社会调查报告-英语家教
这是迈入大学校门后的第一个暑假,本来是想要找份兼职在学校待一个月,然后再回家好好放松下,摆好心态,精力充沛的迎接大二的课程。但是还是舍不得想要回家。为了让在家的假期生活同样的精彩,在这个暑假我进行了一份家教实践活动。现将该次实践情况做以下报告
实践对象:初中二年级学生(该学生成绩较差)
实践目的:主要是辅导其完成暑期作业中的英语部分,并借此对该生二年级所学英语作复习、巩固、提高,使其对即将学习的三年级知识作初步了解,为三年级的学习打下一个良好的铺垫。 实践时间:20xx年7月14日—20xx年8月12日
实践过程:在整个过程最初的两三天里,我并没有贸然地进行实质性的教学活动。我首先翻阅了该生一学期的作业及考试试卷,又向其家长了解了一些情况,我对该生的基本情况有了初步掌握:该生基础较差。单词,句型,语法,这些最基本的方面都比较薄弱.
在此,并没有一一列举每天的教学过程及感受,只是列举了比较有特点的几天.如下:
20xx年7月14日:第一天,第一次去给那小男孩上课的情形依旧历历在目,我破例地早早起了床,虽离上课还有一个小时,可我早已整装待发。前一晚,我甚至兴奋得失眠。一路上我的心都是砰砰直跳,
是紧张还是兴奋,我自己都分不清了,只记得心里不住的对自己说:“第一份工作,好好干,加油!”全力的投入,两个小时的时间,讲解完成了5页的内容,另外有补充很多的句型跟单词,感觉相当有成就感。但是现在想想,只是自己很单纯的在讲,没有注意到相互之间的交流与互动,有点在演独角戏的感觉,我想还是由于经验不足吧.
20xx年7月15日:在后面的题目讲解中陆续的有出现前面讲解及补充过的内容,但是问问题时小孩子却一问三不知,很茫然的样子。然后领他翻到前面讲解过相对应的题目,旁边赫然有我标的注释。问他为什么,他解释说看不懂我写的东西。。。。我有点泄气了。。。
20xx年7月16日:经过反复的思考,既然我写的东西他看不懂,我就试着引导他让他自己添加重要的语言点。吸取前面的教训,主动的询问他有什么地方不懂,有什么意见。他提出我讲解的速度太快,有点跟不上我的进度。虽然有些不太开心被人指出不足,但还是比较虚心的反思了下.在后面的讲解过程中我试着放慢速度,并嘱咐他对于自己先前不懂的题目在讲解后一定要常常翻翻看看,加深印象。
20xx年7月20日:这几天在补充讲解到重要句型的时候,尝试着互动交流。教他例句,试着引导他自己翻译句子,并且自己编些例句。借此,希望他能够逐渐培养起学习英语的兴趣。同时中间有穿插些名人事例啊,有趣的传说,字谜游戏等,让他感到其实英语是很有趣的,试着培养他对英语学习的兴趣。
20xx年7月26日:试着提问前面的内容,结果仍然不太清楚。我有些急了,但是想到为人师嘛,于是我耐住性子,跟他一起翻注释,一起记忆,同时提醒些技巧之类。每天划出些重要的句法,让他回去加强单词的背诵,并且在第二天的时候讲解部分中穿插着提问。
20xx年8月2日:这几天通过提问发现他掌握的还好,基本上还是很满意的。看着自己的学生每天一点点的进步,心里特别特别地开心.呵呵,为人师的感觉,真好!
最后讲解的是作文部分,是篇看图作文,具体讲了下思路,引导他自主的完成。难的句子不会写,引导他写些简单的句子穿插起来。从简单的句子开始,教他不要着急太难的句子,经过简单的句子的练习,肯定会越来越好的.
最后与他一起归纳整理了重要时态的用法。
最后一节课,讲了些自己的学习经验,并以身说法,告戒他好好把握现在的时光好好念书。不知道他能不能体会到这种心情呢。。。
实践体会:
转眼间,一个炎热的假期就要过去了。蓦然回首,不能不感慨光阴似箭般的那份无奈。当准备收拾心情,重整出发时,发现原来匆匆的假期里多了一份沉沉的充实.很感谢有这样的一次家教实践,我学到了很多,也懂得了很多:
第一,从事教学工作需要“耐心”:面对一个仅初中二年级的学生,他对知识接受和记忆的方式和能力都有其特点和限制,我们在教学中不能从自身主观出发“想当然之”。对学生在学习中所遇到的障碍要“耐心”的讲解,一遍不行就两遍,两遍不行三遍,同时也应该反省自己的教学方式是否对路,切忌“简单粗暴”。通过这次实践,学会了时刻提醒自己要“沉得住气”,自己偏急燥的性格也得到了一定的改变。
第二,从事教学工作需要与人“交心”:在教学中不能够“闭门造车”、“一叶障目,不视泰山”,要多与外界交流,掌握更多的信息,丰富自己的教育背景。我注意了与家长的交流,一方面更深入了解学生的情况,有利于我“有的放矢”;另一方面我及时将教学进展及时反馈给家长,有利于家长的配合与支持。同时,我还向多位我以前的老师请教,他们的经验都给了我莫大的帮助。
第三,自己平时行为过与懒散,经常我行我素。经过这次,我懂得了:准时是对别人的一种最最起码的尊重。特别是想要成为老师的话,为人师表很重要.
第四,我理解体会到了作为一名老师沉甸甸的责任感。
经过了一个月的家教生涯,现在的我对于“老师”这个称谓不再陌生,当别人称呼我“老师”时,没有了昔日的羞涩,有人说教师是太阳底下最神圣的职业。虽然我的兼职只是沾上了“教师”的丁点边,
可我分明感到这两个字给我带来的豪迈感。然而当告别了家教职务时,原先最熟悉的称谓,只留下陌生的印象.
从一个学生通过家教可以尝试一下为人师的感觉(虽然这并不是真正的老师)。师者,所以传道授业解惑也!虽然讲的知识不难,难的却是怎样讲得更懂,让学生更明白、透彻??
我一直认为想当一个合格的老师并不容易,所以总觉得有点战战兢兢,有一点惶恐又有一点虚荣。惶恐的是生怕会误人子弟、耽误了学生的前程;虚荣的是想不到自己也会当别人的老师。也许当好老师和其他职业一样,只要有一个赤子之心,则就没有了万难的事。
已经大二了,是应该考虑自己未来的时候了。有时候很难想明白自己究竟想要的是什么,想拥有怎样的人生。通过这次家教,体会到了老师的不易,更感觉到了自己身上沉甸甸的责任。
也许当老师不会成为我的职业,甚至作为第二职业都很难。但是有一天,我很希望自己能够自创门派,传播自己所掌握和创造的知识
每天的太阳都是新的,但每天的太阳并不都是灿烂的。每天傍晚从家教中心回来,虽然感觉有点儿累,但是我的暑假也因此而充实.
宝贵的第一次家教工作给了我很深的感触,受益非浅;也使我又成长了,同时看清楚了自己要走的路.要加油了!
第二篇:英语家教材料
1、一般现在时
主要用于下面几情况:
1) 描述当前时间内经常出现、反复发生的动作或存在的状态。
在这种情景中,句子常带有表示频率的时间状语:always , everyday , often , once a week (month , year , etc.) , sometimes , seldom , usually等等,以表示句中的动作或状态是习惯性的、经常性的。例如:
They raise ducks as a sideline .他们以养鸭为副业。
She doesn't often write to her family, only once a month. 她不常给家里写信,仅一月一封而已。 I cycle to work every day .我每天骑自行车上班。
It seldom rains here .这儿很少下雨。
2)仅为了描述状态、性质、特征、能力等等。
这里的目的是为了"描述现阶段的动作或状态",其重点"不是强调动作发生的时间、或进行的状态"。例如:
He can speak five foreign languages .他能说五种外语。
That is a beautiful city .那是座美丽的城市。
Changjiang River is one of the longest rivers in the world. 长江是世界上最长的河流之一。 She majors in music .她主修音乐。
All my family love football .我全家人都喜欢足球。
My sister is always ready to help others . 我妹妹总是乐于助人。
3) 陈述客观事实、客观真理。
顾名思义,客观的情况是"没有时间概念"的;也"不会在意动作进行的状态"。例如:
The sun rises in the east .日出东方。
The earth goes around the sun .地球绕着太阳转。
Ten minus two is eight.十减二等于八。
Light travels faster than sound .光的速度比声音的速度快。
The United States lies by the west coast of the Pacific Ocean. 美国位于太平洋西岸。
4) 根据英文语法规定,当主句的谓语动词是一般将来时,那么时间或条件状语从句的谓语动词只能用一般现在时来表示将来要发生的动作。例如:
I'll tell him the news when he comes back. 他回来时,我将告诉他这个消息。
If you take the job, they will talk with you in greater details.
如果你接受这份工作,他们将和你谈谈细节。
用于一般现在时的副词,除了上面提到的一些表示频率的以外,常见的还有:now, today , nowadays等等。
2、一般过去时
主要是用来描述在过去某个时候发生的动作或存在的状态。它也可以用来表示在过去某段时间里经常发生的习惯性动作。这一点在表达意义上与一般现在时相同,只是所在的时间区域不同而已。由于它的主要作用如此,所以在使用一般过去时的句子里常常有一个意义较具体的过去时间状语。这也是它与现在完成时的最大区别之一。
一般过去时由谓语动词的过去式表示,也就是说动词词末要加-ed(除不规则动词外)。常和一般过去时连用的过去时间状语有:last night (week ,
month , year , century , etc.) , yesterday , the day before yesterday , yesterday morning
( afternoon , evening ) , in 1999 , two hours ago ( one week ago , tree years ago , ?)等等。
使用一般过去时,在某种意义上说就是要强调动作或状态发生或存在于过去的某个时候。"过去"的时间概念有两层意思:一是指"现在某个时间"以前的时间;二是指"说话、写文章的那个时间点"以前的时间,在这个意义上,"现在的那个时间点"是很小很小的,甚至于小到无法量化的程度。例如:
He got his driving license last month. 他上个月拿到了驾照。
--Where's Jim? 吉姆在哪里?
--He just went out.他刚刚出去。
3、一般将来时
主要用来描述将要发生的动作或存在于未来的情况。这里所说的"将来时间"是指"说话、写文章那一刻以后的时间"。它的表示方法主要有如下几种:
1)shall / will + 动词原形这种表示方法是说,动作在现在或目前还未发生,要在将来的某个时间内发生;它没有主观性,是"纯粹的将来动作"。例如:
I shall / will not be free tomorrow .我明天没空。
He will arrive here this evening .他今晚抵达这里。
2) be( am / is / are ) + going +不定式
这种表示方法主要是说明A)"说话人的意图、打算";B)"某种可能性" 。例如:
A) He is going to spend his holidays in London . 他打算在伦敦度假。
Who is going to speak first? 谁先发言?
B) It is going to rain soon .马上要下雨了。
Is he going to collect any data for us? 他会帮我们收集资料吗?
If you go to New Zealand, you are going to like the place. 如果你去新西兰,你会喜欢上那个地方的。
3) be( am / is / are ) + 不定式表示方法描述两钟情况:
按计划安排要发生的动作,这个动作发生的时间一般不会很远; 要求或命令他人做某事。例如:
A) The new bridge is to open to traffic in three days. 新桥三天后通车。
The factory is to go into production before National Day. 这家工厂国庆节前投产。
B) You are not to bring any mobile communication means into the exam-room . 任何移动通讯工具都不得带入考场。
You are to stay home until your mother comes back. 你妈回来之前你不要出去。
4) 用一般现在时或现在进行时(限于某些动词)表示按计划安排要发生的事。这种表示方法实际上已经在上面"一般现在时之4)"中谈过。主要强调"按计划安排要发生的事"。例如:
Do you get off at the next stop? 你下一站下车吗?
The plane takes off at 11:00 a.m. 那架飞机上午十一点起飞。
Mr. Reider is leaving for New York next week. 里德先生下周动身去纽约。
4、过去将来时
表示过去的某时以后将要发生的动作。但这个"将来"时间绝不会延伸到"现在";而仅限于"过去时间区域内"。由此可以看出,含这个时态的句子常带一个表示"过去某个时间点"的状语。这个状语或是一个短语,或是一个句子。这个时态常用于:
A)宾语从句或间接引语中;B)表示过去习惯性的动作;C)表示过去情况中的"愿望"、"倾向",多用于否定句。例如:
A) When I thought about it , I wondered what their reaction would be . 当我考虑这件事时,我想知道他们的反应是什么。
She told me that she would go on trip to Europe the next day. 她告诉我,她第二天要去欧洲旅行。
He didn't expect that we would all be there. 他没料到我们会全在那儿。
B) During that period , he would do morning-exercises every day. 在那段时间,他每天早锻炼。 Whenever he had time, he would help his mother with some housework. 无论他什么时间有空,他总是帮他妈妈干点家务活。
C) No matter how difficult the work was , he would keep on doing it until he accomplished it . 不管工作有多难,他总会坚持不懈地把它干完。
They knew that we would never permit such a thing. 他们知道我们绝不会允许发生这样的事。 Even after the lecture ended, the audience would not leave . 甚至在讲座结束之后,听众仍不肯离去。
5、现在进行时
主要用来描述"说话、写文章的当刻"正在发生的动作,或是"现阶段"一直在进行的动作。它适用于下面的情况:
1)"说话、写文章的当刻"正在发生的动作。例如:
They are having a football match .他们正在赛足球。
She is writing her term paper. 她正在写学期论文。
Someone is asking for you on the phone. 有人找你听电话。
2)"现阶段"一直在进行的动作。这种情况并不是说某个动作在说话的那会儿正在发生,而是说某个动作在当前一段时间内一直在进行着,或是重复地发生着。例如:
He is preparing for CET Band Six. 他在为大学英语六级考试作准备。
How are you getting along with your new job? 你那份新工作干得怎么样?
3)表示说话人的情感,如:赞许、批评;喜欢、厌恶等。这时的动作并不是正在发生或进行,而是表示经常性,相当于"一般现在时"所描述的情况。例如:
He is always thinking of others , not of himself . (表示赞许)他总是为他人着想,而不为自己。 She is often doing well at school. (表示满意)她在学校学习挺不错的。
Are you feeling better today? (表示亲切)你今天觉得好一些吗?
One of my roommates is constantly leaving things about.(表示不满)我的一个室友老是乱扔东西。
Some sellers are often knocking at our door and promoting their products to us .(表示不喜欢) 有些推销员老是敲我家的门,向我们推销他们的产品。
4)表示在近期按计划或安排要发生的动作,用于这种情况仅限于少量的动词,如:go , come , leave ,arrive , see , have , lunch( 吃午饭 ) , return, dine ( 进餐,尤指晚餐 ) , work , sleep , stay , play , do , wear( 穿,戴 ) 等。例如:
I'm dinning out with my friends this evening. 今晚我将和朋友在外面吃饭。
An American professor is giving a lecture this afternoon. 今天下午一位美国教授要来作报告。 We are having a holiday next Wednesday. 下周三我们放假。
Are you staying here till next week? 你要在这儿呆到下星期吗?
6、过去进行时
主要表示在过去的某个时间点上正在发生、进行的动作。由于它的定义是表示在过去的某个时间点上正在发生、进行的动作,所以,句子常带有一个表示"过去某个时间点"的状语。这个状语可能是短语,词组,或是一个从句。也可能是通过上下文来表达这层意思。过去进行时主要用于下面的情景中:
1)表示在过去某时刻正在进行的动作,例如:
At this moment yesterday, I was packing for camp.昨天这个时候,我正在收拾东西去露营。 When I came to see her last time, she was writing an article.上次我来看她的时候,她正在写一篇文章。
What were you doing at eight last night ? 昨晚八点钟你在做什么?
2)用于故事的开头,交代故事发生的背景情况。
过去进行时所描述的动作是"正在进行",所以,在这种情景中用"过去进行时"可以给读者一种"动感",从而能使文章更加生动活泼。例如:
One night, he was typing in his study . Suddenly , a man broke into his house and cut off the electricity ? .一天晚上,他正在书房里打字。突然,一个人闯进屋来,切断了电源??
3)(仅限少数动词)表示在过去的未来时间要发生的动作。例如:
When National Day was coming near , they began to make a plan for the holiday .国庆节即将来临的时候,他们开始制订度假计划。
She told me that she was going to Hainan for her holiday. 她告诉我她将去海南度假。
My friend said to me that he was lunching with one of his customers that day .我朋友对我说,他今天要与他的一位客户一块儿吃午饭。
We left there when it's getting dark. 天快黑的时候,我们离开了那儿。
7、将来进行时
主要表示:A)在将来某时候正在进行的动作;B)预计、安排即将发生或势必发生的动作。例如:
A)在将来某时候正在进行的动作:
You can have a meeting in my office on Friday . I won't be using it. 星期五你可以在我的办公室开会。那会儿我不用它。
What will you be doing tomorrow morning? 明天上午你做什么?
It won't be long before that we will be making a new computer for more advanced calculation. 不久我们就要造一部新计算器进行更高级的运算。
I can't go to the party tonight . I'll be seeing off a friend .今晚我不能参加聚会了。我要给一位朋友送行。
B)预计、安排即将发生或势必发生的动作:
在这里,将来进行时与一般将来时很接近,但是前者强调动作"按计划、安排要发生;间或也表示委婉、客气",而后者只表示"动作会在未来时间发生"。
We shall be meeting at the school gate .我们在校门口见面。
What shall we be doing next ? 我们干什么?
If you don't do so , you will be facing great difficulties.你如果不这样做就会面临很大的困难。 Shall I be interrupting you if I stay here for a while? 要是我在这儿呆一会儿,会干扰你们吗?
8、现在完成时
对于初接触现在完成时的人来说,往往会产生一种茫然,因为它似乎与一般过去时相似。那就是,这两种时态描述的动作都始于过去。其实不然,现在完成时主要表示,发生在过去的动作延续到现在刚刚完成、或许还要延续;侧重于这个动作对现在带来的结果、产生的影响、积累的总和等等。而一般过去时则只不过是表示动作发生在过去的什么时候。弄清了这一区别,就很容易理解现在完成时了。它主要适用于下面的几种情况:
1)表示截止现在业已完成的动作
By now, I have collected all the data that I need .到现在为止,我已收集到了我所需的全部资料。 She has read 150 pages today .她今天已看了150页。
We haven't met for many years .我们已多年没见了。
They have developed a new product .他们研制成功了一种新产品。
2)表示发生在过去而对现在产生影响、带来结果的动作
Have you had your dinner? 你吃晚饭了吗?
She has been to the United States. 她已去美国了。
You have grown much taller.你长高了许多。
3)表示过去发生的动作持续到现在,并可能还要延续
It has been five years since he joined the army .他参军五年了。
They have learned English for eight years .他们已学了八年的英语了。
So far we've only discussed the first five chapters.至今我们还只讨论了前五章。
几点注意
1)一个句子应该用什么时态只能取决于它需要表达的意思,以及它所处的语言环境。例如: He speaks English .(一般现在时,说明动作发生的经常性。)
He spoke English when he was in New Zealand .(一般过去时,说明动作发生的时间。) He is speaking English.(现在进行时,说明动作正在进行。)
He has spoken English for three years since he came to the USA.(现在完成时,这里说明动作的总和。)
He has been speaking English since he came to the USA. (现在完成进行时,强调动作的连续性。)
2)在含有时间状语从句或条件状语从句的主从复合句中,如果主句的谓语动词是一般将来时,
那么从句的谓语动词就只能用一般现在时来表示将来时;如果主句的谓语动词是过去将来时,那么从句的谓语动词就只能用一般过去时来表示过去将来时。
例如:I will not play tennis if it rains tomorrow.
I would not play tennis if it rained the next day.
3) 有些动词表示无法持续的动作,它们一般不宜用于进行时态中。这类动词常见的有:be , believe , consist , find , forget , hate , have , hope , hear , know , like , love , notice , prefer , remember , see , seem , smell , suggest , taste , understand , want , wish , sit down , stand up 等等。
Be动词若是用于进行时态,可表示暂时、短暂的情况或表现。例如:
Tom is being a good boy today .汤姆今天很乖。
He is being childish .他这样做是耍孩子气。
You are not being modest .你这样说不太谦虚。
4)关于现在完成时的时间状语问题.
A. 凡是"完成时态"都表示,不知道也不管动作发生的具体时间, 所以在使用现在完成时的句子里,不可以带有表示具体过去时间的状语,如:yesterday , last week ( month , year , etc. ) , two weeks ago , in 1999等;但常和有些副词连用,如: just , before , already , often , never , ever , not?yet , always等等。
B. 在以when提问的特殊疑问中不能用现在完成时。另外,ago不能用于现在完成时的句子里,因为它表示从现在算起的以前某个时间,属于表示具体过去时间的状语。但是可以用before 来表示"以前"的意义,因为它只表示"以前",而不知什么时候的以前。
C. 如果是不表示连续性的动词用于现在完成时的句子,不可以和以for表示的"一段时间"的状语连用。在这种情况下,应该用"It has been ? ;since?"的句式来表达。如:
He has joined the army for five years. (错误)
It has been five years since he joined the army.(正确)
请用正确的动词和时态填入下列各词:
1. He __________ back a month ago. (come)
2. My mother often tells me __________ in bed. (not read)
3. I must take it back the day after tomorrow. You can only __________ it for 24 hours. (保存)
4. Why have you kept me __________ here for so long a time? (wait)
5. Please come to our meeting if you __________ free tomorrow. (be)
6. She __________ to the Great Wall several times. (goes)
7. In his letter, he said that he __________ us very much. (miss)
8. The film __________ for nearly fifteen minutes when I got to the cinema. (be)
9. He said he became __________ in physics. (interest)
10. This film is worth __________. (see)
11. He went to school instead of __________ home. (go)
12. In the old days it was difficult for the poor to __________ a job. (找)
13. It's cold outside, so you'd better __________ your coat. (穿上)
14. He is hungry. Please give him something __________. (eat)
15. Please don't waste time __________ TV every evening. You should word hard at English. (watch)
16. We found the window __________. (break) 17. You have dropped your pencil. __________. (拾起来) 18. Mother often tells me __________ too late. (not come home) 19. You had better __________ by bus, or you will be late. (go) 20. I will __________ Li Ming the good news as soon as I see him. (告诉) 21. Great changes __________ in our country since 1978. (take place) 22. I __________ my daughter since last month. (hear from) 23. It __________ me two days to write the article. (花费) 24. Don't touch that __________ child. (sleep) 25. Every time he tried to start the car, the wheels __________ deepersintosthe mud. (sink) 26. When I got home, I found that my room __________ breaksintosand a lot of things __________. (steal) 27. If I had arrived there earlier, I __________ him. (meet) 28. I didn't remember __________ her the book before. (give) 29. He called at every door, __________ people the exciting news. (tell) 30. Yesterday Mary couldn't finish her homework, so she has to go on __________ it this afternoon. (do) 31. We __________ football when it began to rain. We had to stop and go home. (play) 32. Xiao Lin __________ from here for about two hours. (be away) 33.swheres__________? Can you find your birth place on the map? Sorry, I can't. (be born) 34. Last night we __________ back home until the teacher left school. (not go) 35. Comrade Li Dazhao __________ in prison in 1927. (put) 36.swheresis professor Lee? He __________ to the library. He'll come back soon. (go) 37. We could not help __________ after we heard the story. (laugh) 38. Would you please __________ me an English-Chinese dictionary when you come? (bring) 39. He told me that he __________ the Great Wall the year before. (visit) 40. I'll tell him the news as soon as he __________ back. (come) 41. The boy __________ by the door is my brother. (stand) 42. Do you remember __________ the film last year? (see) 43. There __________ a physics test next Monday. (be) 44. __________ I finish my homework in class? (必须)
No, you needn't.
45. I'm sorry you've missed the last bus. It __________ ten minutes ago. (leave)
46. Wei Fang is heard __________ English every morning. (hear)
47. John stopped __________ a rest (have) because he __________ for three hours. (work)
48. I'm sorry to have kept you __________. (wait)
49. A new theatre __________ now. (build)
50. The boys __________ basketball on the playground are my classmates. (play)
一、并列连词:
(一)连词的概念:
连词是一种虚词,不能担任一个句子成分。连词在句中主要起连接词与词、短语与短语及句子和句子的作用。它主要是包括并列连词和从属连词。
(二)并列连词的分类:

例句:Slow but sure. 要慢而稳。
She’ll be back either this week or next week. 她将在这周或下周回来。
I went and she went also. 我去了,她也去了。
(三)并列连词的用法:
1、 并列连词and和or:
①and 和or 是用得最多的并列连词,可以连接:
a. 两个并列的动词:
We were singing and dancing all evening. 整个晚上我们都在唱歌跳舞。
b. 名词、形容词等:
This apple is big and red.
Would you like fish or beef?
c. 两个并列的分句(句子):
I said it and I meant it. 我说话算数。
②and 可连接两个分句,表示递进关系。
Give him an inch and he will take a mile. 他会得寸进尺。
③or可连接分句,表示“否则”:
Don’t drive so fast or you’ll have an accident. 别开这么快,不然你会出车祸。
2、 表示意思转折的连词:but, yet:
①but和yet的用法:
The weather will be sunny but cold. 天气会晴朗但很冷。
It is strange, yet true. 这很奇怪,却是真的。
②however, still 等为副词,但可起连接作用,表示意思的转折---“但是”或“然而”。
a. however:
His first response was to say no. Later, however, he changed his mind.
他的第一反应是不行,但后来他改变了主意。
b. still:
It’s raining; still I’d like to go. 天在下雨,但我还是要去。
③词组all the same:
She is naughty, all the same we have to laugh at her jokes.
她很调皮,但对她的恶作剧我们还是要发笑。
3、表示因果的连词:
① for可以表示“因为”,但引导的不是从句,而是并列分句,对前面情况加以解释,常用逗号把它和前面的分句分开,这在书面语中比较多见。
The days were short, for it was now December.
白天很短,因为现在已经是十二月。
She must have gone out early, for she had not come for breakfast.
她肯定一早出去了,因为她没来吃早饭。
② so 表示结果,可译为“因此”、“所以”。
Our cases were heavy, so we took a taxi.
我们的箱子很重,因此我们坐了出租车
③ therefore 为副词,也表示同样的意思---“因此”,可放句前:
He had gone; she therefore gave the money to me.他走了,于是她把钱给了我。
4、both... and 的用法
A man should have both courage and perseverance.一个人既要有勇气又要有毅力。
【难点】
5、就近原则:
1)neither?nor?
Neither Lucy nor Lily is a League member.
2)not only?but also?
Not only you but also he likes football.
3)either?or?
Either Jim or Peter is right.
4)not?but?
Not Jim but Peter broke the cup.
6、as well as的用法:
I have read one of his novels as well as a few of his plays.
我读过他的一本小说和几个剧本。
二、从属连词:
1
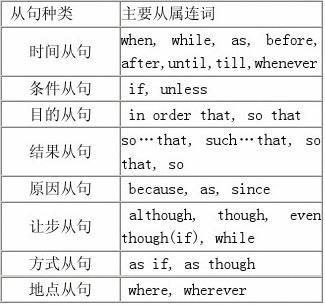

[说明]that, whether, if 等从属连词可引导名词从句,在句中担任主语、宾语等。
2.引导时间状语从句的连词(重点):
when: Don’t get excited when you talk. 讲话时别激动。
while: We must strike while the iron is hot. 我们要趁热打铁。
as: He smiled as he passed. 他经过时笑了笑。
before: It will be five years before we meet again. 要五年后咱们才能再相见。 after: I’ll tell them after you leave. 我将在你走后告诉他们。
until, till: I propose waiting till the police get here. 我建议等警察来了再说。 since: How long is it since you came to London? 你到伦敦有多久了?
whenever: Whenever it is possible, they play outside. 一有机会他们就到外面玩耍。
3.引导条件状语从句的连词(重点):
1)条件状语从句主要由if, unless, supposing(suppose)引导:
if: If it rains tomorrow , we will have to stay at home.
unless: I won’t write unless he writes first. 我不写信,除非他先给我写。
2)条件状语从句还有其他形式:(难点)
You will always have a home as long as I have anything.
只要我有家产,你就永远会有一个家。
4.引导目的状语从句的连词:(重点)
in order that:
I lent him 500 yuan in order that he can go for a holiday.
我借给他50英镑,使他能去度假。
so that:
Ask her to hurry up with the letters so that I can sign them.
让她快点把信打好,以便我能签字。
5.引导结果状语从句的连词:
1)结果状语从句主要由so…that和such…that 引导:
so…that:
He was so fat that he couldn’t get though the door.
他胖得连门都过不去了。
such…that:
Jim made such a noise that his sister told him to be quiet.
吉姆吵成那样,他姐姐让他安静点。
He shut the window with such force that the glass broke.
6.引导原因状语从句的连词:
because: Because it rained he took a taxi. 由于下雨他叫了一辆出租车。 as: As you’re sorry, I’ll forgive you. 既然你悔悟了,我就原谅你。
Since: Since you will go there, I will go too.
7.让步状语从句的连词:
although / though:
Though / Although it is not large, the room was light . 房间虽然不大,采光却很好。 even if:
They’ll stand by you even if you don’t succeed. 即使你不成功,他们也会支持你。
8.引导方式状语从句的连词
as: You ought to do as I tell you. 你应当照我说的做。
like: She can’t draw like her sister can. 她不能像她姐姐那样画画。
as if / as though:
He looked about as if looking for something. 他四处看了看,仿佛在找什么似的。
9.引导地点状语从句的连词:(难点)
where: I’ll drive you where you’re going. 你到哪儿我都可以开车送你去。 wherever: We’ll go wherever you say. 你说哪里我们就到哪里。
everywhere:
Everywhere he went, he was introduced as the current US champion.
不管他到哪里,人们都介绍他是当前的美国冠军。
no matter where:
Keep your mobile phone with you no matter where you are.
不管在哪里你都要带着手机。
10.引导比较状语从句的连词:
than: You sing better than I do. 你的歌唱的比我好。
as: That’s not so simple as it sounds. 那事并不像听起来那么简单。
11. 引导其他从句的连词:
1)引导主语从句和宾语的连词有that和whether, if 可以引导宾语从句:
that: She always complains that he is down on her. 她老是抱怨他看不起她。 whether: I don’t know whether you like flowers. 我不知道你喜不喜欢花。
2)that和whether 还可以引导表语从句:
that: The fact is that he doesn’t really try. 事实是他没有真正去努力。 whether: The point is whether we ought to recommend him. 问题是我们是否应当推荐他。
1. That was a long_______ dull talk.
A. so B. and C. so that D. or 2. _______ the parents_________ their children wanted to move to the country.
A. Both, as well as B. Neither, nor
C. Either, and D. Both, also
3. He won't live in town, _____will his wife.
A. either B. neither C. also D. too
4. Charlie took the job,_______ he did it very well.
A. so B. yet C. and D. so that
5. My grandfather is in his eighties, ______he is still in good health.
A. or B. but C. so D. for
6. — It's nothing serious. Just stay in bed for one or two days. ______ take it easy. — All right.
A. Still B. And C. But also D. But
7. Think it over_________ you will find a way.
A. or B. so C. and D. that
8. Cooper can _____speak Chinese________ read and write it.
A. not only, but also B. both, also
C. not only, and still D. either, and
9. I would like to go swimming, ______he won't.
A. and B. for C. nor D. but
10. Don't stand at the door. ________come in_________ go out.
A. Both, and B. Either, or
1. I asked him _________dog it was.
A. whose B. which C. who's D. where
2. They go to concerts of modem music_________ they really like it.
A. because B. if C. though D. after
3. Find out_________ they are going this evening and ask_________ may join them.
A. whether, that B. where, whether
C. what, if D. where, why
4. His talk was_________ dull_________ we all got bored.
A. as, as B. very, that
C. so. as D. so, that
5. Mother asked Charlie_________ lie had stayed out so late.
A. how B. why C. when D. where
6. My daughter bought a new ring, but she didn't want to tell me_________ it really cost.
A. how often B. how many
C. how much D. how long
7. Can you tell me_________ the time is.
A. what B. how much C. how long D. which
8. Do you think_________ the new cartoon will be shown on TV next week?
A. whether B. that C. when D. where
9. Tell me_________ of these coats you prefer.
A. what B. that C. which D. who
10. — Do you always go to work on foot?
— Not always._________ it rains, I usually go to work by bus.
A. When B. While C. As D. Whether
11. The thief was caught_________ he was leaving the store.
A. as B. after C. before D. until
12. We learned a little Japanese_________ we were in Japan.
A. as B. since C. till D. while
13. you won't help me, I must do the exercise myself.
A. For B. Now that C. So that D. While
14. The singer tried his best he might win the prize.
A. so that B. as C. till D. if
15. It's not it was yesterday.
A. so, that B. so, as C. very, as D. as, than
16. I left for home A. until B. after C. while D. so
17. We all stood on the chairs _______we could see the actors clearly.
A. because B. before C. after D. so that
18. I'm glad that you will come, but tell me ________you will arrive.
A. after B. before C. when D. if
19. He has made great progress in his studies, but he's working even harder ______all of us.
A. than B. as C. like D. of
20. ______ he wasn't interested in music, he came to the concert.
A. Since B. Though C. When D. As
