本科专业职业生涯设计开题报告书

第二篇:毕业设计_开题报告_基于RFID技术的车辆自动识别系统的设计
毕业设计(论文)材料之二(2)
本科毕业设计(论文)开题报告
题目:
课 题 类 型: 设计□ 实验研究□ 论文□ 学 生 姓 名:
学 号:
专 业 班 级:
学 院:
指 导 教 师:
开 题 时 间:
201 年 月 日
一、毕业设计内容及研究意义
设计的内容:
本文介绍了一种RFID技术的车辆自动识别系统的设计。该系统可在车辆行驶状态下识别车辆身份并采集相关信息、可应用于电子部停车收费、停车场管理及门禁管理等。射频识别技术,英文全称为 Radio Frequency Identification(简称为 RFID),是指相关的无线电技术在自动设备识别(AVI, Automatic Vehicle Identification)领域中的具体应用。该技术利用无线射频方式进行非接触的双向通信,以达到识别并交换数据的目的。可用于识别高速运动物体并可同时识别多个射频识别标签,而且操作快捷方便,不怕油渍、灰尘污染等恶劣环境,特别适合于实现系统的自动化且不易损坏。 作为快速、实时、准确采集与处理信息的高新技术和信息标准化的基础,RFID已被公认为本世纪十大重要技术之一。 研究背景及研究意义:
随着科学技术的发展和人民生活水平的提高,汽车已经成为普及的交通工具,如何才能实现对汽车行之有效的管理成为一个难题,而使高效化、智能化的车辆管理系统进入大众化的小区是本课题的研究方向。 目前国内很多公司都开发了用于车辆电子档案管理的自动化系统,其核心设计思想是“用数据库来管理车辆电子档案”,信息的管理查询通过 Web 方式实现。其提供的功能主要包括车辆使用申请、车辆状况查询等。这类系统建立在完整的车辆、人员数据档案的基础上,实现用车申请-审批-调度过程的电子化。一般系统还为具有不同角色的用户,分别提供车辆信息、驾驶员信息、车辆维修、保养情况,车辆调配情况等的查询功能。
由于很多用户还需要掌握车辆出入的时间以及在外的运行情况,以便对各个部门以及各个车辆进行核算,因此很多系统也提供了这类车辆的管理功能。采用车辆自动识别技术,可以很容易实现车辆出入控制。但获取车辆在外的运行数据则较为复杂,一般做法是要求车辆外出回来后,必须登记外出记录,记录运行时间、公里数、耗油量等,管理人员再手动录入到数据库中。这种手段一方面加重了管理人员的工作负担,另一方面,上报的数据误差较大,并且容易受到人为因素的干扰,造成弄虚作假的现象。
为了解决上述问题,我们开发了小区车辆智能管理系统。该系统将车辆电子档案、车辆自动识别和车辆运行数据采集三项技术融为一体,当车辆外出回来后,车内的车载卡设备会将采集的运行数据通过RFID 无线射频技术自动上报给监测设备,并由监控软件实时地更新到数据库中。这种完全电子化的手段杜绝了徇私舞弊,能更加有效地实现对车辆、人员的管理。
二、RFID的研究现状及发展趋势
RFID是一种非接触式的自动识别技术,智能卡具有非接触、阅读速度快、无磨损、寿命长、便于使用的特点,在国内外都取得了巨大发展。
国内外发展现状 :
国外:从全球的范围来看,美国已经在 RFID 标准的建立,相关软硬件技术的开发和应用领域走在世界的前列。欧洲 RFID标准追随美国主导的 EPCglobal 标准。在封闭系统应用方面,欧洲与美国基本处在同一阶段。日本虽然已经提出 UID 标准,但主要得到的是本国厂商的支持,如要成为国际标准还有很长的路要走。RFID在韩国的重要性得到了加强,政府给与了高度的重视,但至今韩国在
RFID的标准上仍模糊不清。
(1) 美国
在产业方面,TI,Intel等美国集成电路厂商目前都在RFID领域投入巨资
进行芯片开发。 Symbol等已经研发出可以同时阅读条形码和RFID的扫描器。
IBM、 Microsoft和 HP等也在积极开发相应的软件及系统来支持RFID的应用。
目前美国的交通、车辆管理、身份识别、生产线自动化控制、仓储管理及物资跟
踪等领域已经开始逐步应用 RFID 技术。在物流方面,美国已有 100 多家企业
承诺支持 RFID应用,这其中包括:零售商沃尔玛;制造商吉列、强生、宝洁;
物流行业的联合包裹服务公司以及政府方面国防部的物流应用。 另外,值得注
意的是美国政府是 RFID应用的积极推动者。按照美国国防部的合同规定,2005
年 1 月 1 日以后,所有军需物资都要使用 RFID 标签;美国食品及药物管理局
(FDA)建议制药商从 2006 年起利用 RFID 跟踪最常造假的药品;美国社会福
利局(SSA)于2005 年年初正式使用 RFID技术追踪 SSA各种表格和手册。
(2) 欧洲
在产业方面,欧洲的 Philips,ST Microelectronics在积极开发廉价的RFID
芯片;Checkpoint 在开发支持多系统的 RFID 识别系统;Nokia 在开发并推广
其能够基于RFID的移动电话购物系统;SAP 则在积极开发支持RFID的企业应用
管理软件。
(3) 日本
日本是一个制造业强国,它在电子标签研究领域起步较早,政府也将RFID
作为一项关键的技术来发展。MPHPT 在 2004 年 3 月发布了针对 RFID 的“关
于在传感器网络时代运用先进的 RFID 技术的最终研究草案报告”,报告中称
MPHPT 将继续支持测试在UHF频段的被动及主动的电子标签技术,并在此基础上
进一步讨论管制的问题。从近来日本RFID领域的动态来看,与行业应用相结合
的基于RFID技术的产上海交通大学硕士学位论文 RFID技术在车辆进出小区智能化管理系统中的应用
国内:我国政府在 1993 年制定的金卡工程实施计划及全国范围的金融卡网
络系统的十年规划,是一个旨在加速推动我国国民经济信息化进程的重大国家级
工程。由此各种自动识别技术的发展及应用十分迅猛。现在,射频识别技术作为
一种新兴的自动识别技术,也将在中国很快地普及。可以说,我国射频识别产品
的市场是十分巨大的,射频识别技术应用状况还处于初级阶段,市场前景非常广
阔。 国内已有几家公司在引进国外的先进技术,开发自己的射频识别系统。现
在,在锦山的一条高速公路上已应用了非接触标签的自动收费,上海的交通一卡
通,北京的机场高速公路上、深圳的皇岗口岸也使用了射频识别系统收费等等。
特别值得一提的是中国的第二代居民身份证采用了RFID技术,这是迄今为止
RFID最大的应用,
中国也因此成为全球最大的 RFID 市场之一。 国内 RFID 研发主要集中在
北京和上海等大城市。目前,上海 RFID 产业链已经初步形成,包括以上海华虹,
复旦微电子,上海贝岭为代表的国内芯片设计企业,以及像上海申博这样的芯片
封装厂商和上海华申为代表的电子标签终端设备厂商。而在系统集成和数据管理
软件平台领域,上海交通大学与Auto ID中国实验室、SAP合作,正在进行电子
标签中间件的开发,至于应用系统开发方面,上海海鼎正在进行 RFID在商业领
域的应用开发。本文介绍的停车场管理系统也是将RFID技术在门禁系统中的应
用。 北京在上游产品的自主开发方面起色不大,但在应用系统的集成方面却发
展较快,该领域实华开、维深电子等企业十分活跃。2004 年 4 月世界 RFID 领域三大标准组织之一的日本 UID中心与实华开签署了协议,宣布成立 UID中国中心。他们把
目标设定为融合EPC 标准、 UID 标准,并向国际标准化组织ISO提出更完善的 RFID标准建议。 在技术方面,Auto ID中国实验室依托于复旦大学,作为全球Auto ID六个实验室之一,在 EPC 技术的研究上保证我国与世界同步,同时又能提供本土化的支持。Auto ID中国实验室的目标是在中国建立开放的 RFID演示平台,并结合中国的应用问题进行理论分析和基础研究,为建立 EPC 国际标准和中国 RFID 标准提供参考依据,促进 EPC 和 RFID 技术在中国的应用并与国际接轨。目前,国内企业和研究机构对参与实验室的研究和演示系统的建立等工作表现出了空前的热情。
发展趋势:
RFID 射频识别技术有着广阔的前景。RFID 射频识别技术被认为最终将取代条形码,然而它的应用不会仅仅局限在供应链、物流零售等方面,随着RFID射频识别技术的进一步发展和市场化,它会在多领域、多行业中大显身手,射频识别技术被广泛应用于汽车生产,交通运输管理,汽车、火车等交通监控,高速公路自动收费系统,停车场管理系统,物品管理,车辆防盗等方面。
1.汽车装配流水线
德国宝马汽车公司在装配流水线上应用射频卡以尽可能大量地生产用户定制的 汽车。宝马汽车的生产是基于用户提出的要求式样而生产的;宝马公司就在其装配流水线上配有RFID系统它们使用可重复使用的射频卡,该射频卡上课带有详细的汽车所需要的所有要求,在每个工作点处都有读写器,这样可以保证汽车在哥哥流水线的位置处能毫不出错的完成装配任务。
2.公路收费
射频技术已经发展成为不停车收费系统的主流识别技术。自动车辆识别(AVI)是利用安装在车内的射频卡(又称电子标签)存储车辆编号及相关信息,安装在车道的射频天线可与该无线电收发器通信,并对其存储内容进行读写操作,从而识别出当前通行车辆。自动车辆识别主要是指工作在5.8GHz频段的短距离(8—30米) 通信技术。
3.停车智能化管理
停车场管理系统采用射频读卡技术,用户特定的感应卡进出停车场,使用感应卡读卡器来分辨停车场在Old Dominion,最新使用的无线电子技术是Symbol生产的手持设备。两年前Old Dominion还在所有的牵引车、拖车、手推车等设备上安装了无线射频识别(RFID)标签,在场区和站门安装了无限天线,所有车辆经过这些地点时自动被记录。
4.公共交通电子车票
射频识别系统,特别是非接触式IC卡应用潜力最大的领域之一就是公共交通领域。使用非接触式IC卡作为电子车票,具有使用方便、可以缩短交易时间、降低运营成本等优势。韩国汉城在19xx年就采用了这一系统,目前,北京的公交车也都加装了电子车票收费系统,将很快投入运营。
RFID 应用分为两个层次,一是在封闭系统内部应用;二是在开放系统中应用。目前RFID 的应用主要是在封闭系统(比如企业或单位内部)应用,使用独立的一套设备、频率、流程和编码标准体系。因此其市场规模受到了极大的限制,但随 RFID技术的发展演进以及成本的降低,RFID 势必向外部拓展,成为一个
开放式的信息共享链条。未来几年内 RFID 技术将主要以供应链的应用为盈利的主体,从采购、仓储、生产、包装、卸载、流通加工、配送、销售到服务,这些供应链上的业务流程和环节来增强企业对商流、物流、信息和资金的掌控能力。RFID 技术的发展趋势必然会朝着标签成本的降低,读写距离的提高,标签存储容量增大,处理时间缩短这些方向前进。
三、毕业设计研究方案及工作计划
1、研究方案
车辆自动识别系统
车辆自动识别系统(Automatic Vehicle Iden—tification,AⅥ),可准确无误地自动识别并采集路网中运行车辆的身份特征信息和法定管理信息,使车辆信息瞬时进入计算机,可为车辆及交通管理部门提供一个实时、动态的车辆信息采集平台。本文采用了RFID技术设计和实现了汽车号牌自动识别系统,该系统的硬件是由读写单元(标签阅读器)和标签号牌组成,阅读器通过线路与计算机的
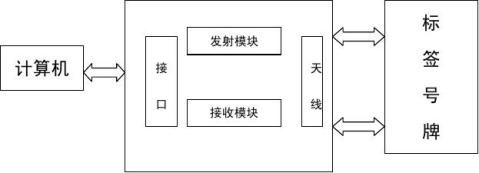
RS32接口通信,其系统硬件框架如图1所示。
图1系统硬件框架
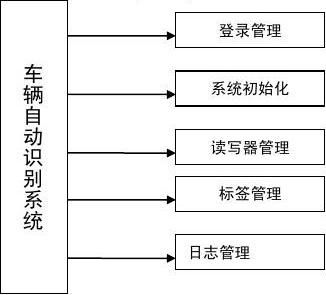
程序通过计算机控制阅读器来对标签进行读写操作,阅读器通过天线发出电磁脉冲,标签接收到这些脉冲并发送已存储的信息到阅读器作为响应,再由阅读器将信号处理后传给计算机,实现对汽车号牌在不同状态(静止、移动,甚至恶劣环境)下的自动识别和管理。系统中的阅读器采用了某厂商生产的8801型号的读写器,该读写器读写距离远,读写速度快,抗干扰能力强。标签包含了具有RFID射频部分和一个超薄天线环路的RFID芯片的RFID电路,这个天线与一个塑料薄片一起嵌入到标签内。标签一般为信用卡大小,因此可以集成到其他产品里面。该系统就把标签集成到汽车牌照中,构成了标签号牌,这样在收发端就无需增加任何其他硬件,也不会增加用户的开销。系统软件方面采用了VB编程,通过VB程序控制读写器来读取号牌标签中的号牌信息,并访问后台数据库,从而完成号
牌数据的判别。软件系统框架如图2所示。
自
该系统环境适应性强,受雨雪、冰雹、灰尘等影响小,可全天候工作,非接触地完成自动识别、跟踪与管理,并且具有可穿透非金属物体进行识别,抗干扰能力强等优点。
图2软件系统框架如
2、工作计划


四、主要参考文献:
1.游战清,李苏剑等编著。无线射频识别技术(RFID)理论与应用。电子工业出版社。
2.Klause Finkenzeller 著。陈大才编译。射频识别(RFID)技术。电子工业出版社
3.尹应增 微波射频识别技术研究 西安电子科技大学博士论文,2002.04
4.沈宇超、沈树群:射频识别技术及其发展状况[J],电子技术应用,20xx年第2期
5.刘 铮、张 兢:非接触式IC卡中的射频识别技术[J],信息技术,20xx年第4期
6.张纲,马庆容,沈磊,俞军. 射频识别技术的现状和发展研究[J]. 半导体技术, 2004,(04) .
7. 张殿东. 无线射频识别(RFID)技术[J]. 电信技术, 2005,(02) .
8. 胡蓉, 雷媛媛, 王慧. 无线射频识别技术(RFID)及其在物联网中的应用
[J]. 科技广场, 2010,(09)
9. 马伏花;基于RFID的车辆自动识别系统信息采集基站的研究与设计[D];湖南大学;20xx年
10. Su M,Hwang Y J,Lee D H,et al. Efficient Authentication for Low Cost RFID Systems[C] .Proc.of International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications. Springer-Verlag, 2005, .
11. Ollivier M M. RFID——A New Solution Technology for Security Problems[C] .Proceedings of European Convention on Security and Detection. Brighton,United Kingdom: 1995,
12.张纲,马庆容,沈磊,俞军. 射频识别技术的现状和发展研究[J]. 半导体技术, 2004,(04)
13. 射频识别技术(RFID)及其应用[J]. 电力信息化, 2006,(03)
An intelligent traffic management expert system with
RFIDtechnology
Abstract
This paper presents an intelligent traffic management expert system with RFIDtechnology. The system provides both practically important traffic data collection and control information and can trace criminal or illegal vehicles such as stolen cars or vehicles that evade tickets, tolls or vehicle taxes. The system architecture consists of an RFID reader, a passive tag, a personal computer, a pair of infrared sensors, and a high-speed server with a database system. Based on RFIDtechnology, the system collects and calculates average speed and average flow information on each road of a district area in a city. It then transmits the messages from all the congested roads in a district area to the server in the district center via a communication program. Through a flooding algorithm, each server in a district center exchanges and updates information with all neighbor servers in other district centers so all that the servers in various district centers can get all the latest congestion messages in a city. Therefore, a dynamic navigation system can find the shortest path that avoids congested roads. Meanwhile, we compare three types of tags for choosing a better solution for e-plates in the future. We also adopt infrared sensors for detecting cars that do not have a tag.
Keywords:Radio frequency identification; Passive tags; Intelligent traffic management; Shortest path
1. Introduction
Traffic management poses many critical challenges in most modern cities, including congestion, traffic violations, car theft, and illegal vehicles. During the past few years, researchers have used GPS, radar sensors, or digital cameras to measure average car speed and maximum flow on a road in order to determine whether a driver is over the speed limit or to provide traffic information to remind drivers to avoid congestion. However, these systems do not systematically collect information to be used in a dynamic traffic guidance system to solve traffic congestion. Additionally, these approaches cannot identify a car’s basic data, and therefore cannot solve the aforementioned problems. In 2003, Wal-Mart first instructed one of its suppliers to start using radio frequency identification (RFID) for managing its supplies (RFID Journal, 2003). Next, the US Department of Defense (DoD) announced a similar RFID mandate for its suppliers in 2004 (Wyld, 2006). With the backing of retail and military giants, RFID is a growing market that is becoming widely important. The widespread use of RFID can automatically track pallets, cases, individual products, and reusable assets such as bins and containers throughout the supply chain. Chao, Yang, and Jen (2007) reviewed the history of RFID in supply chain management, the supermarket checkout process, and private issues. They wrote that RFID global sales are expected to reach US$70 billion by 2008.
Tajima (2007) developed a theory of how RFID can be used in supply chain management to sustain a competitive advantage. Under the theory, he developed four propositions. Through them we can see that RFID technology has strategic competitive value. He mentioned 15 benefits that have been realized and divided them into two parts, throughout the supply chain (specifically, reduced shrinkage, reduced
material handling, increased data accuracy, faster exception management, and improved information sharing) and major supply chain participants (specifically, production tracking, quality control, supply and production continuity, material handling, space utilization, asset management, reduced stockouts, customer service, lower inventory). Using RFID can achieve three benefits: automation, closed-loop tracking, and supply chain visibility. Ayoade (2006) explored RFID system security and privacy. He recommended a method called APF (Authentication Processing Framework) to cope with this problem. APF requires an RFID reader to authenticate itself with the APF database before it can access tags. Bottani and Rizzi (2008) assessed an economic justification for the FMCG (Fast-moving Consumer Goods) supply chain. The results show that RFID with pallet-level tagging generates positive profits throughout the supply chain. However, adopting case-level tagging yields negative results.
RFID applications have been studied in many areas as well. Recently, RFID has even been applied in the health care industry to improve efficiency of operation. Fisher and Monahan (2008) emphasized that RFID technology has become the standard for hospitals to trace inventory, identify patients, and manage personnel. They found that hospital nurses felt that they were subject to excessive surveillance by RFID technology. Additionally, using RFID technology increased their workload because they also operate the RFID devices. The Anaheim Fire Department in Orange County (2008), California uses RFID technology in inventory management and replenishment of its medical supplies. Cabuenes hospital (2008) in Asturias, Spain, used RFID readers and tags to monitor patients for accelerating treatment and to provide doctors and nurses with a wide range of important information. Owing to the breadth of the above applications, in this paper, we first bravely use a passive RFID reader and tags to handle traffic data collection, traffic management, shortest road paths, and tracing of illegal vehicles.
2. Framework for the intelligent traffic management expert system
The framework for the system comprises a passive tag, an RFID reader, two antennas, a personal computer or a control card with a microprocessor, a pair of infrared sensors, and a high-speed server with a database system (see Fig. 1). The type of the reader is an Alien 9780 (915 MHz) and the tags are Types 1, 2, and 3, as shown in Fig. 2a. The tags belong to Class 1, which is written only once but read multiple times. Their power comes from the reader’s RF transmission. The infrared sensors use a 6-V cut-off filter. The connection between the infrared sensors and the power supply is presented in Fig. 2b. The front-end device connects to the back-end server via a wireless network. The tag is pasted on the windshield a car. The reader detects data and sends it back to the high-speed back-end server via a wireless network, storing it in the database. The software we used includes JSP, Java, and MySQL. The server then calculates the average speed and maximum flow. For building the system, we must make two assumptions: (1) An electronic plate is adopted nationwide. (2) RFID readers exist in urban areas and in all highway toll stations.
For calculating the average speed of a car, we deployed two antennas (see Fig. 3). The effective sensing angle is 60°. The maximum detected effective distance is 15 m. The distance between the two antennas is 12 m. Thus, we set d = 12. Vehicle speed is calculated by the equation , where t1 is the detected time of the antenna 1 and t2 is the discovered time of the antenna 2. d is the distance between the antennas. Since the distance between antennas 1 and 2 is known, it is easy to determine the vehicle’s speed. After 30 samples of the vehicle’s speed have been collected, the system computes the average speed. Actually, we need only use one antenna to measure car speed. Hence if the first discovered time of a car, t1, and the last discovered time of a car, t2, and the detected distance of an antenna, diameter of the circle (d = 2 radius), are known, then the car speed is very easy to get. Wen and Hsu developed and implemented an automatic navigation system with a dynamic algorithm to avoid congested roads with a very low speed (for example, speed 15 km/h).
3. Functions of the system
Through the query V-QUERY, a user can search for basic and critical information such as personal data, vehicle data, fuel tax, license tax, highway toll fees, and tickets. It is worth mentioning that individual privacy and security are very important. Thus, the system has a security mechanism that refers to a security matrix to set up personal privileges. Thus, the system only allows access to authorized data. In Fig. 4, it presents the login menu to only arrow the authorized users to access the system. Fig. 5 shows the car owner’s personal data including id number, name, sex, birthday, address, telephone, blood type, etc. Fig. 6 presents the owner’s vehicle data, such as id number, type, engine number, body number, color, volume, issue date, and so on. Fig. 7 illustrates the driver’s fuel tax status that clearly shows whether the owner has paid the fuel tax (charged in Taiwan). Similarly, Fig. 8 presents whether the owner has paid the license tax. When a car passes an RFID reader and the owner has not paid tickets, fuel tax, or license tax, the system will sound an alarm and take a photo. If the car is a stolen car or a suspicious car, the system will also sound an alarm. Hence, an on-duty officer may ask the driver to pull over. Furthermore, one key application is to deduct or accumulate toll fees (see Fig. 9) or other fees, for instance gas fees or different kind of goods or service fees. A billing statement will be sent to the owner by the end of each month.
4. Conclusions and future work
This paper proposes a framework for an intelligent traffic management expert system (ITMES). The main functions of the system are to trace criminal vehicles and to help the police if a car owner has not paid vehicle tax, license tax, or tickets. It also collects and calculates average speed and the maximum flow of a section of road in a city area. Thus, a dynamic guided system can use the information provided by ITMES to find a path that avoids traffic congestion. To explore the practical efficiency of the system, we implemented the ITMES to examine all factors using JSP, JAVA, and MySQL. Furthermore, to validate and verify it, we compared the RFID reader’s maximum distance and detected speed using Types 1, 2, and 3 tags.
Although we have developed a working ITMES, there are still several ways in which we can further improve its functions. In particular, we can extend its functions to assist a company’s payment collection, including retail businesses, department stores, restaurants, or various other industries. In addition, it can be integrated with a traffic light system to control or divert traffic. It can also be applied to manage ships, motorcycles, bicycles, or precious goods. Moreover, an artificial neural network or other improved knowledge management tools may be included in the future to provide better traffic control and management. Finally, building a fast and efficient fuzzy logic reasoning engine will also be one of our major future research goals.

