16.等产量曲线
是指在这条曲线上的各点代表投入要素的各种组合比例,其中的每一种组合比例所能生产出来的产量都是相等的。
17.需求弹性
说明需求量对某种影响因素变化的反映程度。用公式表示就是需求量变动率与影响因素变动率之比。
18.产品转换曲线
也称生产可能性曲线。在这条曲线上的任何点,都代表企业在资源给定的条件下能够生产的各种产品最大可能产量的可能组合。
19.完全垄断
如果一个行业只有一家企业,而且它所生产的产品没有其他产品可以替代,新企业的进入又有很大障碍,这就产生完全垄断。
20.边际收益递减规律
在技术水平不变的情况下,当把一种可变的生产要素投入到一种或几种不变的生产要素中时,最初这种生产要素的增加会使产量增加,但当它的增加超过一定限度时,增加的产量将要递减,最终还会使产量绝对减少。
简述价格弹性与销售收入之间的关系。
两者关系是:如果需求是富有弹性的,那么提高价格会使收入收入降低;如果需求使单元弹性的,则变动价格并不影响销售收入;如果需求是缺乏弹性的,则提高价格会使销售收入增加。
22.比较机会成本与会计成本这两个概念的异同。
机会成本是某种稀缺资源投入到某一用途后丧失的其他用途的收益。会计成本是会计学意义上的成本,它是指企业在经营时所发生的各项开支,这些开支是支出货币的记录,一般都在会计账目上得以反映,因而也叫历史成本。会计成本不是决策成本,而机会成本是决策成本。会计成本往往不能反映企业经营中的实际代价,因而要进一步考虑机会成本。
23.作为完全竞争的市场,必须具备哪些条件?
答:完全竞争市场结构的最基本特征是:在这个市场里,产品的价格完全由市场决定,企业只是价格的接受者,对定价无能为力。必须具备以下四个条件:
一、买者和买者很多。
二、产品是同质的
三、生产者出入这个行业是自由的
四、企业和顾客对于市场的信息是很灵通的。
24.企业的定价目标最主要的有哪些?
答案:企业定价的目标是企业选择定价方法和定价策略的出发点和根据。企业的定价目标主要有以下四种:以盈利作为定价目标;以扩大销售作为定价目标;以稳定价格作为定价目标和以应付竞争作为定价目标。
25.假定某企业的生产函数为 ,其中劳动(L)的价格为3元,资本(K)的价格为5元。生产10个单位的产品,应投入L和K各为多少时才能使成本最低?
,其中劳动(L)的价格为3元,资本(K)的价格为5元。生产10个单位的产品,应投入L和K各为多少时才能使成本最低?
解:当产量一定时,要使成本最小化,所满足的条件为:
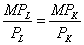
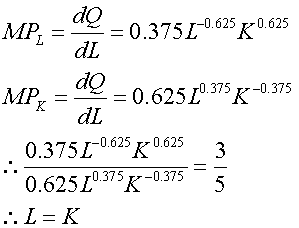
把L=K代入 中,且Q=10时,有L=K=10
中,且Q=10时,有L=K=10
某企业根据市场调查开发一种新产品,经会计部门核算:固定成本为62000元,平均变动成本为1.8元/件,产品价格为3元/件,为确保达到目标利润为40000元,试计算企业的产量最少为多少件?
解:企业最小的产量
27.完全竞争的成本固定不变行业包含许多厂商,每个厂商的长期总成本函数为:
LTC=0.1q3-1.2q2+11.1q(q为每个厂商的年产量)。试计算厂商长期平均成本为最小的产量和销售价格。
解:厂商长期平均成本:
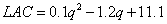
当厂商长期成本最小时有: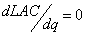
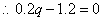
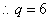
当厂商达到长期均衡时,有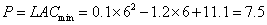
大昌公司产品X的需求函数为:Q=36-10PX+20PY+0.04I,其中PX为产品本身的价格,PY为相关产品的价格,I为居民收入。当PX=10元,PY=16元,I=4000元时,
求:(1)产品X的价格弹性;
(2)产品X的交叉弹性;
(3)两种产品是互补还是相互替代?
解:产品X的价格弹性为: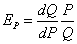
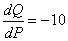 ,当PX=10,PY=16,I=4000时,Q=416
,当PX=10,PY=16,I=4000时,Q=416
所以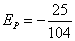
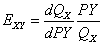
所以: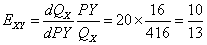
所以两种产品是替代的。
完全竞争厂商的短期成本函数为TC=0.04q3-0.8q2+10q+5,如果此时的市场价格P=10元。求厂商利润最大化时的产量及其利润总额。
解: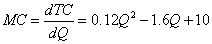
完全竞争厂商达到短期均衡时: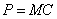
所以: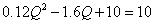
所以: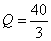
所以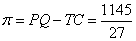
30. 试论述决定商品的需求价格弹性的主要因素及具体影响。
答:决定商品价格弹性的因素主要有:
(1)商品是生活必需品还是奢侈品,生活必需品的价格弹性小,奢侈品的价格弹性大。
(2)可替代物品越多,性质越接近,弹性就越大。
(3)购买商品的支出在人们收入中所占的比重,比重大的商品,其价格弹性就大,如果只看短期,其弹性就小。
(4)时间弹性也影响弹性的大小。同样的商品,从长期来看,其弹性就大,如果只看短期,其弹性就小。
第二篇:厦门大学20xx年 继续教育试题 英语
《英语1》复习题
I. Reading Comprehension:
Passage 1
In the water around New York City is a very small island called Liberty Island. On Liberty Island there is a very special statue called the Statute of Liberty. It is one of the most famous sights in the world.
The Statue of Liberty was a gift from the people of France to the people of the United States. The statue was made by a French sculptor named Frederic Auguste Bartholdi. The inner support system was designed by Gustave Eiffel, the same man who made the famous Eiffel Tower in Paris.
Liberty, of course, means freedom, and the Statue of Liberty was given to the United States to celebrate the one-hundredth anniversary of U.S. independence from England. The statue was built in France, taken apart piece by piece and then rebuilt in the United States. It was opened for the public on October 28, 1886.
As you might expect, the statue is very big. Visitors can ride an elevator from the ground to the bottom of the statue. If they want to, they can then walk up the 168 steps to reach the head of the statue where they can look out and enjoy the beautiful sight of the city of New York.
1. A good title for this selection is _____.
A. Famous Sights in the World B. Liberty Island
C. The Statue of Liberty D. A Gift from France
2. The word “sights” in the first paragraph means ______.
A. a small present or gift B. a kind of postcard
C. the power of seeing D. something that you can see
3. The statue was built in ______.
A. France B. the United States
C. England D. Liberty Island
4. We may conclude that the elevator does not ______.
A. go fast enough B. cost a lot of money
C. go to the top D. both A and B
5. The man who made the part of the statue that we can see on the outside was ______.
A. an unknown architect B. Bartholdi
C. Eiffel D. both B and C
(答案:CDACB)
Passage 2
When an English traveler was to return home from Sweden, he found that he had only enough money left to get a ticket back to England. He decided that as it was only a two days’ voyage he could get home without eating anything. So he bought a ticket with the little money he had and went on board the ship.
He closed his ears to the sound of the lunch bell, and when dinner time came, he refused to go down to the dining room, saying that he did not feel well.
The following day he did not get up until breakfast was over, pretending that he had overslept. At lunch time, too, he kept out of the way. By dinner time, however, he was extremely hungry. “I can’t stand this any longer,” he said to himself. “I must have something to eat.” At the dinner table he ate everything put in front of him. When he was quite satisfied he felt stronger and called the waiter.
“Bring me the bill,” he said to the waiter.
“The bill?” said the waiter in surprise.
“Yes,” answered the traveler.
“There isn’t any bill here,” said the waiter. “On this ship meals are already included in the ticket.”
6. When the traveler was going back home, he found that ________.
A. he still had enough money to buy the ticket and something to eat
B. he had not enough money left for the ticket back to England
C. he had more than enough money left to buy a ticket back to England
D. the money he had with him was enough only for a ticket back to England
7.He decided to eat nothing during the voyage because _________.
A. the voyage was not very long
B. he used to have a meal every other day
C. he had no money left
D. he had some food with him
8.Which of the following statements is true?
A. He didn’t feel well on the first day of the voyage.
B. He overslept the following day.
C. He didn’t have lunch on the ship.
D. He had only one lunch on the ship.
9.By dinner time the next day, the traveler _________.
A. was too weak to stand on his feet
B. could not bear it any longer
C. felt stronger than ever
D. was quite satisfied with what he had achieved
10.When the traveler asked for the bill, the waiter was surprised because _________.
A. the traveler spent too much money on the food
B. the traveler was a stranger to the waiter
C. the traveler’s voice was too loud
D. meals were free of charge on that ship
(答案:DCCBD)
Passage 3
Different as they are, advertisements are alike in one important way. They have the same purpose, to get people to buy something.
In the days of the cave men there was no advertising. There was no need for it. But as soon as people began to make things to sell, advertising was found to be useful. The businessmen of ancient Egypt employed "criers" to walk through the streets shouting or singing about the things they wanted to sell. Newsboys still "cry" their papers now.
In the Middle Ages businessmen hung picture signboards over their shop door showing what they had to sell. A large picture of a shoe above a shop door meant that it was a shoemaker's shop. It suggested buying shoes or having old ones mended.
As more things were made to be sold, advertising grew. Today advertising is one of the biggest businesses. A great many people work at the advertisement. Every year billions of dollars are spent on advertising.
Advertising helps sell more things to more people. This in turn makes it possible to produce more things to sell. Sometimes it even helps make things cost less. Radios, for example, used to cost much more than they do because they were turned out slowly and expensively by hand. But advertising made more people want radios. When producers began making them by the thousands, they found quicker and cheaper ways of doing the job.
11. Advertising is almost all made ___________.
A. by people who sell things B. by people who buy things
C. by employed "criers" D. by ancient Egyptians
12. All advertisements are the same in that ___________.
A. they are of the same color B. they help sell things
C. they are made on television D. they often look alike
13. It is not mentioned in the passage that__________.
A. advertising can be in both spoken and written forms
B. advertising on TV is much preferred
C. the cave men did not make any advertisement
D. advertising today employs many "criers"
14. Radios used to cost much more than they do today because_____________.
A. people did not advertise
B. no one wanted to buy them
C. they were made slowly by hand
D. they were made quickly by machines
15. Advertising which is one of the biggest businesses probably began __________.
A. in the days of the cave men B. in the Middle Ages
C. in the modern time D. when there were things to sell
(答案:ABBCD)
II. Vocabulary and Structure
1. She is a ______ woman who is certain of her ideas and actions.
A. significant B. aware C. confident√ D. intense
2. —That man alone over there — who is he?
— ____________.
A. He is a student B. He is Doctor Took √
C. A driver, I suppose D. He's drunk
3. — Hi, is Mary there, please?
— __________.
A. Hold on. I’ll get her√ B. No, she isn’t here
C. Yes, she live here D. Yes, what do you want
4. The boss refused to give any _______ on the fact that his workers were out of jobs.
A. response B. comment√ C. answer D. reply
5. The story he is telling is so ________ that some of the listeners begin to ask him to stop.
A. pleasant B. horrible√ C. healthy D. exciting
6. People working in the government should not _________________ business affairs that might change their political judgment.
A. engage in√ B. hope for C. choose between D. pick on
7. Robin thought that the best _______ to learning a foreign language is the study of the spoken language.
A. method B. way C. means D. approach √
8. It is very difficult for the time being to ________ how much money is needed.
A. account B. assume C. ranges D. estimate √
9. — “Merry Christmas and Happy New Year to you!”
— “________.”
A. Thank you, the same to you √ B. I hope so
C. I wish so D. I’m glad to hear that
10. Good managing of a company ________ great efforts.
A. calls on√ B. calls out C. calls in D. calls at
11. It was in China ________ Dr. Bethune gave his life to the cause of the revolution.
A. that √ B. where C. in which D. at which
12. The young professor ______ himself as an international leader in the field of mathematics.
A. established√ B. built C. founded D. found
13 --- I believe we've met somewhere before.
--- No, _______________.
A. it isn't the same B. it can't be right
C. I don't think so √ D. I’d rather not
14. — Would you like to have dinner with us this evening?
— ___________.
A. OK, but I have to go to a meeting now
B. No, I can’t
C. Sorry, but this evening I have to go to the airport to meet my parents√
D. I don't know
15. — Excuse me, but can you tell me the way to the airport?
— ____________.
A. Don’t ask that B. Sorry, I’m a stranger here√
C. No, I can’t say that D. No, you’re driving too fast
16. He ran ________ no one could catch him.
A. so fast as B. very fast that C. that fast so D. so fast that √
17. _______ coming of the Space Age, a new area has been added to the study of the planets.
A. While B. It is the C. When the D. With the √
18. To be frank, I' d rather you ________ in the case.
A. will not be involved B. not involved
C. not to be involved D. were not involved √
19. After a long period of regular exercise, I now ____________ much less than I used to.
A. weigh√ B. like C. grow D. increase
20. If you think that the illness might be serious you should not ______ going to the doctor.
A. put off √ B. hold back C. put away D. hold up
21. Our neighbour said that if we made more noise he would ________________ us to the police.
A. inform of B. complain about √
C. report to D. care for
22. On our trip out of the country we visited ______ in England.
A. relationship B. relations C. relatives √ D. personnel
23. Most people have no real idea how to change to healthy food, and Maureen was no ________.
A. foundation B. possibility C. exception√ D. ignorance
24. The teacher praised and rewarded the good ________ of his students in class.
A. status B. behaviour √ C. function D. signal
25. The book offers some advice about how to make a good ________ at job interviews.
A. attitude B. appearance C. effect D. impression √
26. --- Do you mind telling me where you’re from?
---___________.
A. Certainly. I’m from London B. Sure. I was born in London
C. Not really, you can do it D. Certainly not. I’m from London √
27. He could be ________ about everything else in the world, but not about Manet, his loving child.
A. visual B. critical√ C. favorite D. essential
28. ________ else goes, I won't.
A. Who B. Whom C. Whoever√ D. He who
29. We also use other forms of communication ________ we may be aware or unaware.
A. to which B. of which√ C. which D. that
30 Listening, speaking, reading, and then writing _______ the basic order in language learning.
A. assists B. constitutes√ C. establishes D. founds
31. ________ 25 years ago next month, the club is holding a party for past and present members.
A. Forming B. Being ing formed
C. Formed √ D. To form
32. The train was ________ slow I was almost two hours late.
A. so√ B. such C. very D. that
33. A man walked in off the street and fell flat ________ his face, unconscious.
A. for B. on √ C. against D. in
34. She ______________ him to help her to find answers to her problems.
A. learned from B. came into C. leaned on√ D. looked at
35. They had to examine the dead tiger before they had a _______ answer as to who killed it.
A. positive√ B. senior C. virtual D. vital
36. Few of the students understand why language is _______ to human beings.
A. aware B. unique√ C. absolute D. continual
37. He always knew what time it was, as if by ________.
A. instinct√ B. imagination C. reaction D. reality
38. The ________ she is in is whether to get married and live her own life or to stay at home supporting the family.
A. trouble B. problem C. choice D. dilemma √
39. When you're in Paris you can't help being ________ of the way the streets are kept clean.
A. effective B. relaxed C. conscious√ D. obvious
40. Twenty years ago it was common to see people _________________ from hunger on the streets in that poor nation, but clearly the situation has improved greatly since then.
A. calling B. preventing C. resulting D. collapsing √
41. If you want to know the train timetable, please ______ at the booking office.
A. acquire B. inquire √ C. request D. require
42. With the job ________, he went to see a film with his colleagues.
A. done √ B. doing C. to do D. do
43. We must ________ our attention on the question of reducing our cost.
A. pay B. focus √ C. absorb D. promote
44. — Good morning, sir. May I help you?
— ____________.
A. No, I don’t buy anything. B. No, I don’t need your help
C. Yes, I need some sugar√ D. Oh, no. That’s OK
45. What a ________ smell! Open the window and air the room.
A. disgusting√ B. pleasing C. powerful D. disturbing
46. He thought that _______.
A. the effort doing the job was not worth B. the effort was not worth in doing the job
C. it was not worth the effort doing the job √ D. it was not worth the effort by doing the job
III. Cloze
Do you know what color an orange is? Is it orange? Not always. Some oranges are green. They can be green in color even if they are 1 and ready to eat. An orange that is orange in color is ___2 __ that has been grown in cool air. Some people who live in very warm places have never seen an orange.
Oranges can be eaten in many __3 __. Some people eat them with sugar. Others put salt on them. Lots of people eat them __4____.
Some people _5 _ an orange in their hands to eat it. Some people use _6_ to help them peel (剥皮) and eat an orange. Many people use a spoon. Some people made a ___7 __ hole in one end of an orange and _8__ the juice. Oranges are often squeezed (挤出 )to make orange juice to drink.
Not all oranges __9__ as food or drink. There is one country _10_ people cut oranges in half and use them to scrub the floor.
1. A. ripe B. big C. heavy D. soft
2. A. the one B. one C. all D. each
3. A. colors B. parts C. ways D. sides
4. A. whole B. full C. all D. plain
5. A. hold B. seize C. grasp D. catch
6. A. knife and fork B. a knife and fork C. knife or fork D. a knife and a fork
7. A. big B. deep C. small D. thorough
8. A. bring out B. break out C. spit out D. suck out
9. A. end up B. complete C. are finished D. use up
10. A. which B. where C. there D. in that
(答案:ABCDA BCDAB)
What should we do to stay healthy? One important rule is to exercise 1 _. The Fang family tries to exercise every day. Lee Fang ___2___ exercise in the morning because he must be at his job at exactly seven o'clock. But he runs every evening. He would rather run than watch TV. He walks a lot, __3___. He walks to school every day, and after school he 4____ different sports with his friends. Lee Fang goes to a yoga class ____5____.
But it wasn't ___6___ this way. Last year Mr. and Mrs. Fang used to ____7___ everywhere, even to the drugstore two blocks away. They thought they had to use the car all the time. They wouldn't walk.
The Fangs all ___8___ better now. And they believe you mustn't be lazy. You ___9___ exercise every day. But you should ___ 10___ to get in shape and stay in shape.
1. A. often B. sometimes C. late D. later
2. A. may not B. can not C. would not D. should not
3. A. either B. also C. too D. again
4. A. watches B. plays C. loves D. practices
5. A. in two weeks B. for two weeks C. after two weeks D. twice a week
6. A. always B. seldom C. usually D. sometimes
7. A. ride B. drive C. fly D. walk
8. A. had B. make C. feel D. feel like
9. A. needn't B. don't C. won't have to D. mustn’t
10. A. try B. want C. wish D. hope
(答案:ABCBD ABCAA)
IV. Translate the following sentences from Chinese into English:
1. “一见钟情”或”瞬间成恨”常视为不成熟的标记。
“Love at first sight” and “instant hate” are often considered signs of immaturity.
2. 使我不安的是,音乐有很大的负面寓意。
What worries me is that music has a very negative message.
3. 我们珍惜自己行动的自由, 劳动的果实和我们的生命。
We hold dear/value our freedom to move about, the fruits of labor and, our own lives.
4. 我敢肯定,那音乐既伤你的耳朵又伤你的大脑。
I'm sure that music is hurting your ears as well as your brain.
5. 我们现在可以在家里通过因特网供应商订购杂货。
Now we can order groceries at home through Internet suppliers.
6. 为了准备接受新挑战,他必须根据事实和经验作出决定。
In order to get prepared for a new challenge, he has to make decisions based on facts as well as experience.
7. 我不假思索的转过身,在愤怒和恐惧中开了枪。
I turn and without really thinking, angry and frightened, I shoot.
8. 要给人留下好印象,你必须要保持你最佳状态的自我。
If you want to make a good impression on other people, you have to be yourself at your best.
9. 行动比言语更为响亮。
Actions speak louder than words.
