科 技 查 新 报 告
项目名称:计算力学的新理论与新方法 成 员:朱生旭、方中勇、姜冬 学 号:
委托日期:20xx年 05 月 13 日 查新机构:青海大学
查新完成日期: 20xx年 05 月 28日

四 文件检索的范围及检索策略
选用的国内数据库

选用的国外数据库


检索策略:
1计算力学
2计算力学的新理论
3计算力学的新方法
4计算力学的新理论与新方法
1 computational mecharies
2 computational mecharies and new theories
3 computational mecharies and new innovations
4 computational mecharies and new theories and new innovations
五 检索结果
参照用户提供的技术要点和主题词,依据上述检索范围和检索式,检索出一百多篇文献,其中一般相关文献40篇,无密切相关文献。检索结果及分析如下:
国内部分:
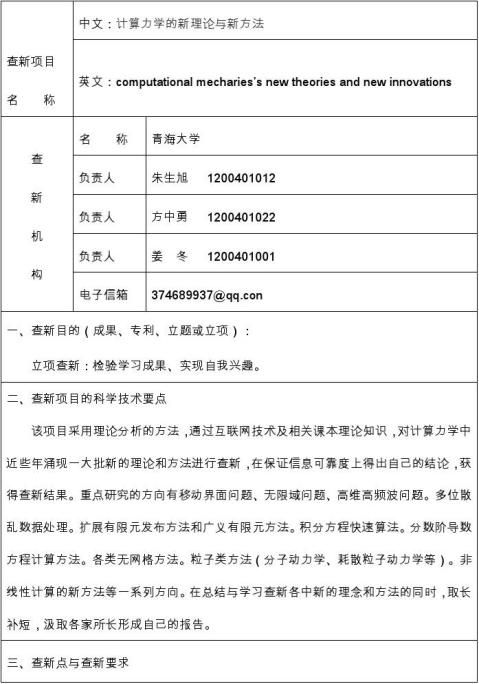
1 2 3 4 5 部分主要介绍了力学的计算方法和研究以及研究前景,力学计算的特点。
6 7 8 9 10 部分主要介绍了力学计算的新理论,国内外研究的发展。
11 12 13 14 15 部分主要介绍了力学的新概念和现代数学的结合和发展,以及在现实中的应用和例题解剖。
16 17 18 19 20部分主要介绍了力学的发展,国际社会的在这领域内的合
作与交流,力学在各个领域内的应用。
国外部分
1 2 3 4 5Part mainly introduces the calculation method and the research and research prospect of mechanics, the characteristics of the mechanical calculation. 6 7 8 9 10Part mainly introduces the mechanical calculation of the new theory, the development of the research at home and abroad. 11 12 13 14 15Part mainly introduces the new concept of mechanics and the combination of modern mathematics and the development, and its application in reality and the anatomy of the sample. 16 17 18 19 20Part mainly introduced the development of mechanics, the international community in cooperation and exchanges in the field of mechanics in various areas within the application.
六 相关内容
1 《计算力学的研究与发展前景》
【作者】 张伟林;
【Author】 Zhang Weilin (Computing Center,Anhui Institute of
Architecture,Hefei,230022)
【机构】 安徽建筑工业学院计算中心!合肥230022;
【摘要】 对计算力学的研究现状作了分析 ,介绍了计算力学中的主要方法 ,其中包括有限差分法、有限元法、边界元法、加权残数法和有限元线法等。又从算法的研究方面讨论了计算力学的研究进展 ,并探讨了计算力学今后的发展趋势。 2《跨国际的中国力学》
【作者】 杨亚政;
【机构】 中国力学学会;
【摘要】 本文综述了中国力学学会2003-20xx年在与国际组织联络、争办大型国际例会、主办自主系列国际会议、期刊国际化等方面所做的一些工作,通过这些工作强化了中国力学的国际学术交流,进一步提高了中国力学在国际的地位。 3《计算力学学科发展邹议》
【作者】 程耿东;
【Author】 Cheng Gengdong (Dalian University of Technology .Dalian, 116023,P. R. China)
【机构】 大连理工大学 116023;
【摘要】 简要回顾我国计算力学学科的发展,着重从模型的建立、算法研究和计算力学软件开发应用三个方面论述了计算力学的研究方向。
4《土建结构中的计算力学》
【作者】 江见鲸;
【Author】 Jiang Jianjing (Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084, P. R.China)
【机构】 清华大学土木工程系 北京 100084;
【摘要】 简要地回顾了计算力学在土建结构工程领域中取得的主要进展,并结合土建结构的特殊性,对计算力学在未来的十年中可能取得的发展作一展望。 5《人事实论与计算力学的发展》
【作者】 王文涛; 谢水波;
【Author】 WANG Wen-tao,XIE Shui-bo(University of South
China,Hengyang,China,421001)
【机构】 南华大学国际交流合作处;
【摘要】 计算力学是众多应用科学尤其是工程技术的基础,基于计算力学分支中的拱坝计算力学与仿真技术的发展,从力学发展历史、坝体混凝土材料本构模型的演化进程等不同角度阐述了相关的科学哲学观点,考察了科学与认识论的关系.并从认识论角度对拱坝计算力学的发展进行预测与判断.
6《国力学学会学术报告》
【作者】 冯西桥; 杨亚政; 赵红平; 陈常青; 任玉新; 王在华; 许春晓; 张来平; 孙德军; 郭旭; 陈伟球; 江五贵; 高凌天;
【机构】 清华大学工程力学系; 中国力学学会; 西安交通大学航天航空学院; 解放军理工大学理学院; 中国空气动力研究与发展中心; 中国科学技术大学近代力学系; 大连理工大学工程力学系; 浙江大学土木工程学系; 南昌航空大学材料科学与工程学院; 清华大学工程力学系 北京 100084; 北京 100080; 北京 100084; 西安 710049; 南京 211101; 绵阳 6210001; 合肥 230027; 大连 116023; 杭州 310027; 南昌 330063;
【摘要】 <正>1会议概况值此中国力学学会50华诞之际,为回顾中国力学的光荣历程、展现我国力学的优秀成果、弘扬中国力学的优秀传统、展望新世纪力学学科的发展趋向,中国力学学会成立50周年暨中国力学学会学术大会′2007(Chinese Conference of Theoretical and Applied
Mechanics-2007,CCTAM’2007)于20xx年8月20~22日在北京召开.大会由中国力学学会主办,39个单位协办.本次大会主席由中国力学学会理事长李家春院士担任,副主席为程耿东、戴世强、樊菁、方岱宁、胡海岩、刘人怀、佘振苏和郑晓静.
7《谈谈计算力学的发展》
【作者】 武际可;
【机构】 北京大学力学系;
【摘要】 本文综述了计算力学的当前发展概况并简要介绍了当前应当注意的若干研究方向.
8《跨世纪的中国计算力学》
【作者】 钟万勰; 程耿东;
【Author】 ZHONG Wanxie; CHENG Gengdong;(Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116023, China)
【机构】 大连理工大学工程力学研究所!大连116023;
【摘要】 简要介绍中国计算力学的形成和发展,回顾了30多年来中国计算力学工作者在计算力学基本理论、方法和应用软件等各方面所取得的成就,展望21世纪中国计算力学的发展和可能的重要研究方向。
9《认识识论与计算力学的发展》
【作者】 王文涛; 谢水波;
【Author】 WANG Wen-tao,XIE Shui-bo(University of South
China,Hengyang,China,421001)
【机构】 南华大学国际交流合作处;
【摘要】 计算力学是众多应用科学尤其是工程技术的基础,基于计算力学分支中的拱坝计算力学与仿真技术的发展,从力学发展历史、坝体混凝土材料本构模型的演化进程等不同角度阐述了相关的科学哲学观点,考察了科学与认识论的关系.并从认识论角度对拱坝计算力学的发展进行预测与判断.
10《计算力学中的现代数学方法的若干问题》
【作者】 韦忠瑄; 孙鹰;
【Author】 WEI Zhong-xuan, SUN Ying (Institute of Sciences,PLA Univ.of Sci.& Tech.,Nanjing 210007,China)
【机构】 解放军理工大学理学院; 解放军理工大学理学院 江苏南京210007; 江苏南京210007;
【摘要】 随着现代科学技术的高速发展 ,计算力学面临许多新课题 ,大范围非线性问题已成为计算力学研究的主攻方向 ,现代数学方法给计算力学的研究提供了强有力的工具。简要综述了计算力学所涉及的若干现代数学领域和方法 ,着重介绍了非线性问题的研究现状和发展 ,包括各类与现代数学密切相关的算法研究、Hamilton力学与辛几何、分叉理论等 ,以期展示现代数学方法在计算力学中的广泛应用。这些方法正在改变着计算力学研究的面貌 ,它们将给这个领域带来新的景象
11《岩土工程图形计算力学的概念方法及应用》
【作者】 魏群; 张国新;
【Author】 WEI Qun1,ZHANG Guoxin2(1.Research Institute of Steel
Structures and Engineering,North China Institute of Water Conservancy and Hydroelectric Power,Zhengzhou,Henan 450011,China;2.China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research,Beijing 100088,China)
【机构】 华北水利水电学院钢结构与工程研究所; 中国水利水电科学研究院;
【摘要】 提出图形计算力学的概念和方法,将计算力学、计算机图形学和现代AutoCAD技术相融合,利用已经发展的比较完备的计算机图形学的理论方法和现代AutoCAD技术提供的三维建模平台,将整个岩体切割成为具有一定方向、一定规模、一定形态和特征面的组合实体,这种图形实体的主要特征、属性、相互接触,嵌入的位置和量值可直接从图形中判断计算。将该算法应用于多种数值方法中,较现有的纯数值计算方法更加直观、简便和可靠,此法和虚拟现实技术相结合,使图形计算力学充满了发展的空间和应用价值。
12《基于塑形力学新方法的弹塑性断裂研究》
【作者】 袁文芳;
【导师】 李铀;
【作者基本信息】 中南大学, 力学, 2014, 硕士
【摘要】 摘要:材料或结构中的缺陷来源于材料本身的冶金缺陷或加工、制造、装配以及使用过程中的损伤,有的直接以裂纹的形式存在,有的是在疲劳载荷的作用下形成的裂纹,有的是在疲劳载荷和残余应力场的联合作用下逐渐形成的裂纹。结构缺陷萌发和扩展为裂纹具有严重的危害性,一方面在于它严重削弱了机械结构的承载能力和耐腐蚀能力,另一方面伴随使用过程中产生的应力集中,将诱发设备发生低应力破坏,甚至导致突发性灾难性事故。因此,研究裂纹问题具有重要的理论意义和工程应用价值。因裂纹导致的断裂形式有多种,已有的断裂判据目前都是只适用于某些特定的裂纹问题,断裂判据本身的局限性使得其应用往往不普遍。很难找到一种适用于大多数裂纹问题的断裂判据和断裂理论。本文从裂
纹尖端应力场出发,运用塑性力学新方法结合实验数据对弹塑性断裂问题进行理论分析与数值模拟,主要的研究内容与结果如下:(1)回顾了线弹性断裂力学和弹塑性断裂力学的发展和研究概况,并介绍了有限元方法在断裂力学中的应用概况。(2)系统介绍了塑性力学求解新方法,新方法的统一基本方程组,统一方程组的物理解释和求解方法。(3)基于塑性力学求解新体系,通过ANSYS计算弹塑性断裂问题的裂...
13《算力学中的现代数学方法的若干问题》
【作者】 韦忠瑄; 孙鹰;
【Author】 WEI Zhong-xuan, SUN Ying (Institute of Sciences,PLA Univ.of Sci.& Tech.,Nanjing 210007,China)
【机构】 解放军理工大学理学院; 解放军理工大学理学院 江苏南京210007; 江苏南京210007;
【摘要】 随着现代科学技术的高速发展 ,计算力学面临许多新课题 ,大范围非线性问题已成为计算力学研究的主攻方向 ,现代数学方法给计算力学的研究提供了强有力的工具。简要综述了计算力学所涉及的若干现代数学领域和方法 ,着重介绍了非线性问题的研究现状和发展 ,包括各类与现代数学密切相关的算法研究、Hamilton力学与辛几何、分叉理论等 ,以期展示现代数学方法在计算力学中的广泛应用。这些方法正在改变着计算力学研究的面貌 ,它们将给这个领域带来新的景象
14《计算力学中的高精度数值分析新方法》
【作者】 曾攀;
【机构】 清华大学机械工程系!北京100084;
【摘要】 提出一种用于获取工程结构静动态力学特性的高精度数值分析新方法———复合单元法 .在对结构进行离散后 ,定义两组自由度坐标体系来描述离散单元的位移场 ,基于节点坐标体系 ,应用常规插值多项式构造出位移场函数UFEM( ξ) ,基于场坐标体系 ,应用经典力学解析解构造出位移场函数UCT( ξ) ,然后将其复合而形成复合位移场U( ξ)和复合形状函数 ,并据此计算复合单元的刚度及质量矩阵 ,最后进行静动力结构分析 .可较大提高计算力学中数值分析的效率和精度 .
15《我国计算力学的发展》
作者】 张伟林;
【Author】 Zhang Weilin (Computing Center,Anhui Institute of
Architecture,Hefei,230022)
【机构】 安徽建筑工业学院计算中心!合肥230022;
【摘要】 对计算力学的研究现状作了分析 ,介绍了计算力学中的主要方法 ,其中包括有限差分法、有限元法、边界元法、加权残数法和有限元线法等。又从算法的研究方面讨论了计算力学的研究进展 ,并探讨了计算力学今后的发展趋势。
16《基于塑形力学新方法的围岩稳定分析与优化研究》
【作者】 姚延化;
【导师】 李铀;
【作者基本信息】 中南大学, 力学, 2013, 硕士
【摘要】 摘要:近年来,我国的隧道及地下工程工程得到了长足的发展,但与此同时,由于各种各样的原因,隧道及地下工程的安全事故也时有发生,这其中包括坍塌和塌方等严重安全事故,严重威胁着施工人员的人身安全并造成巨大的财产损失。如何安全又经济的对隧道及地下工程进行设计与施工,在当前形势下愈发重要。隧道及地下工程的围岩稳定性一直是岩土工程界研究的重点,但由于实际工程的岩土地质情况较为复杂,所以目前的围岩稳定性判别并没有统一的标准。本文从围岩应力场出发,运用塑性力学新方法结合工程实践进行理论分析与数值模拟,主要的研究内容如下:(1)回顾了隧道围岩稳定性研究和优化设计的发展现状,总结了围岩稳定分析和优化设计的若干问题和发展方向。(2)系统介绍了导致围岩失稳的各种因素和当前常见的三种围岩稳定判据。(3)运用塑性力学新方法结合工程对隧道的应力状态进行研究分析,并就塑性力学新方法求出的应力场与经典方法求出的应力场进行对比分析。(4)依据塑性力学新方法推导出不同强度准则的圆形硐室临界破坏深度,并对非圆形截面的应力状态和围岩稳定性情况进行研究,分析了直墙圆拱截面不同直墙高度对围岩稳定性的影响。(5)以骡坪隧道为工程实例
17《力学发展及与工程的关系》
作者】 蒲琪;
【Author】 PU Qi( Department of Civil Engineering,Xuzhou Institute of Architectural Technology, Xuzhou,Jiangsu 221008,China )
【机构】 徐州建筑职业技术学院土木工程系 江苏徐州221008;
【摘要】 力学源自于物理学中的经典力学 .力学从研究自然规律发展到为自然科学服务 ,为工程技术服务 ,并在服务中发展自己的理论 ,产生了许多新的力学分支 .结合自己的工程实践 ,介绍了实验力学走向工程实际的多种模式 ,阐述了实验力学与计算力学的关系 ,讨论了 2 1世纪实验力学的发展前景 . 18《工程结构分析的状态空间理论及其应用》
【作者】 沈小璞;
【导师】 王建国;
【作者基本信息】 合肥工业大学, 结构工程, 2009, 博士
【摘要】 随着大型、复杂公共建设项目的兴起,对于结构分析的要求也日益提高。在最近时期,结构分析理论方法研究也已获得了长足的发展。由于状态空间方法自身特点,使得近10多年来,状态空间法开始在建筑、路桥、水利、机械、环境等工程结构领域活跃起来。尤其是对这些领域的力学行为分析,状态空间法表现出强大的优越性。因此,本文在阐明了传统分析方法的局限性的基础上,介绍了状态空间理论在工程结构分析领域的应用情况,指出了状态空间理论应用到工程结
构分析中的巨大优势,同时,针对其不足之处,提出了自己的观点和分析方法,建立工程结构分析的状态空间理论。本论文的研究内容覆盖了多个学科领域,具有现实意义和理论价值。本文研究的主要内容有:1、状态方程组的建立。选择对偶的应力与位移分量作为状态变量,构造平面问题与空间问题的状态变量函数,通过数学变换和变分原理建立状态方程组。2、复杂结构静、动力响应计算的新理论与算法。根据各类不同的工程结构静、动力控制方程,利用哈密尔顿原理导出有限元状态方程,对时间域,为状态方程解;对空间域,为有限元数值解。研究应用现代控制论中的若干算法及计算力学的有限元方法对有限元状态方程进行解算,获得工程结构构...
19《中国力学学会20xx年》
【机构】 中国力学学会办公室;
【关键词】 中国力学学会; 学术活动计划; 会议名称; 力学工作者; 学术会议; 计算力学; 论坛交流; 北四环; 生物力学; 实验力学; 20《材料力学性能测试技术的进展与趋势》
【作者】 陈文哲;
【Author】 CHEN Wen-zhe (Fujian University of Technology,Fuzhou 350108,China)
【机构】 福建工程学院;
【摘要】 着重阐述了力学性能测试技术与方法的发展趋势和特征,以及在力学性能测试过程应该值得注意的重要测试条件和参数。介绍了近年来关于力学性能测试新技术的特点,主要以微纳材料和薄膜材料测试技术的发展和应用为例。指出了未来在力学性能测试新技术领域应引起重视和值得研究的方向。
1《MAGING 》
Optical examination of microscale features in pathology slides is one of the gold standards to diagnose disease. However, the use of conventional light microscopes is partially limited owing to their relatively high cost, bulkiness of lens-based optics, small field of view (FOV), and requirements for lateral scanning and three-dimensional (3D) focus adjustment. We illustrate the performance of a computational lens-free, holographic on-chip microscope that uses the transport-of-intensity equation, multi-height iterative phase
retrieval, and rotational field transformations to perform wide-FOV imaging of pathology samples with comparable image quality to a traditional transmission lens-based microscope. The holographically reconstructed image can be digitally focused at any depth within the object FOV (after image capture) without the need for mechanical focus adjustment and is also digitally
corrected for artifacts arising from uncontrolled tilting and height variations between the sample and sensor planes. Using this lens-free on-chip
microscope, we successfully imaged invasive carcinoma cells within human breast sections, Papanicolaou smears revealing a high-grade squamous
intraepithelial lesion, and sickle cell anemia blood smears over a FOV of 20.5 mm2. The resulting wide-field lens-free images had sufficient image resolution and contrast for clinical evaluation, as demonstrated by a pathologist’s blinded diagnosis of breast cancer tissue samples, achieving an overall accuracy of ~99%. By providing high-resolution images of large-area pathology samples with 3D digital focus adjustment, lens-free on-chip microscopy can be useful in resource-limited and point-of-care settings.
Copyright ? 2014, American Association for the Advancement of Science
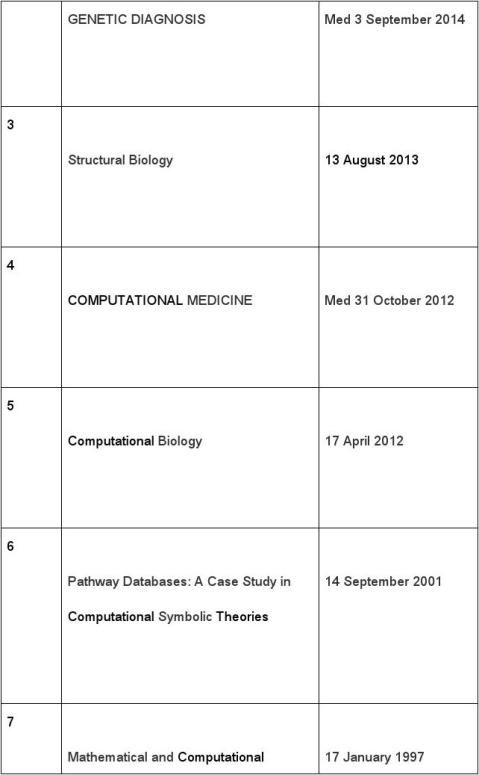
2《GENETIC DIAGNOSIS 》
Less than half of patients with suspected genetic disease receive a molecular diagnosis. We have therefore integrated next-generation sequencing (NGS), bioinformatics, and clinical data into an effective diagnostic workflow. We used variants in the 2741 established Mendelian disease genes [the
disease-associated genome (DAG)] to develop a targeted enrichment DAG panel (7.1 Mb), which achieves a coverage of 20-fold or better for 98% of bases. Furthermore, we established a computational method [Phenotypic Interpretation of eXomes (PhenIX)] that evaluated and ranked variants based on pathogenicity and semantic similarity of patients’ phenotype described by Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) terms to those of 3991 Mendelian
diseases. In computer simulations, ranking genes based on the variant score put the true gene in first place less than 5% of the time; PhenIX placed the correct gene in first place more than 86% of the time. In a retrospective test of PhenIX on 52 patients with previously identified mutations and known
diagnoses, the correct gene achieved a mean rank of 2.1. In a prospective study on 40 individuals without a diagnosis, PhenIX analysis enabled a
diagnosis in 11 cases (28%, at a mean rank of 2.4). Thus, the NGS of the DAG followed by phenotype-driven bioinformatic analysis allows quick and effective differential diagnostics in medical genetics.
Copyright ? 2014, American Association for the Advancement of Science
3《Structural Biology》
The annual meeting of the AAAS, held in San Francisco on 14 to 19 January, attracted the largest turnout for several years. More than 6000 are estimated to have attended. The meeting, which was held in conjunction with the winter meeting of the American Physical Society and the annual meeting of the
American Association of Physics Teachers, was reminiscent in some respects of the big AAAS annual gatherings of the late 1960s and early 1970s—even down to the presence of demonstrators, this year from the animal rights movement. Some highlights of the more than 250 sessions:
4《COMPUTATIONAL MEDICINE 》
The atrial G protein (heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide–binding protein)–regulated inwardly rectifying K+ (GIRK1 and GIRK4) heterotetrameric channels underlie the acetylcholine-induced K+ current responsible for vagal inhibition of heart rate and are activated by the G protein βγ subunits (Gβγ). We used a multistage protein-protein docking approach with data from published structures of GIRK1 and Gβγ to generate an experimentally testable
interaction model of Gβγ docked onto the cytosolic domains of the GIRK1 homotetramer. The model suggested a mechanism by which Gβγ promotes the open state of a specific cytosolic gate in the channel, the G loop gate. The predicted structure showed that the Gβ subunit interacts with the channel near the site of action for ethanol and stabilizes an intersubunit cleft formed by two loops (LM and DE) of adjacent channel subunits. Using a heterologous expression system, we disrupted the predicted GIRK1- and Gβγ-interacting residues by mutation of one protein and then rescued the regulatory activity by mutating reciprocal residues in the other protein. Disulfide cross-linking of channels and Gβγ with cysteine mutations at the predicted interacting residues yielded activated channels. The mechanism of Gβγ-induced activation of GIRK4 was distinct from GIRK1 homotetramers. However, GIRK1-GIRK4 heterotetrameric channels activated by Gβγ displayed
responses indicating that the GIRK1 subunit dominated the response pattern. This work demonstrated that combining computational with experimental
approaches is an effective method for elucidating interactions within protein complexes that otherwise might be challenging to decipher.
1. 5《Computational Biology 》
Because of the inherent complexity of coupled nonlinear biological systems, the development of computational models is necessary for achieving a
quantitative understanding of their structure and function in health and disease. Statistical learning is applied to high-dimensional biomolecular data to create models that describe relationships between molecules and networks. Multiscale modeling links networks to cells, organs, and organ systems. Computational approaches are used to characterize anatomic shape and its variations in health and disease. In each case, the purposes of modeling are to capture all that we know about disease and to develop improved therapies tailored to the needs of individuals. We discuss advances in computational medicine, with specific examples in the fields of cancer, diabetes, cardiology, and neurology. Advances in translating these computational methods to the clinic are described, as well as challenges in applying models for improving patient health.
6《Pathway Databases: A Case Study in Computational Symbolic Theories 》
Because of the inherent complexity of coupled nonlinear biological systems, the development of computational models is necessary for achieving a
quantitative understanding of their structure and function in health and disease. Statistical learning is applied to high-dimensional biomolecular data to create models that describe relationships between molecules and networks. Multiscale modeling links networks to cells, organs, and organ systems. Computational approaches are used to characterize anatomic shape and its variations in health and disease. In each case, the purposes of modeling are to capture all that we know about disease and to develop improved therapies tailored to the needs of individuals. We discuss advances in computational medicine, with specific examples in the fields of cancer, diabetes, cardiology, and neurology. Advances in translating these computational methods to the clinic are described, as well as challenges in applying models for improving patient health.
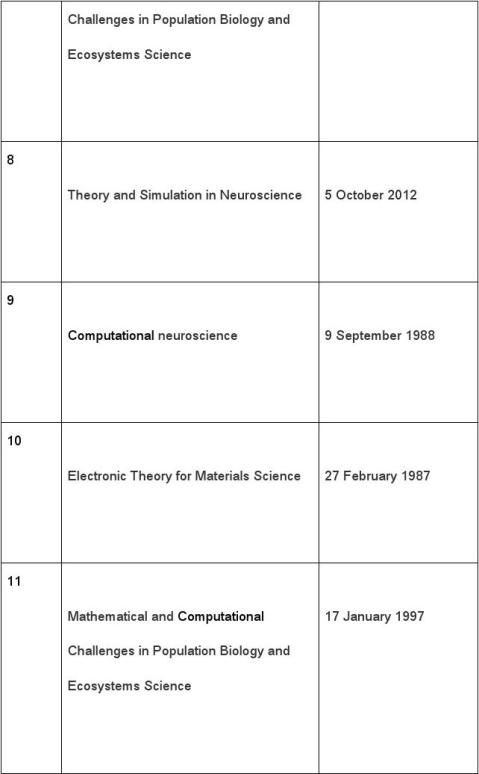
7《Mathematical and Computational Challenges in Population Biology and Ecosystems Science 》
Mathematical and computational approaches provide powerful tools in the study of problems in population biology and ecosystems science. The subject has a rich history intertwined with the development of statistics and dynamical systems theory, but recent analytical advances, coupled with the enhanced
potential of high-speed computation, have opened up new vistas and presented new challenges. Key challenges involve ways to deal with the collective dynamics of heterogeneous ensembles of individuals, and to scale from small spatial regions to large ones. The central issues—understanding how detail at one scale makes its signature felt at other scales, and how to relate phenomena across scales—cut across scientific disciplines and go to the heart of algorithmic development of approaches to high-speed computation. Examples are given from ecology, genetics, epidemiology, and immunology. 8《Theory and Simulation in Neuroscience 》
In coming to understand the world—in learning concepts, acquiring language, and grasping causal relations—our minds make inferences that appear to go far beyond the data available. How do we do it? This review describes recent approaches to reverse-engineering human learning and cognitive
development and, in parallel, engineering more humanlike machine learning systems. Computational models that perform probabilistic inference over hierarchies of flexibly structured representations can address some of the deepest questions about the nature and origins of human thought: How does abstract knowledge guide learning and reasoning from sparse data? What forms does our knowledge take, across different domains and tasks? And how is that abstract knowledge itself acquired?
9《Computational neuroscience 》
In coming to understand the world—in learning concepts, acquiring language, and grasping causal relations—our minds make inferences that appear to go far beyond the data available. How do we do it? This review describes recent approaches to reverse-engineering human learning and cognitive development and, in parallel, engineering more humanlike machine learning systems. Computational models that perform probabilistic inference over hierarchies of flexibly structured representations can address some of the deepest questions about the nature and origins of human thought: How does abstract knowledge guide learning and reasoning from sparse data? What forms does our knowledge take, across different domains and tasks? And how is that abstract knowledge itself acquired?
10《Electronic Theory for Materials Science 》 Advances in transition state theory and computer simulations are providing new insights into the sources of enzyme catalysis. Both lowering of the activation free energy and changes in the generalized transmission coefficient (recrossing of the transition state, tunneling, and nonequilibrium contributions) can play a role. A framework for understanding these effects is presented, and the contributions of the different factors, as illustrated by specific enzymes, are identified and quantified by computer simulations. The
resulting understanding of enzyme catalysis is used to comment on alternative proposals of how enzymes work.
11《Mathematical and Computational Challenges in Population Biology and Ecosystems Science》 Mathematical and computational approaches provide powerful tools in the study of problems in population biology and ecosystems science. The subject has a rich history intertwined with the development of statistics and dynamical systems theory, but recent analytical advances, coupled with the enhanced potential of high-speed computation, have opened up new vistas and presented new challenges. Key challenges involve ways to deal with the collective dynamics of heterogeneous ensembles of individuals, and to scale from small spatial regions to large ones. The central issues—understanding how detail at one scale makes its signature felt at other scales, and how to relate phenomena across scales—cut across scientific disciplines and go to the heart of algorithmic development of approaches to high-speed computation. Examples are given from ecology, genetics, epidemiology, and immunology.
12《Mathematical and Computational Challenges in Population Biology and Ecosystems Science》 The gain, loss, and modification of gene regulatory elements may underlie a substantial proportion of phenotypic changes on animal lineages. To
investigate the gain of regulatory elements throughout vertebrate evolution, we identified genome-wide sets of putative regulatory regions for five vertebrates, including humans. These putative regulatory regions are conserved nonexonic elements (CNEEs), which are evolutionarily conserved yet do not overlap any coding or noncoding mature transcript. We then inferred the branch on which each CNEE came under selective constraint. Our analysis identified three extended periods in the evolution of gene regulatory elements. Early vertebrate evolution was characterized by regulatory gains near transcription factors and developmental genes, but this trend was replaced by innovations near extracellular signaling genes, and then innovations near posttranslational protein modifiers.
13《Insights into Innovation》
The gain, loss, and modification of gene regulatory elements may underlie a substantial proportion of phenotypic changes on animal lineages. To investigate the gain of regulatory elements throughout vertebrate evolution, we identified genome-wide sets of putative regulatory regions for five vertebrates, including humans. These putative regulatory regions are conserved nonexonic elements (CNEEs), which are evolutionarily conserved yet do not overlap any coding or noncoding mature transcript. We then inferred the branch on which each CNEE came under selective constraint. Our analysis identified three extended periods in the evolution of gene
regulatory elements. Early vertebrate evolution was characterized by regulatory gains near transcription factors and developmental genes, but this trend was replaced by innovations near extracellular signaling genes, and then innovations near posttranslational protein modifiers.
14《Meeting global challenges: Discovery and innovation through convergence 》 This article outlines some of the principal issues in the development of numerical methods for the prediction of flows over aircraft and their use in the design process. These include the choice of an appropriate mathematical model, the design of shock-capturing algorithms, the treatment of complex geometric configurations, and shape modifications to optimize the aerodynamic performance.
15《Cooling Energy-Hungry Data Centers 》 Light facilitates exploration of quantum phenomena that illuminate the basic properties of nature and also enables radical new technologies based on these phenomena. The critical features of quantum light that underpin the opportunities for discovery and application are exceptionally low noise and strong correlations. Rapid progress in both science and technology has been stimulated by adopting components developed for optical
telecommunications and networking, such as highly efficient detectors, integrated photonic circuits, and waveguide- or nanostructure-based nonlinear optical devices. These provide the means to generate new quantum states of light and matter of unprecedented scale, containing many photons with quantum correlations across space and time. Notably, networks with only several tens of photons are already beyond what can be efficiently analyzed by current computers.
16《Mathematical and Computational Challenges》
We argue that an understanding of the faculty of language requires substantial interdisciplinary cooperation. We suggest how current developments in linguistics can be profitably wedded to work in evolutionary biology,
anthropology, psychology, and neuroscience. We submit that a distinction
should be made between the faculty of language in the broad sense (FLB) and in the narrow sense (FLN). FLB includes a sensory-motor system, a conceptual-intentional system, and the computational mechanisms for
recursion, providing the capacity to generate an infinite range of expressions from a finite set of elements. We hypothesize that FLN only includes recursion and is the only uniquely human component of the faculty of language. We further argue that FLN may have evolved for reasons other than language, hence comparative studies might look for evidence of such computations
outside of the domain of communication (for example, number, navigation, and social relations).
17《Quantum optics: Science and technology in a new light 》 We argue that an understanding of the faculty of language requires substantial interdisciplinary cooperation. We suggest how current developments in linguistics can be profitably wedded to work in evolutionary biology, anthropology, psychology, and neuroscience. We submit that a distinction should be made between the faculty of language in the broad sense (FLB) and in the narrow sense (FLN). FLB includes a sensory-motor system, a conceptual-intentional system, and the computational mechanisms for recursion, providing the capacity to generate an infinite range of expressions from a finite set of elements. We hypothesize that FLN only includes recursion and is the only uniquely human component of the faculty of language. We further argue that FLN may have evolved for reasons other than language, hence comparative studies might look for evidence of such computations outside of the domain of communication (for example, number, navigation, and social relations).
18《Insights into Innovation 》 Light facilitates exploration of quantum phenomena that illuminate the basic properties of nature and also enables radical new technologies based on these phenomena. The critical features of quantum light that underpin the opportunities for discovery and application are exceptionally low noise and strong correlations. Rapid progress in both science and technology has been
stimulated by adopting components developed for optical telecommunications and networking, such as highly efficient detectors, integrated photonic circuits, and waveguide- or nanostructure-based nonlinear optical devices. These provide the means to generate new quantum states of light and matter of unprecedented scale, containing many photons with quantum correlations across space and time. Notably, networks with only several tens of photons are already beyond what can be efficiently analyzed by current computers.
19《Meeting global challenges》
Thermonuclear fusion is a highly efficient energy source for the stars; however, attempts to harness the process of fusion for energy production on Earth have been stymied by many difficult challenges. One of the most frustrating is the significant leakage of energy from magnetically confined plasmas, which is due to so-called anomalous transport. In their Perspective, Krushelnick and Cowley discuss recent work to understand the basis of this anomalous
transport and find ways to control it. An approach that has created excitement in the fusion community involves the creation of transport barriers, that is,
regions of plasma with just the right conditions to reduce turbulence that leads to energy leakage. Recently a combination of experimental and computational advances has led to increased understanding of these transport barriers in
fusion plasmas, potentially bringing the use of controlled fusion as an energy source much closer.
20《The Faculty of Language》
Our awareness of the global nature of major problems facing our planet is relatively new and demands global responses for which neither the scientific community nor the general public is well prepared. To meet such global
challenges requires the engagement of people and their leaders from diverse cultures and experiences. While many sectors of society must become involved, the scientific community has a special role in preparing for these challenges. It is impossible to consider here all of the roles of scientists and engineers in this transformation, whether advancing knowledge of nature, translating new insights into innovations, or educating future generations. But few would disagree that in the long term, discovery and innovation are central to effectively meeting these challenges. Yet it is often difficult to link discovery and innovation to their impact because of the years of development required before a discovery matures to a level that can be adopted on a global scale. I highlight below how some organizations are planning to accelerate the
transition from discovery to innovation to address some of the great challenges facing society. As an illustration, I discuss the history of the transition from discovery to innovation at the molecular level in life sciences. At the end, I
comment on how further convergence of physical, mathematical, engineering, and social sciences with life sciences will accelerate innovation.
七 查新结论
该查新项目是计算力学的新理论新方法的研究,通过对上述文献的分析,并与本查新项目相比,得出结论:
国内外已有许多对计算力学新理论新方法的研究和众多的试验,并且得出了许多相关理论和数据,对于目前国际国内研究情况来看,这方面并不是太成熟,还有很大的发展。
综上所述,研究计算力学的新理论与新方法的研究,提出各种方法与理论相结合并且与现代数学紧密结合是很必要的,在最优方法和理论的提出可以为现代社会的发展最初很大的贡献。
查新员(签字): 姜冬 查新员职称: 学生 方中勇
朱生旭
审核员(签字): 审核员职称:
(科技查新专用章)
年 月 日
