西安电子科技大学计算机学院
《操作系统实验》
实验报告
姓 名:
学 号:
班 级:
一、题目
实验1:LINUX/UNIX Shell部分
(一)系统基本命令
1.登陆系统,输入 whoami 和 pwd ,确定自己的登录名和当前目录;
登录名 admixx , 当前目录 /root
2.显示自己的注册目录?命令在哪里?
a.键入 echo $HOME,确认自己的主目录;主目录为 /root
b.键入 echo $PATH,记下自己看到的目录表; /usr/lib/qt-3.3/bin:/usr/kerberos/sbin:/usr/kerberos/ bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/X11R6/bin:/root/bin
c.键入 which abcd,看看得到的错误信息;
/usr/bin/which: no abcd in (/usr/lib/ qt-3.3/bin:/usr/kerberos/sbin:/usr/kerberos/ bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/X11R6/bin:/root/bin
再键入 which ls 和 which vi,对比刚刚得到的结果的目录是否在a.、b.
两题看到的目录表中;
alias ls=’ls—color=tty’
/bin/ls
/bin/vi
3.ls 和 cd 的使用:
a.键入 ls, ls -l , ls -a , ls -al 四条命令,观察输出,说明四种不同使用方式的区别。
ls : 列出目录内容 ls –l : 以长格式详细显示文件信息 ls –a : 列出所有文件,包括以 . 文件 ls –al : 以长格式显示当前目录下的所有文件
b.利用 cd 转到 /bin, /sbin , /etc , /dev,再利用 ls 列出各个目录的内容, 如果"迷路",可以利用 pwd 确定位置,或键入cd , cd ~ 观察效果.
cd , cd ~的区别: cd : 回到上层目录 cd ~ : 可进入用户的HOME目录
(二)基本操作
1.用 cp 将 /usr/share 目录下的 exercise 子目录连同目录下的文件拷贝到自己的主目录下,然后进入自己的 exercise 目录.
2.输入/输出重定向和 cat,more 等显示命令的配合使用:
a.输入 cat 命令列出目录下 longtext 文件中的内容;
b.输入 cat 命令列出目录下 longtext 文件中的内容,是否发现一屏显示不完?是
c.使用 more 命令列出 longtext 的内容;
d.输入 cat hello.txt> hello2.txt,再输入 cat hello.txt>>hello2.txt,再检查hello2.txt的内容有何变化;说明>与>>的区别。
>是把hello.txt的内容覆盖在hello2.txt内>>是把hello.txt的内容续写在hello2.txt内
e.对比两条命令: more longtext 和 cat longtext | more ,两者有何不同点?
more longtext 显示出已经显示出来的内容的百分比 cat longtext | more不显示
f.执行命令 echo <hello.txt ,观察发生了什么?
啥都没发生 但如果输入echo >hello.txt 文档就会被清空
g.输入命令 cat <<end ,看看屏幕上的反应:出现>符号 并可以输入文档
h.设计一条命令,使该命令可以从标准输出中读入;
cat <<end > hello3.txt cat hello3.txt 就可以看到
( 参考答案:cat <<end > hello3.txt )
3.特殊字符:
输入 cat [also a text].txt,看看能否打开目录下的[also a text].txt文
件,若不能,该怎么办? 输入cat “[also a text].txt”
(参考答案:cat \[also \ a\ text\].txt)
4.文件链接:
a.用 ln 命令为目录下的longtext文件建立一个硬链接,链接名为longtext2, 然后把longtext复制一个新文件longtext3,用 cat 命令将 hello.txt 的内容追加到longtext 的末尾,再用 diff 命令比较longtext,longtext2和longtext3,看看有什么结果,特别是比较一下longtext和longtext2是否相同;
longtext和longtext2一直是相同的 在longtext后续写hello.txt之后,longtext和longtext2均与longtext3不同了
b.用 ln 命令给longtext3建立一个符号链接longtext4,用 cat 命令看看longtext4;然后删去longtext3,再用 cat 命令看看longtext4,是否有什么不同?
没有不同
c.删去longtext2,看看能否用 cat 命令看到longtext? 能
d.试着执行 ln -s ./abcde ./nulllink,看看是否能建立文件链接. 不能
5.查找命令 find:
用 find 命令查找当前目录下所有以del开头或以del结尾的文件,并将其删除,要求删除前征求用户许可.
find ./ -name del*
rm –i del*
find ./ (-name del/* -o -name \*del \) -exec rm -i {} \;
find ./ (-name del/* -o -name \*del \) -exec -ok rm {} \;
6.文件的属性:
a.用 ls -l 列出 exercise 目录下所有的文件和目录,观察其权限位;
b.将hello2.txt 的读权限去掉,看看还能否用 cat 打开该文件; 不能
c.将 program 目录的读权限去掉,看看是否能用 ls 命令看到其中内容?
不能
(三)Shell程序设计
编写一个Shell过程完成如下功能:
1.合并两个$1、$2文件为$3,并显示。
2.如果缺少$3,那么先报告缺少$3,将合并后的内容输出到CHENG.TXT,显示。
3.如果缺少$2、$3那么先报告缺少$2、$3,只显示$1的内容。
if test -f "$3"
then cat $1 $2>$3
cat $3
else if test -f "$2"
then echo "$3 is not a file or not in this directory"
cat $1 $2>CHENG.TXT
cat CHENG.TXT
else echo "Neither $2 or $3 is a file or in this directory"
cat $1
fi
fi
实验2:

源程序:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
# define BUFFERSIZE 32
int main(){
pid_t pid;
int status;
int fd[2];
char buf[BUFFERSIZE]="This is a pipe\n";
if(pipe(fd)<0){
printf("pipe error\n");
exit(1);
}
pid=fork();
if(pid<0){
printf("fork errot\n");
exit(1);
}
if(pid==0){
printf("child process:\n"); //child process
printf("pid=%d\n",getpid());
printf("ppid=%d\n",getppid());
printf("gid=%d\n",getgid());
printf("write:%s\n",buf);
close(fd[0]); //close write
write(fd[1],buf,sizeof(buf));//write
exit(1);
}
else{ //parenr process
if(pid!=wait(&status)){
printf("wait error\n");
}
printf("parent process:\n");
printf("pid=%d\n",getpid());
printf("ppid=%d\n",getppid());
printf("gid=%d\n",getgid());
实验3:
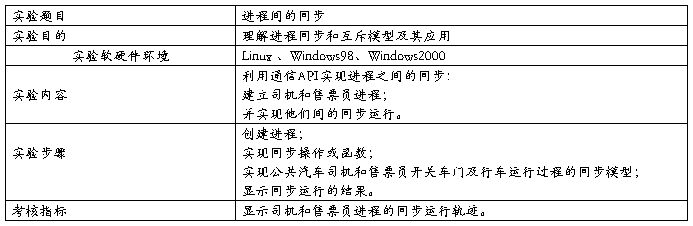
司机进程代码:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
char SEM_NAME1[]= "s1";
char SEM_NAME2[]= "s2";
int main()
{
int i;
sem_t *s1;
sem_t *s2;
s1 = sem_open(SEM_NAME1, O_CREAT, 0644, 0);
if(s1 == SEM_FAILED)
{
perror("unable to create semaphore");
sem_unlink(s1);
exit(-1);
}
s2 = sem_open(SEM_NAME2, O_CREAT, 0644, 0);
if(s2 == SEM_FAILED)
{
perror("unable to create semaphore");
sem_unlink(s2);
exit(-1);
}
for (i=0; i<=2; i++) {
printf("[driver] reach station, stop car\n");
sem_post(s2);
printf("[driver] waiting closing door\n");
sem_wait(s1);
printf("[driver] leaving station\n");
printf("car is running\n");
}
sleep(2);
sem_close(s1);
sem_close(s2);
sem_unlink(SEM_NAME1);
sem_unlink(SEM_NAME2);
_exit(0);
}
售票员进程代码:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
char SEM_NAME1[]= "s1";
char SEM_NAME2[]= "s2";
int main()
{
int i;
sem_t *s1;
sem_t *s2;
//create & initialize semaphore
s1 = sem_open(SEM_NAME1, 0, 0644, 0);
if(s1 == SEM_FAILED)
{
perror("unable to create semaphore");
sem_close(s1);
exit(-1);
}
s2 = sem_open(SEM_NAME2, 0, 0644, 0);
if(s2 == SEM_FAILED)
{
perror("unable to create semaphore");
sem_close(s2);
exit(-1);
}
for (i=0; i<=2; i++) {
sem_wait(s2);
printf("[conductor] open door, passenger, close door\n");
sem_post(s1);
printf("[conductor] waiting reaching station\n");
}
sem_close(s1);
sem_close(s2);
_exit(0);
}
运行结果:
结果分析:利用PV操作实现司机进程和售票员进程之间的同步。设司机进程的信号量为S1,售票员进程信号量为S2。当车到站时,停车,进行操作V(S2),P(S1)。此时司机进程被挂起,售票员进程开始进行。售票员进程先进行P(S2)操作,若之前未进行V(S2)则被挂起,否则进程继续执行,打开车门。待人上完后关车门,进行V(S1)操作,唤醒被挂起的司机进程。汽车再次离站开出。
实验4:
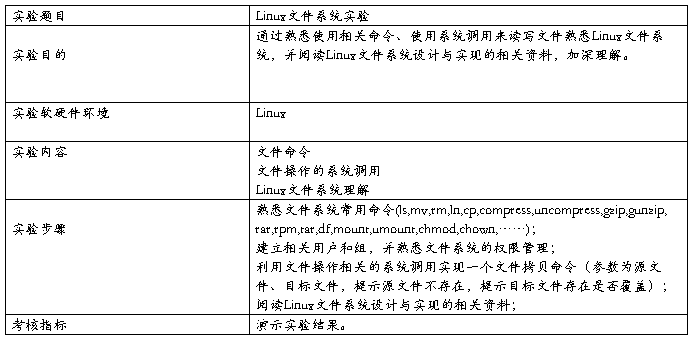
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define BUFF_SIZE 1024
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int src_file,dest_file;
int real_read_len;
unsigned char buff[BUFF_SIZE];
char cover;
//argc is not correct
if(argc!=3){
printf("Error use copy!\n");
printf("Example:\n");
printf("copy src_file dest_file\n");
exit(1);
}
//judge wheather src_file exists
if((access(argv[1],F_OK)!=0))
{
printf("source file dosen't exist.\n");
exit(-1);
}
//judge the existence of the dest_file
if((access(argv[2],F_OK)==0))
{
printf("dest_file already exists.cover it?\n");
printf("yes [y] or not [n]?\n");
scanf("%c",&cover);
if(cover=='n')
exit(1);
else
printf("cover it!\n");
}
//Open src_file read only
src_file=open(argv[1],O_RDONLY);
//If the dest_file is not exsit, then create new one
dest_file=open(argv[2],O_WRONLY|O_CREAT,666);
//Open error
if(src_file<0||dest_file<0){
printf("Open file error\n");
printf("Can't copy!\n");
printf("Please check cmd : copy src_file dest_file\n");
exit(1);
}
//Copy src_file to dest_file
while((real_read_len=read(src_file,buff,sizeof(buff)))>0){
write(dest_file,buff,real_read_len);
}
//close fd
close(dest_file);
close(src_file);
return 0;
}
程序分析:本程序主函数接受两个参数,为源文件目录和目标文件目录。首先程序尝试打开源文件,若无法打开表明源文件不存在。之后尝试打开目标文件,若成功打开目标文件表明目标文件已存在,询问用户是否覆盖。若目标文件打开失败表明目标文件不存在,创建目标文件并将源文件的内容复制到目标文件中。
