成绩:优秀
《文献检索和和阅读》实习报告
课程名称:吴旗油田吴93井区长6油层组
流动单元研究
姓 名:※※※
班 级:研061
授课教师:于澄洁
完成日期:20##年12月14日

目 录
一中国期刊全文数据库……………………………2
二中国优秀硕博士学位论文全文数据库…………8
三中国学位论文全文数据库………………………16
四 中国专利全文数据库……………………………22
五国家科技图书文献………………………………26
六 美国石油工程师学会会议论文…………………29
七 美国工程索引……………………………………38
八 美国专利全文数据库……………………………48
九 欧洲专利全文数据库……………………………50
十 Springer全文电子期刊…………………………52
十一 OCLC FirstSearch联机检索系统…………59
十二 外文期刊整合服务系统………………………65
十三 ScienceDirect全文数据库……………………66
十四文献综述………………………………………70
一、中国期刊全文数据库
1.
灰色系统储层流动单元综合评价方法
【英文篇名】 Comprehensive evaluation method of reservoir flow unit with grey system
【作者中文名】 宋子齐; 杨立雷; 王宏; 李燕; 孙丽娜;
【作者英文名】 SONG Zi-qi; YANG Li-lei; WANG Hong; LI Yan; SUN Li-na(Xi'an Petroleum University; Xi'an 710065; China);
【作者单位】 西安石油大学; 西安石油大学 陕西西安; 陕西西安;
【文献出处】 大庆石油地质与开发, Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 编辑部邮箱 20##年 03期
期刊荣誉:中文核心期刊要目总览 ASPT来源刊 中国期刊方阵 CJFD收录刊
【关键词】 灰色系统; 流动单元; 综合评价; 分类特征; 分析方法; 实际应用;
【英文关键词】 grey system; flow unit; comprehensive evaluation; classification feature; analysis method; practical application.;
【摘要】 针对陕北斜坡中部特低渗透储层储集性能和渗流结构差异大、流动层带复杂的特点,利用灰色系统理论研究测井、钻井取心及有关地质资料,匹配、拟合和提取参数,统计分析特征值及其综合评价储层流动单元的方法。通过该区长3、长4+5特低渗储层流动单元类型和流动层带指标分析,综合考虑储层微观孔隙几何特征、沉积、成岩特征、岩性、物性及地层参数分布特征等10个参数,在其聚类分析基础上,确定了Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ类流动单元及其评价划分准则。利用矩阵分析、标准化、标准指标绝对差的极值加权组合放大及综合归一,实现了灰色系统理论集成和综合储层的多种信息,从不同角度分析评价该区特低渗透储层性质、特征和差异,指出了该Ⅰ、Ⅱ类好的流动单元分布发育的规模和范围虽然较小,但它们的渗流能力和储集能力明显较好,它们的区域和层位,是该区特低渗透储层含油有利区预测评价的主要方向。
【英文摘要】 Aiming at the large difference between the reservoir accumulation behavior and percolation structure,as well as the complex flow zones in extra-low permeability reservoir in the middle of Shanbei Slope,gray system method is used for the study of logging,drilling core and relevant geology information,matching and extracting parameters,along with the statistical analysis of characteristic value and comprehensive evaluation of flow unit.Through the index analysis of flow unit types and flow zones in extra-low ...
【DOI】 CNKI:ISSN:1000-3754.0.20##-03-017
2.
致密砂岩气藏储层流动单元划分方法及随机模拟
【英文篇名】 The Classification and Stochastic Modeling of Flow Units in Tight Gas Reservoir
【作者中文名】 唐海发; 彭仕宓; 赵彦超;
【作者英文名】 TANG Hai-fa1; PENG Shi-mi1; ZHAO Yan-chao21.Faculty of Resources and Information; China University of Petroleum; Beijing 102249; China2.Faculty of Earth Resources; China University of Geosciences; Wuhan 430074; China;
【作者单位】 中国石油大学资源与信息学院; 中国地质大学资源学院 北京;
【文献出处】 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 编辑部邮箱 20##年 03期
期刊荣誉:中文核心期刊要目总览 ASPT来源刊 CJFD收录刊
【关键词】 致密砂岩气藏; 储层; 流动单元; 随机模拟;
【英文关键词】 tight sand gas; reservoir; flow unit; stochastic modeling;
【摘要】 针对致密砂岩气藏开发中所面临的难题,以及流动单元划分中存在的问题,提出了一套致密砂岩储层流动单元划分新方法。根据流动单元的定义及其地质意义,在取心井定性和定量分析的基础上,确定了孔隙度、渗透率、流动层指数和Winland r35四个参数作为流动单元划分的指标。应用储层层次分析的研究思路,结合致密砂岩气藏的工业气流标准,识别了渗流屏障,并通过聚类分析、判别分析等统计学方法建立了连同体内部流动单元的定量识别模式,实现了流动单元由取心井到非取心井的定量识别,最后利用序贯指示模拟方法建立了流动单元的三维地质模型。进一步研究表明,应用储层流动单元方法不仅精细地刻画了河流相储层的空间非均质性,而且不同的流动单元对应着不同的开发效果。其中,A类流动单元开发效果最好,B类流动单元开发效果次之,是挖潜的主要目标,C类流动单元开发效果最差。
【英文摘要】 Many problems are encountered during the development of tight gas.Most of them are due to the reservoir heterogeneity.The authors present a novel methodology of flow unit definition in tight gas reservoir aimed to improve the reservoir description.Based on the definition of flow unit and its geological meanings,and combined with the qualitative and quantitative analysis of the cored wells,four parameters-porosity,permeability,FZI and Winland r35 are integrated into the classification of flow units.Further,t...
【基金】国家“973”项目(2002CCA00700)
【DOI】CNKI:ISSN:1671-5888.0.20##-03-008
3.
储层动态流动单元研究——以别古庄油田京11断块为例
【英文篇名】 Reservoir dynamic flow unit models of Jingll block in Bieguzhuang Oilfield
【作者中文名】 李海燕; 彭仕宓; 刘风喜;
【作者英文名】 Li Haiyan; Faculty of Resource and Information; China University of Petroleum(Beijing); Beijing City; 102249; China;
【作者单位】 中国石油大学(北京)资源与信息学院; 中国石化股份胜利油田分公司桩西采油厂 北京; 山东东营;
【文献出处】 油气地质与采收率, Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 编辑部邮箱 20##年 02期
期刊荣誉:中文核心期刊要目总览 ASPT来源刊 CJFD收录刊
【关键词】 动态流动单元; 陆相储层; 判别函数; 流动层指数; 剩余油;
【英文关键词】 dynamic flow unit; terrestrial reservoir; discriminant function; flow zone index; remaining oil;
【摘要】 流动单元是油气储集最小宏观地质单元,它综合反映了储层的岩性、物性及微观孔喉特征。在分析流动单元定义的基础上,针对高含水期油田开发,提出动态流动单元的概念和定量划分方法。以别古庄油田京11断块为例,从取心井入手,通过优选参数,将储层流动单元划分为4种类型,建立了各类流动单元的数学判别函数,对非取心井进行了流动单元划分,并应用序贯指示模拟建立了不同含水期动态的流动单元模型。研究表明,不同含水期储层流动单元类型受储层物性和流体性质的变化所控制,其分布是动态变化的,动态流动单元能够描述不同开发阶段油水运动规律相似的储集带的动态变化,不同开发阶段的剩余油分布与储层动态流动单元关系密切。实践证实了动态流动单元对剩余油预测的准确性,表明应用动态流动单元方法预测高含水期油田剩余油分布和提高采收率更具有实际意义。
【英文摘要】 Flow unit is the smallest macro-geological one in oil and gas reservoir,which reflects reservoir lithology,physical features and microscopic pore throat characteristics. Based on the analysis of the definition of flow unit, a new concept of dynamic flow unit and its quantitative classification methods are advanced especially for the high water cut oilfield development. Taking Jing11 block of Bieguzhuang Oilfield as an example, the reservoir flow units are divided into four types after parameter optimization...
【DOI】 CNKI:ISSN:1009-9603.0.20##-02-019
4.
储层流动单元研究新技术在油田开发中的应用
【英文篇名】 New Technology Applications of Reservoir Flow Unit in Oil Field Development
【作者】 江波;
【作者单位】 江苏南京华东规划设计院;
【刊名】 内蒙古石油化工 , Inner Mongolian Petrochemical Industry, 编辑部邮箱 20##年 04期
期刊荣誉:ASPT来源刊 CJFD收录刊
【关键词】 流动单元; 流动带指标(Fz); 三维储集体;
【英文关键词】 Flow unit Flow zone index 3D reservoir;
【摘要】 流动单元研究提供了精细解剖砂体,表征砂体内部非均质性的新方法。本文在传统流动单元划分的基础上应用流动带指标新方法(F z)进行储层流动单元的定量划分,为合理进行油田开发动态分析提供依据,同时开辟了一个可预测可操作的有效流动单元研究方法。
【英文摘要】 Research of Flow units is new method to describe the fine structure and the inner heterogeneous of sandstone.The applications of flow zone index is new method to quantify reservoir flow units which is precede traditional method,is benefit to oil field performance.
【DOI】 cnki:ISSN:1006-7981.0.20##-04-005
5.
储层动态流动单元及剩余油分布规律
【英文篇名】 Reservoir Dynamic Flow Unit and Remaining Oil Distribution
【作者】 高博禹; 彭仕宓; 陈烨菲;
【英文作者】 GAO Bo-yu(1); PENG Shi-mi(1); CHEN Ye-fei(2) (1.School of Resource and Information Technology; University of Petroleum; China; Beijing; 2.Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development; PetroChina; China);
【作者单位】 中国石油大学资源与信息学院; 中国石油勘探开发研究院;
【刊名】 吉林大学学报(地球科学版) , Journal of Jiling University (Earth Science Edition), 编辑部邮箱 20##年 02期
期刊荣誉:中文核心期刊要目总览 ASPT来源刊 CJFD收录刊
【关键词】 动态流动单元; 流动层指数; Kozeny-Carman公式; 渗透率纵向非均质性; 剩余油;
【英文关键词】 dynamic flow unit; flow zone indicator; Kozeny-Carman formulation; vertical permeability heterogeneity; remaining oil;
【摘要】 从应用Kozeny-Carman公式推导 FZI的过程出发,根据对大量岩心样品的统计分析,研究了FZI的基础定义和物理意义。结果表明:具有相近 FZI值的岩心样品具有较大的孔隙度、渗透率变化范围,不一定属于同一类流动单元。FZI值不能准确地表征影响流体流动的岩石物理性质,单纯采用FZI值作为划分储层流动单元的标准是值得商榷的。分析流动单元的定义及研究目的,针对高含水期油田开发,提出动态流动单元的概念和定量划分方法。以胜坨油田沙二段 3 砂组为例进行的研究结果表明:不同开发阶段的剩余油分布与储层动态流动单元关系密切,通过建立不同含水期的流动单元动态模型,应用动态流动单元方法研究高含水期油田剩余油分布规律更具有实际意义。
【英文摘要】 In accordance with the FZI deduction process from Kozeny-Carman formulation, the fundamental concept and physical significance of FZI were studied based on the statistical analysis of core data. The result indicates that the core samples with similar FZI value may have a wide range of porosity and permeability and are not necessarily belong to a same flow unit. It is questioned if the FZI value could be used as criteria to classify flow units, because it cannot accurately describe the core physical characte...
【基金】 国家重大基础研究前期研究专项基金资助(2002CCA00700)
6.
流动单元四维动态演化仿真模型研究
【英文篇名】 Four-dimensional dynamic simulation models for flow unit
【作者】 张继春; 彭仕宓; 穆立华; 孙以剑; 李建敏;
【英文作者】 ZHANG Ji-chun1 PENG Shi-mi1 MU Li-hua2 SUN YI-jian3 LI Jian-min3(1.Research Center of Oil Recovery; China University of Petroleum; Beijing; China; 2.Departmentof Petroleum Exploration and Development; Jidong Oilfield; Tangshan; 3.Research Institute of Exploration and Development; Huabei Oilfield; Renqiu; China);
【作者单位】 中国石油大学提高采收率研究中心; 冀东油田勘探开发处; 华北油田勘探开发研究院; 河北唐山; 河北任丘;
【刊名】 石油学报 , Acta Petrolei Sinica, 编辑部邮箱 20##年 01期
期刊荣誉:中文核心期刊要目总览 ASPT来源刊 中国期刊方阵 CJFD收录刊
【关键词】 油气储集层; 流动单元; 水驱开发; 物性参数; 动态演化; 四维模型;
【英文关键词】 oil and gas reservoir; flow unit; waterflooding development; physical property parameter; dynamic evolution; four-dimensional dynamic simulation model;
【摘要】 流动单元是油气储集最小宏观地质单元,应用室内岩心样品不同注入体积倍数驱替实验、不同开发阶段完钻井的测井参数评价及大量生产动态资料,研究分析了不同成因流动单元在水驱开发过程中储层宏观物性参数的演化规律,进而建立各类参数的数学演化模式,找出其相应物性参数的变化因子。并借助工作站三维地质建模软件Earthvision,在原始三维地质属性参数模型研究的基础上,加载物性参数变化因子,并经数据处理和结果提取,形成各类流动单元随开发过程的四维动态系列演化仿真模型,揭示和预测了不同开发阶段流动单元内部油水运动特点及剩余油分布状况。
【英文摘要】 Flow unit is the smallest macro-geological unit in oil and gas reservoir. By the use of laboratory displacement test of core samples with different porous volume factor, logging parameter evaluation data of completed wells in different development period and a number of production performance data, the evolution laws of reservoir's macro-physical property parameters for flow units with different geneses in the course of waterflooding development were studied and analyzed. The mathematical evolution models f...
【基金】 中国石油天然气股份公司“十五”重点科技攻关项目(No.010102 1 2)部分研究成果。
【DOI】 CNKI:ISSN:0253-2697.0.20##-01-00E
7.
流动单元四维动态演化仿真模型研究
【英文篇名】 Four-dimensional dynamic simulation models for flow unit
【作者】 张继春; 彭仕宓; 穆立华; 孙以剑; 李建敏;
【英文作者】 ZHANG Ji-chun1 PENG Shi-mi1 MU Li-hua2 SUN YI-jian3 LI Jian-min3(1.Research Center of Oil Recovery; China University of Petroleum; Beijing; China; 2.Departmentof Petroleum Exploration and Development; Jidong Oilfield; Tangshan; 3.Research Institute of Exploration and Development; Huabei Oilfield; Renqiu; China);
【作者单位】 中国石油大学提高采收率研究中心; 冀东油田勘探开发处; 华北油田勘探开发研究院; 河北唐山; 河北任丘;
【刊名】 石油学报 , Acta Petrolei Sinica, 编辑部邮箱 20##年 01期
期刊荣誉:中文核心期刊要目总览 ASPT来源刊 中国期刊方阵 CJFD收录刊
【关键词】 油气储集层; 流动单元; 水驱开发; 物性参数; 动态演化; 四维模型;
【英文关键词】 oil and gas reservoir; flow unit; waterflooding development; physical property parameter; dynamic evolution; four-dimensional dynamic simulation model;
【摘要】 流动单元是油气储集最小宏观地质单元,应用室内岩心样品不同注入体积倍数驱替实验、不同开发阶段完钻井的测井参数评价及大量生产动态资料,研究分析了不同成因流动单元在水驱开发过程中储层宏观物性参数的演化规律,进而建立各类参数的数学演化模式,找出其相应物性参数的变化因子。并借助工作站三维地质建模软件Earthvision,在原始三维地质属性参数模型研究的基础上,加载物性参数变化因子,并经数据处理和结果提取,形成各类流动单元随开发过程的四维动态系列演化仿真模型,揭示和预测了不同开发阶段流动单元内部油水运动特点及剩余油分布状况。
【英文摘要】 Flow unit is the smallest macro-geological unit in oil and gas reservoir. By the use of laboratory displacement test of core samples with different porous volume factor, logging parameter evaluation data of completed wells in different development period and a number of production performance data, the evolution laws of reservoir's macro-physical property parameters for flow units with different geneses in the course of waterflooding development were studied and analyzed. The mathematical evolution models f...
【基金】 中国石油天然气股份公司“十五”重点科技攻关项目(No.010102 1 2)部分研究成果。
【DOI】 CNKI:ISSN:0253-2697.0.20##-01-00E
8.
流动单元四维动态演化仿真模型研究
【英文篇名】 Four-dimensional dynamic simulation models for flow unit
【作者】 张继春; 彭仕宓; 穆立华; 孙以剑; 李建敏;
【英文作者】 ZHANG Ji-chun1 PENG Shi-mi1 MU Li-hua2 SUN YI-jian3 LI Jian-min3(1.Research Center of Oil Recovery; China University of Petroleum; Beijing; China; 2.Departmentof Petroleum Exploration and Development; Jidong Oilfield; Tangshan; 3.Research Institute of Exploration and Development; Huabei Oilfield; Renqiu; China);
【作者单位】 中国石油大学提高采收率研究中心; 冀东油田勘探开发处; 华北油田勘探开发研究院; 河北唐山; 河北任丘;
【刊名】 石油学报 , Acta Petrolei Sinica, 编辑部邮箱 20##年 01期
期刊荣誉:中文核心期刊要目总览 ASPT来源刊 中国期刊方阵 CJFD收录刊
【关键词】 油气储集层; 流动单元; 水驱开发; 物性参数; 动态演化; 四维模型;
【英文关键词】 oil and gas reservoir; flow unit; waterflooding development; physical property parameter; dynamic evolution; four-dimensional dynamic simulation model;
【摘要】 流动单元是油气储集最小宏观地质单元,应用室内岩心样品不同注入体积倍数驱替实验、不同开发阶段完钻井的测井参数评价及大量生产动态资料,研究分析了不同成因流动单元在水驱开发过程中储层宏观物性参数的演化规律,进而建立各类参数的数学演化模式,找出其相应物性参数的变化因子。并借助工作站三维地质建模软件Earthvision,在原始三维地质属性参数模型研究的基础上,加载物性参数变化因子,并经数据处理和结果提取,形成各类流动单元随开发过程的四维动态系列演化仿真模型,揭示和预测了不同开发阶段流动单元内部油水运动特点及剩余油分布状况。
【英文摘要】 Flow unit is the smallest macro-geological unit in oil and gas reservoir. By the use of laboratory displacement test of core samples with different porous volume factor, logging parameter evaluation data of completed wells in different development period and a number of production performance data, the evolution laws of reservoir's macro-physical property parameters for flow units with different geneses in the course of waterflooding development were studied and analyzed. The mathematical evolution models f...
【基金】 中国石油天然气股份公司“十五”重点科技攻关项目(No.010102 1 2)部分研究成果。
【DOI】 CNKI:ISSN:0253-2697.0.20##-01-00E
9.
流动单元四维动态演化仿真模型研究
【英文篇名】 Four-dimensional dynamic simulation models for flow unit
【作者】 张继春; 彭仕宓; 穆立华; 孙以剑; 李建敏;
【英文作者】 ZHANG Ji-chun1 PENG Shi-mi1 MU Li-hua2 SUN YI-jian3 LI Jian-min3(1.Research Center of Oil Recovery; China University of Petroleum; Beijing; China; 2.Departmentof Petroleum Exploration and Development; Jidong Oilfield; Tangshan; 3.Research Institute of Exploration and Development; Huabei Oilfield; Renqiu; China);
【作者单位】 中国石油大学提高采收率研究中心; 冀东油田勘探开发处; 华北油田勘探开发研究院; 河北唐山; 河北任丘;
【刊名】 石油学报 , Acta Petrolei Sinica, 编辑部邮箱 20##年 01期
期刊荣誉:中文核心期刊要目总览 ASPT来源刊 中国期刊方阵 CJFD收录刊
【关键词】 油气储集层; 流动单元; 水驱开发; 物性参数; 动态演化; 四维模型;
【英文关键词】 oil and gas reservoir; flow unit; waterflooding development; physical property parameter; dynamic evolution; four-dimensional dynamic simulation model;
【摘要】 流动单元是油气储集最小宏观地质单元,应用室内岩心样品不同注入体积倍数驱替实验、不同开发阶段完钻井的测井参数评价及大量生产动态资料,研究分析了不同成因流动单元在水驱开发过程中储层宏观物性参数的演化规律,进而建立各类参数的数学演化模式,找出其相应物性参数的变化因子。并借助工作站三维地质建模软件Earthvision,在原始三维地质属性参数模型研究的基础上,加载物性参数变化因子,并经数据处理和结果提取,形成各类流动单元随开发过程的四维动态系列演化仿真模型,揭示和预测了不同开发阶段流动单元内部油水运动特点及剩余油分布状况。
【英文摘要】 Flow unit is the smallest macro-geological unit in oil and gas reservoir. By the use of laboratory displacement test of core samples with different porous volume factor, logging parameter evaluation data of completed wells in different development period and a number of production performance data, the evolution laws of reservoir's macro-physical property parameters for flow units with different geneses in the course of waterflooding development were studied and analyzed. The mathematical evolution models f...
【基金】 中国石油天然气股份公司“十五”重点科技攻关项目(No.010102 1 2)部分研究成果。
【DOI】 CNKI:ISSN:0253-2697.0.20##-01-00E
10.
流动单元四维动态演化仿真模型研究
【英文篇名】 Four-dimensional dynamic simulation models for flow unit
【作者】 张继春; 彭仕宓; 穆立华; 孙以剑; 李建敏;
【英文作者】 ZHANG Ji-chun1 PENG Shi-mi1 MU Li-hua2 SUN YI-jian3 LI Jian-min3(1.Research Center of Oil Recovery; China University of Petroleum; Beijing; China; 2.Departmentof Petroleum Exploration and Development; Jidong Oilfield; Tangshan; 3.Research Institute of Exploration and Development; Huabei Oilfield; Renqiu; China);
【作者单位】 中国石油大学提高采收率研究中心; 冀东油田勘探开发处; 华北油田勘探开发研究院; 河北唐山; 河北任丘;
【刊名】 石油学报 , Acta Petrolei Sinica, 编辑部邮箱 20##年 01期
期刊荣誉:中文核心期刊要目总览 ASPT来源刊 中国期刊方阵 CJFD收录刊
【关键词】 油气储集层; 流动单元; 水驱开发; 物性参数; 动态演化; 四维模型;
【英文关键词】 oil and gas reservoir; flow unit; waterflooding development; physical property parameter; dynamic evolution; four-dimensional dynamic simulation model;
【摘要】 流动单元是油气储集最小宏观地质单元,应用室内岩心样品不同注入体积倍数驱替实验、不同开发阶段完钻井的测井参数评价及大量生产动态资料,研究分析了不同成因流动单元在水驱开发过程中储层宏观物性参数的演化规律,进而建立各类参数的数学演化模式,找出其相应物性参数的变化因子。并借助工作站三维地质建模软件Earthvision,在原始三维地质属性参数模型研究的基础上,加载物性参数变化因子,并经数据处理和结果提取,形成各类流动单元随开发过程的四维动态系列演化仿真模型,揭示和预测了不同开发阶段流动单元内部油水运动特点及剩余油分布状况。
【英文摘要】 Flow unit is the smallest macro-geological unit in oil and gas reservoir. By the use of laboratory displacement test of core samples with different porous volume factor, logging parameter evaluation data of completed wells in different development period and a number of production performance data, the evolution laws of reservoir's macro-physical property parameters for flow units with different geneses in the course of waterflooding development were studied and analyzed. The mathematical evolution models f...
【基金】 中国石油天然气股份公司“十五”重点科技攻关项目(No.010102 1 2)部分研究成果。
【DOI】 CNKI:ISSN:0253-2697.0.20##-01-00E
11.
应用流动单元寻找油田有利挖潜区的新思路
【英文篇名】 A new method of searching the advantaged potential area of oil field by utilizing flow units
【作者】 谢俊; 武英利; 梁会珍; 张万里;
【英文作者】 XIE Jun~1; WU Ying-li~1; LIANG Hui-zhen~1; ZHANG Wan-li~2(1. Shandong University of Science and Technology; Tai′an; Shandong; China; 2. Xi′an Petroleum University; Xi′an; Shaanxi; China);
【作者单位】 山东科技大学; 西安石油大学; 山东泰安; 陕西西安;
【刊名】 西北地质 , Northwestern Geology, 编辑部邮箱 20##年 04期
期刊荣誉:ASPT来源刊 CJFD收录刊
【关键词】 流动单元; 油藏描述; 剩余油; 挖潜区;
【英文关键词】 flow unit; reservoir description; remaining oil; advantaged potential area;
【摘要】 储层流动单元在石油勘探开发领域方面的应用已引起国内外专家学者的广泛关注,但其研究目前主要局限在"静"的方式上,即采用储层静态多参数聚类分析方法研究储集体的宏观非均质单元,而很少考虑油藏实际生产的动态资料,如,注采井网、射孔状况、开采强度、开采措施等。笔者在分析流动单元研究现状的基础上,认为将准确的流动单元划分与定量的剩余油描述有机结合,即"动静"结合,是寻找有利挖潜区的最佳方法,并运用实例说明了该方法在油田生产实践中的应用,对提高油田采收率具有重要的指导意义。
【英文摘要】 Extensive attention has been paid to reservoir flow units being used in the field of exploration and development of oil field , but the study is restricted in the static way—the macroscopic heterogeneity is studied by clustering method in virtue of only the static reservoir parameters, seldom the dynamic production data such as injection-production well pattern, perforating parameter, development status, adjustment measures. The authors analyzed the study status of flow unit, considered that the combine of...
【DOI】 CNKI:ISSN:1009-6248.0.20##-04-008
二、中国优秀硕博士学位论文全文数据库
1. 濮城油田沙二上2+3油藏流动单元研究
【英文题名】Flow Units Study for No.2+3 Sand Group of the Upper of ES2 Oil Recovery in Pu Cheng Oil Field
【作者中文名】李中超;
【导师】陈程; 陈昊;
【学位授予单位】中国地质大学(北京);
【学科专业名称】石油与天然气工程
【学位年度】2006
【论文级别】硕士
【网络出版投稿人】中国地质大学(北京)
【网络出版投稿时间】20##-06-22
【关键词】流动单元; 分类评价; 建模; 高含水油藏;
【英文关键词】flow unit; classification and estimation; modeling; mature oil field;
【中文摘要】针对濮城油田沙二上 2+3 油藏的地质及开发特征,在对流动单元研究技术的研究历史和最新进展研究的基础上,提出了流动单元划分对比、分类、预测(建模)、评价及其在剩余油预测和挖潜中的应用等一整套工作思路,为高含水油田的开发调整提供了依据。在系统分析了濮城油田沙二上 2+3 油藏储层的各种动静态资料的基础上,弄清了其沉积、微构造、隔夹层、流动单元分布规律,建立了该油田流动单元模型,通过开发动态分析及油藏数值模拟,揭示了剩余油形成机理、分布规律,指导了油田开发调整。取得的主要认识如下: 1、通过高分辨率层序地层对比,将濮城油田沙二上 2+3 砂组在原来 14 个小层的基础上细化为 19 个小层(短期旋回),细化后,使得无法解决的部分层内矛盾转化为层间矛盾,为开发调整提供了一定的依据; 2、依据分析化验资料,采用神经网络算法,设计了相应的物性解释软件,在对测井资料区域化校正基础上,对未取心井储层进行了分段相控物性解释; 3、将概率分布图引入到流动单元分类中,通过对各种储层指标的对比和筛选,确定了濮城油田沙二上 2+3 流动单元划分、识别、分类标准,分类参数主要选取渗透率、流动系数、储集系数等,形成了流动单元...
【英文摘要】According to reservoir geological and development's character no. 2+3 sand group ofthe upper of ES2 oil recovery in Pu Cheng oil field, based on the early study of flow unitby others, a set of methodology for flow unit recognition, correlation, classification,prediction (modeling), evaluation and its application in the remaining oil prediction andimproved oil recovery is founded, which gives a new way for mature oil field improvingits recovery. The study makes it clear that such characters as facies, micro-...
【DOI】CNKI:CDMD:2.2006.060251
2、靖安油田大路沟一区长2储层精细油藏描述
【英文题名】 Fine Reservoir Description of Chang2 Reservoir of Yanchang Formation in the First Part of Dalugou Area of Jing'an Oil Field
【作者中文名】 陈欢庆;
【导师】 曲志浩;
【学位授予单位】 西北大学;
【学科专业名称】 矿物学、岩石学、矿床学
【学位年度】 2006
【论文级别】 硕士
【网络出版投稿人】 西北大学
【网络出版投稿时间】 20##-08-01
【关键词】 精细油藏描述; 高分辨率层序地层学; 沉积微相; 流动单元; 地质建模;
【英文关键词】 fine reservoir description; high-resolution sequence stratigaphy; sedmentary microfacies; flow unit; modeling of geology;
【中文摘要】 本文以现代精细油藏描述新的理论作为指导,运用石油地质学、高分辨率层序地层学、沉积学、储层地质学、储层三维地质建模等理论与技术方法,进行了靖安油田大路沟一区长2储层精细油藏描述研究。研究中采用新的地质、地球物理测井、录井、试油及各种分析测试资料,从小层精细划分与对比、沉积微相、储层综合评价分类、流动单元、地质建模等多方面进行分析,并最终建立了油藏的三维精细地质模型。研究结果对鄂尔多斯盆地靖安油田大路沟一区延长组长2油藏的勘探和开发具有重要的理论意义和实践价值。 通过研究所取得的主要成果与创新有: 1、首次将高分辨率层序地层学原理与等高程切片法、动静态资料验证法等技术方法相结合,用于研究区长2油藏的小层划分与对比,有效地克服和避免了以往单纯的沉积旋回在鄂尔多斯盆地岩性油气藏中划分小层所遇到的困难和错误,准确地建立了研究区目的层油藏的等时地层格架,并丰富了河流相储层小层划分与对比理论。 2、结合区域沉积背景,进行了油藏范围内的沉积微相研究,在确定辫状河沉积亚相的基础上分别识别出河道、河道砂坝、废弃河道、河道间和河漫滩等五种微相类型。同时对研究区目的层的岩相特征进行了分析。在上述研...
【英文摘要】 Based on the new theories of modern fine reservoir description , by using theories and techniques of the petroleum geology ,high-resolution sequence stratigaphy ,sediments ,reservoir geology ,modeling of geology, carried out the research of the fine reservoir description of Chang2 reservoir of Yanchang Formation in the First part of Dalugou Area of Jing'an Oil Field. In these studies ,the new geology ,well logging of physical geography ,well gathering ,test oil ,chemical analysis date and all other useful d...
【DOI】 CNKI:CDMD:2.2006.090004
3.薄互层砂岩油藏(沈67断块)剩余油分布与挖潜优化研究
【英文题名】 The Study on the Residual Oil Distribution Regulation and Development Optimization of Remaining Potential Reserves in the Thin Interbedded Sand Reservoir in Fault Block Shen 67, Liaohe Oilfield
【作者中文名】 许宁;
【导师】 吕延防; 张方礼;
【学位授予单位】 大庆石油大学;
【学科专业名称】 地质工程
【学位年度】 2006
【论文级别】 硕士
【网络出版投稿人】 大庆石油大学
【网络出版投稿时间】 20##-11-15
【关键词】 薄层; 砂岩; 剩余油分布; 挖潜; 油藏数值模拟; 沉积微相;
【英文关键词】 Thin sand zone; residual oil distribution; development potential reserves; reservoir numerical simulation; sedimenation microfacies;
【中文摘要】 本论文以典型薄互层砂岩油藏沈67断块为例,在全油田测井资料标准化基础上,通过多井数字处理及评价,精确确定储层岩性、物性、含油性参数,并针对本区测井数据的特点,研究本区储层级别分类,以提高对储层的解释精度;通过分析测试及生产动态资料,分析储层在长期开采过程中储层渗流通道和孔隙结构的变化,预测储层中的大通道,为调整注采关系服务。借助先进的GOCAD储层三维建模软件系统,建立起反映研究区储层空间非均质的三维模拟模型,通过数值模拟,精确预测井间储层参数变化规律及剩余油分布规律,以期为该类型油田开发中后期的合理、有效调整发挥积极作用。 通过本次研究,形成了适应薄互层砂岩油藏的描述及开发调整的一些新观点: (1)薄互层砂岩油藏纵向层次分析及横向结构分析的新观点 (2)应用细分沉积相技术,从成因上深入研究储层 (3)不同规模储层概率相新观点及其研究技术 (4)基于三维模型基础上的整体油藏数值模拟技术 (5)相控注水、单元重组及分层系二次开发 经过多年的开发,油田已进入高含水开发阶段,为了确保油田更长期的稳产,除进行主力油层的开发层系调整外,还要对薄差油层、表...
【英文摘要】 The paper Studies on typical thin interbedded sand reservoir Fault block Shen 67 to generalize the residual oil distribution regulation and measures to develop the potential reserves for this kind of reservoir. In this study, the reservoir lithology, physical property and oil bearing parameter are accurately defined through the multi-well data processing and evaluation first, based on the standardized logging data of the whole oil field, then the reservoir classifiin order to improve the reservoir inte...
【DOI】 CNKI:CDMD:2.2006.172426
4.储层流动单元研究在沈67块精细油藏描述中的应用
【英文题名】 The Application of the Study on the Reservoir Flow Unit in Reservoir Description in Block Shen67
【作者中文名】 王威;
【导师】 刘晓冬; 李军生;
【学位授予单位】 大庆石油大学;
【学科专业名称】 地质工程
【学位年度】 2006
【论文级别】 硕士
【网络出版投稿人】 大庆石油大学
【网络出版投稿时间】 20##-11-15
【关键词】 储层流动单元; 油藏描述; 储层三维建模; 油气分布规律; 沈67块;
【英文关键词】 reservoir flow unit; reservoir description; reservoir 3D modeling; oil and gas distribution regularity; Block Shen67;
【中文摘要】 本文以野外露头研究、现代沉积调查、密井网解剖等资料的地质知识库为理论指导,综合岩心、测井、吸水剖面以及分层测试等静态、动态资料,运用精细构造解释对沈67块目的层段储层构造形态、断层的倾角、分布及密封性进行研究,研究单砂体的起伏变化所显示的微构造特征,包括小高点、小构造、小断层等,描述微构造剩余油富集的有利圈闭及微构造与剩余油的关系;运用非均质油藏渗流地质学分析等技术从层内、层间和平面3个方面,分析了沈67块夹层、隔层、砂体垂向韵律、孔渗等物性对储层非均质性的影响,在沈67块目的层段地层、微构造、沉积微相、储层非均质性、油层分布等地质特征研究基础上,利用流动单元划分技术进行了储层流动单元研究,在沉积模型、构造模型以及非均质模型的基础上,结合储层测井参数解释结果,分别建立了油藏规模、小层规模的储层三维地质模型,基本上掌握了沈67块目的层段各种参数及其空间分布规律,建立了1个相对准确反映油气藏非均质性的储层地质模型,弄清了研究区储层结构类型及砂体的空间展布、砂体连续性及砂体间的连通性。对指导油气田的勘探和开发,提高勘探的成功率和开发阶段的采收率具有重要的意义。
【英文摘要】 With field ourcrop, modern sedimentation investigation and dense pattern study as theoretical guidance, coupled with coring, logging, water in-take profiled and individual layer test data, this paper addresses the reservoir structure style, fault dip, distribution and confining ability in Block Shen67 by using precise structure interpretation, micro structure characteristics due to single sand relief change, including minor highs, small structures and faults, residual oil of microstructures and the rel...
【DOI】 CNKI:CDMD:2.2006.172357
5.濮城油田沙二上2+3油藏流动单元研究
【英文题名】 Flow Units Study for No.2+3 Sand Group of the Upper of ES2 Oil Recovery in Pu Cheng Oil Field
【作者中文名】 李中超;
【导师】 陈程; 陈昊;
【学位授予单位】 中国地质大学(北京);
【学科专业名称】 石油与天然气工程
【学位年度】 2006
【论文级别】 硕士
【网络出版投稿人】 中国地质大学(北京)
【网络出版投稿时间】 20##-06-22
【关键词】 流动单元; 分类评价; 建模; 高含水油藏;
【英文关键词】 flow unit; classification and estimation; modeling; mature oil field;
【中文摘要】 针对濮城油田沙二上 2+3 油藏的地质及开发特征,在对流动单元研究技术的研究历史和最新进展研究的基础上,提出了流动单元划分对比、分类、预测(建模)、评价及其在剩余油预测和挖潜中的应用等一整套工作思路,为高含水油田的开发调整提供了依据。在系统分析了濮城油田沙二上 2+3 油藏储层的各种动静态资料的基础上,弄清了其沉积、微构造、隔夹层、流动单元分布规律,建立了该油田流动单元模型,通过开发动态分析及油藏数值模拟,揭示了剩余油形成机理、分布规律,指导了油田开发调整。取得的主要认识如下: 1、通过高分辨率层序地层对比,将濮城油田沙二上 2+3 砂组在原来 14 个小层的基础上细化为 19 个小层(短期旋回),细化后,使得无法解决的部分层内矛盾转化为层间矛盾,为开发调整提供了一定的依据; 2、依据分析化验资料,采用神经网络算法,设计了相应的物性解释软件,在对测井资料区域化校正基础上,对未取心井储层进行了分段相控物性解释; 3、将概率分布图引入到流动单元分类中,通过对各种储层指标的对比和筛选,确定了濮城油田沙二上 2+3 流动单元划分、识别、分类标准,分类参数主要选取渗透率、流动系数、储集系数等,形成了流动单元...
【英文摘要】 According to reservoir geological and development's character no. 2+3 sand group ofthe upper of ES2 oil recovery in Pu Cheng oil field, based on the early study of flow unitby others, a set of methodology for flow unit recognition, correlation, classification,prediction (modeling), evaluation and its application in the remaining oil prediction andimproved oil recovery is founded, which gives a new way for mature oil field improvingits recovery. The study makes it clear that such characters as facies, micro-...
【DOI】 CNKI:CDMD:2.2006.060251
6.克拉玛依五2西克下组砾岩油藏储层流动单元研究
【作者】董同武;
【导师】张廷山; 蓝光志;
【学位授予单位】西南石油学院;
【学科专业名称】矿产普查与勘探
【学位年度】2005
【论文级别】硕士
【网络出版投稿人】西南石油学院
【网络出版投稿时间】20##-01-11
【关键词】砾岩油藏; 低渗透率; 流动带指标; 流动单元划分; 剩余油;
【英文关键词】Conglomerate reservoir; Low permeability; Flow zone index; Division of flow unit; Remaining oil;
【中文摘要】储层流动单元研究是国外20世纪80年代中后期开始兴起的一种储层非均质研究方法。储层流动单元是指储集体空间上具有相同渗流特征的三维连续储集体,是储层中最小流体储集和运动单元。 通过对五2西克下组沉积、成岩、储层构造特征和开发动态认真分析研究,在单砂层划分和沉积微相描述的基础上,进一步识别复合砂体中的单砂体,应用FZI(流动层带指标)对各连通单元及其内部储层质量进行划分和评价,在连通砂体内进行流动单元的划分,建立孔隙度、渗透率和饱和度测井评价模型,为非取芯井各层段流动单元的划分提供有效数据体,研究了该区流动单元的边界条件,认清流动单元的空间分布,并预测剩余油的分布规律,得出以下结论和认识: 1、静态储层地质参数与流体动态变化参数综合表征是流动单元研究显著特点,流动单元过程不但受储层非均质性自身条件和流体性质的影响,同时还受开发方式等外部条件的影响,但储层非均质性是根本。 2、流动单元强调连通体内部渗流特征的差异,在同一流动单元内部,影响流体流动(渗流)的地质因素、流体因素和外部生产措施因素相同,则具有相同的水动力学特征和渗流特征。 ...
【英文摘要】The research on reservoir flow unit is a method of heterogeneity of reservoir, which sprang up in later 1980s. The definition of reservoir flow unit is a 3D successive volume of reservoir rock with the same character of seep and the least unit of deposit and moving fluid.By strict analysis and research on sediment, diagenesis, characteristics of reservoir structure and dynamic development of reservoir in western Wu2 district, single sandbody was identified form multiple sandbody based on division of single ...
【DOI】CNKI::CDMD:10615.2.2005.1827
7、储层流动单元研究及其应用
【英文题名】 Research on Reservoir Flow Unit and Application
【副题名】 以大港枣南油田为例
A Case from Zaonan Oil Field
【作者中文名】 段贺海;
【导师】 吴淦国; 樊太亮;
【学位授予单位】 中国地质大学(北京);
【学科专业名称】 构造地质学
【学位年度】 2005
【论文级别】 博士
【网络出版投稿人】 中国地质大学(北京)
【网络出版投稿时间】 20##-07-19
【关键词】 流动单元; 储层建筑结构; 开发方案; 数值模拟;
【英文关键词】 Flow Unit; Reservoir Structure; Engineer project; Simulation;
【中文摘要】 在对储层流动单元研究成果深入调研的基础上,开展了对储层流动单元的系统研究,包括流动单元划分方法研究、流动单元综合分析、储层三维建模、油藏数值模拟、油藏工程分析、开发方案的制定和开发效果的预测等。枣南油田孔一段V油组储层为例开展了储层流动单元的实例研究和方案的实施。 应用高分辨率层序地层学研究理论和层次分析方法进行了等时地层单元的划分,建立了包括准层序、小层、单砂层和成因单砂体在内的多级地层格架并对小层、单砂体层、成因砂体等级别的储层进行了参数解释和集总。 进行了小层及成因砂体两个层次储层的微相类型划分并提出了比例相的概念,认为利用河道主体砂岩的比例描述单砂体层乃至小层的微相特征可以防止平均化现象,更准确的描述微相展布。分析了储层成岩作用类型及特征,通过薄片资料对储层微单元体复杂成岩系统进行了量化表征并研究了各类成岩作用对储层物性的贡献比率。 通过对储层确定性插值剖面和切片的分析,建立了储层建筑结构模型,总结了储层结构样式并研究了储层结构模型的形成机理。认为成因砂体作为自然连通体,这一级别的储层不但具有可操作性,而且对其进行深入研究可对开发中后期油田的生产具有十分重要的现实意...
【英文摘要】 A comprehensive research is carried out on Reservoir Flow Units and Its Application, including division of Reservoir Flow Units, relations between Reservoir Flow Units to production responses, 3D reservoir modeling, reservoir simulation and engineering project. A case is from Zaonan Oil Field adapted.The structure of isochronal stratum is builded by the high- frequency sequence stratigraphy and hiberarchy analysis methods including parasequence layer, sand body and genie sand body. Reservoir property parame...
【DOI】 CNKI:CDMD:1.2005.102589
8.砾岩低渗透油藏注水开发后期流动单元研究
【作者】胡新平;
【导师】李允; 闻玉贵;
【学位授予单位】西南石油学院;
【学科专业名称】石油与天然气工程
【学位年度】2005
【论文级别】博士
【网络出版投稿人】西南石油学院
【网络出版投稿时间】20##-01-11
【关键词】流动单元; 砾岩油藏; 低渗透; 油田开发后期; 宕相单元;
【英文关键词】flow unit; conglomerate reservoirs; low permeability; latter period of oilfield development; lithofacies unit;
【中文摘要】流动单元的提出从油藏地质角度进一步解剖和精细刻画出层间、平面和小层内部及孔喉规模上的储层非均质特性;同时也表征出了流体在储层中运动的轨迹和差异,是储层地质与油藏开发动态有机结合的桥梁和纽带。其井间对比及空间结构问题更需要露头和现代沉积的精细研究及随机建模予以解决。在这些综合交叉科学研究和庞杂的技术系列工程中,本文选择准噶尔盆地西北缘砾岩低渗透攻关难题,从注水开发后期要解决的实际矛盾出发,突出实用性是关键,探索出了一套适合本地区油藏地质特点的流动单元研究理论和技术方法,不断地向砾岩低渗透油藏极限采收率挑战。 块状非均质砾岩油藏注水开发要比层状砂岩油藏复杂得多,低渗透非线性渗流注水开发难度大,因此开展砾岩低渗透油藏流动单元研究目前在国内外尚处于前缘性研发阶段。在跟踪分析近20年国内外流动单元研究方面最新动态的基础上,本文认为流动单元是介于静态地质和油藏动态的交叉学科,必须考虑流体因素,等渗流特征是最基本性质,而不仅仅是沉积微相研究和储层评价,只有将流体性质和外部采油工艺措施条件引入其中,才能反映出目前油水在储集体空间上的渗流差异。因而论文从流动单元细分与对比、边界条件...
【英文摘要】The views of flow unit point out that heterogeneity of reservoirs should be deeply studied and interpreted in terms of reservoir geology, from interbed, latitude and thin-layer to pore-throat. They can also be used to pose the orbits and differences of reservoir fluids. So the study of flow unit is a bridge connecting reservoir geological characteristics and dynamic oil developments. The inter-well-contrasting and frame-building are depended on delicate study of modern sediments and random modeling. Out of ...
【DOI】CNKI::CDMD:10615.2.2005.2171
9.
中国北方典型陆相油藏注水开发中后期流动单元研究
【英文题名】Study on the Flow Units of Typical Continental Oil Reservoir of Northern China During Medium-late Stage of Waterflood
【作者】师永民;
【导师】肖荣阁;
【学位授予单位】中国地质大学(北京);
【学科专业名称】矿物学、岩石学、矿床学
【学位年度】2005
【论文级别】博士
【网络出版投稿人】中国地质大学(北京)
【网络出版投稿时间】20##-07-19
【关键词】流动单元; 陆相非均质油藏; 油田开发中后期; 注水开发; 岩相单元;
【英文关键词】flow unit; continental facies anisotropic reservoir; medium-late stage of oilfield development; water-flood; litho-facies units;
【中文摘要】流动单元研究是国外80年代中后期开始兴起的一种综合描述油田开发过程中油水运动差异,水驱油效率差异和剩余油饱和度分布差异等流体分布和变化过程的应用基础学科和前缘学科。它的含义是指储层内部构成相同渗流能力的三维连续储集体,在同一流动单元内储层的岩性、物性、内部建筑结构相同或相近,流体性质和开采方式接近,造成水淹特征相同或接近,渗流性相对独立;其外部具有较好的隔挡界面或渗流屏障。流动单元的理论基础是建立在储层沉积学、测井地质学、油层物理、渗流力学和现代数学之上,遵循高频率等时地层格架条件下储层连通体内部流体等渗流原理、叠加原理、延展原理和层次单元分析方法。本文选择松辽盆地南部葡北油田葡I 组油层、大庆长垣西部龙虎泡油田萨尔图油层、大庆长垣中部杏树岗油田杏13 井区葡I 组油层、吉林红岗油田萨尔图油层和克拉玛依油田五2西克下组砾岩低渗透油藏作为研究实例,从注水开发后期要解决的实际矛盾出发,突出实用性是关键,探索出了一套适合中国陆相非均质油藏特点的注水开发中后期流动单元研究理论和技术方法。研究思路和创新点在于认为流动单元是介于静态地质和油藏动态之间的交叉学科,必须考虑流体因素和采油工艺措...
【英文摘要】The studies of flow units belong to a kind of application science or advancing edge subject born in 1980s, which widely describe fluid distribution and fluid flowing process during development of a oilfield: moving differences between oil and water, efficiency differences for waterflood oil, and distribution differences of the residual-oil-saturation, etc. The definition of flow units is three-dimension continuous reservoirs, and the lithological, physical and internal structure characteristics of a same fl...
【DOI】CNKI::CDMD:82501.2.2005.2578
10.
喇嘛甸油田北北块河流相储层流动单元划分
【英文题名】Classification of Fluvial Reservoir Flow Unit in the North Part of the North Section in Lamodian Oil Field
【作者】于生云;
【导师】李椿; 黄伏生;
【学位授予单位】大庆石油学院;
【学科专业名称】矿产普查与勘探
【学位年度】2004
【论文级别】硕士
【网络出版投稿人】大庆石油学院
【网络出版投稿时间】20##-05-14
【关键词】沉积相; 灰色关联法; 流动单元; 储层非均质性; 剩余油;
【英文关键词】Sedimentary facies; the Grey Association Method; Flow unit; Reservoir heterogeneity; Residual oil;
【中文摘要】随着油田的不断开发,我国东部许多老油田已进入高含水期开采阶段,保持油气产量的稳定面临严竣的挑战,而高含水油田稳产的关键取决于对剩余油分布的认识程度。八十年代以来,随着对储层流动单元研究的不断深入,它越来越广泛地被应到油藏描述和剩余油研究中来,流动单元研究对于认识储层的非均质性、提高油藏描述精度、搞清剩余油分布具有重要的理论意义和实际意义。 首先,本文以喇嘛甸油田北北块聚合物驱井网葡I1-2砂岩组为研究目的层,应用储层建筑结构解剖的知识和河流-三角洲相油层对比方法,绘制了各沉积单元的沉积相带图,为平面流动单元的划分提供了地质基础,同时,划分了垂向流动单元。 在划分平面流动单元的多种方法中,经过对比,发现灰色关联法划分的流动单元不但能体现成因特征,而且能较好的与生产动态相吻合,所以选用了灰色关联法作为划分平面流动单元的最佳方法。用此法把研究区储层划分为A、B、C、D四种不同类型的流动单元,并提出了平面流动单元有三种分布形式:独立分布型、平面联合型、垂向复合型。 在流动单元划分基础上,对研究区储层的非均质性进行了详细的描述。 结合油藏工程...
【英文摘要】With the development of oil fields,many old reservoirs in the east of China enter the high water-bearing development period.Sustaining a high and stable production rate faces severe challenge .The key to preserve oil output in high water cut period is dependent upon the understanding degree to the properties of residual oil distribution.From 1980's,while the study of the reservoir flow unit was proceeded alongside,it has been more widely utilized to characterize reservoir feature and remnant oil distribu...
【DOI】CNKI::CDMD:10220.2.2004.0715
三、中国学位论文全文数据库
1.
【论文题名】:白豹油田长3、长4+5储层评价及有利区预测研究
【作者】:潘玲黎
【作者专业】:油气田开发工程
【导师姓名】:宋子齐
【授予学位】:硕士
【授予单位】:西安石油大学
【授予单位新名或规范名称】:
【授予学位时间】: 20060515
【分类号】: TE321 P612
【关键词】:白豹油田、沉积微相、有利流动单元、含油有利区、储层评价、储层预测。
摘要:
本文以沉积学、测井地质学、测井解释技术为指导,综合岩心、钻测井、分析化验及开发资料对白豹油田长3、长4+5特低渗储层进行评价,筛选相对高渗高产含油有利区,阐明有利油气富集方向及规律,为油田增储上产提供了有利目标区。其主要成果和认识如下:①对该区1400km2范围100余口探井、评价井及开发井长3、长4+5地层进行了小层对比划分,完成了地层对比骨干剖面、构造、储层和油藏研究图件。②研究了单井相序组合、剖面和平面微相展布特征及规律,确认了该区长3、长4+5三角洲前缘亚相的4个微相,以其水下分流河道和河道叠置型河口坝微相为最为有利成藏相带。③开展了该区储层特征综合研究,阐明了特低渗透储层四性关系、储集特征及孔隙结构特征。④利用灰色系统理论流动单元研究了该区特低渗储层综合评价,按其渗流能力和储集能力把储层划分为Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ类流动单元,相应的储层评价为一、二、三、四类。认为该区Ⅰ、Ⅱ类好的流动单元分布发育规模和范围虽然较小,但它们圈定的区域和层位控制了含油有利区主要范围。⑤采用有利沉积、储集相带和初试产量及测井解释分析,特别是利用有利流动单元拟合各种控制因素圈定含油面积,以及研究特低渗储层测井建立有效厚度下限及夹层扣除标准确定各油层有效厚度,分别从长4+511等目的层段预测和筛选含油有利区24个。这些含油有利区控制的范围是该区特低渗储层增储上产的主要方向,他们不仅反映出河道主体带中部向南西方向含油有利区连片的规模及范围,而且勾画出中部油藏与南西部华池油藏连片延伸趋势、形态和特征,为该区油田进一步滚动扩边开发提供了可靠依据。
文摘语种:中文文摘
论文页数:1-63
数据库名:中国学位论文全文数据库
2.
【论文题名】:砂(砾)岩油藏储层流动单元研究——以沙南油田沙丘5井区为例
【作者】:马斌
【作者专业】:矿产普查与勘探
【导师姓名】:罗明高
【授予学位】:硕士
【授予单位】:西南石油大学
【授予单位新名或规范名称】:
【授予学位时间】: 20060601
【分类号】: P618.130.2
【关键词】:沙南油田、沙丘区、砂岩油藏、储层流动单元、渗流屏障。
【摘要】:
本文在对储层流动单元研究方法进行深入调研的基础上,开展了对储层流动单元的系统研究,包括流动单元划分方法研究、流动单元综合评价、流动单元与油田开发动态相关关系分析等。并以沙南油田沙丘5井区为例开展了储层流动单元的实例研究。 此次研究以层次分析思想为指导,首先采用“旋回对比、厚度控制、不同相带区别对待”的方法进行了地层单元的划分对比,建立了包括小层、单砂层在内的多级地层格架。利用岩心分析化验成果刻度测井资料,建立了物性解释模型,并对储层进行了解释和参数统计。 然后,从定量研究的角度,分别采用了概率统计法和系统聚类分析法对取心井段进行了流动单元划分,运用概率统计法将该区流动单元划分为4类。在取心井划分流动单元的基础上,选取了有效孔隙度φe、渗透率K、孔隙体积与颗粒体积之比φz、油藏品质指数RQI,流动带指数FZI、泥质含量Vsh,共6个影响渗流的主要参数来刻画流动单元。对非取心井使用逐步判别分析法,建立了流动单元判别模型,进行了流动单元划分。综合参考各类储层特有的沉积模式、水流能量分布规律和平面非均质特征,对流动单元平面、剖面及空间展布进行了描述。 通过对研究区流动单元划分结果分析发现,流动单元的成因及其影响因素是十分复杂的,主要包括沉积作用、成岩作用和构造作用,而沉积作用对流动单元特性和分布的影响最为基础和重要。同一流动单元内具有相似的渗流特性,每个流动单元的渗透率、孔隙度等储层物性在一定范围内变化,不同流动单元之间储、渗能力差异显著,且有明显的边界。流动单元渗流屏障包括沉积泥岩隔夹层、成岩胶结带、封闭性断层等,研究表明沉积泥岩隔夹层和钙质胶结带是本油藏油水运动的主要屏障。 应用方面以小层流动单元划分结果为基础,对流动单元的产吸剖面、单井初期产能进行了分析。结果发现流动单元类型与储层的产吸状况对应较好,油井初期产能与Ⅰ-Ⅱ类流动单元厚度也有着很好的对应关系,说明流动单元分布对油田开发起着一定的控制作用,流动单元的合理划分对开发方案调整具有良好的指导作用。 通过本次研究,形成了对本地区砂(砾)岩储层流动单元研究的一套系统研究思路、方法,构建和完善了相关知识体系结构。论文的研究思路和方法对其它油田流动单元研究也具有较大的参考和适用价值。
【文摘语种】:中文文摘
【论文页数】: 1-78
【数据库名】:中国学位论文全文数据库
3.
【论文题名】:新民油田沉积微相及流动单元研究
【作者】:王继平
【作者专业】:矿产普查与勘探
【导师姓名】:马世忠
【授予学位】:硕士
【授予单位】:大庆石油学院
【授予单位新名或规范名称】:
【授予学位时间】: 20050316
【分类号】: P618.13、TE327
【关键词】:沉积微相、流动单元、剩余油分布、河流相储层、低渗透油田、地质构造。
【摘要】:
本文以新民油田扶杨油层为例,综合运用精细沉积微相研究、储层非均质性研究和流动单元研究三项技术方法,对河流相储层非均质性、渗流规律及剩余油分布规律进行了深入研究。 新民油田扶杨油层属“低渗透”储层,储层主要为分流河道,为弄清生产过程中出现的各种矛盾及水淹规律,掌握剩余油的分布特征,本次研究在垂向上把小层细分为时间单元,每一个沉积时间单元对应一个河道期。然后对每一个沉积时间单元进行精细沉积微相研究,利用同一沉积时间单元每一井点的成因信息、沉积微相及组合理论模式、区域沉积模式(沉积体系、水系方向、相类型等)大量信息,准确确定沉积时间单元平面微相,其中以单一分流河道的识别和废弃河道的识别为关键。在沉积微相研究基础上,从宏观上对储层非均质性进行了详细分析,认为新民油田储层非均质性主要受控于分流河道规模和废弃河道的弯度,非均质性随河道规模变小而增强,随废弃河道弯度增大而增强。在此基础上,运用储存系数和渗流系数在单一河道内部进行流动单元划分,将储层分为四类流动单元。最后运用沉积微相和流动单元成果对储层内的水淹规律和剩余油规律进行研究,认为流动单元A水淹程度高,剩余油饱和度低,而流动单元B剩余油饱和度高、分布面积大,剩余油潜力最大。
【文摘语种】:中文文摘
【论文页数】:1-60
【数据库名】:中国学位论文全文数据库
4.
【论文题名】:丘陵油田西山窑组油藏精细描述
【作者】:梁晓伟
【作者专业】:岩石学、矿物学、矿床学
【导师姓名】:孙卫
【授予学位】:硕士
【授予单位】:西北大学
【授予单位新名或规范名称】:
【授予学位时间】: 20040501
【分类号】: P618.13
【关键词】:西山窑组、油藏精细描述、高分辨率层序地层、沉积微相、储层地质特征、流动单元
【摘要】:
该文以丘陵油田西山窑组油藏为例,运用现代油藏精细描述的最新理论作为指导,应用石油地质学、高分辨率层序地层学、沉积学、构造地质学、储层地质学等多学科的理论与研究技术方法,进行了西山窑油藏的油藏精细描述研究.研究中综合运用最新的三维地震、测井、录井、钻井、测试及分析化验等资料,结合丘陵油田西山窑油藏断裂发育、构造破碎、砂体发育不稳定的特点,采用高分辨率层序地层学、储层地质学、流动单元研究等油藏精细描述的多种新方法,并与油田生产动态资料相结合,从构造、沉积、储层、流动单元等多个层次和方面,开展了西山窑油藏精细描述,建立了油藏的精细地质模型,并进行了有利相带的评价和预测,对于吐哈盆地丘陵油田西山窑油藏的开发有重要的理论价值和实践意义.该文研究所取得的主要成果与创新有:1、将高分辨率层序地层学的原理和方法首次运用于研究区,对研究区西山窑组地层进行了重新划分与对比,克服了以往地层对比方法的不足,准确地建立了研究区油藏地层格架.2、利用涵盖研究区的最新三维地震资料、钻井资料,重新认识和确定了研究区构造和断层的发育展布特征,分析了构造和断层的存在对油水分布和注水开发的影响;并通过静态与动态相验证,在研究区新划分出陵306井断层、陵613井断层两条过井小型逆断层.3、在前人对研究区大相研究的基础上,首次进行了油藏范围内的沉积微相研究,分析了各种砂岩成因类型和岩石组合特征,分别识别出扇三角洲前缘水下分流河道微相、扇三角洲前缘水下分流河道内外侧微相、扇三角洲前缘席状砂微相、扇三角洲前缘水下分流河道间砂滩坝等微相,使沉积微相的研究与油田开发的实际相结合.4、进行了西山窑组储层地质学的研究,分析了研究区储层的岩石学特征、成岩作用特征;首次详细地研究了西山窑组储层砂体的空间展布特征、物性及含油性分布特征;从层内、层间及微观的角度,分析了西山窑组储层的非均质性;5、运用聚类分析的数学方法,对研究区储层进行了综合分类评价,对储层有了全面的认识.6、首次进行了西山窑油藏储层流动单元的研究.应用聚类分析和判别分析方法进行多参数流动单元分析,将研究区储层划分出三种类型的流动单元,分析了不同流动单元的纵向、平面展布特征,分析了不同流动单元的渗流特征.7、对西山窑油藏储层有利相带进行了评价,并对不同成因砂体的水驱特征进行了分析,对西山窑油藏有利区域进行了预测.
【文摘语种】:中文文摘
【论文页数】: 1-87
【数据库名】:中国学位论文全文数据库
5.
【论文题名】 开发中后期油藏描述技术的研究与应用
【论文作者】 姚瑞香
【专业名称】 油气田开发工程
【导师姓名】 王洪辉 王德明
【授予学位】 硕士
【授予单位】 成都理工大学
【授予时间】 20010501
【 分类号 】 TE327
【 关键词 】 高含水油藏 精细描述 剩余油分布
【论文页数】 68页
【文摘语种】 中文文摘
【 文 摘 】 该文从油层精细对比入手,对油藏的微构造研究技术,细分沉积微相技术,流动单元研究技术,储层物性及流体空间分布规律研究技术,数值模拟技术等进行了详细的分析总结,提出了适应大港油田油藏描述的综合应用技术,为进一步寻找剩余油的分布提供了技术保证.
6.
【论文题名】 高分辨率层序地层学储层地质研究中的应用-以濮城油田沙三上亚段为例
【论文作者】 张尚锋
【专业名称】 古生物学与地层学(含:古人类学)
【导师姓名】 伊海生 黄继均 李祥辉
【授予学位】 硕士
【授予单位】 成都理工学院
【授予时间】 20000501
【 分类号 】 P534 P618.13
【 关键词 】 濮城油田 沙三上亚段 储集砂体 扇三角洲 高分辨率 层序地层学 储层流动单元
【论文页数】 58页
【文摘语种】 中文文摘
【 文 摘 】 濮城油田是东濮凹陷重要的油气聚集区之一,沙河街组沙三段沙三上亚段是该油田主要产层,油湖泊扇三角洲沉积体系组成.该文在详细的聚心井观察的基础上,结合测井和地震剖面资料,对沙三上亚段储集层进行为系统的高分辨率层序地层学研究.应用高分辨率层序地层学理论和方法,对地层进行划分和等时地层对比,着重讨论短期基准面旋回层序结构类型,地层响应过程与沉积和等时地层对比,着重讨论短期基准面旋回层序结构类型,地层响应过程与沉积动力学的关系,及相对应的沉积微相演化序列、堆叠情况,保存状况等,并建立各级次基准面旋回等时地层对比格架.在此基础上对储层的发育规律进行讨论,重点阐述了储集层几何形态,岩石物性与沉积体系和基准面变化及A/S比值的关系, 最后讨论了储层流动单元的划分类型及储层流动单元评价,提出濮城油田沙三上亚段储层流动单元包括单一和复合型两种,储层流单元的评价级别分为极好型、好型、一般型和差型.这将对濮城油田开发决策起到帮助作用.
7.
【论文题名】 碎屑岩储层流动单元划分方法研究
【论文作者】 李凤娟
【专业名称】 矿物学、岩石学、矿床学
【导师姓名】 刘立 高福红
【授予学位】 硕士
【授予单位】 吉林大学
【授予时间】 20010501
【 分类号 】 P618.1
【 关键词 】 大庆油田萨中地区 沉积单元 流动单元划分 软件系统
【论文页数】 82页
【文摘语种】 中文文摘
【 文 摘 】 该文较系统地研究了大庆油田萨中地区的流动单元划分方法.在纵向上,利用高分辨率层序地层学理论进行流动单元划分方法研究.结果表明,研究区内的沉积单元(或成因单元)相当于高分辨率层序地层系统的准层序,是储层流动单元纵向划分的最小可制图单元,在平面上,流动单元划分的关键是参数的选择.该文采用6参数主因子参数组进行流动单元平面划分.另外,在划分方法研究的基础上,为了进一步推广应用研究结果,编制了储层流动单元划分软件系统.该软件不仅适合于研究区,对其它地区的流动单元划分也具有重要的借鉴意义.
8.
【论文题名】 砂砾岩储层流动单元四维模型研究
【论文作者】 孔凡群
【专业名称】 地质学
【导师姓名】 李任伟 刘泽荣
【授予学位】 博士
【授予单位】 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所
【授予时间】 20020301
【 分类号 】 P618.23
【 关键词 】 东营凹陷 砂砾岩 流动单元 核磁共振测井 储层模型 油藏预测
【论文页数】 129页
【文摘语种】 中文文摘
【 文 摘 】 该文综合应用沉积学和石油地质学、储层地质学、晶体表面物理学和动静态油藏描述、测井地质学的新概念、新方法和新技术手段,最大限度地应用计算机技术,系统地分析研究了东营凹陷永安镇油田沙三下段、沙四上段两种成因类型的砂砾岩体的流动单元的识别和划分及评价.首次建立沙三下段、沙四上段两种成因类型砂砾岩储层流动单元的单井模型、剖面模型、平面模型、核磁测井模型、微观网络模型、四维地质模型和仿真模型,揭示了两种砂砾岩储层流动单元的形成机理和油气富集分布规律.建立了沙三下段、沙四上段两种成因类型砂砾岩储层流动单元的识别参数优选、识别、分类和评价标准,给流动单元静态模型的建立奠定了坚实的基础,揭示了流动单元宏观和微观几何形态静态变化规律,并指导油田开发.该文首次建立了沙三下段、沙四上段两种成因类型砂砾岩的核磁测井模型,不仅揭示了砂砾岩中储层孔隙度和渗透率的特征和分布规律,还揭示了可动流体的形成和分布.该文首次建立了砂砾岩储层四维模型和数学模型,揭示了两种成因类型储层在宏观、微观参数及油气在四维空间的分布和演化规律,同时还能预测油水分布,指导油田开发
9.
【论文题名】 龙虎泡油田精细油藏描述及剩余油分布规律研究
【论文作者】 柴立新
【专业名称】 矿产普查与勘探
【导师姓名】 葛肖虹
【授予学位】 硕士
【授予单位】 吉林大学
【授予时间】 20020501
【 分类号 】 PE172.35 TE327
【 关键词 】 大庆油田 精细地质 沉积特征 沉积界面 精细沉积相 剩余油富集区 油田开发潜力
【论文页数】 98页
【文摘语种】 中文文摘
【 文 摘 】 龙虎泡油田是大庆油田有限责任公司第九采油厂的主力油田,原油产量已在20万吨以上连续稳产了15年,是大庆外围油田中的高效开发油田.经过数十年的开发,龙虎泡油田已经进入中含水期,油井已多层多方向见水,随含水上升主力油层产量递减加快,非主力层接替稳产困难,全油田产量呈下降趋势.该文运用精细地质研究的理论及方法,结合现代沉积学理论,依据测井资料反映的沉积特征和沉积界面,以及大型河流-三角洲沉积储层特有的沉积规律和沉积模式,由大到小、由粗到细逐级解剖龙虎泡油田砂体几何形态和内部结构,系统地描述了储层宏观和微观非均质特征.通过精细沉积相研究,将原萨、葡、高油层的5个油层组43个小层进一步细分为72个沉积单元,并确定了各沉积单元内单砂层的相带展布规律;通过储层非均质性研究,搞清了各级非均质的特征及对油田开发的影响;通过精细构造研究,落实了微幅度构造的分布范围和井间同生断层的位置;通过流动单元研究,将目的层段划分为三种类型的储层流动单元;通过剩余油分布规律研究,搞清了剩余油富集区,明确了油田开发潜力,从而为油田开发调整提供了依据.
10.
【论文题名】 规整填料塔中液流体力学行为的研究及传质模型的建立
【论文作者】 张红彦
【专业名称】 化学工程
【导师姓名】 王树楹
【授予学位】 博士
【授予单位】 天津大学
【授予时间】 19991201
【 分类号 】 TQ052
【 关键词 】 填料塔 规整填料 液体混合行为 液膜厚度 传质模型
【论文页数】 127页
【文摘语种】 中文文摘
【 文 摘 】 采用脉冲法系系统测量了一系列液速和气速下规整填料250Y、350Y及复合规整填料250Y+125X、350Y+125X层内的液相混合行为.应用时域最小乘法得到液相的轴向有效流速轴向 混合系数和径向混合系数等参数.建立了规整填料塔内液体分布模型.模型反映了液体的填料上呈膜状分散流动、结点处发生混合以及壁流的特点.根据填料片上液膜受力分析,引入有效得力加速度的概念,利用降膜理论,求得了填料层内任一通道内的液膜厚度和流速以及填料塔内平均液膜厚度和持液量.根据"淹没"理论和"Kelvin-Helmholtz"不稳定性理论,对波纹填料塔内的液泛机理进行了研究.为了考察气相和液相返混结传质效率的影响程度,该文以串联的混合池表征真实的液体流动,针对三种形式的塔板(气相预混逆流塔板,气 相不预混顺流塔板及气相不预混逆流塔板)和规整填料提出了计算气相返混和液相返混对效 率影响的混合池模型,并对不同工交进行了模拟计算.根据波纹填料的结构特点,该文分别定义了填料塔的气液流动单元和传质单元.分别建立了这两种传质单元内的传质模型,确定了各传质单元的之间连接条件和整个边界层的边界条件,从而建立了整个填料塔的传质模型.
11.
【论文题名】 唐家河开发区东三段储层精细描述
【论文作者】 李志勇
【专业名称】 沉积学
【导师姓名】 穆曙光 石占中
【授予学位】 硕士
【授予单位】 西南石油学院
【授予时间】 20000401
【 分类号 】 P618.13
【 关键词 】 层序 孔隙结构 非均质性 渗流屏障 连通体
【论文页数】 89页
【文摘语种】 中文文摘
【 文 摘 】 该文针对油田在开发过程中所暴露出的主要矛盾和油田生产急待解决的地质问题,对主力油组东三段储层从沉积相、储层物性及孔隙结构特征、粘土矿物及储层敏感性分析、储层宏观非均质特征、流动单元研究、剩余油分布特征等方面进行精细地描述.
四、中国专利全文数据库
1.
申请号: 200580001382.9 申请日: 2005.01.24
名称:储层评价方法
公开公告号: CN1898640 公开(公告)日:2007.01.17
主分类号: G06F7/48(2006.01)I 分案原申请号:
分类号: G06F7/48(2006.01)I
颁证日: 优先权: 2004.1.30 US 60/540,770
申请(专利权)人:埃克森美孚上游研究公司
地址:美国德克萨斯州
发明(设计)人:L·H·小兰第斯;P·N·基能顿;L·A·瓦尔满得;S·A·可汗 国际申请: 20##-01-24 PCT/US2005/001932
国际公布: 20##-08-18 WO2005/076124 英
进入国家日期: 2006.05.17
专利代理机构:北京纪凯知识产权代理有限公司
代理 人:赵蓉民
摘要
本申请在此描述评价储层的方法。其中至少一种方法包括提供一个具有多个单元的三维储层架构;将一个或多个不变的储层性质值分配给部分或全部单元,以提供第一个三维储层模型(图1A,项30);通过用一个或多个可变的储层性质值填充部分或全部单元来更新第一个三维储层模型,从而提供第二个三维储层模型(图1B,项70);以及通过用一个或多个由地震数据导出的储层性质值填充部分或全部单元来更新第二个三维储层模型,以提供第三个三维储层模型(图1B,项120)。本申请还描述了其它方法
2.
申请号: 200580001364.0 申请日:2005.01.24
名称: 储层模型建立方法
公开(公告)号: CN1898675 公开(公告)日:2007.01.17
主分类号: G06G7/48(2006.01)I 分案原申请号:
分类号: G06G7/48(2006.01)I
颁证日: 优先权: 2004.1.30 US 60/540,794
申请(专利权)人: 埃克森美孚上游研究公司
地址: 美国德克萨斯州
发明(设计)人: L·H·小兰迪斯;P·N·格勒恩顿
国际申请: 20##-01-24 PCT/US2005/003103
国际公布: 20##-08-18 WO2005/074592 英
进入国家日期: 2006.05.16
专利代理机构:北京纪凯知识产权代理有限
公司代理人:赵蓉民
摘要
本发明公开了多种储层模型的产生方法。所述方法至少其中之一包括提供具有多个单元的第一架构,其中所述第一架构是储层架构,且所述方法提供具有多个单元的第二架构,其中所述第一架构的体积大于所述第二架构的体积。
3
1.
申请号: 9410735
1.3申请日: 1994.07.08
名称: 自然电位测井识别油水层的方法
公 开 (公告) 号: CN1114711 公开(公告)日: 1996.01.10
主 分 类 号: E21B47/00 分案原申请号:
分类号: E21B47/00
颁证日: 优先权:
申请(专利权)人:李昌平
地址: 063200河北省唐海县冀东石油勘探开发公司
发 明 (设计)人: 李昌平 国际申请:
国际公布: 进入国家日期:
专利代理机构: 石油工业专利服务中心 代理人: 冯风
摘要
本发明通过测井资料解释,在低阻出油、高阻出水的地区,识别储层的含油性,它利用自然电位与电阻率测井的导向相关性计算对比系数,突出含油性因素,然后利用待测试层与已知含水层的对比系数计算待测试层的含水系数,通过交汇图分区,确定油层、油水层、水层、致密层和负压层。
4.
申请号: 02114486.9申请日: 2002.03.28
名称:碳氢比地层流体饱和度测井方法
公开(公告)号: CN1381734 公开(公告)日:2002.11.27
主分类号: G01V9/00 分案原申请号:
分类号: G01V9/00
颁证日: 优先权:
申请(专利权)人: 王振信
地址: 473132河南省南阳市河南油田测井公司中原区53号楼3单元4楼2号
发明(设计)人: 王振信 国际申请:
国际公布: 进入国家日期:
专利代理机构: 代理人:
摘要
一种碳氢比地层流体饱和度测井方法,采用直接探测地层流体中的碳、氢元素丰度,并以它们的比值为基础,定量或定性评价储层的含油或剩余油饱和度及水淹程度,从而判断和识别油气、水、干层及水淹层。该方法的核物理依据、地质基础、响应方程、含油饱和度模型、解释机理和解释方法以及设计思路,完全不同于碳氧比和RST测井方法,其效果优于上述方法。该方法基本摆脱了孔隙度的限制、矿化度的影响,解释机理科学新颖,改变了传统的参数选择模式,应用范围较广,不仅适用于高孔、高渗、高或低矿化度储层,而且也适用于低孔、低渗、低矿化度储层,均能取得良好的地质效果。
5.
申请号: 02152379.7申请日: 2002.12.05
名称: 双重神经网络储层预测方法
公开(公告)号: CN1504762 公开(公告)日: 2004.06.16
主分类号: G01V1/28 分案原申请号:
分 类号: G01V1/28
颁证日: 优先权:
申请(专利权)人:大庆石油管理局
地址: 163357黑龙江省大庆市红岗区杏五井物探公司研究所
发明(设计)人: 张向君 国际申请:
国际公布: 进入国家日期:
专利代理机构:大庆知文知识产权代理有限公司
代理人:贾乐强
摘要
一种双重神经网络储层预测方法。解决了神经网络在储层预测中预测结果精度低的问题。包括一个自组织映射网络和若干个BP神经网络,其特征在于:先将地震特征参数输入到自组织映射网络,自组织映射网络将根据输入地震特征参数的不同,输出时将地震特征参数划分为不同的类别,每一类别地震特征参数对应于地下不同的沉积相带;再将自组织映射网络划分的各类结果分别作为各BP神经网络的输入参数,使得各BP神经网络得以在沉积相带的约束下对储层进行预测。利用该预测方法预测储层含油气符合率为80%-95%,预测精度高。
6.
申请号: 200310112949. 申请日: 2003.12.29
名称: 一种油井油气水动态测井方法
公开(公告)号:CN1635262 公开(公告)日: 2005.07.06
主分类号: E21B47/00 分案原申请号:
分类号: E21B47/00;E21B47/09;E21B47/10;E21B47/12
颁证日: 优先权:
申请(专利权)人: 佟云龙;陈平;罗汉林
地址: 100011北京市西城区六铺坑石油管委会
发明(设计)人: 佟云龙;陈平;罗汉林 国际申请:
国际公布: 进入国家日期:
专利代理机构:北京市中实友知识产权代理有限责任公司
代理人:刘天语
摘要
本发明是可以适用于低矿化度地层的一种油井油气水动态测井方法,采用中子寿命测井仪记录油井地层勘探、生产井采出和剩余油分布情况,步骤是:a.用中子寿命测井仪记录油井尚未注入热中子吸收剂的中子寿命曲线;b.向油井中注入钆溶液,然后封闭筒内蹩压,时间不少30-60分钟;c.记录中子寿命曲线。本发明中子俘获截面大,利于示踪剂在地层渗透扩散,取得资料准确实用。用量少,不易被地层吸收,经济性好,施工方便。可为找寻出水井段,为卡水、堵水增油、发现未动用储层,解决层间干扰,增产挖潜提供依据,定量计算单层剩余油饱和度,为多井分层剩余油评价提供基础资料。
7.
申请 (专利) 号: 94205651.5 申 请 日: 1994.03.30
名 称: 油藏模拟器
公开 (公告) 号: CN2187820 公开(公告)日: 1995.01.18
主 分 类 号: G09B23/00 分案原申请号:
分 类 号: G09B23/00
颁 证 日: 1994.12.24 优 先 权:
申请(专利权)人: 石油大学(华东)
地 址: 257062山东省东营市泰安路149号石油大学科研处
发明 (设计)人: 吴晓东; 王木乐; 张琪; 李明忠 国 际申请:
国 际 公 布: 进入国家日期:
专利代理机构: 石油工业专利服务中心 代 理 人: 赵东冶
申请 (专利) 号: 03100889.5 申 请 日: 2003.01.24
名 称: 优化三元复合驱驱油方案的方法
公 开 (公告) 号: CN1429966 公开(公告)日: 2003.07.16
主 分 类 号: E21B43/22 分案原申请号:
分 类 号: E21B43/22
颁 证 日: 优 先 权:
申请(专利权)人: 大庆油田有限责任公司
地 址: 163453黑龙江省大庆让胡路区
发 明 (设计)人: 戚连庆 国 际 申 请:
国 际 公 布: 进入国家日期:
专利 代理 机构: 北京纪凯知识产权代理有限公司 代 理 人: 鲁兵
摘要
本发明公开了优化三元复合驱驱油方案的方法,是在三维地质模型上进行数值模拟研究,在三维驱油实验模型上进行物理模拟驱油实验,并将两者相结合确定三元复合驱驱油方案。本发明采用数值模拟研究这一高科技手段,对三元复合驱的驱油特征、驱油机理进行了深入研究,获得新的认识,由此提出三元复合驱研究必需在三维模型上进行的研究方法,并通过数值模拟研究驱油方案中三元段塞体积变化、三元段塞前后聚合物段塞设置和体积变化对驱油效果的影响,推荐出驱油方案,在此基础上,又通过驱油实验优化出较目前采用驱油方案采收率提高3-5%,投入化学剂成本降低30-50%,从而使经济技术效益大幅度提高的驱油方案。
主权项
一种优化三元复合驱驱油方案的方法,其特征在于:在三维地质模型上进行数值模拟研究,在三维驱油实验模型上进行物理模拟驱油实验,并将两者相结合确定三元复合驱驱油方案。
8.
申请(专利)号:87212170
申 请 (专利) 号:87212170
名 称:带油藏式含油轴承
公 开 (公告) 号:CN87212170
公开(公告)日:1988.04.06
主 分 类 号:
分案原申请号:
分 类 号:F16C33/10
颁 证 日:
优 先 权:
申请(专利权)人:石家庄煤矿机械厂
发 明 (设计)人: 苗健; 宁继民; 乔峰; 胡占琪
国 际 申 请:
国 际 公 布:
进入国家日期:
专利 代理 机构:
代 理 人:左燕生
摘要:
一种带油藏式含油轴承,是在含油轴承非运转外圆表面上加工一螺旋槽,利用轴承与轴承座孔的过盈配合形成封闭的油藏,可达到对含油轴承充分自补油的效果,可使轴承长期保持良好的运转状态,延长使用寿命。
主权项:
一种带油藏式含油轴承,由粉末冶金含油轴承所构成,其特征在于该轴承基体1的外圆表面有螺旋槽2,与轴承座孔配合,形成一条封闭的螺旋油藏。
五、国家科技图书文献中心
1、【正题名】:塔巴庙区块下石盒子组低渗透致密砂岩储层流动单元研究
【个人作者姓名】:唐海发; 彭仕宓; 赵彦超
【作者单位】:中国石油大学,北京,102249; 中国石油大学,北京,102249;中国地质大学,湖北,武汉,430074
【会议录\文集名】:第二届全国特种油气藏技术研讨会
【文献其他题名】:第二届全国特种油气藏技术研讨会
【出版年】:2006
【页码】:p.310-314
【总页数】:5p
【会议年】:2006
【会议召开地点】:长沙
【馆藏号】:H052673
【关键词】:致密砂岩储层; 气藏描述; 流动单元
【分类号】:P618.130.2; TE155
【正文语种】:CHI
【文摘】:本文以塔巴庙区块上古生界下石盒子组低渗透致密砂岩储层为例,针对低渗透致密砂岩储层低孔、低渗、成岩作用强、微观孔隙结构复杂等特点,提出了一套旨在提高气藏描述精度的流动单元划分新方法.在深入剖析流动单元的概念及其影响因素的基础上,确定了孔隙度、渗透率、流动层指数和Winland r35四个参数作为流动单元定量划分的指标,通过聚类分析、判别分析等统计学方法建立了致密砂岩储层流动单元的定量识别模式,实现了流动单元由取心井向非取心井的定量划分,将致密砂岩储层的流动单元划分为三种类型,在此基础上详细研究了储层流动单元的特点及其变化规律,最后采用序贯指示随机模拟方法建立了流动单元的三维地质模型,揭示了流动单元的三维空间展布特征.
2、【正题名】:高邮凹陷阜宁组低渗透储层精细评价方法研究
【个人作者姓名】:施振飞; 钱敏刚; 杨加太; 温新房
【作者单位】:江苏石油勘探局地质测井处,江苏省扬州市,225002;江苏石油勘探局地质测井处,江苏省扬州市,225002; 江苏石油勘探局地质测井处,江苏省扬州市,225002;江苏石油勘探局地质测井处,江苏省扬州市,225002
【会议录\文集名】:第四届中俄测井国际学术交流会
【文献其他题名】:第四届中俄测井国际学术交流会论文集
【出版年】:2006
【页码】:p.233-237
【总页数】:5p
【会议年】:2006
【会议召开地点】:海南三亚
【馆藏号】:H052111
【关键词】:低渗透储层; 精细解释; 储层成因; 岩心分析; 测井资料
【分类号】:P631.81; TE348
【正文语种】:CHI
【文摘】:本文以高邮凹陷阜宁组低渗透储层为例,从宏观和微观角度对低渗透率储层成因机理进行了系统地研究,对影响储层物性的因素进行了综合分析.在研究岩心分析化验资料、试油测试资料等多种资料的基础上,从岩性特征、储层特征、沉积特征及成岩作用等方面进行了分析,利用多种方法对低孔低渗储层从多角度进行了精细解释处理.并通过各项测井新技术的应用对流体性质进行了识别;并利用XMAC测井资料对地应力进行了分析,得出了各项岩石参数、最大水平主应力、最小水平主应力、井壁稳定性等信息,并分析了压裂层位及射孔参数选择的原则.在利用产油指数及流动单元方法分析产能的基础上,综合各类信息,指明了该区阜宁组储层下一步勘探开发区块.
3、 【正题名】:低渗含裂缝储层流动单元控制的地质建模
【个人作者姓名】:周锋德; 姚光庆; 魏忠元; 刘斌; 黄郑
【作者单位】:中国地质大学,资源学院,湖北,武汉,430074; 中国地质大学,资源学院,湖北,武汉,430074;中国地质大学,资源学院,湖北,武汉,430074; 中国石化河南油田分公司,河南,南阳,473100;中国石化河南油田分公司,河南,南阳,473100
【会议录\文集名】:20##年中国西部复杂油气藏地质与勘探技术研讨会
【文献其他题名】:中南大学学报(自然科学版)
【出版年】:2006
【页码】:p.149-154
【总页数】:6p
【会议年】:2006
【会议召开地点】:长沙
【馆藏号】:H053097
【关键词】:油藏地质; 裂缝储层; 储层流动
【分类号】:P618.130.25; P548
【正文语种】:CHI
【文摘】:本文对低渗含裂缝储层流动单元控制的地质建模进行了探讨。文章建立了宝浪油田低渗含裂缝储层的精确的物性参数的三维地质模型,分析了该地区储层物性的特征及其影响因素,分别从表征岩石结构参数的流动带指数的角度和裂缝动、静态响应特征的角度,建立了以测井数据和动态数据为基础的流动单元模型。
4、【正题名】:一种流动单元自动分层新方法
【个人作者姓名】:张福明; 李洪奇; 邵才瑞; 李元江; 刘洪涛
【作者单位】:中国石油大学,东营,257061; 中国石油大学,东营,257061; 中国石油大学,东营,257061;中国石油大学,东营,257061; 中国石油大学,东营,257061
【会议录\文集名】:第三届全国沉积学大会
【文献其他题名】:第三届全国沉积学大会论文摘要汇编
【出版年】:2005
【页码】:p.117-118
【总页数】:2p
【会议年】:2005
【会议召开地点】:成都
【馆藏号】:H049799
【关键词】:储层流动; 流动单元; 自动分层; 剩余油
【分类号】:P618.130.21
【正文语种】:CHI
【文摘】:本文基于岩心和测井资料,提出一种合理实用的自动分层新方法,在储层精细研究中的应用,根据流动单元或“储层综合流动因子”在平面上的分布,可以预测剩余油的富集区域。
5、【正题名】:运用聚类分析和判别分析划分储层流动单元
【个人作者姓名】:陈长伟; 徐兴科; 薛林福
【作者单位】:吉林大学地球科学学院,吉林省,长春市,130061;吉林大学地球科学学院,吉林省,长春市,130061; 吉林大学地球科学学院,吉林省,长春市,130061
【会议录\文集名】:中国地球物理学会第二十一届年会
【文献其他题名】:中国地球物理学会第二十一届年会论文集
【出版年】:2005
【页码】:p.139
【总页数】:1p
【会议年】:2005
【会议召开地点】:长春
【馆藏号】:H050930
【关键词】:聚类分析; 储层流动单元; 储层参数分析法; 储层层次分析法
【分类号】:P618.13
【正文语种】:CHI
【文摘】:储层流动单元是指影响流体流动的岩性和岩石物理性质在内部相似的、垂向上和横向上连续的储集带,是目前国内外油气储层研究的前沿课题.本文紧紧围绕储层流动单元的定义,运用多种数学方法,使得同一流动单元内储层物性差异尽可能小,而使不同的流动单元之间储层物性差异尽可能大.本文提供的划分方法是基于早期大量基础地质工作之上(包括构造研究、层序地层学分析和沉积相沉积微相分析),是对单一砂层进行储层流动单元平面划分.
6、【正题名】:低渗透油藏储集层流动单元研究
【个人作者姓名】:张爱卿; 程红卫
【作者单位】:中国石油勘探开发研究院开发所,北京,100083; 青海油田分公司勘探院,青海,736202
【会议录\文集名】:中国石油学会第一届油气田开发技术大会暨20##年中国油气田开发科技进展与难采储量开采技术研讨会
【文献其他题名】:中国石油学会第一届油气田开发技术大会论文集
【出版年】:2005
【页码】:p.85-93
【总页数】:9p
【会议年】:2005
【会议召开地点】:青岛
【馆藏号】:H051174
【关键词】:低渗透油藏; 油藏精细描述; 渗流能力; 储集层; 流动单元; 油田开发
【分类号】:TE348; TE321
【正文语种】:CHI
【文摘】:对于低渗透油藏,描述储集层非均质性是开发地质研究的一个重要内容.在以往的油藏非均质性研究中,是通过描述储集层的渗透率级差、变异系数和突进系数来表达储集层内部的渗透率变化的,这些参数可以为油藏工程研究提供一定的研究基础.但对于有一定厚度的低渗透储集层,却无法准确描述层内渗流能力的变化规律.通过流动单元和准流动单元研究,可以从以往的用储集层非均质系数描述,深入到用储集层内部相对均质体划分来反映储集层渗流能力的差异,实现低渗透储集层的精细描述.在油藏精细描述研究阶段,采用流动单元/准流动单元研究方法,利用测井解释的物性成果(按每米8个点的数据),将储集层分解为相对均质体,就可以准确描述储集层内部不同部位渗流能力的差异、变化规律和组合特征,达到了深化储集层非均质性研究的目的,实现流动单元/准流动单元建模,为油藏精细描述和油藏精细数值模拟奠定了基础.为低渗透高含水老油田的后期调整提供地质依据.
六、美国石油工程师学会会议论文
1.
Paper Number 111912-MS
Title Akpo, Nigeria: From Seismic Interpretation to Geomodel
Authors Timothy Oluyemi Itiola, Bruno Michel, and Martine Bez, TOTAL, Tour La Coupole, Paris La Defense, France
Source Nigeria Annual International Conference and Exhibition, 6-8 August , Abuja, Nigeria
Copyright 2007. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Preview Abstract
Akpo is a very light oil to condensate gas field located offshore Niger Delta, discovered end 1999 by Akpo-1 well at a water depth of 1350m, by SAPETRO (operator) – Total TUPNI (technical advisor) and PETROBAS in OPL246.
As for some other turbiditic fields, modelling of the 5 to 20m thick individual channels was the main challenge as they act as the elementary flow units of the reservoir. Although such flow units are under the current available seismic resolution, the developed methodology with object modelling constrained by sedimentological interpretation and seismic derived Vclay cube, allowed to provide reservoir engineers with geologically representative model to be able to simulate properly the flow behaviour and further estimate the reserves.
Introduction
Akpo is a condensate to very light oil field located offshore Niger Delta, in OML130 (ex OPL246), approximately 135km from the shore in water depth ranging from 1100m to 1700m. The block was awarded during the first round of deep offshore blocks allocation under the Production Sharing Contract (PSC) of 1993 and the study area is fully covered by a 3D survey shot between 1998 and 1999. The 3D seismic data set was processed and interpreted for the location of first exploratory well, Akpo 1 which turned out to be a success in 2000. To date, four appraisal wells with two geological sidetracks have been drilled as at summer 20## and the resulting total of seven penetrations have been delineated into five reservoirs. The main reservoir (Reservoir A at the top of the structure) is a channel-levee system situated on the eastern flank of the Akpo structure and is the focus of this paper. The area is characterised by Miocene reservoirs which consist of turbiditic lobe and channel complexes deposited in a deep water environment. Results from the wells have confirmed the complex nature of hydrocarbon distribution in this turbidite depositional system. With the advent of new technological innovations, it was decided in 20## to reprocess the original 3D seismic data. The objective was to use long offset AVA (Amplitude Variation with Angle) attributes to ensure the best possible reservoir characterisation. This has resulted from the experience of TOTAL that long offset AVA has been proven to be a very useful exploration tool for deep offshore Africa. Ultimately, seismic derived pseudo-Vclay cube was generated for the field and extensively used for the interpretation.
2.
Paper Number 105014-MS
Title Porosity Partitioning and Flow Unit Characterization From an Integration of Magnetic-Resonance and Borehole-Image Measurements
Authors Aditi Pal, Kapil Seth, and Udit Guru, Schlumberger, and R.R. Tiwari and D. Dasgupta, ONGC Ltd.
Source SPE Middle East Oil and Gas Show and Conference, 11-14 March 2007, Kingdom of Bahrain
Copyright 2007. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Preview Abstract
The petrophysical evaluation of carbonate reservoirs in terms of predicting the hydrocarbon potential is trivial. However, it is difficult to correctly predict the fluid flow in the absence of proper characterization of the different flow units encountered in these reservoirs. The process of identifying the flow units becomes non-trivial in the presence of extensive diagenesis process affecting the original depositional texture. The conventional triple combo logs gives an average response when logged against diagenetically altered zone thus overlooking or under-estimating diagenetic features occurring in micro scale. It becomes imperative to look at both micro and macro scale heterogeneity for evaluation of such reservoirs, which has a direct impact on the production, and water injection scheme of such reservoirs.
The NMR data and image based secondary porosity estimation recorded in this well were used for partitioning the porosity into micro, meso and macro porosity. Borehole image logs have been interpreted in terms of defining the connectivity of the features seen on the image. This is then used to define a high-resolution connectivity index. An integrated approach using the NMR and the image is being proposed to identify such high permeability streaks that can explain the production performance or the water injection behavior at a later stage of development of the field. Based on the porosity partitioning technique an improved permeability estimate is made. The production results confirm the findings of this study.
3.
Paper Number 88521-MS
Title The Mapping of Hydraulic Flow Zone Units and Characterisation of Australian Geological Depositional Environments
Authors S. Biniwale, P. Behrenbruch, The University of Adelaide
Source SPE Asia Pacific Oil and Gas Conference and Exhibition, 18-20 October 2004, Perth, Australia
Copyright 2004. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Preview Abstract
The Carman-Kozeny formulation has been used as a basis to provide a new perspective of flow zone units (FZUs), by mapping similar rocks in terms of “Characteristic Envelopes”, for different geological depositional environments. A large amount of data, covering several fields and different Australian basins, has been analysed.
The methodology has been used for well-to-well correlation, reverse modelling for better identification of depositional trends, diagenetic affects and grain characteristics. It is also shown how photomicrographs, scanning electron micrographs (SEM), and log shapes can be incorporated in a detailed analysis. The method is ideal for validating plug samples used in special core analysis. It is shown how various data types, geological attributes and engineering parameters can be integrated. Results from such analysis can then be used in consistent model preparation and better quantification of petroleum recovery efficiency.
4.
Title: The Origin and Resource Potential of Residual Oil Zones
Authors: L.S. Melzer, Melzer Consulting, and G.J. Koperna and V.A. Kuuskraa, Advanced Resources Intl. Inc.
Source: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, 24-27 September, San Antonio, Texas, USA
Copyright: 2006. Society of Petroleum Engineers.
Abstract:
Tectonics and active aquifers beneath oil-bearing reservoirs can be powerful forces in trapping large quantities of residual oil. In regions of the world where basin uplift (or subsidence) has created basinal tilt or where the oil columns are underlain by active aquifers, significant quantities of oil may have been swept from the original oil accumulation. In these situations, the once horizontal producing oil-water contact (OWC) transitions to a tilted interface across the field, creating a new and higher OWC. Below the new and now tilted OWC, there now exists a thick reservoir interval of immobile oil, called the residual oil zone (ROZ).
In the past, the ROZ was only water productive and therefore avoided. Today, with the advent of CO2 EOR and several demonstration projects, this oil zone (often quite comparable in residual oil saturation with the waterflood swept interval in the main pay zone) has been shown to be a technically viable target for additional oil recovery.
In the Permian Basin, OWC tilts have been mapped in many of the oil fields, particularly in the Permian age San Andres and Grayburg reservoirs. Examination of well logs clearly shows the presence of significant ROZs (often with 100’s of feet in thickness) below the tilted producing OWC. Throughout the middle portion of the interval, the oil saturation is near residual oil saturation. The oil in place, due to ROZ thickness, is often on par with the original oil in place in the MPZ, representing a large, significant undeveloped oil resource.
This paper discusses the origin and resource potential of ROZs. The paper examines how: 1) regional or local basin tilt; 2) breached and reformed seals; and/or 3) altered hydrodynamic flow fields can form ROZs. Subsequently, the paper examines, using geologic and reservoir modeling, how key oil reservoir and aquifer properties influence the shape, size and resource potential of ROZs.
Introduction:
The concept of a modern oil or gas basin as a pure hydrostatic environment has undergone significant revision in recent years. The presence of fresh water aquifers underlying deep oil reservoirs has long been recognized as a challenge to the hydrostatic concepts and observations of tilted oil and gas water contacts is now recognized as another. The controlling parameters and mathematical relationships of tilted oil/water contacts (OWCs) were worked out in pioneering work done by M. K. Hubbert1 while working for Shell over fifty years ago. However, the commercial significance of these subsurface hydrodynamic conditions was largely ignored until recent years when geologists attempted to use the concept of hydrodynamic displacement of hydrocarbons to explain and locate subtle traps. This concept, best described Berg et al2, is that enhanced hydrodynamic conditions displaced oil previously trapped within relatively static subsurface conditions leading to subsequent entrapment under conditions where no structural closure exists. Some small oilfields were discovered using the methodology and specific examples have been described in the Billings Nose area of eastern Montana2.
Working somewhat concurrently, petroleum engineers have examined, carefully described and modeled what we have come to call transition zones at and beneath the OWC in attempts to explain observed transitions from 100%-produced-oil intervals to those that produce only a skim of oil during primary or waterflood production. Advancements in understanding capillary pressures and their influence on relative oil/water permeability curves have come to be staples of technology and reservoir modeling.
5.
Title: A New Integrated Approach to Obtain Reliable Permeability Profiles From Logs in a Carbonate Reservoir
Authors: P. Balossino and F. Pampuri, ENI E&P, and C. Bruni and K. Ebzhasarova, KPO b.v.
Source: SPE Russian Oil and Gas Technical Conference and Exhibition, 3-6 October, Moscow, Russia
Copyright: 2006. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Abstract:
Permeability is one of the key petrophysical parameters in reservoir evaluation. Information about permeability is commonly derived from cores and test data, that generally cover only part of the reservoir section, but can also be derived from logs, and then extrapolated to uncored intervals and wells. Two logs provide such information: acoustic and nuclear magnetic resonance. In the Karachaganak Field, an approach based on the acoustic tool was preferred because of the textural characteristics of the vuggy carbonate reservoir.
The approach relies also on the use of image logs to obtain a detailed description of reservoir rocks texture and discriminate between rocks with primary interparticle porosity or very small vugs and lithotypes with multi modal distribution of pores, enlarged and touching vugs.
More than 900 meters of core have been used to validate the permeability log derived from the analysis of Stoneley waves in 25 wells from this field. A correlation between the validated log derived permeability and the textural facies from image logs, has allowed the relationship between permeability variations and the geological framework to be established.
The results have been compared with dynamic data from production logging through the definition of flow units from Stoneley wave-derived permeability and porosity log data and the use of a Stratigraphic Modified Lorenz Plot to identify possible fluid entry points.
Three main permeability trends have been identified:
for undolomitised or patchily dolomitised biohermal deposits.
for pervasively dolomitised lithologies characterised by lower mean permeability values.
for facies characterised by well developed vuggy porosity with enhanced dissolution phenomena (touching vugs, microfracturing etc.)
Besides the presence of very high K values clearly unmatchable by log derived matrix permeability has been highlighted by some well test result. This great difference suggests the presence of fracturing improving matrix characteristics in the volume investigated by the test and the well performances. The comparison of log derived permeability and well test results has given a new perspective in the interpretation of well test results with respect to the geological framework and a well defined sequence stratigraphic model. The extension of this methodology to new wells could improve the knowledge of the petrophysical characteristics of the reservoir and allow better prediction of reservoir productivity.
Introduction:
The paper presents a new interpretative methodology that integrates wireline and image logs, cores and tests data to describe vertical trends of the main petrophysical parameters and correlate them throughout the reservoir. The study has been mostly focused on understanding the complex variations in the porosity-permeability relatioship in a carbonate reservoir and made use of the flow unit concept and partially of the graphical method described by Gunter et al. (Ref. 1).
Porosity and permeability are key petrophysical parameters for a detailed reservoir description. The first one can be confidently obtained from cores and logs. But, especially in complex reservoirs, image logs can add valuable information about texture and porosity types distribution. Permeability is usually derived from core measurements and from the interpretation of production tests. As is well known, there are no wireline logs that directly measure permeability. However continuous permeability profiles can be extracted from the analysis of the Stoneley waves acquired by an acoustic tool or from NMR T2 distribution and the use of the Coates equation. In this latter case a good correlation must exist between pore size and pore connectivity.
6.
Title: Early Determination of Reservoir Flow Units Using an Integrated Petrophysical Method
Authors: Gunter, G.W., Finneran, J.M., Amoco EPTG; Hartmann, D.J., DJH Energy; Miller, J.D., Amoco E&P
Source: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, 5-8 October, San Antonio, Texas
Copyright: Copyright 1997, Society of Petroleum Engineers, Inc.
Abstract:
This paper uses case histories to introduce a graphical method for easily quantifying reservoir flow units based on geologic framework, petrophysical rock/pore types, storage capacity, flow capacity, and reservoir process speed. Using these parameters and four graphical tools, this paper outlines a quantitative approach to transform rock-type-based zonations into petrophysically based flow units that can be input into a numerical flow simulator. This method provides a tool for determining the minimum number of flow units to input into a numerical flow simulator that honors the foot-by-foot characteristics at the wellbore.
A flow unit is a stratigraphically continuous interval of similar reservoir process speed that maintains the geologic framework and characteristics of rock types. Rock types are representative reservoir units with a distinct porosity-permeability relationship and a unique water saturation for a given height above free water level.
The ideal data for this method is continuous core porosity, permeability, and saturation information drawn from throughout the entire reservoir. If such a data set is not available, it is necessary to calibrate wireline log data with core information to produce reliable estimates of porosity, permeability, and saturation. A full discussion of these data transforms are beyond the scope of this paper.
The four graphical tools used to determine flow units are: Winland porosity-permeability cross plot, Stratigraphic Flow Profile (SFP), Stratigraphic Modified Lorenz Plot (SMLP) and Modified Lorenz Plot (MLP).
This method begins by establishing rock types within a geologic framework. The geologic framework allows the flow units to be interpreted within a sequence stratigraphic model determining well-to-well correlation strategies. The key flow unit characteristics to be identified are barriers (seal to flow), speed zones (conduits), and baffles (zones that throttle fluid movement).
This integrated, petrophysically based method of determining flow units has been successfully used in a wide array of reservoirs. We have applied it to young, unconsolidated sediments; structurally complex naturally fractured/vuggy carbonates; low permeability "tight" formation gas sands; diagenetically altered carbonates; complex mixed lithologies; and interbedded sand-shale sequences.
The earlier in the life of a reservoir this process is used, the greater the understanding of future reservoir performance. This method allows the user to employ the least number of flow units and honor the character of the foot by foot data for simulation studies.
Key Definitions
Due to various working definitions of some of these terms in the literature, it is necessary to define the key terms used in this approach:
Rock Types
Rock/Pore Types - are units of rock deposited under similar conditions which experienced similar diagenetic processes resulting in a unique porosity-permeability relationship, capillary pressure profile and water saturation for a given height above free water in a reservoir.
Winland Plot - a semi-log crossplot of permeability (mD) versus porosity (%), with isopore throat lines (R35 Ports). R35 Ports correspond to the calculated pore throat radius (microns) at 35% mercury saturation from a mercury injection capillary pressure test. They can be calculated directly from Winland's equation (eq. 1) or other equations based on permeability and porosity. In equation 1, permeability is input in millidarcies and porosity in percent.
7.
Title: Enhanced Reservoir Description: Using Core and Log Data to Identify Hydraulic (Flow) Units and Predict Permeability in Uncored Intervals/Wells
Authors Amaefule, Jude O., Altunbay, Mehmet, Core Laboratories; Tiab, Djebbar, U. of Oklahoma; Kersey, David G., Keelan, Dare K., Core Laboratories
Source SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, 3-6 October, Houston, Texas
Copyright: Copyright 1993, Society of Petroleum Engineers, Inc.
Abstract:
Understanding complex variations in pore geometry within different lithofacies is the key to improved reservoir description and exploitation. Core data provide information on various depositional and diagenetic controls on pore geometry. Variations in pore geometrical attributes in turn, define the existence of distinct zones (hydraulic units) with similar fluid-flow characteristics. Classic discrimination of rock types has been based on subjective geological observations and on empirical relationships between the log of permeability versus porosity. However for any porosity within a given rock type, permeability can vary by several orders of magnitude, which indicates the existence of several flow units.
In this paper, a new, practical and theoretically correct methodology is proposed for identification and characterization of hydraulic units within mappable geological units (facies). The technique is based on a modified Kozeny-Carmen equation and the concept of mean hydraulic radius. The equation indicates that for any hydraulic unit, a log-log plot of a "Reservoir Quality Index," (RQI), which is equal to 0.0314 k/ , versus a "Normalized Porosity Index" ( x) which is equal to /(1- ) should yield a straight line with a unit slope. The intercept of the unit slope line with z= 1, designated as the "Flow Zone Indicator" (FZI), is a unique parameter for each hydraulic unit. RQI, z and FZJ are based on stressed porosity and permeability data measured on core samples.
FZI is then correlated to certain combinations of logging tool responses to develop regression models for permeability predictions in cored and uncored intervals or wells. The proposed technique has been successfully tested in clastic rocks from East Texas, South America, West Africa, South East Asia and Far East Asia, as well as carbonate sequences from West Texas and Canada. This paper documents the theoretical development, validates and characterizes the hydraulic units, and presents predicted versus actual permeability data to demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed technique.
Introduction
One of the most important existing and emerging challenges of geoscientists and engineers is to improve reservoir description techniques. It is well recognized that improvements in reservoir description will reduce the amount of hydrocarbon left behind pipe. Accurate determination of pore-body/throat attributes and fluid distribution are central elements in improved reservoir description. Many reservoir description programs, though detailed, have not included descriptions at the pore-throat scale. Yet, pore-throat attributes control initial/residual hydrocarbon distribution and fluid flow. Because they are readily available, continuous sources of data, logging tool responses are often used to draw inferences about lithology, depositional and diagenetic sequences, and fluid content. These inferences are based on empirical models utilizing correlations among tool responses, rock and fluid properties. In many instances, unfortunately, the correlation models can not be used globally because of the influences of factors not fully considered by the models. Factors include (a) the presence of potassium-feldspar, zircon, etc. causing erroneously high calculated Vsh from the gamma ray; (b) microporosity in kaolinite, chert, etc. leading to high apparent water saturation calculations; and (c) siderite, pyrite, barite, and smectite influencing the resistivity, density and neutron log calculations.
8.
Title: Air Injection and Waterflood Performance Comparison of Two Adjacent Units in Buffalo Field: Economic Analysis
Authors: V.K. Kumar, El Paso Production Co., and D. Gutierrez, SPE, R.G. Moore, SPE, and S.A. Mehta, SPE, U. of Calgary
Source: SPE Eastern Regional Meeting, 11-13 October, Canton, Ohio, USA
Copyright: 2006. Society of Petroleum Engineers
6.
Title: Case Study: Optimizing Hydraulic Fracturing Performance in Northeastern United States Fractured Shale Formations
Authors: J. Paktinat, J.A. Pinkhouse, N. Johnson, and C. Williams, Universal Well Services Inc.; G.G. Lash, State U. of New York–Fredonia; and G.S. Penny and D.A. Goff, CESI Chemical
Source: SPE Eastern Regional Meeting, 11-13 October, Canton, Ohio, USA
Copyright: 2006. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Abstract:
The primary purpose of stimulating fractured shale formations is to extend the drainage radius by creating a long fracture sand pack that connects natural fractures and increases flow channels to the wellbore. However, most of the fracturing pad fluid leaks off into natural fractures resulting in shorter effective fracture lengths and a significant damage zone surrounding the fracture. This is due in part to inadequate fluid loss control properties of the injected fluid and high capillary forces that retain fluid in the formation. Surfactants are used to lower high capillary forces and help well cleanup of the injected fluids. However, many of these additives adsorb rapidly within the first few inches of the shale formation, reducing their effectiveness and resulting in phase trapping of the injected fluid.
In this work, laboratory data is presented for various fracturing fluids with different surface activity pumped into the Rhinestreet Shale. Recent fracture treatments have been successful utilizing a slick water treatment consisting of water and dry polyacrylamide polymer with and without surfactants. Commonly used surfactants as well as a microemulsion system are evaluated in this study.
Laboratory data is presented illustrating how a microemulsion accelerates post fracturing fluid cleanup in tight shale cores. Addition of microemulsion to the fracturing fluid also results in lowering pressure to displace injected fluids from low permeability core samples and proppant packs. When microemulsion is incorporated at 2 gpt within the fracturing fluid; the relative permeability to gas is increased substantially while water saturation is decreased. This alteration of the fracturing fluid effectively lowers the capillary pressure and capillary end effect associated with fractures in low permeability reservoirs by as much as 50%, thus mitigating phase trapping and therefore permitting an increased flow area to the fracture, hence longer effective fracture lengths.
Introduction:
Organic-rich, low permeability shale deposits are becoming increasingly vital to the production of natural gas. This burgeoning interest is driven largely by increased natural gas prices and improved completion technologies. There is probably no better example of the role of technology in natural gas recovery than the Late Mississippian Barnett Shale of the Forth Worth Basin, which is providing an analog for exploration of similar unconventional reservoirs throughout North America. Nevertheless, there is no universal production model applicable to each and every unconventional reservoir. Indeed, most vary in terms of basic stratigraphic facies distribution, mineralogy (i.e., quartz content, clay type and content), natural fracture parameters (length, orthogonal spacing, connectivity, anisotropy), porosity and permeability, and rock mechanical properties.
Among the tight, organic-rich shale deposits beginning to generate interest among explorationists are the Upper Devonian Rhinestreet shale and Middle Devonian Marcellus shale of the Appalachian Basin. Several recently drilled wells targeting the Rhinestreet and Marcellus shale in southwestern Pennsylvania have been fractured. This paper describes the laboratory experiments and field case studies comparing various conventional surfactants (CS) including an aliphatic ethoxylate (AE), cationic (CAT), and a microemulsion (ME) fluid system to determine their leakoff and adsorption properties when injected into a 6 foot laboratory shale packed column. Unless otherwise noted, AE was the surfactant used in the CS examples. A laboratory comparison study of these systems was used to select additive combinations to apply within the fracturing fluid to restore pad leakoff efficiencies and improve flowback of injected fluid from fractured shale gas wells.
9.
Title: Depositional Modelling of Champion Field, Brunei: Assessing the Impact of Reservoir Architecture on Secondary Recovery
Authors: D.F. Hadley, E. Arochukwu, SPE, K. Nishi, SPE, M. Sarginson, H. Salleh, and M. Omar, Brunei Shell Petroleum Sdn. Bhd.
Source: SPE Asia Pacific Oil & Gas Conference and Exhibition, 11-13 September, Adelaide, Australia
Copyright: 2006. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Abstract:
Champion is a multi-billion bbl STOIIP oilfield offshore Brunei. It is a mature field with over 250 producing wells. Oil production commenced in 1972, and production to date is less than 20% of the oil initially in place. The feasibility of increasing recovery through a major waterflooding programme is currently under evaluation. Potential incremental oil recovery is 8%.
Significant capital investment (up to 140 new wells and 10 new jackets) will be required to realise this opportunity. It is, therefore, important to capture the full range of possible subsurface scenarios early in the study. A fundamental first step in the integrated modelling workflow has been to develop an understanding of the depositional and tectonic history of the field in order to create static models that capture the range of uncertainty in geometry and properties of the reservoirs. Data from core, well logs, seismic and outcrop analogues have been integrated to produce depositional models, highlighting uncertainties in reservoir architecture as they would impact potential waterflood recovery. Two broad types of reservoir interval have been recognised:
stacked shoreface parasequences, which form the majority of Champion reservoirs. In general, these comprise a gradational succession from basal offshore-transition zone heterolithics to amalgamated low angle cross-stratified sandstones of the lower shoreface zone. Correctly considering stacking patterns and degree of vertical connectivity between sands is important to the success of a waterflood.
tidally-dominated sediments, comprising tidal channel fill or bar complexes set in a background of mud to sand-dominated tidal flat facies have been recognised. For these sediments, channel sand geometry, orientation and internal permeability anisotropy are crucial to predicting fluid flow.
The results of the sedimentological review have been used to create a series of 2D cross sectional dynamic simulation models, covering the range of depositional environments, and a range of connectivity scenarios. The main conclusion of this study is that water is the preferred injection fluid for all of the Champion field reservoir intervals studied. Water typically gives a 15-20% (absolute) higher oil recovery factor than gas.
The impact of the sedimentology review and modelling is that it will enable early selection of water as the injection fluid. This means that surface engineering work can focus on water injection scenarios, reducing the time required to identify a preferred development plan and accelerating project implementation.
Introduction:
The Champion field has been producing oil since 1972, with current production of less than 20% of the STOIIP. Reserves replacements from infill drilling are becoming increasingly difficult to find, so a new approach was called for. In 1997, development focus was on “halting the decline in production by locating and exploiting remaining undeveloped reserves using primary depletion, rather than economically marginal secondary recovery methods” [1]. Since then, oil prices have risen from US$23 to US$50+ per barrel (average annual US crude oil prices, inflation adjusted, data source: www.inflationdata.com), and a major secondary recovery project, with economies of scale applied to the whole field instead of isolated reservoirs, now becomes attractive.
A scouting study, carried out in 2004, has identified that Champion field could produce an additional 8% of the STOIIP over a period of 28 years, if a major secondary recovery project could be put in place. The scouting study indicated that the scale of investment under consideration could be up to 140 new wells, 10 new well jackets and associated pipelines, and injection facilities. One of the major recommendations of the scouting study was that the traditional piecemeal approach to the development of Champion should be abandoned in favour of a more holistic apporoach.
To this end, the three separate field teams previously responsible for the field development were merged, and a new integrated team structure put in place, with over 30 staff, comprising subsurface and surface.
10.
Title: From Straight Lines to Deconvolution: The Evolution of the State of the Art in Well Test Analysis
Authors: A.C. Gringarten, Imperial C.
Source: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, 24-27 September, San Antonio, Texas, USA
Copyright: 2006. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Abstract:
Well test analysis has been used for many years to assess well condition and obtain reservoir parameters. Early interpretation methods (using straight-lines or log-log pressure plots) were limited to the estimation of well performance. With the introduction of pressure derivative analysis in 1983 and the development of complex interpretation models that are able to account for detailed geological features, well test analysis has become a very powerful tool for reservoir characterization. A new milestone has been reached recently with the introduction of deconvolution. Deconvolution is a process which converts pressure data at variable rate into a single drawdown at constant rate, thus making more data available for interpretation than in the original data set, where only periods at constant rate can be analyzed. Consequently, it is possible to see boundaries in deconvolved data, a considerable advantage compared to conventional analysis, where boundaries are often not seen and must be inferred. This has a significant impact on the ability to certify reserves.
The paper reviews the evolution of analysis techniques over the last half-century and shows how improvements have come in a series of step changes twenty years apart. Each one has increased the ability to discriminate between potential interpretation models and to verify the consistency of the analysis. This has increasing drastically the amount of information that can be extracted from well test data and more importantly, the confidence in that information.
Introduction:
Results that can be obtained from well testing are a function of the range and the quality of the pressure and rate data available, and of the approach used for their analysis. Consequently, at any given time, the extent and quality of an analysis (and therefore what can be expected from well test interpretation) are limited by the state-of-the-art in both data acquisition and analysis techniques. As data improve, and better interpretation methods are developed, more and more useful information can be extracted from well test data.
Early well test analysis techniques were developed independently from one another and often gave widely different results for the same tests1. This has had several consequences: (1) an analysis was never complete, because there always was an alternative analysis method that had not been tried; (2) interpreters had no basis on which to agree on analysis results; and (3) the general opinion was that well testing was useless, given the wide range of possible results.
Significant progress was achieved in the late 70’s and early 80’s with the development of an integrated methodology based on signal theory and the subsequent introduction of derivatives. It was found that, although reservoirs are all different in terms of depth, pressure, fluid composition, geology, etc., their behaviors in well tests were made of a few number of basic components that were the same everywhere, every time. Well test analysis was about finding these components, which could be achieved in a systematic way, following a well-defined process. The outcome was a well test interpretation model, which defined how much and what kind of knowledge could be extracted from the data. The interpretation model also determined which of the various published analysis methods were applicable and when. Importantly, the integrated methodology made well test analysis easy to learn and repeatable. The evolution of the state-of-the art in well test analysis throughout these years can be followed from review papers that have appeared at regular intervalsin the petroleum literature1-5.
七、美国工程索引
1.  Remaining oil formed by water breakthrough in fractures
Remaining oil formed by water breakthrough in fractures
Wu, You-Jia (Southwest Petroleum University); Li, Jian; Zhao, Ming; Jia, Li-Ping; Zhao, Zhong-Hua Source: Xinan Shiyou Daxue Xuebao/Journal of Southwest Petroleum University, v 29, n 3, June, 2007, p 36-38 Language: Chinese
ISSN: 1000-2634
Publisher: Science Press
Abstract: Water breakthrough in fractures is quite common in igneous rock and metomorphic rock fractured reservoirs developed by water injection, the high yield wells located near fractures are, in general, the ones with most serious water breakthrough. The fractured reservoirs are characterized by several high yield wells which determine most of reserves and productivity in all the oilfield. Taking the igneous rock reservoirs in Kelamayi and inner Mongolia, which are developed by water flooding, as an example, research implies there are quite a few high yield wells in igneous rock and metemorphic rock reservoirs flooded by water quickly when the wells are flooded due to water breakthrough, if the measurement stopping water injection and forcing drainage is adapted, the output of the wells will recover a lot. The reason that the dynamic performance of production occurs is that after water breakthrough flow in fractures communicates, the flow with lower mobile viscosity forms water lock to seal the mobile oil in channels. In the view of that, the mechanism of water breakthrough in fractures and vugs and the distribution model of remaining oil after water breakthrough are presented. (10 refs.)
Database: Compendex
2.  Remaining oil enrichment areas in continental waterflooding reservoirs
Remaining oil enrichment areas in continental waterflooding reservoirs
Li, Yang (SLOF, Sinopec); Wang, Duan-Ping; Liu, Jian-Min Source: Shiyou Kantan Yu Kaifa/Petroleum Exploration and Development, v 32, n 3, June, 2005, p 91-96 Language: Chinese
ISSN: 1000-0747 CODEN: SKYKEG
Publisher: Science Press
Abstract: The remaining oil in heterogeneous continental reservoirs at high water-cut stage is generally dispersed with accumulation in certain areas, controlled by reservoir compartmentation. Reservoir compartmentation models caused by fault, interbed and preferential flowing path are put forward, their control on remaining oil accumulation and distribution is expounded and the mechanism of remaining oil accumulation is revealed. Technologies for prediction of low-grade fault, interbed and preferential flowing path are developed, whose application in Shengli Oilfield is effective. (20 refs.)
Database: Compendex
3.  Research on the remaining oil research by geology
Research on the remaining oil research by geology
Huang, Wei-Gang (State Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation, Southwest Petroleum Institute); Guo, Ping; Xu, Yan-Mei Source: Xinan Shiyou Xueyuan Xuebao/Journal of Southwestern Petroleum Institute, v 27, n 3, June, 2005, p 5-7 Language: Chinese
ISSN: 1000-2634 CODEN: XSXUEG
Publisher: Science Press
Abstract: At the present, most oilfields in China have come into the period of high water cut and the remaining oil widely dispersed, and the production has obvious downtrend. Acquaintance with the residual oil and development has been an important research subject, and also a difficult subject worldwide. The concentration of the remaining oil in reservoir is controlled by production dynamics and geological factors. During production, the factors hardly change in short time, yet, barely affected by human factors. Address way is widely utilized in research of remaining oil. (6 refs.)
Database: Compendex
4、  Light oil recovery from cyclic CO2 injection. Influence of gravity segregation and remaining oil
Light oil recovery from cyclic CO2 injection. Influence of gravity segregation and remaining oil
Thomas, J. (Louisiana State Univ); Berzins, T.V.; Monger, T.G.; Bassiouni, Z. Source: Proceedings - SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, v Gamma, Enhanced Oil Recovery/General Petroleum Engineering, 1990, p 609-616
CODEN: PSAEE3
Conference: Proceedings: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition 1990 Part 1 (of 5), Sep 23-26 1990, New Orleans, LA, USA
Publisher: Publ by Soc of Petroleum Engineers of AIME
Abstract: This paper presents results of an experimental and numerical investigation of the CO2 huff 'n' puff process for the enhanced recovery of light oil. The objective of the investigation was to increase our basic understanding of the process by examining the effects of a gas cap, gravity override, and remaining oil saturation on oil recovery. In laboratory corefloods, the CO2 huff 'n' puff process was physically modelled using Berea sandstone with live and dead oil systems. Live oil was used in a vertical core at pressures above and below the bubble-point to study the influence of a gas cap. Stock tank oil was used in horizontal cores at immiscible conditions to study the effects of gravity segregation and remaining oil saturation. The cyclic process was also modelled using a three-dimensional fully-compositional reservoir simulator. Coreflood and numerical simulation results indicate that the presence of a gas cap, gravity segregation and higher remaining oil saturation improve process performance. (8 refs.)
Ei controlled terms: Oil Well Production -- Enhanced Recovery - Petroleum Reservoir Engineering - Carbon Dioxide
Classification Code: 511 Oil Field Equipment and Production Operations - 512 Petroleum and Related Deposits - 804 Chemical Products Generally
Database: Compendex
5、 4D probabilistic inversion to detect remaining oil in troll west oil rim
4D probabilistic inversion to detect remaining oil in troll west oil rim
Kleemeyer, M. (Norske Shell AS); Dankbaar, J.W.M.; Staples, R.; Stammeijer, J.G.F. Source: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 68th European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers Conference and Exhibition, incorporating SPE EUROPEC 2006, EAGE 2006: Opportunities in Mature Areas, v 3, Society of Petroleum Engineers, 68th European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers Conference and Exhibition, incorporating SPE EUROPEC 2006, EAGE 2006: Opportunities in Mature Areas, 2006, p 1474-1478
Conference: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 68th European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers Conference and Exhibition, incorporating SPE EUROPEC 2006, EAGE 2006: Opportunities in Mature Areas, Jun 12-15 2006, Vienna, Austria
Publisher: Society of Petroleum Engineers
Abstract: The 4D ROVER (Remaining Oil Volume Estimation And Redistribution) project aimed to provide a quantitative measure of remaining oil in the oil rim from the Troll West field, by deploying the Shell proprietary probabilistic layer-based inversion tool to the license partners. Due to structural complexity of the static model, the three reservoir fluids and a complicated 4D signal, a stepwise inversion approach proved most successful, solving for the most uncertain reservoir parameters first. (2 refs.)
Ei controlled terms: Crude petroleum - Petroleum reservoirs - Probabilistic logics - Problem solving
Classification Code: 512.1 Petroleum Deposits - 512.1.1 Oil Fields - 721.1 Computer Theory, Includes Formal Logic, Automata Theory, Switching Theory, Programming Theory - 723.4 Artificial Intelligence
Database: Compendex
6、Application and appraisal of the remaining oil saturation monitor technology in the Henan light oil field
Dang, Yong-Feng (University of China Geology); Wang, Cheng; Li, Ai-Hong; Li, Run-Hua Source: Xinan Shiyou Xueyuan Xuebao/Journal of Southwestern Petroleum Institute, v 28, n 1, February, 2006, p 43-45 Language: Chinese
ISSN: 1000-2634 CODEN: XSXUEG
Publisher: Science Press
Abstract: During the high water-cut later stage, the main parameters have changed very greatly such as underground oil state and permeability etc. and it was not only concerned with the appraisal index of oil reservoir store layer and developed level, but also the choice of the developing way and the adjustment direction in the future were determined. Thus, Henan oilfield successively introduced the new logging technology such as the remaining oil saturation-RMT, PND-S, boron neutron life - span logging. It owns the different style for evaluating and describing the rich oil area and layer segment in different oil reservoirs when it was used in monitor scene and at the same time it provided the technical support for measure of increasing oil, production stabilization and water cut controlling in oilfield. (2 refs.)
Database: Compendex
八、美国专利全文数据库
1、oil filter
United States Patent 7,299,932
Inventors: Morita; Shoji (Kanagawa, JP)
Assignee: Hitachi, Ltd. (Tokyo, JP)
Appl . No.: 11/678,898
Filed: February 26, 20##
Abstract: An oil filter is provided which comprises a housing main body, a cover attached to the housing main body on the lower side thereof, an inner tubular member axially movably disposed in a recessed portion of the housing main body, a seal member interposed between the inner tubular member and the cover so as to provide a seal therebetween, a biasing unit for urging the inner tubular member in the direction to protrude from the recessed portion, and a filter element disposed in an oil flowing space between the housing main body and the cover, wherein when the cover is in a sate of being attached to the housing main body, the inner tubular member is pushed down into the recessed portion of the cover against a bias of the biasing unit.
PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To provide a remaining oil amount-detecting device for a fuel tank which can surely perform a display of a remaining oil amount, an alarming for a fuel-feeding time of the fuel tank, an oil-leakage alarming when an oil leakage occurs, and a water residing alarming when water as an impurity is accumulated while corresponding to the size of the fuel tank which is arbitrarily selected.
SOLUTION: This remaining fuel amount-detecting device for the fuel tank is equipped with a control device 3 which computes a remaining oil amount based on a liquid level-detecting signal from an ultrasonic liquid-level meter 2 installed in the fuel tank 1, and a remaining oil amount-alarming part 40 which displays the remaining oil amount when receiving a signal from the control device. The control device computes the remaining oil amount by a remaining oil amount-computing part 32 based on a maximum liquid level set value which is set by an initial value-setting part 30 and the liquid level- detecting signal, and the remaining oil amount and a fuel-feeding alarming amount are compared and judged. When the remaining oil amount is judged to be at the fuel-feeding alarming amount or less, a fuel-feeding alarm is displayed on an alarming part 41.
COPYRIGHT: (C)2004,JPO
Current U.S. Class: 62/470 ; 62/85
Current International Class: F25B 43/02 (20060101)
Field of Search: 62/84,85,469,470,473
2、Methods and apparatus for heating oil production reservoirs
United States Patent 7,243,721
Inventors: Arnaud; Johnny (Houston, TX), Beard; B. Franklin (Houston, TX), Schwartz; Merle W. (Houston, TX)
Assignee: Hydrotreat, Inc. (Houston, TX)
Appl. No.: 10/973,668
Filed: October 25, 20##
Abstract: Methods and apparatus employing inert gases injected into the lower level of sloping underground oil-bearing formations as a driving mechanism and water injected into the upper level of the formations as a gas blocking mechanism for increasing and extending the production of oil from underground formations is described. An oil production system to produce oil from a viscous reservoir is provided including at least one production well, a fluid injection well, and a heating system functionally associated with the at least one production well, the heating system having at least one electrical heating well adapted to direct power from a power supply at surface to the reservoir to heat the reservoir. Hydraulically-operated crude oil pumps are also provided.
Current U.S. Class: 210/443 ; 184/6.24; 210/136; 210/232; 210/450
Current International Class: B01D 35/30 (20060101); B01D 35/153 (20060101)
Field of Search: 210/232-238,440,443,444,450,453,454,398
3、Non-hydrogenated canola oil for food applications
United States Patent 7,238,852
Inventors: Fan; Zhegong (Delran, NJ)
Assignee: Cargill, Incorporated (Wayzata, MN)
Appl. No.: 10/869,422
Filed: June 16, 20##
Abstract: A non-hydrogenated canola oil having superior oxidative stability and fry stability useful for food applications is disclosed, as well as seeds, plant lines and progeny thereof from which the oil is derived.
Current U.S. Class: 166/372 ; 166/303
Current International Class: E21B 43/00 (20060101)
Field of Search: 166/372,303,305.1,250.15
4、Seeds, oils and seed meals produced from Sinapis alba
United States Patent 7,279,618
Inventors: Raney; John Philip (Clavet, SK), Rakow; Gerhard F. (Saskatoon, CA)
Assignee: Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, as Represented by Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada (Saskatchewan, CA)
Appl. No.: 10/204,142
Filed: February 16, 20##
PCT Filed: February 16, 2001
PCT No.: PCT/CA01/00183
371(c)(1),(2),(4) Date: January 06, 2003
PCT Pub. No.: WO01/60145
PCT Pub. Date: August 23, 2001
Abstract: The present invention provides oil seeds obtained from Sinapis alba that have a high level of oleic acid (from about 72 to about 84% by weight), a low level of erucic acid (from 0.0 to about 0.2% by weight), low levels of p-hydroxybenzyl glucosinolate and benzyl glucosinolate (each less than or equal to about 0.1 mole per g seed), or a combination thereof. Also provided are plants that produce such oil seeds. Also disclosed are oil seeds having high levels of erucic acid (greater than about 55% by weight) and low levels of p-hydroxybenzyl glucosinolate and benzyl glucosinolate (each less than about 0.1 mole per g seed), and plants that produce such oil seed.
Current U.S. Class: 122/348 ; 122/488; 405/128.85
Current International Class: F22B 37/16 (20060101)
Field of Search: 122/1B,1C,19.2,34,235.12,332,348,412,420,468,488 405/128.1,128.8,128.85
九、欧洲专利全文数据库
1、REMAINING OIL REMOVAL DEVICE AND OIL SEPARATION APPARATUS USING THE SAME
Publication number:JP2006035147
Publication date:20##-02-09
Inventor:YAMAUCHI HAJIME
Applicant:YAMAUCHI HAJIME
Classification:- international:
B01D43/00; B24B55/12; C02F11/00; C02F11/08; B01D43/00; B24B55/00; C02F11/00; C02F11/06;
- European:
Application number:JP20040221009 20040729
Priority number(s):JP20040221009 20040729
Also published as:CN1727073 (A)

 Abstract of JP2006035147
Abstract of JP2006035147
PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To realize oil separation with good efficiency by reducing a ratio of the oil remaining in a powdery substance discharged from a cyclone in an oil separation apparatus.
SOLUTION: The subject remaining oil removal device is constituted such that air is fed to the powdery substance 100 discharged from the cyclone 7 using a blower 73 and the remaining oil is ignited to scatter the oil. At this time, a rotary valve 72 is mounted between a discharge port of the cyclone 7 and a storage part 71 such that ignition of the oil at the storage part 71 is not transmitted into the cyclone 7.
COPYRIGHT: (C)2006,JPO&NCIPI
2、APPARATUS FOR DISCHARGING REMAINING OIL
Publication number: KR20040032578
Publication date: 20##-04-17
Inventor: KIM SEUNG IL
Applicant: HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Classification:
- international: F01M11/04; F01M11/04; (IPC1-7): F01M11/04
- European:
Application number: KR20020061777 20021010
Priority number(s): KR20020061777 20021010
View INPADOC patent family
View list of citing documents
 Abstract of KR20040032578
Abstract of KR20040032578
PURPOSE: An apparatus for discharging remaining oil is provided to rapidly discharge oil remaining in an engine to the outside by supplying hot air when oil is replaced. CONSTITUTION: An apparatus includes an air pump(110) generating wind at fixed pressure for discharge of oil; a heater(120) heating the wind generated in the air pump over fixed temperature so as to drop down viscosity of oil so that the oil is easily discharged; a first tube(210) and a second tube(220) supplying an oil injection port and an oil filter of an engine(50) with heated air, respectively, when the oil of the engine is replaced; an oil pump(300) installed on the second tube to supply oil at fixed pressure to the oil filter of the engine; and a supply valve(350) installed to the second tube, and supplying the oil filter with air supplied selectively from the oil pump and from the heater. A first connector(410) and a second connector(420) are connected to ends of the first tube and the second tube, and connected to the engine oil injection port and the oil filter of the engine, respectively
3、Method for finding remaining oil by boron and neutron life well-logging instrument
Publication number: CN1149100
Publication date: 1997-05-07
Inventor: LIU YING (CN); CHEN YONGSHENG (CN); YANG FENGTONG (CN)
Applicant: LIU YING (CN)
Classification:
- international: E21B47/00; E21B47/10; G01V5/04; E21B47/00; E21B47/10; G01V5/00; (IPC1-7): E21B47/10
- European:
Application number: CN19961008617 19960626
Priority number(s): CN19961008617 19960626
View INPADOC patent family
View list of citing documents
 Abstract of CN1149100
Abstract of CN1149100
A method for finding residual petroleum with boron element and neutron life logger features that the boron element solution as tracer is filled into oil-water well in low-mineralized oil field for tracking measurement, and a neutron life logger is used to measure out the distribution of residual petroleum in oil-bearing stratum, resulting in high recovery of low-mineralized oil field.
4、CONTROL METHOD FOR REMAINING OIL AND CONTROLLER FOR REMAINING OIL USING THE SAME
Publication number: JP2001280586
Publication date: 20##-10-10
Inventor: YAMAZAKI RYOICHI; SAITO MAKOTO
Applicant: MITSUBISHI MOTORS CORP
Classification:
- international: F16N29/00; F16N29/00; (IPC1-7): F16N29/00
- European:
Application number: JP20000091361 20000329
Priority number(s): JP20000091361 20000329
 Abstract of JP2001280586
Abstract of JP2001280586
PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To provide a control method for remaining oil, capable of surely controlling the amount of oil remaining in a work. SOLUTION: This method adopts a method of suspending a transmission structure A on a pallet 2 on a conveyor 1 from the pallet 2 to a prescribed position and extracting a great amount of transmission oil filled in the structure A therefrom for an operation test until a value of weight, including a remaining amount of oil weight preliminarily set, while measuring only the weight of the structure A. whereby a prescribed oil amount can be left in the structure A accurately, without being influenced by the scattering of weight of product of the pallet 2 and flowing-out of oil.
十、Springer全文电子期刊
1、
A simplified spreadsheet program for estimating future growth of oil and gas reserves
期刊 Natural Resources Research
出版社 Springer Netherlands
ISSN 1520-7439 (Print) 1573-8981 (Online)
期 Volume 7, Number 2 / 1998年6月
DOI 10.1007/BF02767709
页 149-155
Subject Collection 地球和环境科学
SpringerLink Date 20##年12月31日
A simplified spreadsheet program for estimating future growth of oil and gas reserves
James W. Schmoker1 and Robert A. Crovelli1
(1) U.S. Geological Survey, 80225 Denver, Colorado
(2) U.S. Geological Survey, Denver Federal Center, Mail Stop 939, Box 25046, 80225 Denver, Colorado
Received: 15 May 1997 Accepted: 11 July 1997
Abstract Reserve growth refers to the typical increases in estimated sizes of fields that occur through time as oil and gas fields are developed and produced. Projections of the future reserve growth of known fields have become important components of hydrocarbon resource assessments. In this paper, we present an algorithm for estimating the future reserve growth of known fields. The algorithm, which incorporates fundamental reserve-growth assumptions used by others in the past, is programmed for a personal computer in the form of formulas for a spreadsheet. The primary advantages of this spreadsheet program lie in its simplicity and ease of use. We also present a library of 17 different growth functions that provides numerical models for predicting the future sizes of existing oil and gas fields in various regions of the United States. These growth functions are formatted for use in the spreadsheet program.
Key words Reserve growth - field growth - oil - gas - resource assessment
2、Application of the modified Arps-Roberts discovery proces model to the 1995 U.S. National Oil and Gas Assessment
期刊 Natural Resources Research
出版社 Springer Netherlands
ISSN 1520-7439 (Print) 1573-8981 (Online)
期 Volume 4, Number 3 / 1995年9月
文章类型 Articles
DOI 10.1007/BF02257576
页 242-252
Subject Collection 地球和环境科学
SpringerLink Date 20##年11月23日
L. J. Drew, J. H. Schuenemeyer and R. F. Mast
Received: 27 December 1994 Revised: 13 March 1995 Accepted: 14 March 1995
Abstract ARDS (version 4.01), a modified version of the Arps-Roberts discovery process model, was used to forecast the remaining oil and gas resources in more than 50 provinces, super-exploration plays, and individual plays in the onshore and offshore United States for the 1995 National Oil and Gas Assessment. The size distribution of oil and gas fields was estimated for the underlying distribution of fields; the size distribution for the remaining fields was calculated to be the difference between this distribution and that of discovered fields. The guidelines that govern the 1995 National Assessment require the underlying size distribution of fields to be estimated by using only data from two standard commercial data files (the NRG Associates field file and the Petroleum Information Inc. well file). However, a variety of situations required further modification of the discovery process modeling system; for example, multiple exploration plays that occurred nearly simultaneously and also displaced each other in time, and the phenomenon of field growth introduced a large bias in the forecasts produced by the discovery process models for some provinces.
3、Effects of crude oil spillage on growth and yield of maize (Zea mays L.) in soils of midwestern Nigeria
期刊 Plant Foods for Human Nutrition (Formerly Qualitas Plantarum)
出版社 Springer Netherlands
ISSN 0921-9668 (Print) 1573-9104 (Online)
期 Volume 56, Number 4 / 20##年12月
DOI 10.1023/A:1011806706658
页 313-324
Subject Collection 化学和材料科学
SpringerLink Date 20##年10月28日
E.O. Ekundayo1, T.O. Emede2 and D.I. Osayande2
(1) Department of Soil Science, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Benin, Benin City, Nigeria
(2) Department of Crop Science, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Benin, Benin City, Nigeria
Abstract The effect of crude oil spillage on growth, productivity and nutrient uptake of maize (Zea mays L.) was assessed in a pot experiment using an Evwreni manifold sample of a petroleum development company, which had aspecific gravity of 0.8778. The Suwan 1 variety of maize was used in the experiment. In crude oil polluted soils, germination was delayed and the germination percentage was significantly affected by oil pollution. Growth was poor in polluted soils using parameters such as plant height, stem girth,ear height, leaf area at four weeks after planting, leaf area at maturity and average length of primary roots as growth indicators. Grain yield was significantly reduced at 95% level of probability with yield (when compared with the control) reduced by as much as 98.6%, 96.5% and 58.3% for preplant,five weeks after planting (5 WAP) and seven weeks after planting (7 WAP) treatments, respectively. Leaf analysis of the maize plants grown in soilscontaminated with crude oil a week before planting (preplant treatment) revealed mean levels of heavy metals (6.18 ppm Zn2+, 0.62 ppm Cu2+,26.24 ppm Fe2+, 10.84 ppm Mn2+, 2.96 ppm Pb2+ and 3.88 ppm Co2+) which are higher than the maximum permissible levels (MPL) for maize in tropical soils. Maize plants that were polluted at other time intervals showed no significant (p>0.05) variation in heavy metal concentrations when compared with the control, and were considered potentiallysafe for human consumption.
Crude oil - Growth - Heavy metals - Human consumption - Maize - Nutrient-uptake - Soil - Spill - Yield
4、Kinetic characterization of enhanced lipase activity on oil bodies
期刊 Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering
出版社 Springer Berlin / Heidelberg
ISSN 1615-7591 (Print) 1615-7605 (Online)
期 Volume 30, Number 4 / 20##年7月
文章类型 Original Paper
DOI 10.1007/s00449-007-0123-2
页 271-279
Subject Collection 化学和材料科学
SpringerLink Date 20##年4月19日
D. K. Allen1, 2 and B. Y. Tao1
(1) Biochemical Engineering Laboratory, Agricultural and Biological Engineering, Purdue University, F.S. Bldg Rm 3239, 745 Agricultural Mall Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907-2009, USA
(2) Present address: Department of Plant Biology, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA
Received: 30 November 2006 Accepted: 16 March 2007 Published online: 19 April 20##
Abstract Enzyme access, kinetic behavior, and protein–protein interactions are critical for explaining reaction of the metabolites contained within the myriad compartments of biological systems. To explore these relationships, the reaction kinetics of oil bodies versus oil emulsions as substrates for lipolytic reactions were measured. The initial rate of hydrolysis for the oil body system was comparatively very low due to a brief latency period. However, the complete activation of the lipase at the interface resulted in an enzyme–membrane complex that was catalytically enhanced 3–15-fold over the emulsion system for substrate concentrations in the measured range of approximately 1–5.5 mM. This disparity is explained by the availability of substrate to the enzyme active site (defined as the availability parameter “A”) which varies between the two substrates by 40-fold. A simple hyperbolic kinetic mechanism is proposed with K m replaced by the parameter, A, to account for this phenomenon, leading to a maximum rate of approximately 1450 IU/mg protein. The interaction is verified through separation of the enzyme–membrane complex which shows nearly double the activity towards an emulsified soybean oil substrate (activity ratio of 5:3) when compared to the native enzyme.
Keywords Heterogeneous catalysis - Interfacial activation - Lipase activation - Oil body - Oleosin - Soybean - Triacylglycerols
5、Encircling the Peak of World Oil Production
期刊 Natural Resources Research
出版社 Springer Netherlands
ISSN 1520-7439 (Print) 1573-8981 (Online)
期 Volume 8, Number 3 / 1999年9月
DOI 10.1023/A:1021646131122
页 219-232
Subject Collection 地球和环境科学
SpringerLink Date 20##年11月2日
Richard C. Duncan1 and Walter Youngquist
(1) Institute on Energy and Man, 5307 Ravenna Place, NE, #1, Seattle, Washington, 98105-3270
Abstract The peak of world oil production, followed by an irreversible decline, will be a watershed in human history. The goal of this paper is to predict the world peak. Production data from 42 countries representing 98% of world oil production, are used rather than reserve estimates. We believe the former is a more reliable indicator of the future for most oil-producing regions, with the exception, to some extent, of the OPEC nations which, at times, observe production quotas. In addition, we recognize that regional and global economic cycles occasionally change demand for oil, so production figures are not always a current indication of oil-field potentials. However, for the longer term, production is a useful measure of true oil-field potential. A judgmental factor also is applied based on the structure, stratigraphy, thermal maturity of oil basins, and volumes of sediments in potential oil basins yet to be fully explored. Combining these factors with the oil production numerical data, we have arrived at 20## for the time of world oil production peak. Alternative fossil fuel sources which might replace conventional oil (defined as oil from wells using only primary and secondary recovery methods) cannot come on stream early enough or in sufficient quantity to significantly affect the peak time. They will merely augment the far end of the world production curve. Our estimates do include recent technological developments in both exploration and production, but these also seem to be a minor factor in establishing the peak. Replacement of oil, to the degree this can be done, by renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydro, or tidal require much time and capital to bring on stream in significant quantity, and only limited world progress has been made in these sources. They likewise do not seem to move the peak significantly. We do recognize, however, given all possible variables, it is likely that our date of 20## may be wrong. The question is how far wrong? We believe it is reasonably close and on-going studies will narrow whatever error exists. Importantly, the peak of oil production will occur within the lifetimes of most people living today.
Oil futures, oil graphs - oil production peaks - alternative fuels
十一、OCLC FirstSearch联机检索系统检索指南
1.
求借信息: 检查你的图书馆的馆藏
世界各地拥有馆藏的图书馆: 104
版权: Copyright © Taylor & Francis Group
著者: Boffetta, G. ; Pécseli, H. ; Trulsen, J.
所属机构: Dipartimento di Fisica Generale, via Pietro Giuria 1, Torino, I-10125, Italy; University of Oslo, Institute of Physics, Box 1048 Blindern, Oslo, N-0316, Norway; University of Oslo, Institute of Theoretical Astrophysics, Box 1029 Blindern, Oslo, N-0315, Norway
题名: Numerical studies of turbulent particle fluxes into perfectly absorbing spherical surfaces
资料来源: Journal of Turbulence 7, no. 22 (2006): 1-16 (16 页)
附加信息: Taylor & Francis; 20060101
标准号码: ISSN: 1468-5248
DOI: 10.1080/14685240600573138
语种: English
登入号: 14685248NX83HH7134114531
数据库: ECO
2.
求借信息: 检查你的图书馆的馆藏
世界各地拥有馆藏的图书馆: 80
版权: Copyright © Taylor & Francis Group
著者: Hengwei, Liu ; Zhongliang, Liu ; Jian, Zhang ; Keyu, Gu ; Tingmin, Yan
所属机构: The Education Ministry Key Laboratory of Enhanced Heat Transfer & Energy Conversation, Beijing Municipal Key Laboratory of Heat Transfer and Energy Utilization, College of Environment and Energy Engineering, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing, 100022, China; Shengli Engineering & Research Institute, Shengli Oil Field Ltd., SINOPEC, Dongying, 257026, China
题名: A new type of dehydration unit of natural gas and its design considerations*
资料来源: Progress in Natural Science 15, no. 12 (2005): 1148-1152 (5 页)
附加信息: Taylor & Francis; 20050101
标准号码: ISSN: 1002-0071
DOI: 10.1080/10020070512331343198
语种: English
识别符: supersonic; swirling flow; dehydration; natural gas
登入号: 10020071W325018872885Q81
数据库: ECO
3.
求借信息: 检查你的图书馆的馆藏
世界各地拥有馆藏的图书馆: 302
版权: © Springer-Verlag
著者: Volkov, K. ; Denisikhin, S. ; Emel'yanov, V.
所属机构: Voenmekh D. F. Ustinov Baltic State Technical University 1st Krasnoarmeiskaya Str. St. Petersburg 190005 Russia
题名: Simulation of the internal dynamics of solid-fuel rocket engines on the basis of the STAR-CD suite
资料来源: Journal of Engineering Physics and Thermophysics 79, no. 4 (2006): 678-684
附加信息: Springer; 20060701
标准号码: ISSN: 1062-0125
DOI: 10.1007/s10891-006-0153-7
语种: English
摘要: Flows in the channels of solid-fuel charges with cross sections having different views in plan and flows in the prenozzle volume and the nozzle unit of a solid-fuel rocket engine have been simulated on the basis of the STAR-CD suite for different types of charges and different designs of the input part of the engine nozzle. The influence of the compressibility, turbulence, geometric factors, and flow rate on the distributions of gasdynamic parameters in the working region of the engine has been investigated.
登入号: 1062012510.1007_s10891-006-0153-7
数据库: ECO
4.
求借信息: 检查你的图书馆的馆藏
世界各地拥有馆藏的图书馆: 361
版权: © Springer-Verlag
著者: Yurinsky, V.
所属机构: Universidade da Beira Interior Rua Marquês d'Ávila e Bolama Covilhã Portugal
题名: On the smallest eigenvalue of the Stokes operator in a domain with fine-grained random boundary
资料来源: Siberian Mathematical Journal 47, no. 6 (2006): 1167-1178
附加信息: Springer; 20061101
标准号码: ISSN: 0037-4466
DOI: 10.1007/s11202-006-0122-6
语种: English
摘要: This article deals with a problem arising in localization of the principal eigenvalue (PE) of the Stokes operator under the Dirichlet condition on the fine-grained random boundary of a domain contained in a cube of size t ± 1. The random microstructure is assumed identically distributed in distinct unit cubic cells and, in essence, independent. In this setting, the asymptotic behavior of the PE as t is deterministic: it proves possible to find nonrandom upper and lower bounds on the PE which apply with probability that converges to 1. It was proved earlier that in two dimensions the nonrandom unilateral bounds on the PE can be chosen asymptotically equivalent, which implies the convergence in probability to a nonrandom limit of the appropriately normalized PE. The present article extends this result to higher dimensions.
识别符: Stokes flow; principal eigenvalue; random porous medium; chessboard structure; infinite volume asymptotics
登入号: 0037446610.1007_s11202-006-0122-6
数据库: ECO
5.
求借信息: 检查你的图书馆的馆藏
世界各地拥有馆藏的图书馆: 282
版权: © IOS Press
著者: Fang, Jiannong ; Owens, Robert G.
所属机构: GEOLEP-ICARE-ENAC, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, 1015 Lausanne, Switzerland; Département de mathématiques et de statistique, Université de Montréal, CP 6128 succ. Centre-Ville, Montréal, QC H3C 3J7, Canada
题名: Numerical simulations of pulsatile blood flow using a new constitutive model
资料来源: Biorheology 43, no. 5 (2006): 637-660 (24 页)
附加信息: IOS Press; 20060101
标准号码: ISSN: 0006-355X
语种: English
摘要: In the present paper we use a new constitutive equation for whole human blood [R.G. Owens, A new microstructure-based constitutive model for human blood, J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. (2006), to appear] to investigate the steady, oscillatory and pulsatile flow of blood in a straight, rigid walled tube at modest Womersley numbers. Comparisons are made with the experimental results of Thurston [Elastic effects in pulsatile blood flow, Microvasc. Res. 9 (1975), 145-157] for the pressure drop per unit length against volume flow rate and oscillatory flow rate amplitude. Agreement in all cases is very good. In the presentation of the numerical and experimental results we discuss the microstructural changes in the blood that account for its rheological behaviour in this simple class of flows. In this context, the concept of an apparent complex viscosity proves to be useful.
识别符: Aggregation; viscoelastic; thixotropic; pulsatile flow; Womersley; complex viscosity
登入号: 0006355Xbir433
数据库: ECO
6.
求借信息: 检查你的图书馆的馆藏
世界各地拥有馆藏的图书馆: 67
版权: © 20## Springer-Verlag
著者: Heese, Oliver ; Fritzsche, Erik ; Heiland, Max ; Westphal, Manfred ; Papavero, Luca
所属机构: Department of Neurosurgery University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf Hamburg Germany; Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf Hamburg Germany
题名: Intraoperative measurement of pharynx/esophagus retraction during anterior cervical surgery. Part II: perfusion
资料来源: European Spine Journal 15, no. 12 (2006): 1839-1843
附加信息: Springer; 20061201
标准号码: ISSN: 0940-6719
DOI: 10.1007/s00586-006-0070-7
语种: English
识别符: Anterior cervical fusion; Dysphagia; Esophagus; Laser Doppler perfusion monitoring
登入号: 0940671910.1007_s00586-006-0070-7
数据库: ECO
7.
求借信息: 检查你的图书馆的馆藏
世界各地拥有馆藏的图书馆: 1
版权: © Springer. Part of Springer Science+Business Media
著者: Guan, Wenna ; Tan, Feng ; Guan, Yafeng
所属机构: Department of Analytical Chemistry & Micro-Instrumentation, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics Chinese Academy of Science Dalian 116012 China
题名: Studies on column size scale-up and flow profile in conical shape liquid chromatographic column of 10° by visualization method
资料来源: Frontiers of Chemistry in China 1, no. 4 (2006): 448-453
附加信息: Springer; 20061201
标准号码: ISSN: 1673-3495
DOI: 10.1007/s11458-006-0059-0
语种: English
识别符: conical chromatography column; flow profile; visualization of chromatographic band; column scale-up; preparative liquid chromatography
登入号: 1673349510.1007_s11458-006-0059-0
数据库: ECO
8.
求借信息: 检查你的图书馆的馆藏
世界各地拥有馆藏的图书馆: 296
版权: © Springer-Verlag
著者: Kirsanov, V. ; Avdeeva, A. ; Avdeev, M.
所属机构: Southern Russian State Technical University (NPI) Novocherkassk; Rostov State Pedagogical University Novocherkassk
题名: Analysis of basic characteristics of cascade air classifiers
资料来源: Chemical and Petroleum Engineering 42, no. 9-10 (2006): 545-551
附加信息: Springer; 20060901
标准号码: ISSN: 0009-2355
DOI: 10.1007/s10556-006-0140-z
语种: English
摘要: A procedure for determination of basic characteristics of air classifiers-the required flow rate of air and the hydraulic resistance of the unit-is proposed on the basis of codification of experimental data. The sequence of the analysis is presented.
登入号: 0009235510.1007_s10556-006-0140-z
数据库: ECO
9.
登入号: CN061742024
BL位置: DSC的书架标记: 8022.642500V
著者: Shoji, M.; Nobe, T.; Tanabe, S.
题名: Thermal Comfort of Task Unit with Isothermal Air Flow Fan and Radiant Panel
页: P52
会议: 9th:; INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE -- 20## Sep : Coimbra, Portugal
姓名: Air distribution in rooms; Roomvent 20##
出版商: Portugal:; University of Coimbra,; 20##
期刊: ROOM VENT -CD-ROM EDITION-; 2004; CONF 9
标准号码: ISBN: 9729797323 (CD-ROM)
资料来源编辑: Gameiro da Silva, M. C.
数据库: PapersFirst
10.
登入号: CN060278529
BL位置: DSC的书架标记: 8253.358000V
著者: Cantore, G.; Fontanesi, S.; Gagliardi, V.; Malaguti, S.
题名: Effects of Relative Port Orientation on the In-Cylinder Flow Patterns in a Small Unit Displacement HSDI Diesel Engine
页: 05SETC-06
会议: Conference; 11th -- 20## Oct : Bangkok
姓名: Small engine technology
出版商: SAE; 20##
期刊: SETC PROCEEDINGS -CD-ROM EDITION-; 2005; 11TH
标准号码: ISBN: 4915219550
数据库: PapersFirst
11.
登入号: CN060173227
BL位置: DSC的书架标记: 4976.300000
著者: Zhao, L.; Adamiak, K.
题名: EHD gas flow in electrostatic levitation unit
页: 639-645
会议: 5th -- 20## Sep : Poitiers, France
姓名: Fifth international electrohydrodynamics
出版商: Elsevier; 20##
期刊: JOURNAL OF ELECTROSTATICS 0304-3886; 2006; VOL 64; NO 7-9
资料来源编辑: Romat, H.; Touchard, G.
数据库: PapersFirst
12.
登入号: CN060071390
BL位置: DSC的书架标记: 1745.203800
著者: Begdouri, H.; Rosario, L.; Rahman, M. M.
题名: IMECE20##-82825 Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer Induced by a Window Air Conditioner Unit and Associated Thermal Comfort
页: 305-312
会议: 20## Nov : Orlando, FL
姓名: Proceedings of the ASME Heat Transfer Division--2005: presented at 20## ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition
赞助者: American Society of Mechanical Engineers.
出版商: New York, N.Y.; American Society of Mechanical Engineers; c2005
期刊: ASME -PUBLICATIONS- HTD; 2005; VOL 376; PART 1
标准号码: ISBN: 0791842215
数据库: PapersFirst
13.
登入号: CN059530627
BL位置: DSC的书架标记: 4542.538350
著者: Wang, Y.; Tung, Y.-K.
题名: Stochastic generation of geomorphological instantaneous unit hydrograph-based flow hydrograph
页: 49-56
会议: Congress; 14TH -- 20## Dec : Hong Kong, China
姓名: International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research
赞助者: International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research.
出版商: International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research,; 20##
期刊: INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RIVER BASIN MANAGEMENT 1571-5124; 2006; VOL 4; NUMB 1
数据库: PapersFirst
14.
求借信息: 检查你的图书馆的馆藏
世界各地拥有馆藏的图书馆: 653
版权: © Oxford University Press
著者: Maseda, Pablo H. ; Fernández, Roberto J.
所属机构: IFEVA-CONICET and Facultad de Agronomía, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Av. San Martín 4453, Buenos Aires C1417DSE, Argentina; To whom correspondence should be addressed. E-mail: fernandez@ifeva.edu.ar
题名: Stay wet or else: three ways in which plants can adjust hydraulically to their environment
资料来源: Journal of Experimental Botany 57, no. 15 (2006): 3963-3977
附加信息: Oxford University Press; 20061201
标准号码: ISSN: 0022-0957
DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erl127
语种: English
摘要: The literature on whole-plant acclimation to drought is reviewed and it is proposed that leaf-level homeostasis in water status is attained during ontogeny largely thanks to whole-plant changes in physical resistance to liquid water flow caused by morphological and anatomical adjustments. It is shown that, in response to water deficits, plant resistance changes at different levels (tissue, organ, individual), levels that are correlated with the time scale of the response. It was found that such adjustments apparently tend to increase resistance to flow in the short term and to reduce it in the long term. A critical view of those findings is provided based on the principle that drought-induced changes cannot be analysed separately from the allometric changes that take place through ontogeny, as for example proposed by the widely cited hydraulic limitation hypothesis. A graphic synthetic model is presented according to which developmental responses to water deficits operate largely through reductions in whole-plant water transport capacity, combined with more or less strong reductions in leaf area (different ‘hydraulic allometries’), depending on the intrinsic tolerance of leaf tissues to partial desiccation. The model is used to show that, as the result of such adjustments, the water transport capacity per unit leaf area can decrease, remain constant, or increase, and it is argued that the expected leaf-level response would be different in each case, respectively involving a decreased, constant, or increased potential for transpiration. The article ends with a plea to collect the evidence needed to evaluate the occurrence of these three different response types across taxa and their association with different environments, including the reanalysis of existing data.
登入号: 00220957exbotjerl127
数据库: ECO
16.
求借信息: 检查你的图书馆的馆藏
世界各地拥有馆藏的图书馆: 1
版权: © Springer. Part of Springer Science+Business Media
著者: Guan, Wenna ; Tan, Feng ; Guan, Yafeng
所属机构: Department of Analytical Chemistry & Micro-Instrumentation, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics Chinese Academy of Science Dalian 116012 China
题名: Studies on column size scale-up and flow profile in conical shape liquid chromatographic column of 10° by visualization method
资料来源: Frontiers of Chemistry in China 1, no. 4 (2006): 448-453
附加信息: Springer; 20061201
标准号码: ISSN: 1673-3495
DOI: 10.1007/s11458-006-0059-0
语种: English
识别符: conical chromatography column; flow profile; visualization of chromatographic band; column scale-up; preparative liquid chromatography
登入号: 1673349510.1007_s11458-006-0059-0
数据库: ECO
十二、外文期刊整合服务系统
1、
Standard facies models to incorporate all heterogeneity levels in a reservoirmodel
Marine and Petroleum Geology
0264-8172, Volume 23, Issue 9-10, 2006, Pages 943-959
D.Mikes; C.R.Geel
Abstract
The construction of reservoir models is frustrated by the fact that core andwell cover only a fraction of the reservoir volume and it is therefore difficult to determinefeatures like facies shape,-size,and -distribution,inter- and intra-facies boundaries and lateraltrends from them.These features are,however,critical to fluid flow and they should necessarily beincorporated in the reservoir model and we therefore propose to systematically describe geometry anddistribution of facies.To this end we make use of 'standard facies models' that a priori containall elements and boundaries of facies for a number of typical depositional environments.
Keywords
Upscaling; Facies; Flow unit; Reservoir model
2、
Applying the Dynamic Two-Step Method to Forecast Remaining Oil Distributionof Lower Series, Xiaermen Oilfield
Journal of China University of Geosciences
1002-0705, Volume 17, Issue 1, 2006, Pages 65-70
Zhou Hong; Tang Chuanyi; Li Zenghui
Abstract
The distribution of remaining oil is often described qualitatively. Theremaining oil distributed in the whole reservoir is calculated according to the characteristics ofthe space distribution of the saturation of remaining oil. Logging data are required to accomplishthis. However, many such projects cannot be completed. Since the old study of remaining oildistribution could not be quantified efficiently, the ''dynamic two-step method'' is presented.Firstly, the water cut of every flow unit in one well at one time is calculated according to thecomprehensive water cut of a single well at one time. Secondly, the remaining oil saturation of theflow unit of the well at one time is calculated based on the water cut of the flow unit at a giventime. The results show that ''dynamic two-step method'' has characteristics of simplicity andconvenience, and is especially suitable for the study of remaining oil distribution at highwater-cut stage. The distribution of remaining oil presented banding and potato form, remaining oilwas relatively concentrated in faultage neighborhood and imperfect well netting position, and thenet thickness of the place was great. This proposal can provide an effective way to forecastremaining oil distribution and enhance oil recovery, especially applied at the high water-cut stage.
Keywords
dynamic two-step method; flow unit; quantitative forecast; remaining oil
十三、ScienceDirect全文数据库
1、The oil reserves production relationship
Andrew PickeringDepartment of Economics, University of Bristol, 8 Woodland Road, Bristol, BS8 1TN, UK
Received 6 April 2006; revised 17 January 2007; accepted 17 January 2007. Available online 22 February 2007.
Abstract
This paper considers the relationship between the extraction rates and remaining reserves of oil. A simple exhaustible resources model suggests a linear extraction rule, with slope terms common to all extractors when discount rates are homogeneous. Differences in pricing behavior and costs determine the intercept. Panel data from the world oil industry exhibit a robust and stable extraction–reserves relationship across countries and through time. Common slopes characterize extraction over large ranges of reserves although there is a concave relationship across non-OPEC members, and a significantly lower estimated slope within OPEC countries. These findings may be explained by risk aversion, differences in discount rates, and measurement error in the reserves data.
Keywords: Oil; Extraction; Reserves; Exhaustible resources; OPEC
JEL classification codes: N5; Q3
Tel.: +44 117 928 8422.
Energy Economics
Volume 30, Issue 2, March 2008, Pages 352-370
2、Beneficial effects versus toxicity of medium-chain triacylglycerols in rats with NASH
Charles S. Lieber1, 2, Leonore M. DeCarli1, Maria A. Leo1, 2, Ki M. Mak2, Anatoly Ponomarenko1, Chaoling Ren2 and Xiaolei Wang2
1Alcohol Research Center, James J. Peters VA Medical Center, 130 West Kingsbridge Road (151-2), Bronx, NY 10468, USA
2Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, NY, USA
Received 29 June 2007; revised 4 September 2007; accepted 13 September 2007. Associate Editor: Y.M. Deugnier. Available online 10 December 2007.
Background/Aims
Replacing long-chain triacylglycerols (LCT) with medium-chain triacylglycerols (MCT) reduces alcohol-induced liver injury. Because of the similarity of the pathogenesis of alcohol-induced liver damage and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), our aim was to assess whether MCT is also beneficial in NASH.
Methods
We used a rat NASH model in which corn oil (35% of total calories) was isocalorically replaced with MCT.
Results
Partial replacement of LCT did not ameliorate hepatic fat accumulation, 4-hydroxynonenal, collagen type I and its mRNA but it increased TNF-α and its mRNA (p < 0.001). However, in rats given the high-fat diet restricted to 2/3 of the amount they were consuming, these adverse effects decreased, with and without MCT including less liver steatosis and lower triacylglycerols, but without beneficial effects of MCT. When 70% of the fat calories were replaced with MCT with no LCT remaining in the diet, no steatosis developed and hepatic TNF-α was low. When all MCT were given with carbohydrates (instead of LCT) hepatic TNF-α also decreased (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
MCT are not hepatotoxic, provided the diet contains no significant amount of LCT. Total replacement of dietary LCT with MCT fed ad libitum is beneficial whereas partial replacement becomes hepatotoxic, unless the dietary intake is restricted.
Keywords: Long-chain triacylglycerols; Medium-chain triacylglycerols; Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; TNF-α
 The authors declare that they do not have anything to disclose regarding funding from industries or conflict of interest with respect to this manuscript. NIH funded study, NIH Grant AT001583.
The authors declare that they do not have anything to disclose regarding funding from industries or conflict of interest with respect to this manuscript. NIH funded study, NIH Grant AT001583. Corresponding author. Address: Alcohol Research Center, James J. Peters VA Medical Center, 130 West Kingsbridege Road (151-2), Bronx, NY 10468, USA. Tel.: +1 718 741 4244; fax: +1 718 733 6257.
Corresponding author. Address: Alcohol Research Center, James J. Peters VA Medical Center, 130 West Kingsbridege Road (151-2), Bronx, NY 10468, USA. Tel.: +1 718 741 4244; fax: +1 718 733 6257.
Journal of Hepatology
Volume 48, Issue 2, February 2008, Pages 318-326
3、Extraction of lactic acid into sunflower oil and its recovery into an aqueous solution
Presented in the Separation Sessions at Chemeca 2006, the 34th Australasian Chemical and Process Engineering Conference, Auckland, New Zealand, 17– 20 September 2006. Organised by the University of Auckland and the Society of Chemical Engineers New Zealand (SCENZ).
T. Haringtona and Md.M. Hossain , a,
, a, 
aDepartment of Chemical and Materials Engineering, The University of Auckland, Private Bag 92019, Auckland, New Zealand
Received 18 November 2006; accepted 10 February 2007. Available online 4 December 2007.
Abstract
Demand for lactic acid is growing, especially, for its use in the production of biodegradable polymer (polylactate). The current method of production and separation of lactic acid is both expensive and unsustainable. This is partly due to the cost and lower efficiency of the current method for separating the lactic acid product from the fermentation media. Therefore, the development of alternative technology that will offer efficiency, economic and environmental benefits is of great importance. One of the promising technologies for recovery of lactic acid from fermentation broth is reactive liquid–liquid extraction. In this paper, processes based on reactive extraction of lactic acid into an organic phase and its recovery into an aqueous phase is examined. The percentages of extraction and recovery are determined by using a small pilot-scale microporous hollow-fibre membrane module (HFMM). Firstly, equilibrium experiments were conducted using organic solutions consisting of Aliquat 336 and trioctylamine (as carriers) and tributyl phosphate and sunflower oil (as solvents) The values of the distribution co-efficient (defined as a ratio of the concentration of lactic acid extracted over that remaining in the aqueous solution at equilibrium) were obtained as a function of feed pH (range 4.0–6.5), composition of the organic phase (ratio of carrier to solvent) and temperature (range 8–40°C). The best extraction was obtained with the organic phase of 15wt% tri-octylamine (TOA), 15% aliquat 336 dissolved in 35 wt% tri-butyl phosphate (TBP) and 35% sunflower oil. The percentage extraction from 0.1 M was approx. 70% after 4 h at pH 5.0 and at 35°C at a recirculating flow rate of 15–20 L/h. Lactic acid was reextracted from the organic phase by using 0.5 M sodium carbonate solution and approx. 90% recovery was obtained in 4 h. These results demonstrate that good extraction and recovery of lactic acid in the hollow-fibre membrane are possible. Also because of its potential for application in situ the process would allow to maintain lactic acid concentration at low levels during the fermentation and to improve productivity by suppressing the product inhibition effects.
Keywords: Extraction; Lactic acid; Carrier; Hollow-fibre membrane; Recovery
十四文献综述
文献综述或文献调研报告:
油气储层流动单元研究综述
油田进入特高含水期开采阶段,储层中剩余油的分布无论在层间和平面,还是在层内和孔隙中都呈高度分散状态,挖潜难度愈来愈大。影响剩余油分布的主要因素有地质和开发两大方面的因素,储层自身复杂非均质体系所造成的不同层次、不同规模的非均质性是导致剩余油高度分散的主要地质因素。如何将剩余油开采出来 ,是石油工作者面临的难题 。自20世纪80年代以来,一种全新的描述储层非均质模型的新方法 ——储层流动单元法应运而生。目前,流动单元法已经成为储层表征和建模的新技术,由此产生的划分流动单元的方法也在不断更新。
1、储层流动单元含义及其研究现状
1.1 储层流动单元的含义
流动单元(flow unit),亦称岩石物理流动单元(petrophysical flow unit)、储层流动单元) (reservoir flow uni t )、水动力流动单元(hydraulic units) ,是垂向及横向上连续的、影响流体流动的、岩石物理性质相似的储集岩体。流动单元法是一种着眼于建立孔喉规模非均质模型的新方法,这种方法将地质和工程方法有机地结合起来,为认识油藏的非均质性提供了有效的手段 。
1.2 国外研究现状
Hearn 等 在对美国怀俄明州 Hartzog Draw油田的 Shannon 砂岩储层进行研究时,将 Shannon砂岩储层划分为 5 种相带 ,进一步研究认为同一相带的不同部位储层质量不同,对生产的控制作用也不尽相同;在此基础上,他们首次提出了岩石物理流动单元的概念,并定义流动单元为横向和垂向上连续的储集带,影响流体流动的岩石物理性质和岩层特点在各处都相似。Hearn 等提出:流动单元是成因单元内流体在横向和垂向上连续流动的空间。Ebanks 对这一概念作了进一步的阐述,认为流动单元是一个储集岩体 a volume of reservoir rock,在这个流动单元内相同和可预测的参数值以及岩石物理性质影响着流体的流动,而与其他储集岩体不同。目前有关流动单元的研究大都沿用这一概念。Rodriguez 等 用渗透率、孔隙度、粒度中值的多坐标交汇法划分流动单元,提出了 2 种划分流动单元的方法: ①根据区域上稳定发育的泥岩层进行划分;②根据相带或相带组合来划分,并建立了利用相带组合划分流动单元的 7 个步骤 ,这实际上是一种定性的研究方法。Barr 等认为流动单元是给定岩石中水力系数相似的层段。Amaefule 等 认为水力单元即为“孔隙几何单元”,是总的油藏岩石体积中影响流体流动的地质和油层物理性能恒定不变并可与其他岩石体积区分开来的有代表性的基本体积REV 。这一概念比 Hearn 等提出的流动单元概念更细,Amaefule 等强调的是“影响流体流动的地质和油层物理性能恒定不变”,而 Hearn 等强调的是“相似性”,并认为流动单元中的渗透率是变化的 ,流动单元仍是一个非均质体。按照这个思路,Amaefule等利用修改的 Kozeney2Carman 方程,推导出划分流动单元的流动层段指标 FZI flow zone)ndex,利用 FZI 可以提高渗透率的解释精度。Sllseth 等 在研究流动单元对水驱动态模拟的影响时构筑了一个面积为25 km 、厚度为25m 的滨外沙坝人造模型,该模型由5个横向上连续的相带组成,每个相带又划分为13个成因相,每个成因相即为一个流动单元。Ti Guangming等在研究阿拉斯加北斜坡 Endicott 油田的储层时对流动单元做到了真正意义上的定量研究。他们从测井资料出发,用流动系数、存储系数、净与毛厚度比3个参数进行聚类分析,每一聚类组为一个流动单元,共划分了4 类,根据取芯井划分结果进一步推广到未取芯井,借助于井间地层对比建立了流动单元的井间分布关系,并定义为:流动单元是一个在横向和垂向上连续的储集岩体,具有相似的岩石物理性质,并影响着流体的流动。Kramer 和 Hamlim 等在研究流动单元时也是以沉积相研究为起点,把每个相或岩相看作一个流动单元,在井间对比时运用了建筑结构知识,将单井级别的流动单元相连结而形成储层流动单元。Alden等提出:压汞曲线上进汞饱和度达 35 %时的孔隙半径R的大小可以岩石中的流体流动和开发动态,因此他们用R值来划分流动单元,并认为流动单元是孔喉半径R均匀分布的、具有相似的岩石物理性质并使流体连续流动的储集层段 intervals 。
近年来,流动单元研究已经在低渗透砂岩储层,尤其是碳酸盐岩等缝洞型复杂储层的表征和建模中得到普遍应用,并在油气田开发中取得了良好的效果 。
1.3 国内研究现状
“八五”中后期流动单元的概念被国内研究者广为接受,特别是自 1989年“第2届国际储层表征技术研讨会”后,大量的国外研究方法被介绍到国内 ,同时国内的一些专家学者也提出了自己对流动单元概念的理解并建立了相关的研究方法。张一伟 最早应用岩石物理相这一概念 ,并将岩石物理相看作沉积相与成岩相的综合。熊琦华等认为,岩石物理相是沉积作用、成岩作用和后期构造作用的综合结果 ,其最终表征的是流体渗流孔隙网络特征的高度概括 ——孔隙模型 ,由岩石骨架、孔隙网络、孔隙内黏土矿物的敏感性、孔隙表面特征4个方面来表征,并论述了岩石物理相的延展原理、叠加原理。裘亦楠等 认为流动单元是指受储层非均质性、隔挡和窜流旁通条件的影响,注入水沿着地质结构引起的一定途径驱油而自然形成的流体流动通道。穆龙新等 又发展了裘亦楠等的思想,认为储层的非均质性由宏观到微观均具有层次性,当油田处在一定阶段,由某一层次的非均质性引起的矛盾为主要矛盾,此时可以把下一层次的非均质性看成是均质的,即作为油水运动的基本单元;因此,“流动单元”概念的内涵应针对开发生产中面临的矛盾而有所变化。他们认为目前的流动单元是指一个油砂体及其内部因受边界限制,由不连续薄隔挡层、各种沉积微界面、小断层及渗透率差异等因素造成的渗透特征相同、水淹特征一致的储层单元。在一个小层或单砂体内部可能细分出多个流动单元,也可能就是油砂体本身。为提高后期高含水厚油层的采收率,主要应解决层内非均质性造成的矛盾,因此厚层内部划分的流动单元应是岩石物理相或孔隙几何形状相。
焦养泉等在研究鄂尔多斯盆地的曲流河和湖泊三角洲沉积体系时,将流动单元定义为建筑结构的一部分,并认为流动单元是指沉积体系内部按水动力条件进一步划分的建筑块体 buildingblocks,它与构成单元 结构要素 属于类似的概念。他们所说的“流动”是指沉积的水动力流动,与Hearn等定义中的“流动”不同,但其划分的结果与成因或岩相类似。姚光庆等 在研究新民油田低渗细粒储集砂岩时指出,岩石物理相是一定规模的储层的岩石物理特性的综合,是流体流动单元的最基本岩石单位,是沉积作用、成岩作用及构造作用对岩石共同作用的综合反映;他们同时指出,岩石物理相的描述比岩石相或成岩相的描述更复杂,但可以借助一些综合化的定量指标来表征,使其简单化并具有可操作性,岩石物理相的分析必须建立在对沉积微相 岩石相 和成岩作用详细分析的基础上。
综上所述可知,储层流动单元是受沉积作用、成岩作用控制而使成因单元内部岩石物理性质具非均质性,从而导致流体在横向和垂向上差异流动的一个储集岩体。流动单元不仅具有相同 似 的沉积特征,而且具有相同似的流动渗流特征,是储层岩石物理特征的综合反映。同一流动单元具有相似的水动力学特征,亦有相似的水淹特点,这就比单纯的沉积特征研究更加深入 ,从而为实现储集层的详细描述并实现静态与动态资料相结合来描述油藏 ,建立准确的地质模型奠定了基础。
2、储层流动单元的划分方法
2.1 流动单元的特征及其成因分类
(1) 断层控制的流动单元。断层对油区内大范围的流体渗流具有很重要的作用。如果断层是封闭的,则隔断了断层两盘之间流体的渗流,起到遮挡作用,形成2 个流动单元;如果断层未封闭,就是一个大型的渗流通道,形成一个统一的流动单。
(2)隔层控制的流动单元。隔层是指油层之间或者开发层系之间的不渗透岩层,在油田注水开发过程中对流体具有隔绝能力。隔层的形成受构造和沉积条件的控制,常由泥岩、粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩、泥质和钙质粉砂岩组成。
(3)夹层控制的流动单元。夹层是指小层或单砂体内的不渗透岩层。它不仅影响流体的垂向渗流,而且也影响流体的水平渗流。由于夹层的存在,改变了整个渗流场的分布,使渗流 油水运动。夹层的分布状况对油水运动产生很大的影响。分布稳定的夹层 ,可将油层上下分成 2 个独立的流动单元;分布不稳定的夹层,使油层上下具有水动力联系,一般表现为注入水下窜。在一个小层或单砂体内部既可能细分出多个流动单元,也可能就是一个流动单元。
(4)渗透率韵律控制的流动单元。渗透率韵律是指砂体内渗透率的高低按一定顺序变化,这种渗透率的差异将直接影响到储层内部流体的渗流特征。垂向上不同的渗透率组合类型和内部不同的非均质程度,对储层渗流特征及油层水洗厚度的影响也不同。按照渗透率的韵律性可以划分出不同的流动单元。对于正韵律油层,由于其下部颗粒粗、渗透率高,向上颗粒变细、渗透率变低,注入水先沿着下部的高渗透层段推进,加上重力的影响 ,因此上部的低渗透层段注入水很难波及 ,全油层中只能有部分厚度被水洗。据此,可以将正韵律油层按渗透率高低的变化,分为2个流动单元。
(5)层理构造控制的流动单元。层理是砂体内部最常见的沉积构造。对岩芯样品的实测结果表明,垂直层理倾斜方向的渗透率比顺着层理纹层延伸方向的渗透率低,因此对斜层理砂岩沿着纹层延伸的不同方向进行注水,其波及状况和驱油效率是不同的。由于层理构造内部纹层方向性的差异,导致其内部流体渗流特征的差异,从而形成不同的流动单元。
(6)裂缝控制的流动单元。储层中若存在裂缝,则裂缝的封闭性和开启性以及裂缝延伸的方向、长短对流体渗流的影响极大。裂缝的存在,使得储层的渗流特征表现出明显的各向异性。
(7)孔隙结构控制的流动单元。储层岩石的孔隙结构是指岩石所具有的孔隙和喉道的几何形状、大小、分布及其连通状况,是油气储层地质学研究的重要内容,属于微观非均质性研究的范畴。喉道的大小和分布及其几何形状是影响储层渗流特征的主要因素。由于孔隙结构的差异导致渗流特征的差异,从而形成不同的流动单元。
2.2 沉积岩相划分法
Jian 等认为识别流体流动单元就是鉴别具有相似岩石物理性质的三维岩体。因此划分流动单元的地质方法是在详细的钻井岩芯沉积学研究的基础上,将储层划分为具有特定沉积、成岩特征的岩相。为了将岩芯研究结果应用于未取芯井中,Jian等采用判别分析方程进行识别,根据取芯井建立判别函数 ,应用建立的模型并结合测井组合资料来定量识别不同的岩相。
2.3 地震属性分析法
(1)利用振幅属性。当砂层厚度大于调谐厚度时 ,利用波峰到波谷的时差随地层厚度增大而呈线性增大的原理 ,用时差求取砂层厚度;反之 ,由于波峰到波谷的相对振幅与厚度满足近线性关系 ,可用振幅代替砂层厚度。因此可以利用井点砂层厚度、振幅值及未知点的振幅值来求得未知点的砂层厚度。
(2)利用波阻抗属性。提取井旁地震子波,结合声波及密度资料合成地震记录,给井旁地震道赋予波阻抗信息,再利用地震记录道振幅与反射系数的相似性及相邻地震记录道的高度相关性,由井旁外推到其他地震道 ,建立波阻抗岩性剖面。由于砂岩的波阻抗值比泥岩大许多,据此可以直观地求得砂体的边界及厚度。
2.4 以地质研究为主的储层层次分析法
该分析法是将高分辨率层序地层学原理、层次界面分析和流动单元定量划分三者融为一体,采用层次分析的一种方法。其思路是:首先应用高分辨率层序地层学旋回等时对比法则,建立高分辨率等时地层格架,并研究其中泥质间隔、夹层的分布;然后在等时地层单元内,按照其中不同级次沉积界面和结构单元的特征,将储层详细解剖到成因砂体或成因单元,并进一步分析界面间沉积、成岩胶结屏障及断层遮挡状况,建立精细的储层结构模型及渗流屏障模型;最后分析影响渗流的储层地质参数,在成因砂体或成因单元内定量划分流动单元,建立储层流动单元分布模型及其三维定量地质模型。这类方法较适用于陆相非均质储层。对流动单元的分级描述,充分体现了Miall 的层次分析思想。
2.5 基于流动系数、存储系数、净与毛厚度比的流动单元划分法
Ti Guangming等在研究阿拉斯加北斜坡Endicott 油田的储层时从测井资料出发,用渗流系数、存储系数和净与毛厚度比3个参数来划分流动单元,其步骤如下:
(1)地层对比。在对储层的地质情况重新认识和测井曲线(特别是伽马、电阻率和孔隙度测井曲线)对比的基础上,确定井间地层关系。
(2)相分层。在取芯井,先将沉积层段划分为代表不同相的主层,每个主层代表一种沉积环境,再利用3个参数(渗透率 k、孔隙度φ和泥质体积分数φB)将主层分为小层,并分别计算每个小层的渗流系数、存储系数、净与毛厚度比 hn / h 。渗流系数 = k·hn / µ(hn为储层的有效厚度;h为总厚度;µ为流体的黏度,反映了地下储集岩体通过流体的能力,可直接反映储层是否具备开发利用价值;存储系数= φ·Ct ·hn(Ct为岩石的压缩系数),是储层存储空间大小的反映。
(3)取芯井流动单元的确定。将一个流动单元视为一个小层组,在同一个小层组中上述 3 个参数值相似,因此可以采用聚类分析法将其划分成不同的流动单元。
(4)油田范围内流动单元的确定。在取芯井上建立岩芯分析资料和测井解释资料之间的统计关系,以此为基础,将流动单元的概念扩展到非取芯井。
2.6 岩石微观孔隙结构法
(1)利用 FZI 值划分流动单元。通过求取岩芯分析数据的FZI值,选定油藏品质指标 RQI 和孔隙体积/颗粒体积之比2个参数,采用聚类分析法来划分岩石物理相,进而划分流动单元,对一系列测井数据进行归一化处理后建立测井数据与岩芯分析确定的流动单元间的关系,采用判别分析法,分别建立各个流动单元的判别函数。
流体流动特征相似的不同层带 流动单元 的存在与否取决于孔隙几何特征的状况,因此可以根据孔喉特征将厚层划分为流动特征相似的不同流动单元。
Kozeny 和 Carmen 利用平均水力半径的概念,应用 Poisseuille 和 Darcy 定律推导出有效孔隙度、渗透率 k 之间的关系式,即 Kozeny-Carmene关系式:
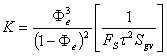 (1)
(1)
式中:Fs为形状系数; 为孔隙介质的迂曲度;
为孔隙介质的迂曲度;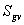 为单位体积颗粒的表面积。
为单位体积颗粒的表面积。
将式(1)两边除以 ,并取平方根,得
,并取平方根,得
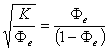
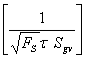 (2)
(2)
如果渗透率的单位用10 -3µm 表示,则定义如下:
RQI=0.0314  (3)
(3)
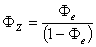 (4)
(4)
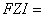
 =
=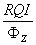 (5)
(5)
式中:RQI 为油藏品质指标;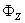 为标准化孔隙度指标;FZI 为流动层段指标。
为标准化孔隙度指标;FZI 为流动层段指标。
式(5)两边取对数,得:
lg (RQI)= lg (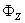 )+lg (FZI) (6)
)+lg (FZI) (6)
式(6)表明:具有相同 FZI 值的样品的lg (RQI)与lg (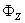 )呈直线关系;具有不同 FZI 值的样品的lg (RQI)与lg (
)呈直线关系;具有不同 FZI 值的样品的lg (RQI)与lg (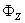 )呈相互平行的直线关系。
)呈相互平行的直线关系。
因此,理论上,在 RQI 与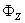 的双对数坐标系上,位于 FZI 值为常数的直线上的样品,属于同一流动单元。
的双对数坐标系上,位于 FZI 值为常数的直线上的样品,属于同一流动单元。
(2 )孔喉半径 R35法。Alden等提出了一种利用孔喉半径R35来划分和评价岩石物理流动单元的方法。R35的值可用 Winland 公式求得:
R35=0.372+0.588lg (K)-0.64 lg (φ) (7)
Alden等根据孔喉半径R35的分布范围将岩石物理流动单元分为 4 种类型:①巨孔喉流动单元,R35>10µm;②大孔喉流动单元,R35为 2~10µm;③中孔喉流动单元,R35为0.5~2.0µ m;④微孔喉流动单元R35 <0.5µm。
3、在油田开发中的意义
研究资料表明,仅依靠二次采油平均采收率为35%,一般估计还有 20%的可动油由于储层的非均质性而未被水驱油过程中的注入水波及到。通过深化对储层非均质性的认识及改善二次采油技术,这部分可动油是完全可以开采出来的 ,因此进一步提高老油田的采收率,其经济效益远远大于边远地区的勘探效益。如何准确地预测油藏剩余油的空间分布、制定合理的开发调整方案、提高采收率 ,已成为稳产、增产的主攻方向。流动单元概念的提出已从一个层的概念发展到一个三维储集体的概念,其成因意义在于可以反映特定的沉积环境和流体流动的特征,从而使其与储层建筑结构紧密地联系起来,成为一个可预测、可操作的地质体。同时,作为储层描述和评价的一种有力的工具,流动单元的研究必将在今后一段时期成为石油地质和石油工程领域中一个新的研究热点。
