大学英语四、六级考试改革方案简介
为适应我国高等教育新的发展形势,深化教学改革,提高教学质量,满足新时期国家对人才培养的需要,20##年初教育部高教司组织选定制定并在全国部分高校开始试点《大学英语课程教学要求(试行)》(以下简称《教学要求》)。《教学要求》规定,大学英语课程的教学目标是:培养学生的英语综合应用能力,特别是听说能力,使他们在今后工作和社会交往中能用英语有效地进行口头和书面的信息交流。自《教学要求》在全国部分院校开始试点以来,广大教师积极参加和关心这次改革,在教学模式、教学手段和教材使用以来,广大教师积极参加和关心这次改革,在教学模式、教学手段和教材使用等各方面做了许多有益的尝试。参加试点的学生也普遍反映新的教学理念和方法大大提高了他们学习英语的兴趣,实现了个性化学习,提高了学习的效率。
为此,作为对我国在校大学生英语能力是否达到《教学要求》的主要鉴定手段的大学英语四、六级考试也必须相应改革,以适应新的形势,使考试更好地为贯彻《教学要求》服务。在教育部高等司的主持和领导下,大学英语四、六级考试改革项目组和考试委员会经过反复研讨和论证,并广泛听取了大学英语第一线教师和学生的意见,制定了《全国大学英语四、六级考试改革方案(试行)》。
大学英语四、六级考试是一种为教学服务的标准化考试。因此,考试的方向是在保持考试的科学性、客观性和公正性的同时,使考试最大限度地对大学英语教学产生正面的导向作用,即通过四、六级考试的改革,引导师生正确处理教学与考试的关系,更合理地使用四、六级考试,使考试更好地为教学服务。大学英语四、六级考试改革的目标是更准确地测量我国在校大学生英语综合应用能力的要求。由于大学英语四、六级考试是一个超大规模的标准化考试,因此考试的改革需前瞻性与可行性相结合,分步实施,既有近期改革目标,又有中长期规划。
近期内,四、六级考试将采取的重要举措之一是改革计分体制和成绩报道方式。自20##年6月考试起,四、六级考试成绩将采用满分为710分的计分体制,不设及格线;成绩报道方式由考试合格书改为成绩报告单,即考后向每位考生发放成绩报告单,报道内容包括:总分、单项分等。为使学校理解考试分数的含义并根据各校的实际情况合理使用考试测量的结果,四、六级考试委员会将向学校提供四、六考试分数的解释。
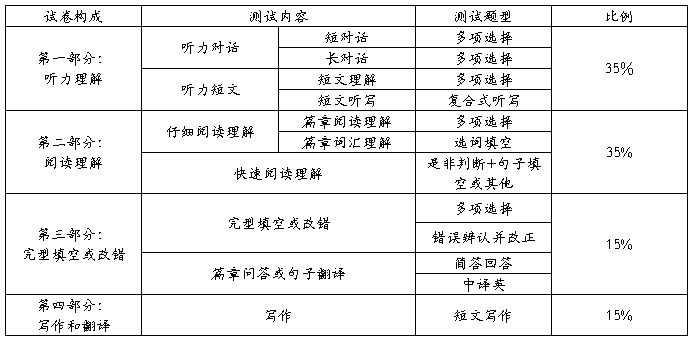
在考试内容和形式上,四, 六级考试将加大在听力理解部分题量和比例,增加快速阅读理解测试,增加非选择性试题的比例。试点阶段的四、六级考试由四部分构成:听力理解、阅读理解、综合测试和写作测试。听力理解部分的比例提高到35%,其中听力对话占15%,听力短文占20%。听力对话部分包括短对话和长对话的听力理解;听力短文部分包括短文听写和选择题型的短文理解;听力题材选用对话,讲座,广播电视节目等更具真实性材料。阅读理解部分比例调整为35%,其中仔细阅读部分(careful reading)占25%,快速阅读部分(fast reading)占10%。仔细阅读部分除测试篇章阅读理解外,还包括对篇章语境中的词汇理解的测试;快速阅读部分测试各种快速阅读技能。综合测试比例为15%,由两部分构成。第一部分为完型填空或改错,占10%;第二部分为短句问答或翻译,占5%。写作能力测试部分比为15%,体裁包括议论文,说明文,应用文等。试点阶段四、六级考试各部分测试内容、题型和所占比例如下表所示:
椐据目前的改革进程,近期内大学英语四、六级考试口语考试仍将与笔试分开实施,继续采用已经实施了五年的面试型的四、六级口语考试(CET-SET)。同时,考委会将积极研究开发计算机化口语测试,以进一步扩大口语考试规模,推动大学英语口语教学。
在考务管理方面,20##年6月起教育部考试中心将启用新的四、六级考试(试点)报名和考务管理系统,严格认定考生报名资格,加强对考场组织和考风考纪的管理,切实做好考试保密工作。具体方案将由教育部考试中心在近期内加行公告。
由于四、六级考试是一个每年涉及上千万考生的超大规模标准化考试。因此考试内容和形式的改革须经过一定规模的试点,对新试卷的有效性和可行性作出科学的论证,并了解师生的反馈。为此,自20##年1月开始,从参加大学英语教学改革试点学生中试行改革后的四级考试,自20##年6月开始以同等方式试行新的六级考试。初步定于20##年1月全面实施医务工作者后的四级考试,20##年6月全面实施改革后的六级考试。考委会将按照<<教学要求>>制定新的四、六级考试大纲和样题,并有时向教师和学生公布。
任何一项大规模化考试的发展都是一个不断改进和完善的过程。四、六级考试十七年的发展历程也证明了这一点。国家改革开放对我国大学生的英语交际能力不断提出更高的要求,因此,四、六级考试中长期改革任务仍十分艰巨。考试委员会将不断研究开发适合四、六级考试的新题型,研究改革后的四、六级考试对教学的后效;同时,充分利用高科技手段,完善考务管理系统,实现四、六级考试网上阅卷(CET-Online Marking),研究计算机化的四、六级考试(CET-CBT),争取在一定考生范围内或在某种能力测试中实现四、六级机考。
大学英语四、六级考试还将进一步完善其考试系列,更好地适应不同层次学校的需要,更有利于分层管理,分类指导。为此,四、六级考委会将根据对目前国内,国际语言测试理论和实践的研究和分析,制订以中国英语学习者为对象,能与国际接轨的英语语言能力等级量表,以更准确地描述我大学生的英语能力。同时,研究开发入学水平考试(CET-Placement Test),用于测量大学生入学时的英语水平,为学校制定切实可行的教学目标提供依据,并采用“平均级点分”等统计手段,更准确地反映教学的进步幅度,以调动广大师生的教学积极性。此外,考委会还将研究开发高端考试(CET-Advanced Level),用于测试学生是否达到<<教学要求>>中“更高要求”所规定的英语综合应用能力,即能以英语为工具,直接参与国际学术会议,国际学术交流等。
答题卡2(Answer Sheet 2)
PartIV Section A Section B PartV
47.[A][B][C][D][E][F][G][H][I][J][K][L][M][N][O] 57[A][B][C][D] 67[A][B][C][D] 77[A][B][C][D]
48.[A][B][C][D][E][F][G][H][I][J][K][L][M][N][O] 58[A][B][C][D] 68[A][B][C][D] 78[A][B][C][D]
49.[A][B][C][D][E][F][G][H][I][J][K][L][M][N][O] 59[A][B][C][D] 69[A][B][C][D] 79[A][B][C][D]
50.[A][B][C][D][E][F][G][H][I][J][K][L][M][N][O] 60[A][B][C][D] 70[A][B][C][D] 80[A][B][C][D] 51.[A][B][C][D][E][F][G][H][I][J][K][L][M][N][O] 61[A][B][C][D] 71[A][B][C][D] 81[A][B][C][D] 52.[A][B][C][D][E][F][G][H][I][J][K][L][M][N][O] 62[A][B][C][D] 72[A][B][C][D] 82[A][B][C][D] 53.[A][B][C][D][E][F][G][H][I][J][K][L][M][N][O] 63[A][B][C][D] 73[A][B][C][D] 83[A][B][C][D] 54.[A][B][C][D][E][F][G][H][I][J][K][L][M][N][O] 64[A][B][C][D] 74[A][B][C][D] 84[A][B][C][D] 55.[A][B][C][D][E][F][G][H][I][J][K][L][M][N][O] 65[A][B][C][D] 75[A][B][C][D] 85[A][B][C][D] 56.[A][B][C][D][E][F][G][H][I][J][K][L][M][N][O] 66[A][B][C][D] 76[A][B][C][D] 86[A][B][C][D]
PartVI Translation (5 minutes)
87.The substance does not dissolve in water
(不管是否加热).
88.Not only (他向我收费太高),but he didn’t do a
good repair job either.
89. Your losses in trade this year are nothing
(与我的相比).
90.On average,it is said,visitors spend only
(一半的钱)in a day in Leeds as in London.
91.By contrast,American mothers were more likely
(把孩子的成功归因于)natural talent.
答题卡1(Answer Sheet 1)
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅……………………………………………………………………………………………………
▅
▅Part II Reading Comprehension(Skimming and scanning) (15minutes)
▅
▅ 1.[Y] [N] [NG] 2.[Y] [N] [NG] 3.[Y] [N] [NG] 4.[Y] [N] [NG]
▅
▅ 5.[Y] [N] [NG] 6.[Y] [N] [NG] 7.[Y] [N] [NG]
▅
▅ 8.Typical customers of a landfill are .
▅
▅ 9.To dispose of a ton of trash in a landfill, customers have to pay tipping fee of .
▅
▅ 10. Materials that are not permitted to be buried in landfills should be dumped at .
答题卡1(Answer Sheet 1)

PartⅠ Writing (30 minutes)
Directions: For this part, you are allowed 30 minutes to write a campaign speech in support of your election to the post of chairman of the student union. You should write at least 120 words following the outline given below in Chinese:
1. 你认为自己具备了什么条件(能力、性格、爱好等)可以胜任学生会主席的工作
2. 如果当选,你将为本校同学做些什么
A Campaign Speech

答题卡2(Answer Sheet 2)
PartⅢ Section A Section B
11.[A] [B] [C] [D] 16.[A] [B] [C] [D] 21.[A] [B] [C] [D] 26.[A] [B] [C] [D] 31.[A] [B] [C] [D]
12.[A] [B] [C] [D] 17.[A] [B] [C] [D] 22.[A] [B] [C] [D] 27.[A] [B] [C] [D] 32.[A] [B] [C] [D]
13.[A] [B] [C] [D] 18.[A] [B] [C] [D] 23.[A] [B] [C] [D] 28.[A] [B] [C] [D] 33.[A] [B] [C] [D]
14.[A] [B] [C] [D] 17.[A] [B] [C] [D] 24.[A] [B] [C] [D] 27.[A] [B] [C] [D] 34.[A] [B] [C] [D]
PartⅢ Section C
Russia is the largest economic power that is not a member of the World Trade Organization. But that may change. Last Friday, the European Union said it would support Russia’s (36) to become a W.T.O member.
Representative of the European Union met with Russian(37) in Moscow. They signed a trade agreement that took six years to(38) .
Russia called the trade agreement(39) .It agreed to slowly increase fuel prices within the country. It also agreed to permit(40) in its communications industry and to remove some barriers to trade.
In(41) for European support to join the W.T.O , Russian president Putin said that Russia would speed up the(42) to approve the Kyoto Protocol, and international(43) agreement to reduce the production of harmful industrial gases.(44)
.
Russia had signed the Kyoto Protocol, but has not yet approved it. The agreement takes effect when it has been approved by nations that produce at least 55 percent of the world’s greenhouse gases.(45)
.
The United States, the world’s biggest producer, withdrew from the Kyoto Protocol after President Bush took office in 2001. So, Russia’s approval is required to put the Kyoto Protocol into effect.
(46)
.
Russia must still reach agreement with China, Japan, South Korean and the United States.
大学英语四级考试试点考试样卷 (试题册)
Part Ⅰ Writing (30 minutes)
注意:此部分试题在答题卡1上。
Part Ⅱ Reading Comprehension (Skimming and Scanning) (15 minutes)
Directions: In this part, you will have 15 minutes to go over the passage quickly and answer the questions on Answer Sheet 1.
For questions 1-7, mark
Y (for YES) if the statement agrees with the information given in the passage;
N (for NO) if the statement contradicts the information given in the passage;
NG (for NOT GIVEN) if the information is not given in the passage.
For questions 8-10, complete the sentences with the information given in the passage.
Landfills
You have just finished your meal at a fast food restaurant and you throw your uneaten food, food wrappers, drink cups, utensils and napkins into the trash can. You don’t think about that waste again. On trash pickup day in your neighborhood, you push your can out to the curb, and workers dump the contents into a big truck and haul it away. You don’t have to think about that waste again, either. But maybe you have wondered, as you watch the trash truck pull away, just where that garbage ends up.
Americans generate trash at an Astonishing rate of four pounds per day per person; which translates to 600,000 tons per day or 210 million tons per year! This is almost twice as much trash per person as most other major countries. What happens to this trash? Some gets recycled (回收利用) or recovered and some is burned, but the majority is buried in landfills.
How Much Trash Is Generated?
Of the 210 million tons of trash, or solid waste, generated in the United States annually, about 56 million tons, or 27 percent, is either recycled (glass, paper products, plastic, metals) or composted (做成堆肥) (yard waste). The remaining trash, which is mostly unrecyclable, is discarded.
How Is Trash Disposed of ?
The trash production in the United States has almost tripled since 1960. This trash is handled in various ways. About 27 percent of the trash is recycled or composted, 16 percent is burned and 57 percent is buried in landfills. The amount of trash buried in landfills has doubled since 1960. The United States ranks somewhere in the middle of the major countries (United Kingdom, Canada, Germany, France and Japan) in landfill disposal. The United Kingdom ranks highest, burying about 90 percent of its solid waste in landfills.
What Is a Landfill?
There are two ways to bury trash:
n Dump—an open hole in the ground where trash is buried and that is full of various animals (rats, mice, birds). (This is most people’s idea of a landfill!)
n Landfill—carefully designed structure built into or on top of the ground in which trash is isolated from the surrounding environment (groundwater, air, rain). This isolation is accomplished with a bottom liner and daily covering of soil.
¨ Sanitary landfill—land fill that uses a clay liner to isolate the trash from the environment
¨ Municipal solid waste (MSW) landfill—landfill that uses a synthetic (plastic) liner to isolate the trash from the environment
The purpose of a landfill is to bury the trash in such a way that it will be isolated from groundwater, will be kept dry and will not be in contact with air. Under these conditions, trash will not decompose (腐烂) much. A landfill is not like a compost pile, where the purpose is to bury trash in such a way that it will decompose quickly.
Proposing the Landfill
For a landfill to be built, the operators have to make sure that they follow certain steps. In most parts of the world, there are regulations that govern where a landfill can be placed and how it can operate. The whole process begins with someone proposing the landfill.
In the United States, taking care of trash and building landfills are local government responsibilities. Before a city or other authority can build a landfill, an environment impact
study must be done on the proposed site to determine:
n the area of land necessary for the landfill
n the composition of the underlying soil and bedrock
n the flow of surface water over the site
n the impact of the proposed landfill on the local environment and wildlife
n the historical value of the proposed site
Building the Landfill
Once the environmental impact study is complete, the permits are granted and the funds have been raised, then construction begins. First, access roads to the landfill site must be built if they do not already exist. There roads will be used by construction equipment, sanitation (环卫) services and the general public. After roads have been built, digging can begin. In the North Wake Country Landfill, the landfill began 10 feet below the road surface.
What Happens to Trash in a Landfill?
Trash put in a landfill will stay there for a very long time. Inside a landfill, there is little oxygen and little moisture. Under these conditions, trash does not break down very rapidly. In fact, when old landfills have been dug up or sampled, 40-year-old newspapers have been found with easily readable print. Landfills are not designed to break down trash, merely to bury it. When a landfill closes, the site, especially the groundwater, must be monitored and maintained for up to 30 years!
How Is a Landfill Operated?
A landfill, such as the North Wake County Landfill, must be open and available every day. Customers are typically municipalities and construction companies, although residents may also use the landfill.
Near the entrance of the landfill is a recycling center where residents can drop off recyclable materials (aluminum cans, glass bottles, newspapers and paper products). This helps to reduce the amount of material in the landfill. Some of these materials are banned from landfills by law because they can be recycled.
As customers enter the site, their trucks are weighed at the scale house. Customers are charged tipping fees for using the site. The tipping fees vary from $10 to $40 per ton. These fees are used to pay for operation costs. The North Wake County Landfill has an operating budget of approximately $4.5 million, and part of that comes from tipping fees.
Along the site, there are drop-off stations for materials that are not wanted or legally banned by the landfill. A multi-material drop-off station is used for tires, motor oil, lead-acid batteries. Some of these materials can be recycled.
In addition, there is a household hazardous waste drop-off station for chemicals (paints, pesticides, other chemicals) that are banned from the landfill. These chemicals are disposed of by private companies. Some paints can be recycled and some organic chemicals can be burned in furnaces or power plants.
Other structures alongside the landfill are the borrowed area that supplies the soil for the landfill, the runoff collection pond and methane (甲烷) station.
Landfills are complicated structures that, when properly designed and managed, serve an important purpose. In the future, new technologies called bioreactors will be used to speed the breakdown of trash in landfills and produce more methane.
注意:此部分试题请在答题卡1上作答;8-10题在答题卡1上。
1. The passage gives a general description of the structure and use of a landfill.
2. Most of the trash that Americans generate ends up in landfills.
3. Compared with other major Industrialized countries, America buries a much higher percentage of its solid waste in landfills.
4. Landfills are like compost piles in that they speed up decomposition of the buried trash.
5. In most countries the selection of a landfill site is governed by rules and regulations.
6. In the United States the building of landfills is the job of both federal and local governments.
7. Hazardous wastes have to be treated before being dumped into landfills.
Part Ⅲ Listening Comprehension (35 minutes)
Section A
Directions: In this section, you will hear 8 short conversations and 2 long conversations. At the end of each conversation, one or more questions will be asked about what was said. Both the conversation and the questions will be spoken only once. After each question there will be a pause. During the pause, you must read the four choices marked A), B), C) and D), and decide which is the best answer. Then mark the corresponding letter on Answer Sheet 2 with a single line through the center.
注意:此部分试题请在答题卡2上作答。
11. A) The man hates to lend his tools to other people.
B) The man hasn’t finished working on the bookshelf.
C) The tools have already been returned to the woman.
D) The tools the man borrowed from the woman are missing.
12. A) Save time by using a computer. C) Borrow Martha’s computer.
B) Buy her own computer. D) Stay home and complete her paper.
13. A) He has been to Seattle many times.
B) He has chaired a lot of conferences.
C) He holds a high position in his company.
D) He lived in Seattle for many years.
14. A) Teacher and student. C) Manager and office worker.
B) Doctor and patient. D) Travel agent and customer.
15. A) She knows the guy who will give the lecture.
B) She thinks the lecture might be informative.
C) She wants to add something to her lecture.
D) She’ll finish her report this weekend.
16. A) An art museum. C) A college campus.
B) A beautiful park. D) An architectural exhibition.
17. A) The houses for sale are of poor quality.
B) The houses are too expensive for the couple to buy.
C) The housing developers provide free trips for potential buyers.
D) The man is unwilling to take a look at the houses for sale.
18. A) Talking about sports. C) Reading newspapers.
B) Writing up local news. D) Putting up advertisements.
Questions 19 to 22 are based on the conversation you have just heard.
19. A) The benefits of strong business competition.
B) A proposal to lower the cost of production.
C) Complaints about the expense of modernization.
D) Suggestions concerning new business strategies.
20. A) It cost much more than its worth.
B) It should be brought up-to-date.
C) It calls for immediate repairs.
D) It can still be used for a long time.
21. A) The personnel manager should be fired for inefficiency.
B) A few engineers should be employed to modernize the factory.
C) The entire staff should be retrained.
D) Better-educated employees should be promoted.
22. A) Their competitors have long been advertising on TV.
B) TV commercials are less expensive.
C) Advertising in newspapers alone is not sufficient.
D) TV commercials attract more investments.
Questions 23 to 25 are based on the conversation you have just heard.
23. A) Searching for reference material.
B) Watching a film of the 1930s’.
C) Writing a course book.
D) Looking for a job in a movie studio.
24. A) It’s too broad to cope with. C) It’s controversial.
B) It’s a bit outdated. D) It’s of little practical value.
25. A) At the end of the online catalogue.
B) At the Reference Desk.
C) In The New York Times.
D) In the Reader’s Guide to Periodical Literature.
Section B
Directions:In this section, you will hear 3 short passages. At the end of each passage,
you will hear some questions. Both the passage and the questions will be spoken
only once. After you hear a question, you must choose the best answer from the
four choices marked A), B), C) and D). Then mark the corresponding letter on
Answer Sheet 2 with a single line through the center.
注意:此部分试题请在答题卡2上作答。
Passage One
Questions 26 to 28 are based on the conversation you have just heard.
26. A) Synthetic fuel. C) Alcohol.
B) Solar energy. D) Electricity.
27. A) Air traffic conditions. C) Road conditions.
B) Traffic jams on highways. D) New traffic rules.
28. A) Go through a health check. C) Arrive early for boarding.
B) Take little luggage with them. D) Undergo security checks.
Passage Two
Questions 29 to 31 are based on the conversation you have just heard.
29. A) Beauty. C) Luck.
B) Loyalty. D) Durability.
30. A) He wanted to follow the tradition of his country.
B) He believed that it symbolized an everlasting marriage.
C) It was through that a blood vessel in that finger led directly to the heart.
D) It was supposed that the diamond on that finger would bring good luck.
31. A) The two people can learn about each other’s likes and dislikes.
B) The two people can have time to decide if they are a good match.
C) The two people can have time to shop for their new home.
D) The two people can earn enough money for their wedding.
Passage Three
Questions 32 to 35 are based on the conversation you have just heard.
32. A) Because there are no signs to direct them.
B) Because no tour guides are available.
C) Because all the buildings in the city look alike.
D) Because the university is everywhere in the city.
33. A) They set their own exams.
B) They select their own students.
C) They award their own degrees.
D) They organize their own laboratory work.
34. A) Most of them have a long history.
B) Many of them are specialized libraries.
C) They house more books than any other university library.
D) They each have a copy of every book published in Britain.
35. A) Very few of them are engaged in research.
B) They were not awarded degree until 1948.
C) They have outnumbered male students.
D) They were not treated equally until 1881.
Section C
Directions: In this section, you will hear a passage three times. When the passage is read for the first time, you should listen carefully for its general idea. When the passage is read for the second time, you are required to fill in the blanks numbered from 36 to 43 with the exact words you have just heard. For blanks numbered from 44 t0 46 you are required to fill in the missing information. For these blanks ,you can either use the exact words you hove just heard or write down the main points in your own words . Finally, when the passage is read for the third time ,you should check what you have written.
注意:此部分试题在答题卡2上;请在答题卡2上作答。
Part IV Reading Comprehension (Reading in Depth)(25 minutes)
Section A
Directions: In this section ,there is a passage with ten blanks .You are required to select one word for each blank from a list of ch0ices given in a word bank following the passage .Read the passage through carefully before making your choices .Each choice in bank is identified by a letter .Please mark the corresponding letter for each item on Answer Sheet 2 with a single line through the center .You may not use any of the words in the bank more than once.
Questions 47 to 56 are based on the following passage.
When Roberto Feliz came to the USA from the Dominican Republic, he knew only a few words of English .Education soon became a 47. “I couldn’t understand anything,” he said. He 48 from his teachers, came home in tears , and thought about dropping out.
Then Mrs. Malave , a bilingual educator, began to work with him while teaching him math and science in his 49 Spanish.“She helped me stay smart while teaching me English ,”he said .Given the chance to demonstrate his ability, he 50 confidence and began to succeed in school.
Today, he is a 51 doctor, runs his own clinic ,and works with several hospitals .Every day ,he uses the language and academic skills he 52 through bilingual education to treat his patients.
Roberto’s story is just one of 53 success stories. Research has shown that bilingual education is the most 54 way both to teach children English and ensure that they succeed academically. In Arizona and Texas, bilingual students 55 outperform their peers in monolingual programs. Calexico, Calif. , implemented bilingual education, and now has dropout rates that are less than half the state average and college 56 rates of more than 90%.In E1 Paso ,bilingual education programs have helped raise student scores from the lowest in Texas to among the highest in the nation.
注意:此部分试题请在答题卡2上作答。

Section B
Directions :There are 2passages in this section .Each passage is followed by some questions or unfinished statement. For each of them there are four choices marked A),B),C),D). You should decide on the best choice and mark the corresponding letter on Answer Sheet 2 with a single line through the center.
Passage One
Question 57 to 61 are based on the following passage.
“Tear ’em apart!” “Kill the fool!” “Murder the referee(裁判) !”
These are common remarks one may hear at various sporting events. At the time they are made ,they may seem innocent enough. But let’s not kid ourselves .They have been known to influence behavior in such a way as to lead to real bloodshed. Volumes have been written about the way word affect us. It has been shown that words having certain connotations (含义) may cause us to react in ways quite foreign to what we consider to be our usual humanistic behavior. I see the term “opponent” as one of those words .Perhaps the time has come to delete it from sports terms.
The dictionary meaning of the term “opponent” is “adversary”; “enemy” “one who opposes your interests. ”Thus, when a player meets an opponent ,he or she may tend to every action no matter how gross ,may be considered justifiable. I recall an incident in a handball game when a referee refused a player’s request for a time out for a glove change because he did not consider them wet enough .The player proceeded to rub his gloves across his wet T-shirt and then exclaimed, “Are they wet enough now?”
In the heat of battle, players have been observed to throw themselves across the court without considering the consequences the such a move might have on anyone in their way. I have also witnessed a player reacting to his opponent’s intentional and illegal blocking by deliberately hitting him with the ball as hard as he could during the course of play. Off the court, they are good friends. Does that make any sense? It certainly gives proof of a court attitude which departs from normal behavior.
Therefore, I believe it is time we elevated (提升) the game to the level where it belongs, thereby setting an example to the rest of the sporting world. Replacing the term “opponent” with “associate” could be an ideal way to start.
The dictionary meaning of the term “associate” is “colleague” ;“friend” ;“companion.” Reflect a moment! You may soon see and possibly feel the difference in your reaction to the term “associate” rather than “opponent”.
注意:此部分试题请在答题卡2上作答。
57. Which of the following statements best expresses the author’s view?
A) The words people use can influence their behavior.
B) Unpleasant words in sports are often used by foreign athletes.
C) Aggressive behavior in sports can have serious consequences.
D) Unfair judgments by referees will lead to violence on the sports field.
58. Harsh words are spoken during games because the players_______.
A) are too eager to win
B) treat their rivals as enemies
C) are usually short-tempered and easily offended
D) cannot afford to be polite in fierce competitions
59. What did the handball player do when he was not allowed a time out to change his gloves?
A) He angrily hit the referee with a ball.
B) He refused to continue the game.
C) He claimed that referee was unfair.
D) He wet his gloves by rubbing them across his T-shirt.
60. According to the passage, players in a game may______.
A) kick the ball across the court with force
B) lie down on the ground as an act of protest
C) deliberately throw the ball at anyone illegally blocking their way
D) keep on screaming and shouting throughout the game
61. The author hopes to have the current situation un sports improved by ________.
A) regulating the relationship between players and referees
B) calling on players to use clean language in the court
C) raising the referee’s sense of responsibility
D) changing the attitude of players on the sports field
Passage Two
Questions 62 to 66 are based in the following passage.
Is there enough oil beneath the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge (保护区) (ANWR) to help secure America’s energy future? President Bush certainly thinks so. He has argued that tapping ANWR’ s oil would help ease California’s electricity crisis and provide a major boost to the country’s energy independence. But no one knows for sure how much crude oil lies buried beneath the frozen earth, with the last government survey, conducted in1998, projecting output anywhere from 3 billion to 16 billion barrels.
The oil industry goes with the high end of the range, which could equal as much as 10% of U.S. consumption for as long as six years. By pumping more than 1 million barrels a day from the reserve for the next two to three decades, lobbyists claim, the nation could cut back on imports equivalent to all shipments to the U.S. from Saudi Arabia. Sounds good. An oil boom would also mean a multibillion-dollar windfall (意外之财) in tax revenues, royalties (开采权使用费) and leasing fees for Alaska and the Federal Government. Best of all, advocates of drilling say, damage to the environment Would be insignificant. “We’ve never had a documented case of an oil rig chasing deer out onto the pack ice,” say Alaska State Representative Scott Ogan.
Not so fast, say environmentalists. Sticking to the low end of government estimates the National Resources Defends Council says there may be no more than 3.2 billion barrels of economically recoverable oil in the coastal plain of ANWR, a drop in the bucket that would do virtually nothing to ease America’s energy problems. And consumers would wait up to a decade to gain any benefits, because drilling could begin only after mush bargaining over leases, environmental permits and regulatory review.As for ANWR’s impact on the California power crisis, environmentalists point out that oil is responsible for only 1% of the Golden State’s electricity output ---and just 3% of the nation’s.
注意:此部分试题请在答题卡上作答。
62. What does President Bush think of tapping oil in ANWR?
A) It will increase America’s energy consumption.
B) It will exhaust the nation’s oil reserves.
C) It will help reduce the nation’s oil imports.
D) It will help secure the future of ANWR.
63. We learn from the second paragraph that the American oil industry _________.
A) shows little interest tapping oil in ANWR
B) expect to stop oil imports from Saudi Arabia
C) tend to exaggerate America’s reliance on foreign oil
D) believes that drilling for ANWR will produce high yields
64. Those against oil drilling ANWR argue that ________.
A) it will drain the oil reserves in the Alaskan region
B) it can do little to solve U.S. energy problem
C) it can cause serious damage to the environment
D) it will not have much commercial value
65. What do the environmentalists mean by saying “Not so fast” (Line1, Psra.3)?
A) Don’t be too optimistic.
B) Don’t expect fast returns.
C) The oil drilling should be delayed.
D) Oil exploitation takes a long time.
.66. It can be learned from the passage that oil exploitation beneath ANWR’s frozen earth
________.
A) involves a lot of technological problems
B) remains a controversial issue
C) is expected to get under way soon
D)will enable the U.S. to be oil independent
Part V Cloze(15 minutes)
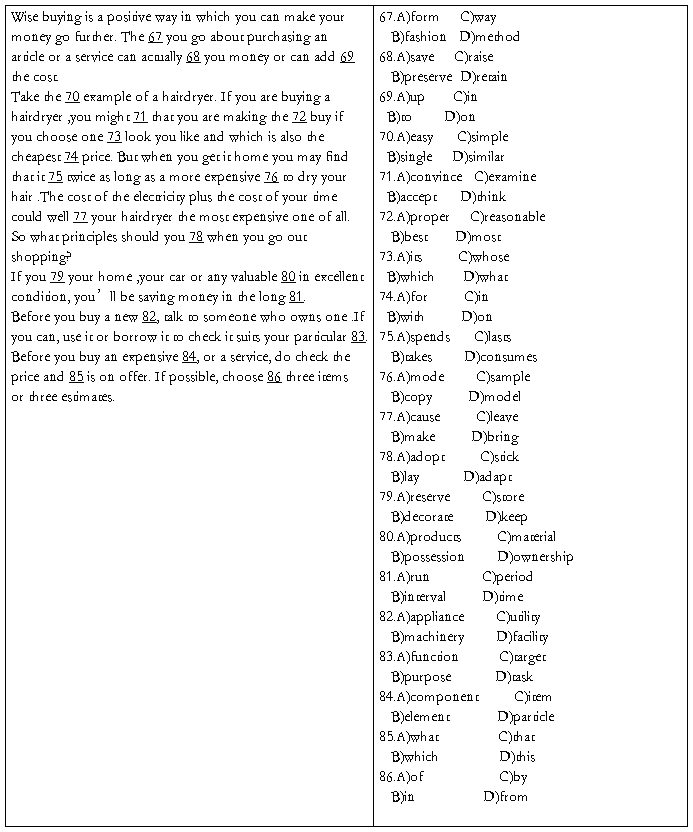
Directions :There are 20 blanks in the following passage .For each blank there are four choices marked A),B),C) and D) on the right side of the paper. You should choose the ONE that best fits into the passage. Then mark the corresponding letter on Answer Sheet 2 with a single line through the center.
注意:此部分试题请在答题卡2上作答。
Part VI Translation (5 minutes)
Directions: Complete the sentences on Answer Sheet 2 by translating into English the Chinese given in brackets.
注意:此部分试题在答题卡2上;请在答题2上作答。
大学英语四级考试试点考试样卷(听力文字稿)
Tape Script of Listening Comprehension
Section A
Directions:In this section, you will hear 8 short conversations and 2 long conversations. At the end of each conversation, one or more questions will be asked about what was said. Both the conversation and the questions will be spoken only once. After each question there will be a pause. During the pause, you must read the four choices marked A), B), C) and D), and decide which is the best answer. Then mark the corresponding letter on Answer Sheet 2 with a single line through the centre.
11. W: Simon, could you return the tools I lent you for building the bookshelf last month?
M: Uh, well, I hate to tell you this… but I can’t seem to find them.
Q: What do we learn from the conversation?
12. W: I’m going to Martha’s house. I have a paper to complete, and I need to use her computer.
M:Why don’t you buy one yourself? Think how much time you could save.
Q: What does the man suggest the woman.do?
13. W: Bob said that Seattle is a great place for conferences.
M: He’s certainly in a position to make that comment. He’s been there so often.
Q: What does the man say about Bob?
14. W: Mr. Watson, I wonder whether it’s possible for me to take a vacation early next month.
M: Did you fill out a request form?
Q: What is the probable relationship between the two speakers?
15. M: Do you want to go to the lecture this weekend? I hear the guy who’s going to deliver the lecture spent a year living in the rain forest.
W: Great! I’m doing a report on the rain forest. Maybe I can get some new information to add to it.
Q: What does the woman mean?
16. W: Wow! I do like this campus: all the big trees, the green lawns, and the old buildings with tall columns. It’s really beautiful.
M: It sure is. The architecture of these buildings is in the Greek style. It was popular in the eighteenth century here.
Q: What are the speakers talking about?
17. M: This article is nothing but advertising for housing developers. I don’t think the houses for sale are half that good.
W: Come on, David. Why so negative? We’re thinking of buying a home, aren’t we? Just a trip to look at the place won’t cost us much.
Q: What can be inferred from the conversation?
18. M: Would you pass me the sports section, please?
W: Sure, if you give me the classified ads local news section.
Q: What are the speakers doing?
Now you’ll hear two long conversations.
Conversation One
W: Hello, Gary. How’re you?
M: Fine! And yourself?
W: Can’t complain. Did you have time to look at my proposal?
M: No, not really. Can we go over it now?
W: Sure. I’ve been trying to come up with some new production and advertising strategies. First of all, if we want to stay competitive, we need to modernize our factory. New equipment should’ve been installed long ago.
M: How much will that cost?
W: We have several options ranging from one hundred thousand dollars all the way up to half a million.
M: OK. We’ll have to discuss these costs with finance.
W: We should also consider human resources. I’ve been talking to personnel as well as our staff at the factory.
M: And what’s the picture?
W: We’ll probably have to hire a couple of engineers to help us modernize the factory.
M: What about advertising?
W: Marketing has some interesting ideas for television commercials.
M: TV? Isn’t that a bit too expensive for us? What’s wrong with advertising in the papers, as usual?
W: Quite frankly, it’s just not enough anymore. We need to be more aggressive in order to keep ahead of our competitors.
M: Will we be able to afford all this?
W: I’ll look into it , but I think higher costs will be justified. These investments will result in higher profits for our company.
M: We’ll have to look at the figures more closely. Have finance draw up a budget for these investments.
W: All right. I’ll see to it.
Questions 19 to 20 are based on the conversation you have just heard.
19.What are the two speakers talking about?
20.What does the woman say about the equipment of their factory?
21.What does the woman suggest about human resources?
22. Why does the woman suggest advertising on TV?
Conversation Two
W: Sir, you’ve been using the online catalogue for quite a while , Is there anything I can do to help you?
M: Well, I’ve got to write a paper about Hollywood in the 30s and 40s, and I’m really struggling. There are hundreds of books, and I just don’t know where to begin.
W:Your topic sounds pretty big. Why don’t you narrow it down to something like…uh… the history of the studios during that time?
M: You know, I was thinking about doing that, but more that 30 books came up when I typed in “movie studios.”
W: You could cut that down even further by listing the specific years you want . Try adding “1930s” or “1940s” or maybe “Golden Age.”
M: “Golden Age” is a good idea. Let me type that in … Hey, look, just 6 books this time. That’s a lot better.
W: Oh… another thin you might consider… have you tried looking for any magaxine or newspaper articles?
M: No, I’ve only been searching for books.
W: Well, you can look up magazine articles in the Reader’s Guide to Periodical Literature. And we do have the Los Angeles.Times available over there. You might go through their indexes to see if there’s anything you want.
M: Okay, I think I’ll get started with these books and then I’ll go over the magazines.
W: If you need any help, I’ll be over at the Reference Desk.
M: Great, thanks a lot.
Questions 23 to 25 are based on the conversation you have just heard.
23. What is the man doing?
24. What does the librarian think of the topic the man is working on ?
25. Where can the man find the relevant magazine articles?
Section B
Directions:In this section, you will hear 3 short passages. At the end of EACH PASSAGE, you will hear some questions. Both the passage and the questions will be spoken only once. After you hear a question, you must choose the best answer from the four choices marked A), B*, C) and D), Then mark the corresponding letter on Answer Sheet 2 with a single line through the centre.
Passage One
In the next few decades people are going to travel very differently from the way they do today. Everyone is going to drive electrically powered cars. So in a few years people won’t worry about running out of gas.
Some of the large automobile companies are really moving ahead with this new technology. F & C Motors, a major auto company, for example, is holding a press conference next week. At the press conference the company will present its new, electronically operated models.
Transportation in the future won’t be limited to the ground. Many people predict that traffic will quickly move to the sky. In the coming years, instead of radio reports about road conditions and highway traffic, news reports will talk about traffic jams in the sky.
But the sky isn’t the limit. In the future, you’ll probably even be able to take a trip to the moon, Instead of listening to regular airplane announcements, you’ll hear someone say, “The spacecraft to the moon leaves in ten minutes. Please check your equipment. And remember, no more than ten ounces of carry-on baggage are allowed.”
Questions 26 to 28 are based on the passage you have just heard.
26. What will be used to power cars in the next few decades?
27. What will future news reports focus on when talking about transportation?
28. What is the special requirement for passengers traveling to the moon?
Passage Two
The period of engagement is the time between the marriage proposal and the wedding ceremony. Two people agree to marry when they decide to spend their lives together.
The man usually gives the woman a diamond engagement ring? That tradition is said to have started when an Austrian man gave a diamond ring to the woman he wanted to marry. The diamond represented beauty. He placed it on the third finger of her left hand. He chose that finger because it was thought that a blood vessel in that finger went directly to the heart. Today, we know that this is not true. Yet the tradition continues.
Americans generally are engaged for a period of about one year if they are planning a wedding ceremony and party. During the time, friends of the bride may hold a party at which women friends and family members give the bride gifts that she will need as a wife. These could include cooking equipment or new clothing.
Friends of the man who is getting married may have a bachelor party for him. This usually takes place the night before the wedding. Only men are invited to the bachelor party.
During the marriage ceremony, the bride and her would-be husband usually exchange gold rings that represent the idea that their union will continue forever. The wife often wears both the wedding ring and engagement ring on the same finger. The husband wears hi ring on the third finger of his left hand.
Many people say the purpose of the engagement period is to permit enough time to plan the wedding .But the main purpose is to let enough time pass so the two people are sure they want to marry each other. Either person may decide to break the engagement. If this happens, the woman usually returns the ring to the man; they also return any wedding gifts they have received.
Questions 29 to 31 are based on the passage you have just heard.
29. What was the diamond ring said to represent?
30. Why did the Austrian man place the diamond ring on the third finger of the left hand of his would-be wife?
31. What is the chief advantage of having the engagement period?
Passage Three
“Where is the university?” is a question many visitors to Cambridge ask, but no one could point them in any one direction because there is no campus. The university consists of thirty-one self-governing colleges. It has lecture halls, libraries, laboratories, museums and offices throughout the city.
Individual colleges choose their own students, who have to meet the minimum entrance requirements set by the university. Undergraduates usually live and study in their colleges, where they are taught in very small groups. Lectures, and laboratory and practical work are organized by the university and held in university buildings.
The university has a huge number of buildings for teaching and research. It has more than sixty specialist subject libraries, as well as the University Library, which, as a copyright library, is entitled to a copy of every book published in Britain.
Examinations are set and degrees are awarded by the university. It allowed women to take the university exams in 1881, but it was not until 1948 that they ,were a warded degrees.
Questions 32 to 35 are based on the passage you have just heard.
32. Why is it difficult for visitors to locate Cambridge University?
33. What does the passge tell us about the colleges of Cambridge University?
34. What can be learned from the passage about the libraries in Cambridge University?
35. What does the passage say about women students in Cambridge University?
Section C
Directions: In this section, you will hear a passage three . when the passage is read for the first time, you should listen carefully for its general idea. When the passage is read for the second time, you are required to fill in the blanks numbered from 36 to 43 with the exact words you have just heard. For blanks numbered from 44 to 46 you are required to fill in the missing information. For these blanks, you can either use the exact words you have just heard or write down the main points in your own words. Finally ,when the passage is read for the third time, you should check what you have written.
Russia is the largest economic power that is not a member of the World Trade Organization. But that may change. Last Friday, the European Union said it would support Russia’s (36)effort to become a W.T.O. member.
Representatives of the European Union met with Russian(37) officials in Moscow. They signed a trade agreement that took six years to (38) negotiate.
Russia called the trade agreement (39)balanced.It agreed to slowly increase fuel prices within the country. It also agreed to permit (40)competition.in its communications industry and to remove some barriers to trade.
In (41) exchange for European support to join the W.T.O>, Russian President Putin said that Russia would speed up the (42) process to approve the Kyoto Protocol, an international (43) environmental agreement to reduce the production of harmful industrial gases. (44) These “greenhouse gases” trap heat in the atmosphere and are blamed for changing the world’s climate.
Russia had signed the Kyoto Protocol, but has not yet approved it. The agreement takes effect when it has been approved by nations that produce at least 55 percent of the world’s greenhouse gases. (45)But currently, nations producing only 44 percent have approved the Protocol. Russia produces about 17 percent of the world’s green-house gases.. The United States, the world’s biggest producer, withdrew from the Kyoto Protocol after President Bush took office in 2001. So, Russia’s approval is required to put the Kyoto Protocol into effect.
(46) To join the W.T.O., a country must reach trade agreements with major trading countries that are also W.T.O. members. Russia must still reach agreements with China, Japan, South Korea and the United States.
大学英语四级考试试点考试样卷(标准答案)
Key
Part II Reading Comprehension (Skimming and Scanning)
1. Y 2.Y 3.N 4.N 5.Y 6.N 7.NG
8.municipalities and construction companies
9.$10 to $40
10. drop-off stations
Part III Listening Comprehension
Section A
11.D 12.B 13.A 14.C 15.B
16.C 17.D 18.C 19.D 20.B
21.B 22.C 23.A 24.A 25.D
Section B
26.D 27.A 28.B 29.A 30.C
31.B 32.D 33.B 34.B 35.B
Section C
36.effort 37.officials 38.negotiate 39. balanced
40. competition 41. exchange 42. process 43. environmental
44. These “greenhouse gases” trap heat in the atmosphere and are blamed for changing the world’s climate.
45. But currently, nations producing only 44 percent have approved the Protocol. Russia produces about 17 percent of the world’s greenhouse gases.
46. To join the W.T.O., a country must reach trade agreements with major trading countries that are also W.T.O. members.
Part I V Reading Comprehension (Reading in Depth)
Section A
47. E 48. I 49. F 50. D 51. J
52. B 53.L 54. H 55. C 56. G
Section B
57. A 58. B 59. D 60. C 61. D
62. C 63. D 64. B 65. A 66. B
Part V Cloze
67.C 68. A 69. B 70. C 71. D
72. B 73. C 74. C 75. B 76. D
77. B 78. A 79. D 80. B 81. A
82.A 83. B 84. C 85. A 86. D
Part VI Translation
87. whether ( it is ) heated or not
88. did he charge me too much / did he overcharge me
89. compared with mine / in comparison with min
90. half as much (money)
91. to attribute their children’s success to
