文献检索课程报告
班级:____________
学号:___________
姓名:__________
一.选题简介:
课题名称:图像场景分类
Image scene classification
关键词:场景 分类
Scene classification
二、文献检索过程:
1,使用CNKI的中国学术期刊网络出版总库
因为场景图像分类是计算机视觉领域中的一个基本问题, 在期刊上应该有所反映。
2, 检索词: 场景分类
检索过程:
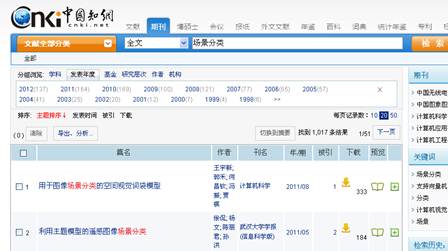
三、资料阅读:
检索结果列表如下
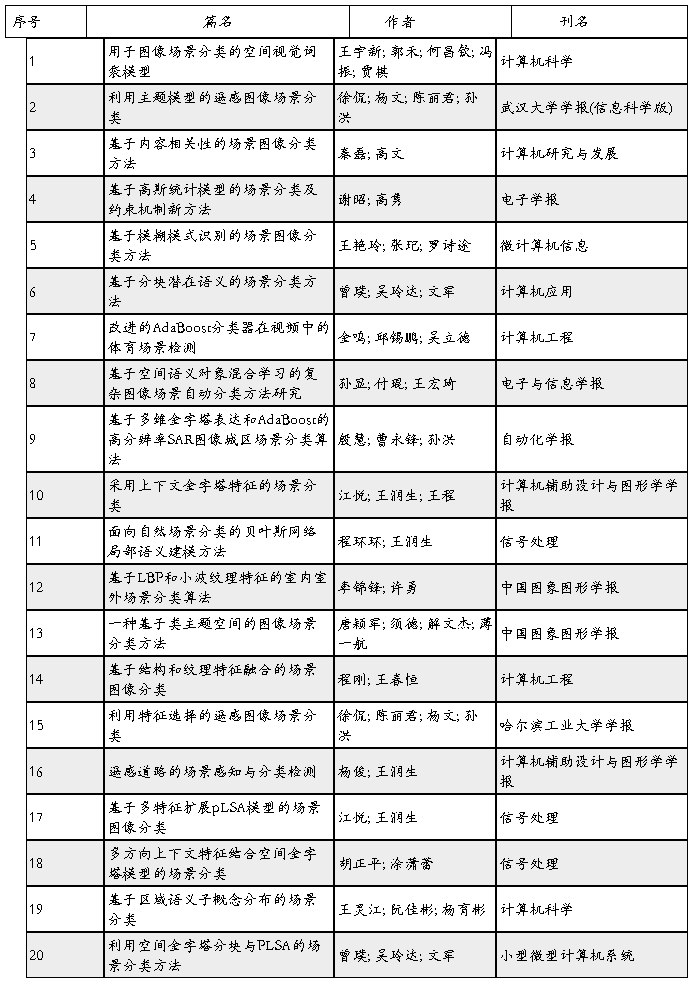
1.使用CNKI的中国学术期刊网络出版总库
 2、使用万方数据平台的学位论文全文数据库
2、使用万方数据平台的学位论文全文数据库
1. 王宇新,郭禾等;用于图像场景分类的空间视觉词袋模型大连理工大学计算机科学与技术学院; 大连理工大学软件学院;20##
以传统的词袋模型为基础,根据同类场景图像具有空间相似性的特点,提出了一种用于图像场景分类的空间视觉词袋模型。首先将图像进行不同等级的空间划分,针对对应空间子区域进行特征提取和k均值聚类,形成该区域的视觉关键词,进而构建整个训练图像集的空间视觉词典。进行场景识别时,将所有空间子区域的视觉关键词连接成一个全局特征向量进行相似度计算。最终的场景分类结果使用V1滤波器和PACT两种特征在支持向量机LIBSVM上获得。 更多还原
2. 徐侃;杨文等;利用主题模型的遥感图像场景分类 武汉大学电子信息学院;
提出了一种基于主题模型与特征组合相结合的遥感图像分类方法。该方法首先对图像进行尺度不变特征变换(SIFT)、几何模糊特征(GB)和颜色直方图特征(CH)提取,接着利用潜在概率语义分析(pLSA)模型分别对所得到的图像特征进行潜在主题的挖掘,然后对所得到的主题概率特征进行组合,最后利用支持向量机(SVM)分类器进行场景分类。实验表明,与传统分类方法相比,主题模型更具优势;与使用单特征相比,特征组合具有更高的分类准确率。
3. 秦磊;高文;基于内容相关性的场景图像分类方法 中国科学院计算技术研究所智能信息处理重点实验室; 中国科学院计算技术研究所;20##
场景图像分类是计算机视觉领域中的一个基本问题.提出一种基于内容相关性的场景图像分类方法.首先从图像上提取视觉单词,并把图像表示成视觉单词的词频矢量;然后利用产生式模型来学习训练集合中包含的主题,和每一幅图像所包含的相关主题;最后用判定式分类器进行多类学习.提出的方法利用logistic正态分布对主题的相关性进行建模,使得学习得到的类别的主题分布更准确.并且在学习过程中不需要对图像内容进行人工标注.还提出了一种新的局部区域描述方法,它结合了局部区域的梯度信息和彩色信息.在自然场景图像集合和人造场景图像集合上实验了提出的方法,它相对于传统方法取得了更好的结果.
4.佟强;图像区域粗糙分割情况下的区域物体分类 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报 2010.22(7)
提出一种改进的语义物体分类方法,可在图像区域分割结果不精确的情况下,对图像区域进行分类.结合统计文本分析中的bag-of-words方法与多示例学习,将图像区域物体切分为若干小图像块,提取图像区域物体的图像特征作为其粗糙语义概念并计算置信度;根据粗糙语义概念进一步提取出各种区域物体类型的语义特征作为其特征语义概念;使用分类器对特征语义概念进行学习,实现了对区域物体的分类.实验结果表明,采用文中方法可在分割粗糙的图像区域上获得很好的区域物体分类准确率.
5.王宇新,用于图像场景分类的空间视觉词袋模型 大连理工大学计算机科学与技术学院大连116023
以传统的词袋模型为基础,根据同类场景图像具有空间相似性的特点,提出了一种用于图像场景分类的空间视觉词袋模型.首先将图像进行不同等级的空间划分,针对对应空问子区域进行特征提取和k均值聚类,形成该区域的视觉关键词,进而构建整个训练图像集的空间视觉词典.进行场景识别时,将所有空间子区域的视觉关键词连接成一个全局特征向量进行相似度计算.最终的场景分类结果使用V1滤波器和PACT两种特征在支持向量机LIBSVM上获得.
6.王同刚,基于中层语义的图像场景分类算法研究 北京交通大学
图像场景分类就是根据图像内容信息,自动地将图像分为诸如海岸、森林、城市等场景。场景分类的方法分为基于底层场景分类和基于中层的场景分类。由于图像底层特征与高层语义之间存在鸿沟,因此基于底层特征难以有效地实现场景分类。本文从图像的底层特征开始阐述,围绕建立中间语义,最终完成图像的场景分类。
视觉词典是中间语义的基础,本文通过提取底层视觉特征,进行K-means聚类生成视觉词语,从而建立视觉词包。图像的描述就由原来的底层特征变为视觉词语的概率分布。由于词典中出现同义和多义的问题,借鉴了文本统计中的LSA思想。我们建立主题模型,利用概率潜在语义分析(PLSA)发现与图像场景相对应的潜在主题,采用最大似然模型完成图像的场景分类。但此方法直接从视觉词语出现的总体情况进行场景分类,并没有到考虑图像的空间分布。鉴于此,我们在原来的基础在将图像进行分块,把每个分块作为一个整体采用PLSA模型提取潜在主题,最后将各个分块的潜在主题向量合并作为支持向量机的输入向量完成图像的场景分类。实验表明,该方法引进了有监督的SVM,虽然增加了时间的复杂度,但此方法的场景分类精度更高。
 使用万方数据平台的外文文献摘要数据库
使用万方数据平台的外文文献摘要数据库
[1].Dongjin Song,Biologically Inspired Feature Manifold for Scene Classification IEEE Transactions on Image Processin。
Many real-world data sets exhibit skewed class distributions in which almost all instances are allotted to a class and far fewer instances to a smaller, but usually more interesting class. A classifier induced from an imbalanced data set has, characteristically, a low error rate for the majority class and an undesirable error rate for the minority class. This paper firstly provides a systematic study on the various methodologies that have tried to handle this problem. Finally, it presents an experimental study of these methodologies with a modification of Decorate algorithm and it concludes that such a framework can be a more valuable solution to the problem. Our method seems to permit improved identification of difficult small classes in predictive analysis, while keeping the classification ability of the majority class in an acceptable level.
[2]CHENG-JUNG TSAI,CHIEN-I LEE.A Multivariate Decision Tree Algorithm to Mine Imbalanced Data[J].WSEAS Transactions on Information Science and Applications,2007,4(1)
The class imbalance problem is an important issue in classification of Data mining. Among the proposed approaches, some of them modify the class distribution of the original data which would worsen the computational burden or might throw away some userful information; some are limited to specific dataset or only applicable to the dataset with numeric attribute; some would take a lot of training time due to the natural property of core techniques such as neural network; and some suffer from determining a proper threshold while the user is unfamiliar with the domain knowledge. In this paper, we proposed the Hierarchical Shrinking decision Tree (HIS-Tree) algorithm to solve these problems. HIS-Tree uses the multivariae test derived from geometric mean measurement as splitting criteria to group minority examples together. By this way, HIS-Tree can avoid discovering rules dominated by the majority examples. Finally, as shown in the experiment, HIS-Tree can predict minority/interesting examples more accurately.
[3]ANDREW ESTABROOKS,TAEHO JO,NATHALIE JAPKOWICZ.A MULTIPLE RESAMPLING METHOD FOR LEARNING FROM IMBALANCED DATA SETS[J].Computational Intelligence,2004,20(1)
Resampling methods are commonly used for dealing with the class-imbalance problem. Their advantage over other methods is that they are external and thus, easily transportable. Although sueh approaches can be very simple to implement, tuning them most effectively is not an easy task. In particular, it is unclear whether oversampling is more effective than undersampling and which oversampling or undersampling rate should be used. This paper presents an experimental study of these questions and concludes that combining different expressions of the resampling approach is an effective solution to the tuning problem. The proposed combination scheme is evaluated on imbalanced subsets of the Reutcrs-21578 text collection and is shown to be quite effective for these problems.
[4]Zhao,XM,Li,X.Protein classification with imbalanced data.[J].Proteins,2008,70(4)
Generally, protein classification is a multi-class classification problem and can be reduced to a set of binary classification problems, where one classifier is designed for each class. The proteins in one class are seen as positive examples while those outside the class are seen as negative examples. However, the imbalanced problem will arise in this case because the number of proteins in one class is usually much smaller than that of the proteins outside the class. As a result, the imbalanced data cause classifiers to tend to overfit and to perform poorly in particular on the minority class. This article presents a new technique for protein classification with imbalanced data. First, we propose a new algorithm to overcome the imbalanced problem in protein classification with a new sampling technique and a committee of classifiers. Then, classifiers trained in different feature spaces are combined together to further improve the accuracy of protein classification.
[5]Gilles Cohen,Melanie Hilario,Hugo Sax et al.Learning from imbalanced data in surveillance of nosocomial infection[J].Artificial Intelligence in Medicine,2006,37(1)
Objective: An important problem that arises in hospitals is the monitoring and detection of nosocomial or hospital acquired infections (NIs). This paper describes a retrospective analysis of a prevalence survey of NIs done in the Geneva University Hospital. Our goal is to identify patients with one or more NIs on the basis of clinical and other data collected during the survey. Methods and material: Standard surveillance strategies are time-consuming and cannot be applied hospital-wide; alternative methods are required. In NI detection viewed as a classification task, the main difficulty resides in the significant imbalance between positive or infected (11%) and negative (89%) cases. To remedy class imbalance, we explore two distinct avenues: (1) a new resampling approach in which both oversampling of rare positives and undersampling of the noninfected majority rely on synthetic cases (prototypes) generated via class-specific subclustering, and (2) a support vector algorithm in which asymmetrical margins are tuned to improve recognition of rare positive cases. Results and conclusion: Experiments have shown both approaches to be effective for the NI detection problem. Our novel resampling strategies perform remarkably better than classical random resampling. However, they are outperformed by asymmetrical soft margin support vector machines which attained a sensitivity rate of 92%, significantly better than the highest sensitivity (87%) obtained via prototype-based resampling.
[6]Wu, G..KBA: kernel boundary alignment considering imbalanced data distribution[J].IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering,2005,17(6)
An imbalanced training data set can pose serious problems for many real-world data mining tasks that employ SVMs to conduct supervised learning. In this paper, we propose a kernel-boundary-alignment algorithm, which considers THE training data imbalance as prior information to augment SVMs to improve class-prediction accuracy. Using a simple example, we first show that SVMs can suffer from high incidences of false negatives when the training instances of the target class are heavily outnumbered by the training instances of a nontarget class. The remedy we propose is to adjust the class boundary by modifying the kernel matrix, according to the imbalanced data distribution. Through theoretical analysis backed by empirical study, we show that our kernel-boundary-alignment algorithm works effectively on several data sets.
[7]Vegard Engen,Jonathan Vincent,Keith Phalp.Enhancing Network Based Intrusion Detection For Imbalanced Data[J].International Journal of Knowledge-Based in Intelligent Engineering Systems,2008,12(5/6)
The application of machine learning to intrusion detection has been researched for several decades, however, with varying degrees of success. This paper focuses on two common techniques: Multi Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) and Decision Trees (DTs). Previous research on these techniques has produced contradictory results concerning their ability to detect particular classes of intrusion. Some of these contradictions are argued to be a result of properties of the data set used for empirical study, the KDD Cup '99 data set, which poses several challenges to learning algorithms. One particular challenge is considered here, learning from imbalanced data, which is an intrinsic problem to intrusion detection. Empirical results show that both the DT and MLP trained with back propagation obtain very poor classification rates of the minor classes, particularly U2R (User to Root) intrusions; the MLP often being unable to detect this class. An evolutionary neural network is employed, in which several evaluation functions are examined. Two general fitness measures are used, which lead to similar behaviour to training an MLP with back propagation. However, when employing evaluation functions that calculate the fitness proportionally to the instances of each class, thereby avoiding a bias towards the major class(es) in the data set, significantly improved true positive rates are obtained whilst maintaining a low false positive rate.
[8]Hong, X.,Chen, S.,Harris, C. J..A Kernel-Based Two-Class Classifier for Imbalanced Data Sets[J].IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks,2007,18(1)
Many kernel classifier construction algorithms adopt classification accuracy as performance metrics in model evaluation. Moreover, equal weighting is often applied to each data sample in parameter estimation. These modeling practices often become problematic if the data sets are imbalanced. We present a kernel classifier construction algorithm using orthogonal forward selection (OFS) in order to optimize the model generalization for imbalanced two-class data sets. This kernel classifier identification algorithm is based on a new regularized orthogonal weighted least squares (ROWLS) estimator and the model selection criterion of maximal leave-one-out area under curve (LOO-AUC) of the receiver operating characteristics (ROCs). It is shown that, owing to the orthogonalization procedure, the LOO-AUC can be calculated via an analytic formula based on the new regularized orthogonal weighted least squares parameter estimator, without actually splitting the estimation data set. The proposed algorithm can achieve minimal computational expense via a set of forward recursive updating formula in searching model terms with maximal incremental LOO-AUC value. Numerical examples are used to demonstrate the efficacy of the algorithm
[9]Su, Chao-Ton.An Evaluation of the Robustness of MTS for Imbalanced Data[J].IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering,2007,19(10)
In classification problems, class imbalance problem will cause bias on the training of classifiers, and will result in the lower sensitivity of detecting the minority class examples. Mahalabobis-Taguchi System (MTS) is a diagnosis and forecasting technique for multivariate data. MTS establishes a classifier by constructing a continuous measurement scale rather than directly learning from the training set. Therefore, it is expected that the construction of an MTS model will not be influenced by data distribution, and this property is helpful to overcome the class imbalance problem. To verify the robustness of MTS for imbalanced data, this study compares MTS with several popular classification techniques. The results indicate that MTS is the most robust technique to deal with the classification problem on imbalanced data. In addition, this study develops a "probabilistic thresholding method" to determine the classification threshold for MTS, and it obtains a good performance. Finally, MTS is employed to analyze the RF inspection process of mobile phone manufacture. The data collected from the RF inspection process is typically an imbalanced type. Implementation results show that the inspection attributes are significantly reduced and that the RF inspection process can also maintain high inspection accuracy.
[10]Khoshgoftaar, T.M.,Van Hulse, J.,Napolitano, A..Supervised Neural Network Modeling: An Empirical Investigation Into Learning From Imbalanced Data With Labeling Errors[J].IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks,2010,21(5)
Neural network algorithms such as multilayer perceptrons (MLPs) and radial basis function networks (RBFNets) have been used to construct learners which exhibit strong predictive performance. Two data related issues that can have a detrimental impact on supervised learning initiatives are class imbalance and labeling errors (or class noise). Imbalanced data can make it more difficult for the neural network learning algorithms to distinguish between examples of the various classes, and class noise can lead to the formulation of incorrect hypotheses. Both class imbalance and labeling errors are pervasive problems encountered in a wide variety of application domains. Many studies have been performed to investigate these problems in isolation, but few have focused on their combined effects. This study presents a comprehensive empirical investigation using neural network algorithms to learn from imbalanced data with labeling errors. In particular, the first component of our study investigates the impact of class noise and class imbalance on two common neural network learning algorithms, while the second component considers the ability of data sampling (which is commonly used to address the issue of class imbalance) to improve their performances. Our results, for which over two million models were trained and evaluated, show that conclusions drawn using the more commonly studied C4.5 classifier may not apply when using neural networks.
四、资料汇总
随着多媒体技术和计算机网络技术的发展,人们接触到的图像数据以前所未有的速度增长。面对海量的图像资源,如何有效地分析、组织和管理图像数据,实现基于内容的图像检索成为多媒体技术的研究热点。场景分类(Scene Classification)任务就是在这种背景下产生的。场景分类根据给定的一组语义类别对图像数据库进行自动标注,为指导目标识别等更高层次的图像理解提供了有效的上下文语义信息。其研究的难点在于如何使计算机能够从人类的认知角度来理解图像的场景语义信息,有效辨别图像场景类内差异性和场景类间相似性。本文在场景的中层语义表示的基础上,着重讨论了如何从场景图像中提出有效的视觉特征,弥合图像低层特征和高层语义之间的语义鸿沟。围绕该问题,本文取得了以下研究成果:提出了一种构建类别视觉辞典的场景分类算法,该算法使用互信息作为特征选择方法来构建类别视觉辞典。根据视觉单词对给定类别的贡献度,从全局视觉辞典中选择对给定类别贡献度高的视觉单词,组成该类的类别视觉辞典,进而生成类别直方图。最终的融合直方图由基于全局视觉辞典的全局直方图和基于类别视觉辞典的类别直方图通过自适应加权合并生成,这种加权合并方法可以使类别直方图和全局直方图通过互相竞争的方式来描述图像。融合直方图不仅可以保留全局直方图的的区分能力,而且通过类别直方图加强了不同类别的相似场景的区分能力,以克服不同场景类别间的相似性问题,提高分类正确率。提出了一种基于不同特征粒度的多尺度多层次场景分类模型(Multi-Scale Multi-Level Generative Model, MSML-pLSA)。该模型由两部分组成:多尺度部分负责从不同尺度的场景图像中提取视觉细节,构建多尺度直方图;多层次部分将对应不同数量语义主题的场景表示线性连接生成最终的场景表示一多尺度多层次直方图MSML-pLSA模型可以在一个统一的框架下整合了不同粒度的视觉信息和语义信息,从而得到更加完善的场景描述。提出了一种使用无监督学习方法提取上下文信息的场景分类算法,该算法将局部视觉单词扩展到上下文视觉单词。上下文视觉单词不仅包含了当前尺度下给定感兴趣区域(Region Of Interest, ROI)的局部视觉信息,而且还包含了ROI相邻区域和相邻粗糙尺度下与ROI同中心的区域包含的视觉信息。通过引入ROI的上下文信息,上下文视觉单词能够更加有效地描述图像场景的语义信息,从而减少了图像场景语义的歧义性,进而减少了场景分类的错误率。研究了基于词包模型(Bag of Words, BoW)表示的特征点的数量对分类正确率的影响。在构建词包模型的过程中,如何选取特征点,以便能更好地表征图像的视觉信息是一个非常重要的工作。在场景分类领域中有一个普遍认同的观点,即较大数量的特征点可以获得较高的分类正确率,但是该观点却没有被验证过。在词包模型的框架下,本文做了大量的实验来验证这个观点,本文采用了四种特征选择方法和三种不同的SIFT特征(Scale Invariant Feature Transform)来改变特征点的数量。实验结果证明特征点的数量可以明显影响场景分类的正确率。
图像场景可能由多个对象(比如:草地,马路,建筑物)所组成。给定一组图像,我们的目标是利用无监督方法发现每一幅图像所包含的对象,然后根据这些对象的分布实现场景的分类。潜在语义分析是由统计文本分析发展而来的产生式模型,它能够发现文档所包含的潜在主题。本文通过研究不同的视觉词汇和潜在主题数目对场景分类性能的影响,我们选择单层SIFT特征作为PLSA的词汇表。然后在此基础上进行改进,实现多层SIFT特征,多种特征融合作为词汇表。采用概率潜在语义分析(PLSA)对词汇表进行分析,实现图像中潜在对象的发现;图像被比作成一篇由若干“视觉词包”所组成的文档,图像中的对象则被看成该图像文档所包含的潜在主题。这样,利用PLSA就可以发现图像中潜在对象的概率分布。基于对象概率分布的场景分类则由K-最近邻分类器来完成的。实验表明,结合PLSA和KNN的分类方法提出的基于多层SIFT特征和多种特征融合的PLSA模型可获得比单层SIFT特征更加理想的场景分类效果。
场景图像分类是计算机视觉领域中的一个基本问题.提出一种基于内容相关性的场景图像分类方法.首先从图像上提取视觉单词,并把图像表示成视觉单词的词频矢量;然后利用产生式模型来学习训练集合中包含的主题,和每一幅图像所包含的相关主题;最后用判定式分类器进行多类学习.提出的方法利用logistic正态分布对主题的相关性进行建模,使得学习得到的类别的主题分布更准确.并且在学习过程中不需要对图像内容进行人工标注.还提出了一种新的局部区域描述方法,它结合了局部区域的梯度信息和彩色信息.在自然场景图像集合和人造场景图像集合上实验了提出的方法,它相对于传统方法取得了更好的结果.
利用整体结构特征和局部纹理特征的优势,采用两级分类器对场景图像进行分类。第1级分类器利用全局结构信息得到候选类别,并通过分类结果判定相似类别对;第2级分类器则利用局部纹理信息区分相似类别,采用分类器的级联综合利用场景图像的整体结构信息和局部纹理信息。实验结果表明,该方法能够做到不同场景类别鲁棒分类,有效区分相似场景类别,提高场景图像的分类准确率
以传统的词袋模型为基础,根据同类场景图像具有空间相似性的特点,提出了一种用于图像场景分类的空间视觉词袋模型。首先将图像进行不同等级的空间划分,针对对应空间子区域进行特征提取和k均值聚类,形成该区域的视觉关键词,进而构建整个训练图像集的空间视觉词典。进行场景识别时,将所有空间子区域的视觉关键词连接成一个全局特征向量进行相似度计算。最终的场景分类结果使用V1滤波器和PACT两种特征在支持向量机LIBSVM上获得。
本学期,我们学习了一门很特别而且很有用的学科,名字叫文献检索,这门课程给我带来了不少收获。文献检索课程是高校教学中不可缺少的一门课程,是素质教育中重要的组成部分,是当代大学生必须掌握的基本技能。文献检索教育是培养我们大学生的信息意识,使我们掌握用手工方式和计算机方式从各种文献或互联网中获取知识和信息的一种科学方法学,是信息素养教育中重要的组成部分,是大学生素质教育中不可缺少的一个环节。高校的文献检索课作为我国高校情报用户教育的主要形式,是学生学习信息知识、掌握信息检索技术、普及信息素质教育的基础课,它和外语、计算机等一样是当代大学生必须掌握的基本技能。所以,对我们来说,文献检索十分有必要。而且我们必须好好掌握这样一门课程。
文献检课程从第五周开始,到十三周结束,在这期间,通过网络学习,我们对计算机检索基础知识、中文数据库检索、专利基础知识及专利数据库检索、常用英文数据库检索等检索知识和方法有了一个深刻的了解;通过上机实验,我们经过实际操作,对清华数据库、维普数据库、方正电子图书数据库以及springer数据库、ei village 2 数据库等各类中英文数据库都加深了印象。同时,学习了具体的文献检索知识,对于我们的日常的学习和工作也很有帮助,例如,当我们需要查询专业课程的相关文献用以学习的时候,我们便可以利用这些文献检索数据库来搜索到我们所需要的论文和书籍。另外,在必要的时候,为了方便搜索,我们还可以在网上申请个人图书馆,专门查询一些自己所需的不易随便下载的文献。
学习了文献检索这门课程,我才发现,通过图书馆的电子资源,我们可以查询到许许多多的有用文献,对我们的学习具有相当大的作用,另外,还让我形成了借助这些数据库进行自主学习的习惯,只要有需要,我就会在这些数据库中查询自己感兴趣的东西,用来丰富自己的综合知识。可以说,通过文献检索的学习,我了解到了很多我以前所不知道的东西,以前在需要学习资料的时候不知道在哪里找,而现在完全不用茫然无头绪了,各种数据库所包含的强大的检索功能和丰富的信息资源,给我提供了很大的帮助。
当然,文献检索这门课程很有用,可是要学好也不是很容易,我们必须多练习、多搜索,经常去查询、去摸索,并且要仔细的静下心来学习,只有真正熟悉了各种数据库的检索方法,掌握正确的检索方法,才能够快速而准确的找到自己真正所需要的文献资料。听过这段时间的学习,我要感谢老师的耐心教学,要感谢同学们的热心指导,感谢你们的帮助让我顺利完成了这门课程,并学到许多有用的东西。
