1. The scientific method is not applicable to the study of economics because economics is not a true science.
A) True
B) False
2. Hypotheses derived from economic analysis can be validated through empirical analysis, but hardly ever with absolute certainty.
A) True
B) False
3. Which of the following statements relates to the concept of efficiency?
A) The absence of waste.
B) Using resources as effectively as possible.
C) Being able to produce more of one good only by producing less of something else.
D) All the above.
E) b. and c. only.
Use the following to answer question 4:
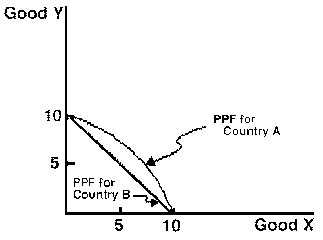
Figure 1
a 4. Figure 1 displays the production-possibilities of two countries. Given that both countries produce five units of x, which of the following best describes country B's production of y?
A) Less than country A's production of y.
B) The same as country A's production of y.
C) More than country A's production of y.
D) Cannot be determined from the graph.
E) None of the above.
a5. Mass unemployment of resources means society operates inside its production-possibility frontier.
A) True
B) False
b6. If two goods use the same resources and the same technology, the production possibilities curve between the two goods will have a positive slope.
A) True
B) False
a7. It is scarcity that makes goods economic goods.
A) True
B) False
e8. Which of the following is the most basic of the subjects with which the study of economics must try to deal?
A) Markets.
B) Money.
C) Profit seeking.
D) The price mechanism.
E) Scarcity.
b9. Poor money management by the government, aside from increasing the unemployment rate, will have a relatively small effect on the economy.
A) True
B) False
bUse the following to answer question 10:
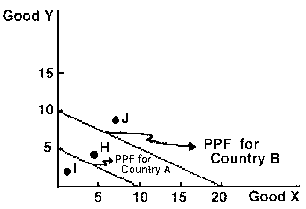
Figure 2
10. In Figure 2, what is Country B's cost of producing 1 unit of x in terms of y?
A) 10 units of y.
B) 1/2 units of y.
C) 5 units of y.
D) 2 units of y.
E) None of the above.
c11. Barter is inconvenient because:
A) bargaining power is unequal between rich and poor.
B) without money, who can define "fair" values?
C) my wants and supplies do not match your supplies and wants.
D) it leads to imperfect competition.
E) all of the above.
d12. The economic role of government in mixed economies can include:
A) provision of public goods.
B) tax collections.
C) income redistribution.
D) all of the above.
E) none of the above.
b13. By the "invisible hand," Smith meant the influence and lobbying of the hidden interest groups.
A) True
B) False
b14. A society which forgoes present consumption:
A) is forced to do so because of excessive consumption within the country in the past.
B) may be devoting new resources to new capital formation.
C) is merely devoting resources to the replacement of capital.
D) expects to consume only that amount tomorrow which was foregone today.
E) does none of the above.
a15. An economic good is valued in part by its scarcity.
A) True
B) False
e16. The statement that roundabout methods of production are often more efficient than more direct methods:
A) means that roundabout methods use the same inputs as more direct methods, except for time, which is not a scarce economic good.
B) means that consumers ought to choose those goods which most lend themselves to roundabout methods of production.
C) means that the most roundabout method is always the most efficient method of producing any output.
D) is false, for direct and indirect methods of production are usually the same in terms of efficiency.
E) suggests that foregone consumption devoted to investment sometimes increases future output in ways that more closely match individual and/or social desires.
e 17. Which of the following statements is true of specialization?
A) Specialization is inconsistent with the idea of individual freedom.
B) Economies that practice a division of labor are morally superior to those that do not.
C) In accepting specialization, a person sacrifices his or her own interests for the sake of society's interest.
D) While specialization has enormous advantages, the costs outweigh them.
E) Increased productivity is more likely to be achieved through specialization.
a18. In an affluent modern society, businesses may have to offer workers more fulfilling jobs.
A) True
B) False
d19. Consumers vote their dollars primarily in:
A) labor markets.
B) land markets.
C) capital markets.
D) goods markets .
E) none of the above.
a20. An example of legal limitations on property rights is the prohibition of pollution.
A) True
B) False
a 21. Lower prices coax out higher quantities demanded along a downward-sloping demand curve.
A) True
B) False
c22. An increase in price will lead to a lower quantity demanded because:
A) suppliers will supply only the smaller amount.
B) quality deteriorates.
C) people will purchase less of the good.
D) all of the above.
E) none of the above.
dUse the following to answer question 23:
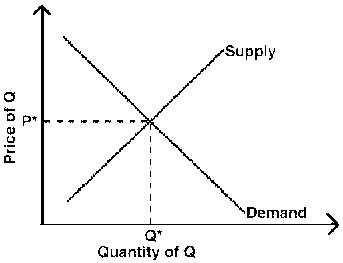
Figure 3
23. Let P* and Q* represent market clearing price and quantity, respectively. Given the supply and demand curves drawn in Figure 3, a reduction in the price of an input used in the production of Q can be expected to cause:
A) P* and Q* to climb.
B) P* to climb while Q* falls.
C) P* to climb while Q* holds steady.
D) P* to fall while Q* climbs.
E) P* and Q* to fall.
Use the following to answer question 24:
Table 1
The Market for Potato Chips
(quantities measured in bags per week)
Price Quantity Supplied Quantity Demanded
$1.00 500 2000
2.00 1000 1750
3.00 1500 1500
4.00 2000 1250
5.00 2500 1000
d 24. According to Table 1, the equilibrium price for potato chips is:
A) $1.00.
B) $2.00.
C) $2.50.
D) $3.00.
E) $4.00.
e a25. Upward-sloping supply curves are the result of:
A) increasing returns to scale.
B) increasing costs of production.
C) changes in government policies.
D) changes in technology.
E) none of the above
b26. To say that a price "clears the market" is to say that everyone who wants that commodity is getting all they want.
A) True
B) False
ba 27. The position of the supply schedule for American-made cars will not be directly affected by which of the following?
A) Union wage rates.
B) Car prices.
C) The possibility of strikes.
D) A change in assembly technology.
E) All of the above will affect supply.
d 28. The demand curve for a normal good will shift to the right if:
A) income increases.
B) population increases.
C) the price of a substitute good increases.
D) all the above.
E) none of the above.
e 29. Given a fixed supply of lamb chops, a reduction in the price of pork chops (close substitutes) will tend to:
A) shift the demand curve for lamb chops to the right.
B) shift the demand curve for pork chops to the right.
C) shift the demand curve for pork chops to the left.
D) raise the price of lamb chops.
E) lower the price of lamb chops.
e30. One reason that supply curves display positive slope is that:
A) expanded production may require the use of superior resources.
B) people are not willing to pay a higher price for more goods.
C) expanded industry output might cause a labor shortage and subsequently increase the wage rate included in the cost of production.
D) extra production brings in the more efficient, lower-cost producers.
E) the law of diminishing returns is important to producers.
b 31. If a 1 percent change in price causes a 5 percent change in quantity demanded, then demand is price inelastic.
A) True
B) False
dc 32. Whenever total expenditure (i.e., total revenue) remains the same after a change in price, the elasticity of demand is:
A) greater than 1.
B) less than 1.
C) equal to 0.
D) equal to 1.
E) equal to infinity.
b 33. If price and quantity sold both decrease from one period to another, we may infer that the law of downward-sloping demand does not operate in that market.
A) True
B) False
cd 34. In "tight" housing markets, rent controls are often applied to hold the price of housing to a "reasonable" level. What is the immediate effect of this price policy with respect to the allocative functions of prices, and the relative incomes of tenants and landlords?
A) The allocative function of prices is impaired, but the tenants are prevented from gaining at the expense of the landlords.
B) The allocative function of prices is not impaired, and the tenants are prevented from gaining at the expense of landlords.
C) The allocative function of prices is impaired, and the tenants who find housing gain at the expense of landlords.
D) The allocative function of prices is not impaired, but the landlords gain at the expense of tenants who do not find housing.
E) None of the above.
e 35. Which of the following inefficiencies might be the result of monopoly power's destroying a competitive equilibrium?
A) Prices too high.
B) Output too low.
C) Wages distorted across the economy.
D) Input prices distorted across the economy.
E) All of the above.
a36. Dollar receipts for sellers of some commodities will be lower at higher prices.
A) True
B) False
eb37. The quantity of a good which a person will purchase will not depend on which one of the following items?
A) The price of the good.
B) His or her tastes.
C) The prices of substitute goods.
D) His or her income.
E) The elasticity of supply.
Use the following to answer question 38:
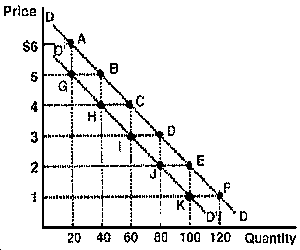
Figure 4
e38. Refer to Figure 4 once again. Suppose that now the demand curve has shifted to D'D'. At what point along D'D' is price elasticity equal to 1?
A) G
B) between G and H.
C) H.
D) between H and I.
E) I.
d39. Rank the supplycurves in the figure below in order of greatest to least price elasticity at the common intersection point.
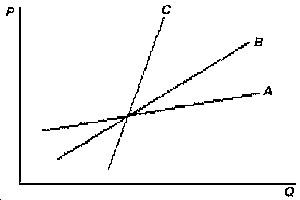
A) C, A, B.
B) B, A, C.
C) B, C, A.
D) A, B, C.
E) None of the above.
c40. A price subsidy of 20 cents per gallon on milk (which does not have a totally inelastic demand curve) will result in a:
A) change in consumer tastes.
B) drop in the equilibrium price of 20 cents per gallon.
C) drop in the equilibrium price of less than 20 cents per gallon.
D) drop in the equilibrium price of more than 20 cents per gallon.
b 41. The law of diminishing marginal utility states that the:
A) ratio of MU to P for luxuries is lower than that for necessities.
B) utility derived from the last unit of the good consumed falls as the consumption of the good increases.
C) ratio of MU to P will be the same for all goods.
D) utility derived from total consumption of a good falls as consumption increases.
E) none of the above.
d42. A consumer is said to be in equilibrium in his or her choice between two goods A and B when:
A) the purchase of good A gives the same satisfaction as the purchase of good B.
B) the last purchase of good A gives the same addition to satisfaction as the last purchase of good B.
C) each penny spent on good A gives the same satisfaction as each penny spent on good B.
D) the last penny spent on good A gives the same addition to satisfaction as the last penny spent on good B.
E) the last pennies spent on goods A and B generate no additions to satisfaction.
a 43. A consumer spends all of her income on two goods, coffee and doughnuts. She purchases coffee at 25 cents a unit with a total utility of 800 and a marginal utility of 12. Doughnuts are purchase at 75 cents a unit with a total utility of 200 and a marginal utility of 24. In order to reach consumer equilibrium, she should consume:
A) less doughnuts and more coffee.
B) more doughnuts but the same amount of coffee.
C) more coffee but the same amount of doughnuts.
D) more doughnuts and less coffee.
E) the same amount of coffee and doughnuts.
d 44. If a person only consumes pickles and peanut butter, he will consume peanut butter up to the point where the:
A) marginal utility of the last unit of peanut butter consumed equals that of the last unit of pickles consumed.
B) total utility of peanut butter consumed equals the total utility of pickles consumed.
C) consumer surplus of peanut butter consumption equals the consumer surplus of pickle consumption.
D) last dollar spent on peanut butter consumption provides the same marginal utility as the last dollar spent on pickle consumption.
E) none of the above.
b45. Water tends to have a low marginal utility because substitutes for it are widely available.
A) True
B) False
dc 46. A good which sells for a higher price than one which is more important for welfare reflects the concept of:
A) complementarity in demand.
B) substitution.
C) marginal or total utility.
D) the paradox of value.
E) law of diminishing marginal utility.
db47. The price of good X is $1.50 and that of good Y, $1. A particular consumer who evaluates the marginal utility of Y to be 30 units, and is in equilibrium with respect to purchases of X and Y, must consider the marginal utility of X to be:
A) 15 units.
B) 20 units.
C) 30 units.
D) 45 units.
E) none of the above.
b48. It is possible to sum individual demand curves to get the market demand curve only when all consumers are exactly alike in their demands.
A) True
B) False
a b49. The paradox of value is not the result of declining marginal utility.
A) True
B) False
c 50. In the figure below, which area represents consumer surplus at a price of 5?
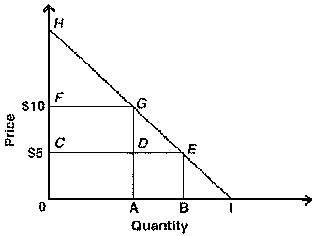
A) OADC.
B) OBEC.
C) CEH.
D) OBEH.
E) CEGF.
b51. Both in number and in dollar value of sales, the individual proprietorship is the dominant form of American enterprise.
A) True
B) False
Use the following to answer question 52:
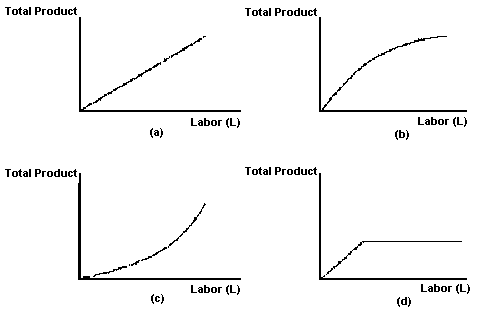
cFigure 5
52. Suppose that two inputs, K and L, are variable and increase at the same rate. Which one of the panels in Figure 5 represents Increasing Return to Scale (IRS)?
A) Panel a.
B) Panel b.
C) Panel c.
D) Panel d.
E) None of the above.
ba53. "Unlimited liability" in partnerships refers to the liability of each partner for her percentage share of any losses incurred, without limit, except for some legal minimum of property she is permitted to keep.
A) True
B) False
b54. The employment of which of the following inputs might be adjusted in the short run?
A) Physical capital.
B) Number of hours worked by labor.
C) Units of energy required per unit output.
D) Units of material required per unit output.
E) None of the above.
ca55. Numerically, the bulk of businesses in the U.S. are:
A) corporations.
B) partnerships.
C) sole proprietorships.
D) farms.
E) mom-and-pop retail shops.
a 56. If incomes were properly distributed, competitive general equilibrium would move resources to the best use for consumers' satisfaction.
A) True
B) False
Use the following to answer questions 57:
Total Product with
Various Input Combinations
Land
Labor 10 15 20
0 0 0 0
1 20 20.67 20.5
2 38 39.33 40.0
3 54 57.00 58.5
4 68 72.67 76.0
5 80 87.33 92.5
6 90 102.00 108.0
b57. Suppose that production were defined by the function recorded in the table above. For diminishing returns to continue to hold for the 7th unit of labor with land equal to 15 units, total product for the combination of [labor =7; land = 15] would have to be less than:
A) 0.
B) 116.67.
C) 115.67.
D) 114.67.
E) none of the above.
Use the following to answer questions 58-59:
Table 2
Total Product with
Various Input Combinations
Land
Labor 10 15 20
0 0 0 0
1 20 20.67 20.5
2 38 39.33 40.0
3 54 57.00 58.5
4 68 72.67 76.0
5 80 87.33 92.5
6 90 102.00 108.0
a58. The production process defined by the function recorded in Table 2 displays diminishing returns in both labor and land.
A) True
B) False
b59. The production process defined by the function recorded in Table 2 displays decreasing returns to scale for labor but not for land.
A) True
B) False
e60. Which of the following is an example of a project that could be observed in the short run?
A) The construction of a new assembly line to match an existing one.
B) The construction of a new assembly line to take advantage of a new technology.
C) The moving of an established assembly line to bring it geographically closer to a market.
D) The sale of an existing assembly line on the scrap market to finance part of a new facility.
E) None of the above.
a61. Horizontal long-run MC is associated with constant returns to scale.
A) True
B) False
d62. A fixed cost is:
A) the cost of any input whose per-unit price has been fixed, whether by long-term contract or by some similar means.
B) a cost whose increases are exactly proportional to increases in output.
C) any component included in average cost which enters in AC as the same fixed per-unit amount, no matter what the level of plant output may be.
D) a cost which the firm would incur even if its output were zero.
E) none of the above.
Use the following to answer questions 63-64:
Table 3
Quantity Variable Cost Total Cost
1 25 40
2 45 60
3 60 75
4 70 85
5 85 100
6 105 120
7 132 147
a63. What is MC between Q = 3 and Q = 4 in Table 3?
A) 10
B) 15
C) 20
D) 25
E) None of the above.
a64. What is AFC at Q = 5 in Table 3?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 7.5
E) 15
a65. Total cost at q + 1 minus total cost at q gives marginal cost for the qth unit.
A) True
B) False
d 66. The balance sheet always balances because:
A) by definition, profit is the residual between revenue and cost.
B) every proper official business statement is audited by a firm of independent accountants.
C) accountants, like statisticians, know how to manipulate the truth.
D) by definition, net worth equals the difference between assets and liabilities.
E) none of the above.
a67. A driver wishes to buy gasoline and have her car washed. She finds that the wash costs $3.00 when she buys 19 gallons at $1.00 each, but that if she buys 20 gallons, the car wash is free. Thus the marginal cost of the twentieth gallon of gas is:
A) –$2.00.
B) $0.00.
C) $1.00.
D) $2.00.
E) none of the above.
68. If a firm produces more goods than it sells and buys more raw materials than it uses up during the year, an inventory adjustment must be made so as not to:
A) overstate earnings for the year.
B) understate earnings for the year.
C) overstate liabilities at the end of the year.
D) understate liabilities at the end of the year.
E) overstate assets at the end of the year.
b69. Both the balance sheet and the income statement indicate the flow of sales, cost, and revenue over the accounting period.
A) True
B) False
b70. In calculating a firm's total costs, which of the following is not included?
A) The owner's expertise.
B) The demand curve facing the firm.
C) The taxes paid by the firm.
D) Non-essential costs, such as advertising and entertainment expenses.
E) Input prices.
b71. The zero-profit point for a perfectly competitive firm occurs where the price equals the minimum point of the:
A) AVC curve.
B) AC curve.
C) MC curve.
D) AFC curve.
E) none of the above.
c a72. In the long run, all costs:
A) lie along a perfectly elastic long-run supply curve.
B) are fixed costs.
C) are variable costs.
D) exhibit constant returns to scale.
E) depend upon the demand structure of the given market.
a73. Pure economic rent is the price paid to a factor of production that is fixed in total supply
A) True
B) False
c74. If, in long run equilibrium, the competitive price of some good is $16.67, then, for each and every firm in the industry,
A) marginal cost > average cost = $16.67.
B) marginal cost < average cost = $16.67.
C) $16.67 = marginal cost = average cost.
D) $16.67 = marginal cost > average cost.
E) $16.67 = marginal cost < average cost.
a75. A tax on the emission of a pollutant from the firms of a competitive industry can be expected to cause the equilibrium quantity demanded and supplied to decline.
A) True
B) False
b e76. In a market economy, the short-run reaction to an excess supply of a commodity after a decrease in demand is:
A) price will rise, but profits fall.
B) price and profits will fall.
C) price will fall, but profits will be unchanged.
D) price will fall, but profits will increase.
E) price and profits will both increase.
a77. In the long run, any firm will eventually leave an industry if:
A) price does not cover at least average total cost.
B) price is not equal to marginal cost.
C) price is higher than average variable cost.
D) price is not at least equal to the minimum of the marginal cost curve.
E) other firms in the industry are leaving.
Use the following to answer question 78:
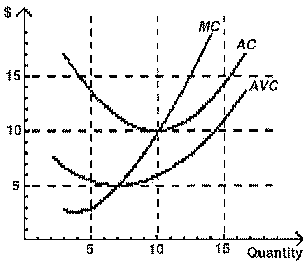
Figure 6
a b78. In Figure 6, the firm's economic profits will equal:
A) 0.
B) $40.
C) $100.
D) $150.
E) none of the above.
c79. Which of the following is incompatible with an efficient economic optimum?
A) Perfect competition.
B) Absence of externalities.
C) Monopoly.
D) All of the above are incompatible.
E) None of the above is incompatible.
db80. Under conditions of decreasing cost:
A) externalities are irrelevant and inapplicable.
B) each of the firms in the industry will continue to produce more output at falling costs per unit.
C) a strong case can be made for supplanting complete individualism by some kind of group action.
D) a few large sellers may come to dominate the industry.
E) monopolization of the industry becomes impossible.
Use the following to answer questions 81-82:
Table 4
P Q
$5 8
$4 12
$3 17
$2 22
$1 27
b81. Suppose an imperfect competitor faces the demand curve defined in Table 4, and its MC is constant at $2.00. If the firm is able to produce at any output level, then it maximizes profits at:
A) P = 5; q = 8
B) P = 4; q = 12.
C) P = 3; q = 17.
D) P = 2; q = 22.
E) none of the above if fixed costs are less than $1.00.
c82. Consider the demand curve given in Table 4. If the imperfectly competitive firm is able to produce at any output level, then the price and quantity which maximize total revenue are:
A) P = 5; q = 8
B) P = 4; q = 12.
C) P = 3; q = 17.
D) P = 2; q = 22.
E) P = 1; q = 27.
b83. Falling marginal revenue facing an individual firm is incompatible with:
A) growth of the firm.
B) perfect competition.
C) oligopoly.
D) barriers to entry.
E) none of the above.
a84. A percentage tax on a monopolist's profit has no effect on the profit-maximizing output as long as the tax is no greater than 100%.
A) True
B) False
b85. A profit-maximizing firm will always try to operate at the level of output at which its average costs are at a minimum, i.e., at the bottom of its U-shaped cost curve.
A) True
B) False
a 86. Steel is an oligopolistic industry in the U.S.
A) True
B) False
b a87. If all firms in an industry sell identical products, then it would never pay to advertise.
A) True
B) False
b 88. The marginal cost schedule facing an imperfect competitor is constant at $12. The demand curve is given in Table 5. The profit maximizing output for this firm is:
Table 5
P Q
$20 6
$19 7
$18 8
$17 9
$16 l0
A) 6 units
B) 7 units
C) 8 units
D) 9 units
E) 10 units
b 89. If a firm's demand curve is horizontal, then the firm's marginal revenue is:
A) less than the price of the product.
B) equal to the price of the product.
C) greater than the price of the product.
D) greater than, equal to, or less than the price of the product, depending on the particular circumstances.
E) not determinable from the above information.
b a90. An imperfect competitor is not willing to increase sales at the prevailing price because to do so would reduce marginal revenue.
A) True
B) False
c91. If price equals P1 for a monopolist good and P2 for a competitive good, then for any single consumer the ratio of marginal utilities, MU1/MU2:
A) is exactly 1, and equal to the ratios of marginal costs, MC1/MC2.
B) is exactly 1, and less than the ratios of marginal costs, MC1/MC2.
C) is exactly 1, and greater than the ratios of marginal costs, MC1/MC2.
D) is exactly 1, and MC1 = MC2
E) cannot be determined on data given.
Use the following to answer questions 92-93:
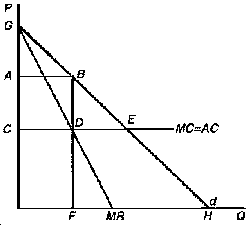
Figure 7
e 92. By the deadweight loss due to monopoly, we mean the area in Figure 7 labeled:
A) PAB.
B) ABCD.
C) FDEQ.
D) PCEB.
E) BDE.
a 93. Consider Figure 7. The cartel solution would occur at point:
A) B.
B) E.
C) H.
D) G.
E) none of the above.
b e94. The "separation of ownership and control" in the large corporation refers primarily to:
A) government limitations on the rights of capital ownership.
B) the ability of a small minority of shareholders or management to exercise effective control.
C) the issuance of voting warrants to management personnel.
D) the lack of diversification of stock ownership.
E) the fact that an officer of the company can sit on the board of directors, even though he may not be a shareholder.
d 95. "There are thousands of 'Ma and Pa' grocery stores in the United States that sell very similar merchandise. Therefore, the retail grocery business must be perfectly competitive." This statement is:
A) correct; grocery stores are like wheat farms, and if wheat farming is perfectly competitive, so is the grocery business.
B) incorrect; since the production of food is nearly perfectly competitive, the distribution of food must be perfectly competitive also.
C) incorrect; grocery stores are best described as oligopolistic.
D) incorrect; the thousands of separate retail grocery markets may best be described as monopolistically competitive with product differentiation determined by location.
E) correct; retail groceries are notoriously unprofitable.
d96. A concentration ratio measures:
A) the number of firms in a perfectly competitive industry.
B) the number of products sold in a monopolistically competitive market.
C) the ratio of the total number of firms in the market to the dollar value of industry revenues.
D) the percent of total industry output that is accounted for by the largest firms.
E) none of the above.
d 97. Monopolistic deviation from P = MC means that:
A) nobody can be made better off without making someone else worse off.
B) goods are being produced efficiently.
C) society is more able to achieve its welfare optimum.
D) someone can be made better off without making someone else worse off.
E) none of the above.
c98. Which of the following best explains why collusive oligopolies are not stable?
A) Companies are inherently hostile to each other.
B) Companies feel they have a moral responsibility not to collude.
C) Each company in the oligopoly can increase its profits by deviating from the agreed upon price and/or quantity.
D) Oligopolies are not unstable; rather they are quite stable.
E) None of the above.
bc99. Many firms practice mark up pricing, since it allows for profit maximization.
A) True
B) False
a100. Strategic interaction is a term used to describe the condition in which a firm's business strategy depends upon its competitors' actions.
A) True
B) False
a101. Private insurance markets sometimes fail to exist under conditions of pervasive moral hazard.
A) True
B) False
b 102. Moral hazard occurs when:
A) people with the highest risk are the most likely ones to buy insurance.
B) insurance reduces a person's incentives to avoid or prevent certain risky events.
C) the government refuses to provide social insurance.
D) risk is spread across markets and time by speculators.
E) none of the above.
d 103. Of prerequisites for the existence of a competitive equilibrium listed below, failure to meet which of them might cause prices to deviate from true social marginal cost?
A) No increasing returns to scale.
B) No externalities.
C) No monopolies or other forms of imperfect competition.
D) Failure to meet any of the above could create a price distorted away from marginal cost.
E) Answers b and c only.
b104. Imperfect competition and externalities are the only sources of difficulty in applying the welfare results of competitive economic theory to reality in the United States in the 1990s.
A) True
B) False
bUse the following to answer question 105:
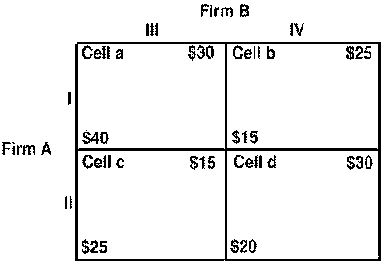
Figure 8
105. Figure 8 shows a payoff table for two firms, A and B. Strategy III is a dominant strategy for A.
A) True
B) False
ba 106. A given person is risk loving through all relevant levels of income. This person, facing the prospect of receiving an extra $5,000 with probability 0.5 and losing $5,000 with probability 0.5, would be willing to buy:
A) more insurance to avoid the risk than if the probabilities were 0.25 and 0.75 of receiving the extra $5,000 and losing $5,000, respectively.
B) less insurance to avoid the risk than if the probabilities were 0.25 and 0.75 of receiving the extra $5,000 and losing $5,000, respectively.
C) the same amount of insurance to avoid the risk than if the probabilities were 0.25 and 0.75 of receiving the extra $5,000 and losing $5,000, respectively.
D) no insurance to avoid the risk even if the probabilities were 0.25 and 0.75 of receiving the extra $5,000 and losing $5,000, respectively.
E) up to $10,000 in insurance if the probability of loss were sufficiently high.
a 107. A speculator who buys low and sells high will tend to smooth both consumption and price variability over time.
A) True
B) False
eUse the following to answer question 108:
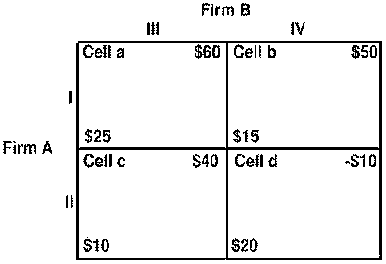
Figure 9
e 108. Figure 9 shows a payoff table for two firms, A and B. Which strategy is a dominant strategy for firm A?
A) Strategy I.
B) Strategy II.
C) Strategy III.
D) Strategy IV.
E) None of the strategies available to firm A is a dominant strategy.
109. An individual who holds marketable government securities now is likely to sell them and hold money instead if he believes that:
A) interest rates will fall far below present levels.
B) interest rates will fall below present levels for 3 months and then will rise above present levels.
C) interest rates will soon rise far above present levels.
D) interest rates will not change from present levels.
E) a substantial price deflation is coming.
110. Which of the following might cause inflation to be higher over the long term than it would otherwise be?
A) Monopoly power in a large industry.
B) An unrestrained externality.
C) Wage discrimination along racial lines.
D) All of the above.
E) None of the above.
111. Changes in real wages are calculated by comparing changes in money wages with changes in the:
A) rate of profits.
B) cost of living.
C) effort of the work.
D) tax rate.
E) none of the above.
112. A large increase in immigration into a country of limited land and resources would, in the short run, cause:
A) the marginal product of capital to fall.
B) the quality and the educational level of the labor force to decline.
C) rents and surplus profits to rise.
D) no change in the marginal product of labor.
E) all of the above.
113. Suppose that tobacco farmers notice that the number of people turning up to claim summer jobs picking tobacco in the Connecticut River Valley has fallen by more than 50%. If it is their intention to hire as many people as before, their best course of action would be to:
A) do nothing because unemployed youth will eventually come asking for jobs at the minimum wage.
B) complain on local TV that parents are not providing enough encouragement to their children to go out and get a job and earn some money.
C) lower the price of tobacco so that lower wages would be economical.
D) offer higher wages to increase the opportunity cost of not working.
E) do none of the above because none of them would work.
114. Unions can work to increase wages by restricting the supply of labor.
A) True
B) False
115. The law of diminishing returns suggests that laws limiting immigration into the United States will raise real wage rates here.
A) True
B) False
116. Minimum wage laws can be expected to reduce employment:
A) when the specified minimum wage is greater than the equilibrium wage.
B) when the specified minimum wage is equal to the equilibrium wage.
C) when the specified minimum wage is smaller than the equilibrium wage.
D) only if unscrupulous employers exploit the monopoly power that the laws provide to them.
E) when any of the above applies depending upon other circumstances.
117. Which of the following is not a major cause of wage differentials in the U.S.?
A) Differences in compensation due to workers tastes and values.
B) Non-competing groups in the labor market.
C) Differences in education across workers.
D) Government imposed wage ceilings.
E) All of the above can be expected to create wage differentials.
118. In a perfectly competitive economy, if people were all alike but some jobs differed in disutility, then there could be:
A) no wage differentials since labor is perfectly mobile.
B) wage differentials that are simply pure economic rents to "noncompeting groups."
C) compensating wage differentials.
D) both equalizing and nonequalizing wage differentials.
E) only nonequalizing wage differentials.
119. The charge for the use of the summit of Mt. Everest by a snow cone company (allowing that the sale of snow cones is the only activity the summit is useful for) is an example of:
A) external economies.
B) pure economic rents.
C) backward-bending supply.
D) the law of diminishing returns.
E) none of the above.
120. Pure economic rent on land of fixed supply is a surplus which can be taxed without causing a decline in productive efficiency.
A) True
B) False
121. One can argue for Ramsey taxes on the basis of economic efficiency.
A) True
B) False
122. If a factor of production receives rent, the rent is determined by the:
A) price of the final good.
B) elasticity of the factor's supply.
C) cost of the factor's inputs.
D) price of all other factors.
E) all of the above.
123. The single-tax movement associated with Henry George refers basically to the notion that:
A) a multiplicity of taxes is administratively costly.
B) pure land rent is a surplus which can be taxed heavily without distorting production incentives or efficiency.
C) the whole of a tax on the owners of a factor in inelastic supply is shifted forward to consumers.
D) any tax on land should be equal to zero, since land is a free gift of nature.
E) none of the above are correct.
124. Low-quality Belgian farmland can earn a higher rent than high-quality Argentine farmland.
A) True
B) False
125. The nominal interest rate plus the percentage price rise equals the real interest rate.
A) True
B) False
Answer Key -- test
1. B
2. A
3. A
4. A
5. A
6. B
7. A
8. E
9. B
10. B
11. C
12. D
13. B
14. B
15. A
16. E
17. E
18. A
19. D
20. A
21. A
22. C
23. D
24. D
25. E
26. B
27. B
28. D
29. E
30. E
31. B
32. D
33. B
34. C
35. E
36. A
37. E
38. E
39. D
40. C
41. B
42. D
43. A
44. D
45. B
46. D
47. D
48. B
49. A
50. C
51. B
52. C
53. B
54. B
55. C
56. A
57. B
58. A
59. B
60. E
61. A
62. D
63. A
64. A
65. A
66. D
67. A
68. B
69. B
70. B
71. B
72. C
73. A
74. C
75. A
76. B
77. A
78. A
79. C
80. D
81. B
82. C
83. B
84. A
85. B
86. A
87. B
88. B
89. B
90. B
91. C
92. E
93. A
94. B
95. D
96. D
97. D
98. C
99. B
100. A
101. A
102. B
103. D
104. B
105. B
106. B
107. A
108. E
109. C
110. E
111. B
112. C
113. D
114. A
115. A
116. A
117. D
118. C
119. B
120. A
121. A
122. A
123. B
124. A
125. B
