昆明理工大学信息工程与自动化学院学生实验报告
( 2013 — 2014 学年第 1 学期)
课程名称:人工智能 开课实验室:信自楼计算机机房442 2013 年12月 20日
一、上机目的及内容
1.上机内容
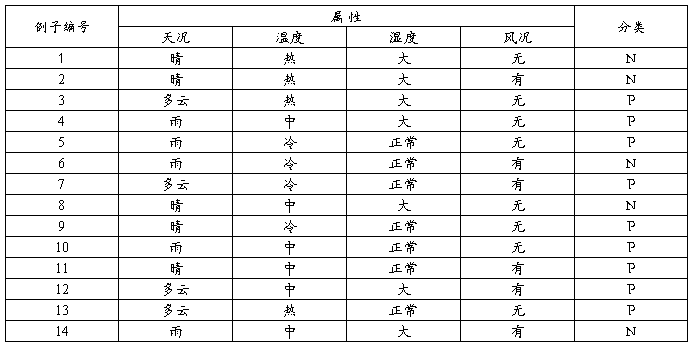
根据下列给定的14个数据,运用Information Gain构造一个天气决策树。
2.上机目的
(1)学习用Information Gain构造决策树的方法;
(2)在给定的例子上,构造出正确的决策树;
(3)理解并掌握构造决策树的技术要点。
二、实验原理及基本技术路线图(方框原理图或程序流程图)
(1)设计并实现程序,构造出正确的决策树;
(2)对所设计的算法采用大O符号进行时间复杂性和空间复杂性分析;
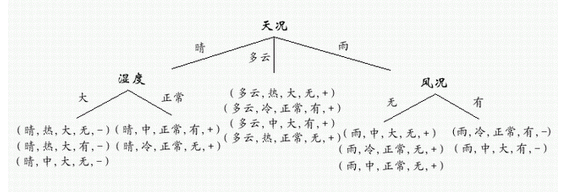
决策树通过把实例从根节点排列到某个叶子节点来分类实例,叶子节点即为实例所属的分类。树上的每一个节点说明了对实例的某个属性的测试,并且该节点的每一个后继分支对应于该属性的一个可能值。
构造好的决策树的关键在于如何选择好的逻辑判断或属性。对于同样一组例子,可以有很多决策树能符合这组例子。人们研究出,一般情况下或具有较大概率地说,树越小则树的预测能力越强。要构造尽可能小的决策树,关键在于选择恰当的逻辑判断或属性。由于构造最小的树是NP-难问题,因此只能采取用启发式策略选择好的逻辑判断或属性。用信息增益度量期望熵最低,来选择分类属性。
算法实现:
天气数据存放在data.txt 中;
第一行为样本数量14和每个样本中属性的数量4; 第二行为每个属性取值的数量; 后面n行皆为例子; 节点数据结构 struct DTNode {
int name; //用 1,2,3,4表示选择的属性,0表示不用分类,即叶节点
int data[D_MAX+1]; //表示此节点包含的数据,data[i]=1,表示包含二维数组data[][]中的第i条数据
int leaf; //leaf=1 正例叶节点;leaf=2 反例叶节点;leaf=0不是节点
int c; //c=1 正类 ;c=0 反类
DTNode *child[P+1]; //按属性值的个数建立子树 };
定义函数:
void Read_data() //从数据文件data.txt中读入训练数据
DT_pointer Create_DT(DT_pointer Tree,int name,int value) //创建决策树
int chose(int *da) //选择分类属性
float Gain(int *da,int p) //计算以p属性分类的期望熵
float Entropy(int *da) //计算数据的熵
int test_leaf(int *da) //测试节点属性
void Out_DT(DT_pointer Tree) //用线性表形式输出建立的决策树
int Class(int *da) //对输入的测试样本分类
全局变量:
FILE *fp;
int p_num; //属性的数量
int pi[P_MAX+1]; //每个属性有几种取值
int d_num; //数据的数量
int data[P_MAX+1][D_MAX+1];//存储训练数据
三、所用仪器、材料(设备名称、型号、规格等或使用软件)
1台PC及VISUAL C++6.0软件
四、实验方法、步骤(或:程序代码或操作过程)
源代码:
main函数:
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include "AttributeValue.h"
#include "DataPoint.h"
#include "DataSet.h"
DataPoint processLine(std::string const& sLine)
{
std::istringstream isLine(sLine, std::istringstream::in);
std::vector<AttributeValue> attributes;
// TODO: need to handle beginning and ending empty spaces.
while( isLine.good() )
{
std::string rawfield;
isLine >> rawfield;
attributes.push_back( AttributeValue( rawfield ) );
}
AttributeValue v = attributes.back();
attributes.pop_back();
bool type = v.GetType();
return DataPoint(attributes, type);
}
void main()
{
std::ifstream ifs("in.txt", std::ifstream::in);
DataSet initDataset;
while( ifs.good() )
{
// TODO: need to handle empty lines.
std::string sLine;
std::getline(ifs, sLine);
initDataset.addDataPoint( processLine(sLine) );
}
std::list<DataSet> processQ;
std::vector<DataSet> finishedDataSet;
processQ.push_back(initDataset);
while ( processQ.size() > 0 )
{
std::vector<DataSet> splittedDataSets;
DataSet dataset = processQ.front();
dataset.splitDataSet(splittedDataSets);
processQ.pop_front();
for (int i=0; i<splittedDataSets.size(); ++i)
{
float prob = splittedDataSets[i].getPositiveProb();
if (prob == 0.0 || prob == 1.0)
{
finishedDataSet.push_back(splittedDataSets[i]);
}
else
{
processQ.push_back(splittedDataSets[i]);
}
}
}
std::cout << "The dicision tree is:" << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < finishedDataSet.size(); ++i)
{
finishedDataSet[i].display();
}
}
AttributeValue:
#include "AttributeValue.h"
#include "base.h"
AttributeValue::AttributeValue(std::string const& instring)
: m_value(instring)
{
}
bool AttributeValue::GetType()
{
if (m_value == "P")
{
return true;
}
else if (m_value == "N")
{
return false;
}
else
{
throw DataErrException();
}
}
Basefun:
#include <math.h>
float log2 (float x)
{
return 1.0 / log10(2) * log10(x);
}
float calEntropy(float prob)
{
float sum=0;
if (prob == 0 || prob == 1)
{
return 0;
}
sum -= prob * log2(prob);
sum -= (1 - prob) * log2 ( 1 - prob );
return sum;
}
DataPoint:
#include <iostream>
#include "DataPoint.h"
DataPoint::DataPoint(std::vector<AttributeValue> const& attributes, bool type)
: m_type(type)
{
for (int i=0; i<attributes.size(); ++i)
{
m_attributes.push_back( attributes[i] );
}
}
void DataPoint::display()
{
for (int i=0; i<m_attributes.size(); ++i)
{
std::cout << "\t" << m_attributes[i].getValue();
}
if (true == m_type)
{
std::cout << "\tP";
}
else
{
std::cout << "\tN";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
DataSet:
#include <iostream>
#include "DataPoint.h"
DataPoint::DataPoint(std::vector<AttributeValue> const& attributes, bool type)
: m_type(type)
{
for (int i=0; i<attributes.size(); ++i)
{
m_attributes.push_back( attributes[i] );
}
}
void DataPoint::display()
{
for (int i=0; i<m_attributes.size(); ++i)
{
std::cout << "\t" << m_attributes[i].getValue();
}
if (true == m_type)
{
std::cout << "\tP";
}
else
{
std::cout << "\tN";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
Header Files
AttributeValue.h:
#ifndef ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_H_
#define ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_H_
#include <string>
class AttributeValue
{
public:
AttributeValue(std::string const& instring);
bool GetType();
std::string const& getValue() const
{
return m_value;
}
private:
std::string m_value;
};
struct AttributeValueCmp
{
bool operator() (AttributeValue const& lhs, AttributeValue const& rhs) const
{
return lhs.getValue() < rhs.getValue();
}
};
#endif
Base.h:
class DataErrException : public std::exception
{
};
float calEntropy(float prob);
DataPoint.h:
#ifndef DATA_POINT_H_
#define DATA_POINT_H_
#include <vector>
#include "AttributeValue.h"
class DataPoint
{
public:
DataPoint(std::vector<AttributeValue> const& attributes, bool type);
bool isPositive()
{
return m_type;
}
int getNAttributes()
{
return m_attributes.size();
}
AttributeValue const& getAttribute(int index)
{
return m_attributes[index];
}
void display();
private:
std::vector<AttributeValue> m_attributes;
bool m_type;
};
#endif
DataSet.h:
#ifndef DATA_POINT_H_
#define DATA_POINT_H_
#include <vector>
#include "AttributeValue.h"
class DataPoint
{
public:
DataPoint(std::vector<AttributeValue> const& attributes, bool type);
bool isPositive()
{
return m_type;
}
int getNAttributes()
{
return m_attributes.size();
}
AttributeValue const& getAttribute(int index)
{
return m_attributes[index];
}
void display();
private:
std::vector<AttributeValue> m_attributes;
bool m_type;
};
#endif
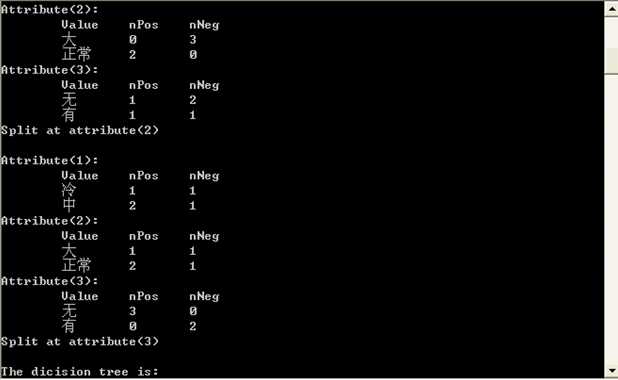
五、实验运行结果

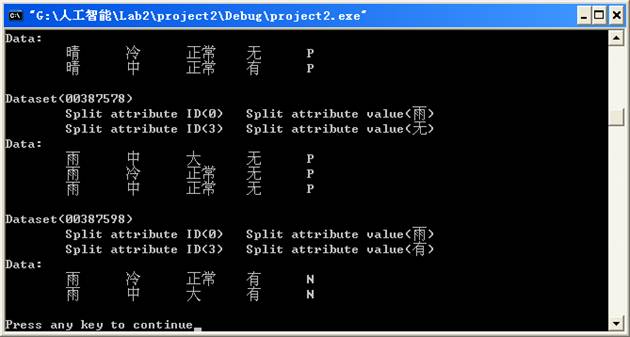

六、实验结果、分析和结论(误差分析与数据处理、成果总结等。其中,绘制曲线图时必须用计算纸或程序运行结果、改进、收获)
做这个实验的时候我遇到了很大的难度,感觉它的要求和自己的实际水平相差很大,虽然老师给了源代码,但是还有好多看不懂,我感到了自己的编程方面的能力还很不足,还需要加强的地方还有很多。通过本次试验,我学习了用Information Gain构造决策树的方法,理解并掌握构造决策树的技术要点,复习程序设计和数据结构课程的相关知识,感觉对课程有了更深入的了解,觉得自己收获了很多。虽然在实验过程中也遇到了很多困难,但在老师和同学的帮助下,顺利完成了实验。我复习了以前学过的c++方面的知识,发现自己不懂的地方实在太多,有好多学过的知识都不太记得了,深刻的认识到自己的能力的不足,有许多方面都需要好好看书,还需要多加练习。总之这次实验让我学到了很多,使我今后的学习更加顺利轻松。
