ever>never.
一、定义:
①表示动作发生的次数副词always,usually, often,sometimes, hardly ever, seldom等。
②表示具体的频率、次数时,一次用once,两次用twice,三次及以上用“基数词+times”。
二、表示频度方面的区别:
① always是频度最大的词,意为"总是;永远"。一般不用于句首,但可用于祈使句中如: I shall always remember my first day at school. Always remember this.
②usually意为"通常",即表示习惯性动作或状态,很少例外,频度仅次于always。如: What do you usually have for breakfast?你通常早餐吃什么?
③often意为"经常",在频度上不如usually那么频繁,其反义词是seldom。often常被very或quite修饰。如: Very often he goes online. Li Ping often does his homework in the afternoon. ④sometimes意为"有时候",频度比often小,表示动作偶尔发生,间断较大。其位置比较灵活,放在句首、句中、句末都可。如: I sometimes go to the library.我有时去图书馆。
⑤seldom意为“很少”;never意为“从不”。这两个副词表示否定意义,动作几乎不会发生。
He boys never eat chocolate and the girls seldom eat it.
⑥hardly具有否定意义,表示“几乎不、简直不”,除非特殊情况,否则不会发生. The boy is so young that he could hardly understand it.
三、频度副词的用法:
通常位于实义动词之前,动词be、助动词、情态动词等之后。
如:We often get together。 Jane usually goes to work by bike.
注:如果有两个助动词,频度副词通常放在第一个助动词后面。
We have never been invited to one of their parties.
She must sometimes have wanted to run away.
四、频度副词与not连用时,表示部分否定;对频度副词进行提问时,要用how often。如:
1.A great scholar is not always a very wise man.大学者未必一定是极聪明的人。
2.We go to the cinema sometimes. How often do you go to the cinema?
Unit 3 I’m more going than my sister.
一、Vocabulary : p123-124
Important words:
1. loudly adv. 喧闹地,大声地
loudly&loud&aloud : 三个词都可作副词,都指“大声地”,在意义上相同,有时可以互换。 aloud重点在于“出声“(能被人听见,但声音不一定很大),常与read,think连用; The teacher always asks us to read aloud.
loud多作形容词;He gave a loud laugh.
loudly多跟表示”喧嚣,抱怨“的动词连用,既可置于动词前,也可置于动词后,与quietly相对。 He complained loudly.
2. hard-working&hard work&work hard:
hard-working: 形容词,意为”勤勉的,努力工作的”;
hard work:名词短语,意为“辛苦的工作”,hard是形容词,修饰不可数名词work; work hard 动词短语,意为“努力工作”,hard是副词,修饰动词work。
Eg. The hard-working boy always does hard work and works hard.
3. win&beat:
win “赢得,获胜”,用作及物动词,其宾语为比赛的项目、奖品或战争等,可以是事或物。 We won the basketball game.
Beat “打赢,战胜?,用于比赛时,其宾语为所战胜的对手。He beat all the wunners in that game.
4. though: ⑴ 副词:“不过,可是,然而”通常用于句末,前面用逗号与句子隔开。与however 同义,不过however前面用句号与句子隔开。
Jim said that he would come; he didn?t,though.
Jim said that he would come. However ,he didn?t come.
⑵连词:”虽然,尽管“,相当于although: 两者皆不能与but同时出现在一个句子中。但是可与副词yet 连用。
Though&although;
①作为连词,两者可以互换使用;
②although常放在句子的开头,二though可以出现在其他的位置,当用来连接词语或短语时,更为常用。 Wiser though poorer 尽管穷一些却更有头脑
③以下情况只用though:
㈠与even连用时,用though表强调:even if =even though “即使......也.....” ㈡though引导的让步状语从句时可以倒装,而although则不能。
Bravely though they fought, they had no chance fo winning.
5. truly adv.副词,真正,确实
true adj. 形容词,真实的,真的,符合事实的
truth:n. 名词 事实,实情 tell the truth
6. care n. 不可数名词:照料;保护;小心 take (good) care of = look after (well) 照顾,照料 Take care (not)to do sth. 当心(不要)做某事 take care =be careful =look out 当心,小心 v动词:关心,在乎 care about 关心,在意 care for 喜欢,照顾
9
7. serious adj. 严肃的,稳重的seriously adv 严重地,重大地 be serious about 对....严肃,认真 take.....seriously 对.......严肃对待 He?s in hospital. I?m afraid he?s seriously ill
8. laugh&smile : 动词笑
laugh:一般表示“出声地(大)笑”不但有面部表情,而且还有声音。 Laugh at 嘲笑某人 smile :一般表示“无声地微笑”,指的是面部表情。Smile at......向.....微笑
9. both 形容词&代词:两个,两个都 当both做代词有以下几种用法:
①做主语时,位于动词用复数,通常位于连系动词、助动词或情态动词之后,行为动词之前。 ②both of + 人称代词的宾格或复数名词(接复数名词时of通常省略)“两者都.......” Both of us want to leave here . Both(of)the books are interesting.
Both of 人称代词宾格= 人称代词主格+both
不能说both of books 但可以说both of the books
③both A and B “A和B都.....;既A又B” both Jim and Tom are my good friends. ④both 与not 连用表部分否定
10.be the same as “和......一样,相同”清后互相比较的名词必须是同一类
be different from “和......不同”
the same ......as “与.....相同”as 后可以接从句,并且在从句中充当一定的成分。As不能换成like,可以说the same ......that 但其含义不同。
This is the same pen as I bought yesterday.(不指同一支笔)
This is the same pen that I bought yesterday.(指同一支笔)
11. reach:不及物动词,“伸手” reach for 伸手取某物
及物动词,“到达,抵达”
reach&get to & arrive:
reach: 及物动词,后面直接接宾语;They reached Hangzhou yesterday.
get to:后接地点名词,如果接there ,here或home的地点副词,to 必须省略;
arrive:不及物动词,后接地点名词时必须接介词at或in,到达学校、商店等小的地方 用at,到达国家、城市等大的地方用in, 接here,there,home等地点副词是不用介词in或at。
12.heart : 名词,内心,心脏
Take heart :鼓起勇气,振作起来 touch one?s heart :触动某人的心灵
Put one?s heart into sth: 用全部精力做某事
13. bring out:①使显现;使表现出: I want to bring out the meaning of the poem.
②bring out the best/worst in sb. 把某人最好的、最坏的一面展现出来
③出版;生产: The company is bringing out a new sports cars.
④拿出,带出:Please bring out your cameras and take some pictures.
14. break down: 出故障 Break into 强行闯入 break off 中断说话
15. similar$ same:
similar: 大致相似的,类似的 be similar to 和.....相似,相当于be like
same:相同的,同样的,前面需要加定冠词the。 Be the same as....与.....相同
16. the other ,the others ,other ,others&another
the other:表示“特指两个或两部分中的另一个或另一部分”,可接单数名词或复数名词。表示两个中的“一个....另一个......”时,用结构:one....the other
the others:特指某一范围的”其他的(人或物)是the other的复数形式。相当于the other+复数名词; You two stay here, the others go with me.
other:作代词或形容词,可修饰可数名词单数或复数;
We learn Chinese, Maths, English and other subjects.
10
others:作代词,泛指“其他的人或物”; Some students are doing homework, others are talking loudly.
another:泛指同类食物中的三者或三者以上的“另一个”,只能代替或修饰单数可数名词。 I don?t like this one. Please show me another.
二、Phrases:
1.which one 10.bring out 19.be good with/at/for/to
2.most outgoing 11.get better grades 20.primary/junior/senior
3.as...........as 12.reach for school
4.the singing competition 13.touch one?s heart 21.care about
5.the most important 14.in fact 22.the same as
6.be talented in music 15.make friends 23.have fun
7.be different from 16.be good at 24.share everything
8.be like mirror 17.the other
9.as long as 18.be similar to
三、用法集荟:
1.have fun doing sth 3.as+形容词或副词的原级(+名词)+as
2.want to do sth 4.be good at doing sth
5.make sb do sth
6.That?s Tara, isn?t it? 反意疑问句:在陈述句后附加一个简短问句,征询肯定或否定的意见,或者希望陈述句所说的得到证实。构成如下:
①肯定的陈述句+否定的简短问句: Lucy is good at swimming, isn?t she?---No, she isn?t. ②否定的陈述句+肯定的简短问句:He isn?t a student,is he?----Yes, he is.
7.It?s+形容词/名词+for sb to do sth. ”做某事对某人来说是......的“ It 是形式主语,动词不定时上真正的主语,sb 为宾格代词或名词。此类的形容词为描述事物的特征的词,如difficult,easy,hard,important,dangerous,necessary,possible等时,其后介词用for。
此句型相当于 it?s +形容词+ that从句:
It?s better for you to live alone for some time.=It?s better that you live alone for some time.
8. It?s+形容词+of sb to do sth. 此句型中的形容词为描述人物品质及性格特征的词,如:nice,kind ,clever,foolish,good,polite,silly等,其后的介词用of。
四、单元语法:形容词和副词的比较级
1.大多数的形容词或副词都有三个级别:原级、比较级、最高级。
2.比较级的定义:比较级表示“更??”,用于两者之间的比较,用来说明“前者比后者更??”。
3.比较级的构成:
(1)规则变化:
a.一般原级形容词或副词的词尾加-er:
b.以字母e结尾的直接在词尾加-r:
c.以“辅音+y 结尾的词,变y为 i,再加-er”:
d.以重读闭音节的单个辅音字母结尾的词,双写辅音字母,再加-er:
e.多音节或部分双音节的形容词在原级前面加more:
f.由“动词+后缀-ing/-ed”构成的形容词,在词前加more:
g.由“形容词+后缀ly”构成的副词,在词前加more:
(2)不规则变化:
11
三、比较级的用法:
(一)当两个人或事物(A和B)进行比较时,我们常用到的句式:
主+谓(系动词、行为动词)+形容词或副词的比较级+than+比较对象
It is colder today than is was yesterday. Your hair is longer than mine. I jumped higher than you. 注:
1.为了加强语气和在形容词比较级前面加much,a lot,a bit,even,still,less,far程度等副词, 不可用very,so,quiet,too等修饰。
He is ever slower than before. Japan is a little larger than Germany.
2.比较级前面可以加上表示具体数量差别的结构,表示具体“大多少”,“小多少”,“长多少”,“短多少”等。
I am two years older than he. The building is 20 meters higher than that one.
3.为了避免重复,我们常常用that代替不可数名词,用those代替可数名词复数形式,用one代替可数名词单数形式。
The climate of Kunming is better than that of Wuhan.
The boys in your class are more active than those in our class.
This shirt is larger than that one.
4.在比较级中,所比较的对象前后两者必须是同种性质的事物,不能异类比较。当than前后所使用的动词相同时,通常用助动词代替后面动词,该动词或助动词可省略。
His idea is newer than mine. He speaks English better than she does.
5.在上下文意思明确的情况下,也可以单独使用比较级。
This coat is too small, can you give me a bigger one?
(二)“比较级+and+比较级”或“more and more +原级(多音节或部分双音节词)意为“越来越.......”Our city is becoming more and more beautiful. He is running more and more slowly.
(三)“the+比较级,the+比较级”意为“越.....,越....”
The more you eat, the fatter you get. The harder you study, the better you get.
(四)as......as..意为“与........一样”,否定形式“not as/so....as”意为“不如.....,与......不一样”,也是一种表达比较的形式,但要注意与含than的句式进行转换。同时as/so....as中用形容词和副词的原级。
He speaks English as well as I. English is less important than Chinese.
Chinese is more important than English. English is not so important than Chinese.
(五)“the more?of the two?”表示“两个当中较......的一个”
The taller of the two boys is my brother.
(六)否定词与比较级表示最高级用法。 I can?t agree more.
Unit4 what’s the best movie theater?
一、Vocabulary:p124-125
Important words:
1.comfortable: adj.舒适的,舒服的.
2.seat: n. 可数名词“座位”
v.seat&sit的区别:
seat: ①及物动词,主语为人,意为“使坐下;使就座”,宾语通常是反身代词; He seated himself at the desk.
②主语是处所时,意为“有........座位,可容纳.......座位”
The room can seat forth people.
12
sit :通常作不及物动词,主语通常是人。May I sit here?
3.close:adj. ①近的(空间和时间上);adv.closely close to 意为“离.....近”
adj. ②亲密的. v. 意为“关上;闭上” closed: adj. open
4.Choose: v. 选择,挑选 n. ..从.......中选择:
5.Service: n. 不可数名词 接待,服务. v. 服务人民:
6.Creative: adj. 有创造力的;创造性的. 创造力: 创造者: 创造:
7.performer: n. 表演者;演员 表演:n. 表演:v.
8.Talent: n. 天资,天赋 对(做)某事有天赋:
有天赋的:adj. 没有天赋的:adj.
9.Common:n. 与.....相同 有相同的特征,(想法、兴趣方面)相同: 同......一样: adj. 共同的,普通的 老百姓:
10.kind: n. 种类;类别 各种各样的: 一种.......: 不同种类的:
adj.和蔼的,有好的: 对某人有好:
kind of :有点,有几分,修饰形容词或副词
11. be up to:①是....的职责;由.....决定. It?s up to sb. to do sth.由某人决定做某事 It is up to me to decide.
②忙于;从事于; to 为介词,后接名词、代词和v-ing形式
All of us are up to good deeds.
③胜任;适合,通常用于否定句或疑问句. He is not up to his job.
④比得上: This new book is not up to that one.
12.everybody:pron. 每个人,相当于everyone.作主语时,位于用单数。
不定代词all,both,every及含有every的不定代词等连用时,并不否定全部,而只否定一部分: ①Not与all连用:“并不是所有的都,并不都”Not att the students like English.
②Not与both连用:“两者并不都”Both of them are not good at dancing.
③Not与every连用,“并不是每个......都”Not everyone is interested in this movie.
13.make up:①编造(故事、谎言);It?s not true. She made is up.
②构成,组成,形成,The committee is made up of six women.
③铺床,整理房间等;We make up our beds immediately after getting up.
④给某人/自己化妆. She made himself up every morning.
14.example:n. 实例,范例 以......为榜样: 给........树立榜样: 举一个例子: For example &such as 的区别:
For example:“例如”,用来列举某一论点或情况,一般只列举同类人或事物中的一个,在句中作为插入语,并且用逗号与前后隔开,可用于句首、句中或句末。
Football, for example,is very popular in the world.
Such as:“例如”,用于列举同类人或事物的几个例子(至少两个)但不能列举全部的内容。 He bought a lot of fruit, such as apples and peaches.
15. Poor: adj.贫穷的,清贫的; 可怜的,不幸的。 富裕的:
穷人: 富人: 年轻人: 老年人:
give:v.提供,给。后接双宾语,即:
give sb(间接宾语). Sth(直接宾语). =give sth.(直接宾语) to sb(间接宾语).
类似的接双宾语的动词还有:bring,teach,tell,show等。
开音乐会: 给予......帮助; give out: give birth to: give up: give back give away give in
16.crowed: adj. 拥挤的 be crowed with
13
crowd: n. 人群,群众
v. 拥挤,充满,挤满
17.no problem:
①用来回答感谢(美国英语中)“不用谢,别客气”相当于You're welcome, Not at all. ---Thank you very much.---No problem.
②用来表示同意或愉快地回答请求,“没问题,小事一桩”
----Could you post the letter for me.----N problem.--
③用来表示有能力做某事,“没问题,步子话下”
---Can you finish the work by yourself. ----No problem.
二、Phrases:
1.movie theater 2.comfortable seats 3.friendly service
4.think about/of sth/doing sth 5.no problem 6.close to....
7.clothes store 8.in town 9.so far
10.10 minutes by bus 11.talent show 12.more and more.....
13.around /all over the world 14.in common 15.and so on
16.all kinds of 17.be up to.... 18.play a role in
19.radio station 20.for example /such as 21.take......seriously
22.give sb sth 23.make up 24.come true
三、用法集荟:
1,Can I ask you some.....? 2.thanks for doing sth
3.How do you like .....?/What do you think of.....?/How do you feel about....?
4.much +形容词或副词的比较级 5.watch sb do/doing sth
6.play a role in doing sth 7one of +可数名词的复数
8.finish +doing sth.
只能接动名词作宾语的动词和短语的有:enjoy,keep, practice, have fun, feel like等。
9.watch sb. do sth.
后接不带to的动词不定式作宾语的感官动词和使役动词有:
半帮助(help)一感觉(feel)二听(listen to/hear)三使(let,make,have)五看(look at /see/watch/notice/observe)
四、单元语法:形容词和副词的最高级用法最高级的定义:最高级表示“最........”,用于三个或三个以上的人或事物进行比较,用来说明其中一个在某方面的最高程度。
五、最高级的构成:
(1)规则变化:
a.一般原级形容词或副词的词尾加-est:
b.以字母e结尾的直接在词尾加-st:
c.以“辅音+y 结尾的词,变y为 i,再加-est”:
d.以重读闭音节的单个辅音字母结尾的词,双写辅音字母,再加-est:
e.多音节或部分双音节的形容词、副词,在原级前面加most:
f.由“动词+后缀-ing/-ed”构成的形容词,在词前加most:
g.由“形容词+后缀ly”构成的副词,在词前加most:
(2)不规则变化:
六、最高级的用法:
(一)当三者或三者以上相比,表达“?是?中最?的”,用“the+形容词(副词)的最高级” 14
的结构,(但当表示副词的最高级时,the可以省略)后面可以加上表示范围的介词短语或从
句。
常用句式:主+谓(be,实义动词)+the+形容词的最高级+(名词)+表示范围的介词短语或
从句
注:表示范围的介词in后面一般接单位或场所的名词;of一般接一群人或事物的代词或名
词。
He is the tallest student in our class. He jumps the highest of the three boys.
This is the best book that I have ever read.
(二)表示“最?的?中之一”,用“one of +the +形容词最高级+复数名词”的结构来表达。
He is one of the best students in our class.
This is one of the most beautiful flowers in the garden.
(三)序数词后用最高级。在表达”第几(长、大、远....)时,用“the+序数词+形容词最高级
+........”。
The Yellow River is the second longest river in China.
(四)、在表达“某人的最....”时,用“某人的+形容词的最高级+名词”结构。
He is my best best friend.
注意:1. 形容词的最高级前面有定冠词the , 而副词的最高级前面定冠词the可以省略;
He works the hardest in his class.
2.在形容词最高级前有物主代词或名词所有格时,不能要定冠词the;
Today is my happiest day.
3.在形容词最高级所修饰的词作表语时,这个被修饰的词常常被省略。
He is the tallest boy in his class.
Unit 5 Do you want to watch a game show?
一、Vocabulary:p125-126
Important words:
1. educational:adj. 有教育意义的
2. hope:v 动词"希望 主要用于两种结构:hope to do sth /hope that
注:hope 后不能接动词不定式作宾语补足语,而只能用wish. wish sb to do sth.
hope&wish:
hope表示一般可以实现的希望。作简略回答时,即 I hope so/ I hope not.
wish表示很难或不大可能实现的希望。
3. stand:v ①忍受:表示对某事到了不能忍受的地步,通常用于否定句和疑问句。 Can?t stand
②站立,,站:
4. happen: v 发生,出现,一般指偶然发生的事。常用于以下结构:
①主语是物,sth. + happen to sb, 意为"某人发生了某事”
②主语是物,sth. +happens +地点/时间,意为“某地/某时发生了某事”
An accident happened on Park Street.
③主语是人,happen,意为“碰巧”,sb.+happens to do sth “某人碰巧做某事"
happen&ake place:
Happen:意为“发生;碰巧”,一般用于偶人或突发性事件。
Take place:意为“发生;举行;举办”一般指非偶然性事件的“发生”,即这种事件的发 生一定有某种原因或事先的安排。
5.expect: v 期待;盼望;预期常用于以下四种结构:
①expect+名词/代词,“期待某事(物)或某人;预计.......可能发生
15
②expect to do sth. 预计做某事:I expect to come back early.
③expect sb. to do sth 期望某人做某事I expect my brother to come back early.
④expect+从句 预计......I expect that I;m come back next Monday.
6. famous: adj. 著名的
be famous for&as&to:
be famous for “因为.....而出名”后接闻名的原因与be known for 同义
This place is famous for its cotton.
be famous as “作为.......而闻名"后接表示职位,名称的词与be known as 同义
He is famous as a great actor in the world.
be famous to “为........所熟知" 后接某部分人
7. successful: adj,获得成功的,有成就的 n. 不可数,成功;可数,指人表示"出人头地的或飞黄腾达“;指物表示”如愿以偿的"
adv. v.
Succeed in sth/doing sth = have success in sth/doing sth=be successful in sth/doing sth=do sth successfully 成功地完成某事
8. Be ready to :①准备做某事
②愿意迅速做某事,乐于做某事
③ be ready for (v+ing )sth/get ready for(v+ing) sth 为......做好准备
9.dress up:①打扮,梳理; dress up sb(主格)/dress sb(宾格)up “盛装打扮某人” ②着特殊的服装,为取乐而穿别人的衣服
10. Take one?s place: 代替,替换 与replace, take the place of ......同义 ~~ in........在哪方面
11. Do a good job :干得好!=do sth well Do the job : 奏效,起作用
12. Come out :①发行,出版 That magazine comes out every Monday.
②出来,出现:The stars came out as soon as it was dark.
③开花,发芽:Some flowers have begun to come out.
④透露,传出:The truth has come out at last.
13. Talk to &talk with& talk about:
talk to: “与.......交谈",侧重强调一方说另一方听:
talk with “与........交谈"侧重强调双方之间互相交谈:
talk about 交谈某事. talk to/with sb about sth
14. ask: v 询问,要求 ask sb about sth 问某人某事 ask for 请求
ask sb for sth 请求某人某事 ask sb to do sth 要求某人某事
15.mind: v 介意后接名词,动名词。 Never mind make up one?s mind
change one?s mind would you mind sb +动词ving sth?
二、Phrases:
1.learn from 8.One of ... 15.A symbol of....
2.find out 9.A pair of 16.Dress up
3.talk show 10.As famous as 17.Take sb?s place
4.do a job 11.Around the world 18.More than
5.soap opera 12.Have a discussion about... 19.Something enjoyable
6.watch a movie 13.One day 20.Interesting information
7.Action movie 14.Such as 21.think of/about
三、用法集荟:
1.let sb to do sth 2.plan/hope/happen/expect to do sth
16
3.how/what about doing sth 4. be ready to do sth 5.try one?s best to do sth
四、单元语法:动词不定式作宾语的用法
动词不定式是一种非谓语动词, 其结构是"to +动词原形",其中to不是介词,而是不定式的符号,称为小品词,动词不定式没有人称和数的变化。动词不定式和其后面的名词等构成动词不定式短语,在句子中可以作主语、表语、宾语、补足语、定语、状语等。
1. 固定短语中的动词不定式作宾语
只能用不定式作宾语的动词(短语)有:want, hope, decide, agree, choose, plan, fail,,attempt, intend, pretend, mean, offer, ask, manage, expect,would like等。
2.”疑问词+不定式“作宾语
know, learn, ask, show, teach,think, guess, understand, decide, explain, tell,advise,find out等
3.believe,think, consider, feel,make等动词用于”动词+it+adj/n+to do sth. “句型中,其中it作形式宾语,而将真正的宾语置于句末。
注:在个别的介词后可用”疑问词+不定式“结构。
Every has his own idea of how to do it.
4. like,love, begin, start等动词后既可接动词不定式也可以接动名词形式,意义上差别不大。
5.句型“it is +adj(for/of sb) + to do sth”中的动词不定式作宾语。
6. Stop, remember, try, forget等动词后面既可以接动词不定式也可以接动名词形式,但意义上有很大差别。
用来询问对方对某人、某物的看法的表达:
What do you think of/about........?=How do you like ......?
= How/What about ......?= how do you feel about .......?=what do you say about.....?
What?s your opinion? /Do you agree ......? /How do you see things like this?
对此类句型的答语通常有:
I love them(very much),fantastic! Wonderful!.......
I can?t stand it. I don?t like them (at all). I don?t mind.......
用来征求别人的意见,向别人提建议的交际用语:
How/what about....?(后接动词ing) Would you mind......?(后接动词ing)
Why don?t you/why not.....?(后接动词原形) Shall I /we.....?.(后接动词原形)
Can/could you please.....?(后接动词原形) Would/will you please.....?(后接动词原形) You?d better/should......(后接动词原形) Let?s ......?(后接动词原形)
应答语:
(1)对别人提出的建议,接受劝告或建议的应答语为:
Great !/wonderful! /That?s a good idea. /All right. /Yes ,please. /Thank you.
(2)拒绝接受对话或建议的应答语:
I?m sorry, but.../ I?m afraid (that)I...../I?d love to, but/Now thanks.
Unit6 I’m going to study computer science
一、Vocabulary:p126-127
Important words:
1.cook : ①可数名词,厨师 ②动词,煮,烧 cooker 可数名词,炊具。
2.violist: 名词,小提琴手。以-ist结尾的职业名词:pianist ,chemist,scientist
17
3.practice:及物动词,练习,后接名词、代词或动词的ing形式作宾语。
常跟动词-ing作宾语的动词(短语):
考虑建议盼原谅(consider,suggest/advise,look forward to,pardon)
承认推迟没得想(admit,delay/put off,fancy)避免错过继续练(avoid,miss,keep/keep on,practice) 否认完成能欣赏(deny,finish,enjoy,appreciate)不禁介意与逃亡(can?r help,mind,escape) 不准冒险凭想象(forbid,risk,imagine)
4. when/while:
when:表示“当....时候”,既指时间点,又指一段时间,when引导的时间状语从句中的动词可以是终止性也可以是延续性动词。When the teacher came in, the children were talking. while:表示“当....时候”仅指一段时间,从句中的动词必须是延续性的,一般强调主从句的动词同时发生。While还可作并列连词,“而”表示对比关系。
Lisa was singing while her mother was playing the piano.
Tom is strong while his younger brother is weak.
5. every day/everyday:
everyday: 每天的,形容词,在句中作定语一般位于名词前面:This is our everyday homework. every day: 每天,副词短语,在句中做状语,一般位于句首或句末:He reads books every day.
6. keep doing /keep on doing: 都有表示“不停地做”区别是:
keep doing :表示动作或状态的持续。He kept standing there for an hour without moving. keep on doing:表示动作的反复,中间有间隔。He kept on coming to offer us hot water.
7. be sure about/of: 对....有把握,相信 常用于一下结构:
①be sure to do sth: 一定会,务必:Be sure to come tomorrow.
②be sure of /about sth: 对....有把握,相信: Are you sure of the time?
③be sure that 从句:相信........主句的主语一定是人,可以替换为It is certain that 从句。 ④make sure that从句/of sth:查明,弄清楚,确保: You make sure that he was watching TV.
8. sound/voice/noise:
sound:“声音”,泛指自然界的一切声音:Sound goes more slowly than light.
voice: “嗓音”,指说话声、歌声、笑声等:I didn?t recognize my mother?s voice on the phone. noise: “嗓音”,指不悦耳,不和谐的声音:The noise kept me awake.
9.promise: ⑴名词,诺言,承诺:make a promise ; keep/break one?s promise
⑵ 动词,承诺,常用于以下结构:
①promise sb sth.=promise sth to sb.许诺给某人某物:He promised me a bike. ②promise to do sth: 许诺做某事:He promised to buy a bike for me.
③promise that 从句:答应......:He promised that he can buy me a bike.
10. common/usual:
common:用于物,指“不稀奇,很平常”;用于人,指“没有职位,不高贵”
usual:指“经常的,惯用的”,强调习惯性的,符合规章制度的或一贯如此。 He wasn?t a herl, but just a common man. Playing chess is his usual pastime.
11. at the beginning of 在......初, at the beginning 起初 from beginning to end 从始至终
12.agree /on/to: be agreement on/about sth 就....达成一致
agree with: 意为“同意某人的话或意见、看法等” He agrees with me.
agree to :意为“同意,应允”只用于事不用于人,其后接事物名词,还可以接动词原形,意为“愿意,答应” They agreed to my new plan.
agree on 意为“就....取得一致意见,在......方面意见一致,宾语只能是某件事情或计划等名词。 They agreed on the project at last.
18
二、phrases:
1.grow up 2. every day 3.be sure about
4.make sure 5.send.......to 6.be able to
7.the meaning of 8.different kinds of 9.in common
10.at the beginning of 11.write down 12.have to do with
13.take up 14.too...to
三、用法集荟
1. Want to do sth 2. Be going to +动词原形 3. Practice doing sth
4. Keep on doing sth 5. Learn to do sth 6. Finish doing sth.
7.promise to do sth 8.help sb. to do sth 9.remember to do sth
10.agree to do sth 11.love to do sth
四、单元语法:be going to 的用法
be going to 的用法
一、be going to 是一种固定结构,它后面要接动词原形,用来表示主观上按计划或安排要
发生的动作。是表示将来时态的形式之一。常与表示将来的tomorrow,next year等时间状语
或when引导的时间状语从句连用。
其各种句式变化借助be动词完成。Be随主语有is,am,are的变化,going to +动词原形。
1. 肯定句:主语+be going to +动词原形+其他。
be going to 结构中的助动词be很少用原形,它一般有三种形式,即:am , is , are 。当
主语是 I 时用am ;当主语是第三人称单数时用is;当主语是其他人称时用are。
I am going to buy something tomorrow morning.明天早上我要去买些东西。
2.否定句:主语+be not going to +动词原形+其他。
They are not going to see the car factory next week.
3.一般疑问句:Be+主语+ going to +动词原形+其他?
答语为:Yes, 主语+ am/is/are. / No, 主语+ isn't/aren't. / No, I'm not.
不过 I am... 在改为一般疑问句时常常改为"Are you ....?"。例如:
-Are they going to see the car factory next week? -Yes, they are. (No, they aren't.)
4.特殊疑问句:疑问词+be+主语+going to +动词原形+其他?
When are you going to see your friends?
二、如果表示计划去某地,可直接用be going to+地点,副词时省to。
We are going to Beijing for a holiday. He is going home .
三、表示位置移动的动词如go,come,leave,start,arrive等常用进行时表示将来。The bus is
coming.
四、表示根据现有情况、某种迹象,判断将要或即将发生的动作。此时不含有主观意图,
只是表示说话人对客观事态发展的判断或推测,此时主语可以是人,也可以是物。例如:
Look at the black clouds. It's going to rain.看那些乌云,快要下雨了。(推测)
五、be going to 与will的区别
be going to与will两者都可表示将要发生的事、将要去做某事,但它们有如下几点差别:
1. be going to 表示近期、眼下就要发生的事情,will 表示的将来时间则较远一些,
如:He is going to write a letter tonight. He will write a book one day.
2. be going to表示根据主观判断将来绝对发生的事情,will表示客观上将来势必发生的事情。 如He is seriously ill. He is going to die. He will be twenty years old.
3. be going to含有“事先经过考虑打算,准备”的意思,而will则没有这个意思,如:She is going
to lend us her book. He will be here in half an hour.
19
4.在有条件从句的主句中,一般不用 be going to,而多用will。
如:If any beast comes at you, I'll stay with you and help you.
5. will可以表示主动为他人做某事或是给出一个承诺,可以翻译为?为?和?会?。 It is very cold. I will make you some hot coffee. If you take part in the election, I will support you.
注意:
⑴There be 句型的be going to 结构为:There is / are going to be... (注意句型中going to 后面的be不能改为have。) 常用来表示将有某事发生。例如:
There is going to be a football match next Saturday in our school.下周六我们学校将有一场足球比赛。 ⑵在以下情况下均不能使用Be going to do 结构:
① will没有人称和数的变化,而 be going to 有人称和数的变化
②表示客观事实或真理时: I will be ten years old next year.
③表示主观意愿用will: I?ll tell you the truth.
Unit7 Will people have robots?
一、Vocabulary:p127-128
1.each/every:
①each 可用于两者、三者或三者以上,侧重个体;而 every 只用于三者或三者以上,侧重整体,不能单独使用。因此用于两者时只能用 each,不能用 every。如:There are trees on each side of the road.
②each单独做主语或each,every修饰的单数名词做主语时,谓语动词应用单数形式。但each of接复数名词或代词作主语时,谓语动词可单可复。
Each /each student/every student has an English book.
Each of the children wants/want to play.
③each 在句中可用于of之前或主语之后;而every在句中则不能这样用。
Each one of then is wrong.
2.pollution: 名词,污染污染物 air pollution noise pollution
动词,pollute 污染 polluted polluted polluting
3. In future/in the future:
In future: 指从今以后的将来,相当于from now on 也可用 for the future代替;
In the future:指将来的某一时间,意指将来
4. must:意为必须,强调主观原因,must是情态动词,没有人称和数的变化;回答must引导的一般疑问句要用must或needn?t: Must you go now? No, I didn?t .
have to:意为不得不,强调客观、外界的原因,有人称、数和时态的变化,进行句式转换时要借助于助动词do/does/did. Mary has to do it by herself.
5.on the earth:在地球上,用作地点状语,位于句末或句首;
on earth:究竟,到底,用在疑问代词或副词后,以加强语气。What on earth do you mean?
6.plant/grow:
plant: 表示种植,一般指:栽入土中“,栽上或种下,是一种涉及时间较短的动作或活动; Don?t plant the flowers before mid-April.
grow:表示种植,包含种下及以后培育的过程,涉及时间较长,可看做是一种过程或状态。
My uncle?s job is to grow flowers.
7.human/person/people/man:
Human: 指包括男人、女人、的“人,人类”指有别于动物、自然景物、机器等特殊群体。 person:无性别之分,常用于数目不太大,而且数目比较精确的场合
people:泛指人们,表示复数概念
20
man :前不带冠词且单独使用时,泛指男人,a man可指一个人,也可指一个男人,一个男子汉。
二、Phrases:
1 on computers 7. play a part in 13.the same...as
2.on paper 8.space station 14.over and over again
3.live to be 200 years old 9.look for 15. get bored
4. free time 10.Computer programmer 16. wake up
5.in danger 11.in the future 17.look like
6. on the earth 12. hundreds of 18.fall down
三、用法集荟:
8.play a part in doing sth 1. will + 动词原形
9.make sb. do sth 2.fewer/more +可数名词复数
10.help sb with sth 3.l ess/more+不可数名词
4.try to do sth 11.there will be +主语+其他
5.have to do sth 12.there is/are +sb/sth++ doing sth
6.6.agree with sb 13.it is +形容词+for/of +sb +to do sth
7.such +名词(词组)如此...
四、单元语法:一般将来时的讲解
1.含义:表示将来某个时间要发生的动作,事情或存在的状态,也表示将来经常或反复发生的动作或事情。
2.常用于此类情况的时间状语有:
tomorrow明天,next year明年,from now on从现在起,in a month一个月之后,in the future将来,等。 today今天,this evening今天晚上,this week这个星期,this month这个月,this year今年等。
3.构成:
①助动词will(所有人称)、shall(用于第一人称)+动词原形 ④be about to +动词原形 ②be going to +动词原形,表示将来。 ⑤be +ving现在进行时表将来时
③be to +动词原形,表将来 ⑥一般现在时表将来
句式:肯定形式:①am/is/are going to + do;②will/shall + do.
否定形式:①am/is/are going not to + do;②will/shall not + do.
4.用法:
⑴will/shall+动词原形:指对将来事物近期或远期的预见,表达个人主观意图以及征求对方意见或表示客气的邀请。在书面语中,shall多用于第一人称;在口语中,will可以用于任何人称。will 在陈述句中用于各人称,在征求意见时常用于第二人称。will not=won't shall not=shan't例如:
Which paragraph shall I read first?Will you be at home at seven this evening?
⑵ be going to +不定式,表示将来:
a. 主语的主观的意图,即将做某事。例如What are you going to do tomorrow? b. 计划,安排要发生的事。例如:The play is going to be produced next month。
c. 有迹象要发生的事。例Look at the dark clouds, there is going to be a storm.
⑶ be +不定式表将来,按计划或正式安排将发生的事。例如:
We are to discuss the report next Saturday.我们下星期六讨论这份报告。
注意:be to 表示客观安排或受人指示而做某事,be going to 表示主观的打算或计划。I am to play football tomorrow afternoon. 明天下午我去踢球。(客观安排)
21
I'm going to play football tomorrow afternoon. 明天下午我想去踢球。(主观安排)
⑷ be about to +不定式,意为马上做某事。例He is about to leave for Beijing.
注意:be about to do 不能与tomorrow, next week 等表示明确的时间状语连用。
⑸现在进行时表将来时
下列动词的现在进行时表示将来时:这类用法限于表示"移动"的动词:come来,go去,leave离开,start出发,begin开始,arrive到达,depart离开,stay逗留,等。
.she is leaving for Wuhan tomorrow.
⑹一般现在时表将来(主将从现)
下列动词come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return的一般现在时可以表示将来,主要用来表示在时间上已确定或安排好的事情。例如:
The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. When does the bus star? It stars in ten minutes.
五、there be 句型的将来时态
Unit8 How do you make a banana milk shake?
一、Vocabulary: p 128-129
Important words:
1.turn on:打开: 通常指打开水龙头、点灯、电视等开关其对应的短语是turn off;
是由动词和副词构成的词组。接代词作宾语时,放在这两个词中间,接名词通常放在后面。 有关turn的短语:turn on/off turn down/up
turn over turn to turn ....into..
open:打开,敞开:通常指把关着或封着的门窗、箱子等打开,其对应的是close。
2.有关make相关的短语:
make the bed make tea make trouble make money make a telephone
make a visit make a decision make a mistake make a living make a noise make sure
3.add to 增加 add up to 总共 add.....to....把....加到....中去
4.cut into /cut off/cut down
5.有关put的短语: put on put away put up put out put/write down put off
二、Phrases:
1.milk shake 2. turn on/off/up/down 3.pour .....into....
4.a cup of yogurt 5.a good idea 6.on Saturday
7.cut up =cut ..into pieces 8.put...into... 9.one more thing
10. A piece of.... 11.at this time 12.a few/few
13.Fill....with.../be full of 14.cover./mix..with.. 15.one by one
三、用法集荟:
1.how many/much 2.let /want sb do sth
3.forget to do/doing sth 4.how to do sth
5.There are many reasons for ..... 6.by doing sth
7.need to do sth 8.make+宾语+形容词
9.It?s time (for sb) to do sth 10. First...Next...Then.. afterwards....Finally...
11. One way to do sth 12. A long time
四、单元语法:可数名词和不可数名词(名词数的讲解)
一、定义: 表示人、地方、事物或抽象概念名称的词叫做名词。名词是任何事物的名称。
二、名词的分类:分为可数名词和不可数名词。
可数名词是表示可以计数的人、事物的名词。不可数名词是表示不可以计数的事物的名词。 22
三、分辨可数名词和不可数名词:
1.可数名词一般有单数和复数两种形式,有些词的单复数形式相同。不可数名词一般不分单数和复数,也不能直接与a/an连用。
2.不定冠词、基数词课直接修饰可数名词,表示数量;而不可数名词在表示数量时则用“不定冠词、基数词+计量单位名词+of+不可数名词。
An apple a piece of bread fours cups of water
3.提问可数名词用how many,提问不可数名词用how much
4.可数名词复数前可用many,sone,any, few,a few等修饰;不可数名词前可用much,some.any等修饰
四、可数名词的复数
4.、规则名词复数形式的构成
绝大多数名词的复数形式由在单数后加-s或-es构成。具体如下:
① 在词末加-s。通常在单数名词之后加词尾-s。
词尾-s在清辅音后读[s];在元音和浊辅音后读[z]; 在[s],[z],[],[]等辅音后读[iz]。 book→books tree→trees house→houses day→days face→faces
② 名词以-s,-x,-z,-ch,-sh 结尾时,加-es,读 [iz]。
glass→glasses brush→brushes box→boxes church→churches bus→buses
③ 名词以元音字母+y结尾时,加-s,读作[z];以辅音字母+ y结尾时,变y为i,再加-es,读[iz];专有名词中的y不变,直接加-s,读[z]。
boy→boys army→armies story→stories factory→factories holiday→holidays
④ 以辅音字母 +o结尾时,一般加-es,读[z]。有生命的东西+es
tomato→tomatoes hero→heroes potato-potatoes volcano-volcanoes 火山
但piano,photo后只加-s,无生命的东西+s:读[z]: piano→pianos photo→photos bamboo→bamboos 竹 radio→radios 收音机studio→studios 工作室 cuckoo→cuckoos 杜鹃 ⑤ 以-f,-fe结尾时,一般先把-f,-fe 变为v,再加-es,读[z]。
leaf→leaves life→lives[laivz] knife→knives shelf→shelves
注意:个别只加-s,读[s]。 roof→roofs gulf→gulfs 海湾proof→proofs belief→beliefs 信念 ⑥ 复合名词复数形式多在主体名词上变化。
shopkeeper→shopkeepers店主 classroom→classrooms film-goer→film-goers常看电影的人 housewife→housewives家庭主妇 tooth-brush→tooth-brushes son-in-law→sons-in-law女婿 vice-premier→vice-premiers副总理 looker-on→lookers-on旁观者passer-by→passers-by过客 必背:当一个名词作定语修饰另一个名词时,其复数形式只需将其主体词变为复数形式。由man和woman构成的复合名词的两个构成部分都要变化。
girl student---girl students new-comer-------new comers新来的人 a man doctor→men doctors男医生 a woman player→ women players女演员
(二)不规则复数形式的构成
①有很多名词的复数形式是不规则的。有些名词以改变元音的方法变为复数,有些辅音也有变化。man→men woman→women foot→feet tooth→teeth mouse→mice
goose→geese鹅ox→oxen公牛 child→children
②单数和复数为同一形式
名词如:deer, fish, sheep, means, Chinese, aircraft, works(工厂), crossroads(十字路), series(系列),species(种类)等名词单复数同一形式。
sheep→ 2 sheep绵羊 fish→ 2 fish鱼Chinese→ 2 Chinese中国人 Japanese→ 2 Japanese日本人 Swiss→ 2 Swiss瑞士人 a deer→two deer 鹿
23
③有些名词只用复数形式:trousers goods货物 clothes glasses scissors arms
④抽象名词一般为不可数名词,但也有些是可数的
hope→hopes希望 idea→ideas主意 job→jobs工作 truth→truths真相opinion→opinions看法 ⑤抽象名词表示具体事例时也用复数
need→needs需要 difficulty→difficulties困难 success→successes 成功者(事)
joy→joys欢乐 worry→worries忧愁 beauty → beauties 美人
⑥物质名词一般不可数,但表示不同类别时也用复数。
tea-teas茶 fruit-fruits水果 steel-steels钢food- foods 这些(不同种类的)食品 fruit- fruits (各种)水果grass- grasses (各种)草
⑦表示连绵不绝的物质、强调单数所表达的意义或用来表明”大量”、”程度很大”的意义时也用复数。
snow-snows雪 sand-sands沙 wood-woods树林 water-waters海洋
⑧有些名词的复数形式具有不同意义。
colours色彩;旗帜 arms手臂;武器 pains苦痛;操心 spirits灵魂;兴致 customs习惯;海关 manners方式;举止forces力量;军队 compasses罗盘;圆规
⑨只有单数形式的名词
a. 有生命的集体名词
cattle 牛 police personnel 人员 people 人民 government 政府 majority 多数 troop 军队 b. 无生命的集体名词:这类名词有些是物质名词包括气体、液体和药品。
clothing 服装 underwear 内衣 furniture 家具 sugar 糖,salt盐, soap肥皂codeine可待因 c. 抽象名词: education, homework, bravery, fun, strength, happiness, honesty, laughter, anger, intelligence, friendship, room, chemistry等。
(三)可数名词和不可数名词各有其不同的修饰语
①只修饰可数名词单数的
如a/an,one,another,either,neither,every,many a等。
I don't like this book, give me another one.我不喜欢这本书, 请另外给我一本。
Neither shoe feels comfortable.两只鞋都感觉不舒服。
An apple a day keeps the doctor away.[谚] 一天一个苹果, 医生不上门(比喻不生病)。
②只修饰可数名词复数的: 如these,those,few,many,a good/great many,a good/great number of,both,several及二以上的数词等。
It is impossible for so few workers to do so much work in a single day.
I'm afraid he did not do very well in the dictation. There were quite a few spelling mistakes in it. Were there many people at the meeting?
③只修饰不可数名词的
如a little,a bit of,much,a great/good deal of,a great/large/small amount of等。
There was so much food that we couldn't eat it all. 食物太多了,我们吃不完。
There's a little bit of time left. 只剩一点儿时间了。
④既可修饰可数名词又可修饰不可数名词的有the,one's,some,any,no,all,a lot of,lots of,plenty of,a large/small quantity of,which,what,other,half,one-third等。
some在解释为 “某一”,any在解释为”任何”时也可修饰可数名词单数。
this和that只能修饰可数名词单数和不可数名词,
last,next,the other和序数词只能修饰可数名词单数和复数。
I need a lot of cloth, for I'm going to make many clothes.
I have some books.我有一些书。 He has waited some time.他等了一会儿了。
24
