中学阶段所学时态的总结
Michael Hur
班级____________姓名____________
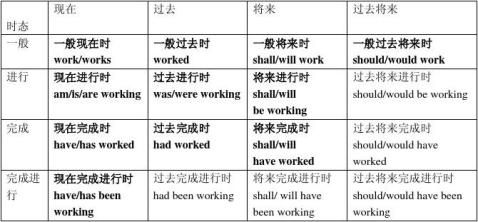
一、 时态表
英语总共有16种时态,4种时间,4种状态,如下图可以得到16种时态,且具有极强的规律性。掌握其中的10-12种基本就能满足高考要求,加粗部分为常用的11种时态。
此表格以动词work为例
二、 时态记忆法
①一般现在时: work/works 现在进行时: be + working 现在完成时:has / have + worked
这三种基本时态形式位于时态表的中心位置,是必须首先记住的。其它形式可推导而出。
②记住了上面三种时态的形式后,可以设想把时间提前至过去,这三种时态的形式就相应地左移一格成为:
一般过去时: worked
过去进行时: was / were + working 过去完成时: had + worked
1
③把时间错后至将来,这三种时态的形式也就相应地右移一格成为:
一般将来时: shall / will + work
将来进行时: shall / will + be working
将来完成时: shall / will + have worked
简而言之,把这三种现在时态形式左移变成三种过去时态形式,只需把第一个动词变成过去式即可(一般现在时谓语只有一个动词,也可把它看成为第一个动词)。与此类似,过去将来时的变化是在一般将来时的基础上把第一个动词变成过去式。把这三种现在时态形式右移变成三种将来时态形式,只需在前面加一助动词shall / will (紧随其后的动词或助动词用原形形式)即可。
三、 各种常见时态的简要介绍
1. 一般现在时
时态结构
do / does
使用说明
1) 描述当前时间内经常出现、反复发生的动作或存在的状态。
在这种情景中,句子常带有表示频率的时间状语:always , every day , often , once a week (month , year , etc.) , sometimes , seldom , usually等等,以表示句中的动作或状态是习惯性的、经常性的。
They raise ducks as a sideline .他们以养鸭为副业。
She doesn't often write to her family, only once a month. 她不常给家里写信,仅一月一封而已。
I cycle to work every day .我每天骑自行车上班。
It seldom rains here .这儿很少下雨。
2)仅为了描述状态、性质、特征、能力等等。
这里的目的是为了"描述现阶段的动作或状态",其重点"不是强调动作发生的时间、或进行的状态"。例如:
He can speak five foreign languages .他能说五种外语。
That is a beautiful city .那是座美丽的城市。
Changjiang River is one of the longest rivers in the world. 长江是世界上最长的河流之一。
She majors in music .她主修音乐。
All my family love football .我全家人都喜欢足球。
My sister is always ready to help others. 我妹妹总是乐于助人。
3) 陈述客观事实、客观真理。
顾名思义,客观的情况是"没有时间概念"的;也"不会在意动作进行的状态"。例如:
2
The sun rises in the east .日出东方。 The earth goes around the sun .地球绕着太阳转。 Ten minus two is eight.十减二等于八。 Light travels faster than sound .光的速度比声音的速度快。 The United States lies by the west coast of the Pacific Ocean. 美国位于太平洋西岸。
2. 一般过去时
时态结构
did
使用说明
主要是用来描述在过去某个时候发生的动作或存在的状态。它也可以用来表示在过去某段时间里经常发生的习惯性动作。这一点在表达意义上与一般现在时相同,只是所在的时间区域不同而已。由于它的主要作用如此,所以在使用一般过去时的句子里常常有一个意义较具体的过去时间状语。使用一般过去时,在某种意义上说就是要强调动作或状态发生或存在于过去的某个时候。"过去"的时间概念有两层意思:一是指"现在某个时间"以前的时间;二是指"说话、写文章的那个时间点"以前的时间,在这个意义上,"现在的那个时间点"是很小很小的,甚至于小到无法量化的程度。
常和一般过去时连用的过去时间状语有:last night (week ,month , year , century , etc.) , yesterday , the day before yesterday , yesterday morning ( afternoon , evening ) , in 1999 , two hours ago ( one week ago , tree years ago , …)等等。
He was here just now. 他刚才还在这里。
What did you do yesterday? 你昨天做了什么事?
We often played together when we were children. 我们小时候常在一起玩。
He used to smoke a lot, but he doesn’t now. 他过去经常抽烟,但现在不抽了。
Whenever we were in trouble, he would help us. 每当我们遇到困难,他都会帮助我们。 At that time she was very good at English. 那时她英语学得很好。
He said he would wait until they came back.
3. 一般将来时
时态结构
will / shall + do
使用说明
主要用来描述将要发生的动作或存在于未来的情况或者将来反复发生的动作或习惯。它的表示方法主要有下列5种:
1) shall / will + do
3
这种表示方法是说,动作在现在或目前还未发生,要在将来的某个时间内发生;它没有主观性,是“纯粹的将来动作”。例如:
I shall / will not be free tomorrow .我明天没空。
He will arrive here this evening .他今晚抵达这里。
2) am / is / are + going + to do
这种表示方法主要是说明 A)“说话人的意图、打算”;B)“某种可能性”。
A) He is going to spend his holidays in London . 他打算在伦敦度假。
Who is going to speak first? 谁先发言?
B) It is going to rain soon .马上要下雨了。
Is he going to collect any data for us? 他会帮我们收集资料吗?
If you go to New Zealand, you are going to like the place. 如果你去新西兰,你会喜欢上那个地方的。
3) be( am / is / are ) + to do
按计划安排要发生的动作,这个动作发生的时间一般不会很远;要求或命令他人做某事。
The new bridge is to open to traffic in three days. 新桥三天后通车。
The factory is to go into production before National Day. 这家工厂国庆节前投产。 You are not to bring any mobile communication means into the exam-room . 任何移动通讯工具都不得带入考场。
You are to stay home until your mother comes back. 你妈回来之前你不要出去。
4) 用一般现在时或现在进行时(限于某些动词)表示按计划安排要发生的事。主要强调“按计划安排要发生的事”。例如:
Do you get off at the next stop? 你下一站下车吗?
The plane takes off at 11:00 a.m. 那架飞机上午十一点起飞。
Mr. Reider is leaving for New York next week. 里德先生下周动身去纽约。
5)be about to do
距离现在很近的时间要发生的事情,不能与时间状语连用。
The talk is about to begin.谈话马上开始了。
He is about to be transferred there.他要被转去那儿了。
4. 现在进行时
时态结构
am/is/are + doing
使用说明
主要用来描述“说话、写文章的当刻”正在发生的动作,或是“现阶段”一直在进行的动作。它适用于下面的情况:
1)“说话、写文章的当刻”正在发生的动作。
They are having a football match .他们正在赛足球。
She is writing her term paper. 她正在写学期论文。
Someone is asking for you on the phone. 有人找你听电话。
4
2)“现阶段”一直在进行的动作。这种情况并不是说某个动作在说话的那会儿正在发生,而是说某个动作在当前一段时间内一直在进行着,或是重复地发生着。
He is preparing for CET Band Six. 他在为大学英语六级考试作准备。
How are you getting along with your new job?你那份新工作干得怎么样?
3)表示说话人的情感,如:赞许、批评;喜欢、厌恶等。这时的动作并不是正在发生或进行,而是表示经常性,相当于“一般现在时”所描述的情况,常与always连用,构成“always + doing”结构。
He is always thinking of others , not of himself . (表示赞许)他总是为他人着想,而不为自己。
She is always doing well at school. (表示满意)她在学校学习挺不错的。
4)表示在近期按计划或安排要发生的动作,用于这种情况仅限于少量的动词,如:go , come , leave ,arrive , see , have , lunch, return, dine , work , sleep , stay , play , do , wear等。
I'm dinning out with my friends this evening. 今晚我将和朋友在外面吃饭。
An American professor is giving a lecture this afternoon. 今天下午一位美国教授要来作报告。
We are having a holiday next Wednesday. 下周三我们放假。
Are you staying here till next week? 你要在这儿呆到下星期吗?
5. 过去进行时
时态结构
Was / were + doing
使用说明
主要表示在过去的某个时间点上正在发生、进行的动作。由于它的定义是表示在过去的某个时间点上正在发生、进行的动作,所以,句子常带有一个表示“过去某个时间点”的状语。这个状语可能是短语,词组,或是一个从句。也可能是通过上下文来表达这层意思。过去进行时主要用于表示在过去某时刻正在进行的动作,例如:
At this moment yesterday, I was packing for camp.昨天这个时候,我正在收拾东西去露营。 When I came to see her last time, she was writing an article.上次我来看她的时候,她正在写一篇文章。
What were you doing at eight last night ? 昨晚八点钟你在做什么?
6. 现在完成时
时态结构
Has / have +done
使用说明
对于初接触现在完成时的人来说,往往会产生一种茫然,因为它似乎与一般过去时相似。那就是,这两种时态描述的动作都始于过去。其实不然,现在完成时主要表示(1)发生在
5
过去的动作延续到现在刚刚完成、或许还要延续;(2)侧重于这个动作对现在带来的结果、产生的影响、积累的总和等等。而一般过去时则只不过是表示动作发生在过去的什么时候。弄清了这一区别,就很容易理解现在完成时了。它主要适用于下面的几种情况:
1) 发生在过去的动作延续到现在刚刚完成、或许还要延续
By now, I have collected all the data that I need .到现在为止,我已收集到了我所需的全部资料。 She has read 150 pages today .她今天已看了150页。
We haven't met for many years .我们已多年没见了。
They have developed a new product .他们研制成功了一种新产品。
It has been five years since he joined the army .他参军五年了。
They have learned English for eight years .他们已学了八年的英语了。
So far we've only discussed the first five chapters.至今我们还只讨论了前五章。
2)表示发生在过去而对现在产生影响、带来结果的动作
Have you had your dinner? 你吃晚饭了吗?
She has been to the United States. 她已去美国了。
You have grown much taller.你长高了许多。
关于现在完成时的时间状语问题
A. 凡是"完成时态"都表示,不知道也不管动作发生的具体时间, 所以在使用现在完成时的句子里,不可以带有表示具体过去时间的状语,如:yesterday , last week ( month , year , etc. ) , two weeks ago , in 1999等;但常和有些副词连用,如: just , before , already , often , never , ever , not…yet , always等等。
B. 在以when提问的特殊疑问中不能用现在完成时。另外,ago不能用于现在完成时的句子里,因为它表示从现在算起的以前某个时间,属于表示具体过去时间的状语。但是可以用before 来表示"以前"的意义,因为它只表示"以前",而不知什么时候的以前。
C. 如果是不表示连续性的动词用于现在完成时的句子,不可以和以for表示的"一段时间"的状语连用。在这种情况下,应该用"It has been … ;since…"的句式来表达。如:
He has joined the army for five years. (错误)
It has been five years since he joined the army.(正确)
7. 过去完成时
时态结构
Had done
使用说明
一、过去完成时的概念
概念:过去完成时表示在过去某一时间或动作之前已经发生或完成了的动作,即"过去的过去( past-in-the-past )"。
请注意下面这个时间轴,体会不同的时间点对应的不同的时间概念和对应的英语时态。尤其是过去的过去在时间轴上的位置。
6




过去的过去 过去的一个时间 现在 将来
过去完成时过去时一般现在时一般将来时
二、过去完成时的判断依据
1. 由时间状语来判定
一般说来,各种时态都有特定的时间状语。与过去完成时连用的时间状语有: ( 1 ) by + 过去的时间点。
如: I had finished reading the novel by nine o'clock last night.
( 2 ) by the end of + 过去的时间点。
如: We had learned over two thousand English words by the end of last term.
( 3 ) before + 过去的时间点。
如: They had planted six hundred trees before last Wednesday.
2. 由"过去的过去"来判定。
过去完成时表示"过去的过去",是指过去某一动作之前已经发生或完成的动作,即动作有先后关系,动作在前的用过去完成时,在后的用一般过去时。这种用法常出现在:
( 1 )宾语从句中
当宾语从句的主句为一般过去时,且从句的动作先于主句的动作时,从句要用过去完成时。在told, said, knew, heard, thought等动词后的宾语从句。如:
She said that she had seen the film before.
( 2 )状语从句中
在时间、条件、原因、方式等状语从句中,主、从句的动作发生有先后关系,动作在前的,要用过去完成时,动作在后的要用一般过去时。如:
When I got to the station, the train had already left.
After he had finished his homework, he went to bed.
三、过去完成时的主要用法
1. 过去完成时表示一个动作或状态在过去某一时间或动作之前已经完成或结束,即发生在"过去的过去"。如:
When I woke up, it had stopped raining.我醒来时,雨已经停了。(主句的动作发生在"过去的过去")
When the police arrived, the thieves had run away. 警察到达时,小偷们早就跑了。
By the time he was twelve, Edison had begun to make a living by himself. 到了十二岁那年,爱迪生开始自己谋生。
2. 过去完成时是一个相对的时态,表示的是"过去的过去",只有和过去某一时间或某一动作相比较时才使用它。如:
He told me that he had written a new book. (had written 发生在 told 之前 )
3. 过去完成时需要与一个表示过去的时间状语连用,它不能离开过去时间而独立存在。此时多与 already , yet , still , just , before , never 等时间副词及 by , before , until 等引导的短语或从句连用。
7
如:Before she came to China, Grace had taught English in a middle school for about five years.
Peter had collected more than 300 Chinese stamps by the time he was ten.
8. 过去将来时
时态结构
Should / would + do
使用说明
表示过去的某时以后将要发生的动作。但这个"将来"时间绝不会延伸到“现在”;而仅限于“过去时间区域内”。(也可以理解做:从过去某个时间看来将来要发生的事情。)由此可以看出,含这个时态的句子常带一个表示“过去某个时间点”的状语。这个状语或是一个短语,或是一个句子。这个时态常用于:
A)宾语从句或间接引语中;B)表示过去习惯性的动作;C)表示过去情况中的“愿望”、“倾向”,多用于否定句。例如:
A) When I thought about it , I wondered what their reaction would be . 当我考虑这件事时,我想知道他们的反应是什么。
She told me that she would go on trip to Europe the next day. 她告诉我,她第二天要去欧洲旅行。
He didn't expect that we would all be there. 他没料到我们会全在那儿。
B) During that period , he would do morning-exercises every day. 在那段时间,他每天早锻炼。
Whenever he had time, he would help his mother with some housework. 无论他什么时间有空,他总是帮他妈妈干点家务活。
C)They knew that we would never permit such a thing. 他们知道我们绝不会允许发生这样的事。
Even after the lecture ended, the audience would not leave . 甚至在讲座结束之后,听众仍不肯离去。
9. 将来进行时
时态结构
shall/will + be +doing
使用说明
将来进行时是指将来某个时间或者某段时间正在进行的或者持续的动作。
I will be sleeping at 12:00p.m. 十二点的时候我将在睡觉。
I will be studying in university at the age of 20.我20岁的时候我将会在大学里学习。
8
① This time next week we shall be working in that factory.下个星期的这时候,我们将在那个工厂
劳动.
② We'll be having a meeting at three o'clock tomorrow afternoon. 明天下午三点,我们将正在开会. ③ When will you be seeing Mr. White 你将什么时候见怀特先生 (语气较委婉客气,下属对上司) ④ The students will be watching TV at seven this evening.今天晚上七点,学生们将正在看电视.
This time next day they will be sitting in the cinema. 明天此时你们正太看电影。
Don't worry, you won't miss her. She will be wearing a red T-shirt and a white skirt at that time. 别担心,你不会认不出她的.她到时会穿一件红色的T恤衫和一条白色的短裙.
10.现在完成进行时
时态结构
Has / have been doing
使用说明
(一)表示从过去某时开始一直持续到现在的动作,并且还将持续下去。
The Chinese have been making paper for two thousand years.中国有20xx年的造纸历史。(动作还将继续下去)
I have been learning English since three years ago.自从三年前以来我一直在学英语。(动作还将继续下去)
(二)表示在说话时刻之前刚刚结束的动作。
We have been waiting for you for half an hour.我们已经等你半个钟头了。(动作说话之前刚刚结束,不再继续下去)
(三)有些现在完成进行时的句子等同于现在完成时的句子。
They have been living in this city for ten years.
They have lived in this city for ten years.他们在这个城市已经住了10年了。
I have been working here for five years.
I have worked here for five years. 我在这里已经工作两年了。
(四)大多数现在完成进行时的句子不等同于现在完成时的句子。
I have been writing a book.(动作还将继续下去)我一直在写一本书。
I have written a book.(动作已经完成)我已经写了一本书。
They have been building a bridge.(动作一直在进行)他们一直在造一座桥。
They have built a bridge.(动作已结束)他们造了一座桥。
(五)表示状态的动词不能用于现在完成进行时。
I have known him for years. I have been knowing...
11.将来完成时
时态结构
will/shall+have+done
9
使用说明
将来完成时用来表示在将来某一时间(或者某一个动作)以前已经完成或一直持续的动作。经常与before+将来时间或by+将来时间连用,也可与before或by the time引导的现在时的从句连用。
They will have been married for 20 years by then. 到那时他们就结婚20年了。 You will have reached Shanghai by this time tomorrow. 明天此时他们就到上海了。 Before long he will have forgotten all about the matter. 不久他就会全然忘记这件事的。 He is somebody now. He will not have remembered his old classmates. 他现在是一个有身份的人了,他可能不会记得老同学了。
Will you have known Kevin for 10 years next month? 到下个月你认识凯文该有10年了吧?
We shall have learned 12 units by the end of this term. 到这个学期末,我们将学完12个单元。
By the time you get home I will have cleaned the house from top to bottom. 你到家之前我将把房子彻底打扫一遍。
we will have been married a year on June 25th. 到6月25日我们俩结婚就满1年了。
时态复习题
姓名_______班级_________
第一部分
1. Sales of CDs have greatly increased since the early 1990s, when people ________ to enjoy the advantages of this new technology.
A. begin B. beganC. have begun D. had begun
2. Turn on the television or open a magazine and you ________ advertisements showing happy families.
A. will often see B. often see
C. are often seeing D. have often seen
3. —I hear Jane has gone to the Holy Island for her holiday.
—Oh, how nice! Do you know when she ________?
A. was leaving B. had leftC. has left D. left
4. —What were you doing when Tony phoned you?
—I had just finished my work and________ to take a shower.
A. had started B. startedC. have started D. was starting
5. I ________ you not to move my dictionary—now I can’t find it.
A. asked B. askC. was asking D. had asked
6. —Has Sam finished his homework today?
—I have no idea. He ________ it this morning.
A. did B. has done C. was doing D. had done
7. —What’s that terrible noise?
10
—The neighbors ________ for a party.
A. have prepared B. are preparingC. prepare D. will prepare
8. Now that she is out of a job, Lucy ________ going back to school, but she hasn’t decided yet.
A. had considered B. has been considering
C. considered D. is going to consider
9. The teacher, with 6 girls and 8 boys of her class, ________ visiting a museum when the earthquake struck.
A. was B. wereC. had been D. would be
10. The discussion ________ alive when an interesting topic was brought in.
A. was coming B. had comeC. has come D. came
11. Because the shop ________ , all the T-shirts are sold at half price.
A. has closed down B. closed down
C. is closing down D. had closed down
12. Let’s keep to the point or we ________ any decisions.
A. will never reach B. have never reached
C. never reach D. never reached
13. My mind wasn’t on what he was saying so I’m afraid I ________ half of it.
A. was missing B. had missedC. will miss D. missed
14. It is said in the book that Thomas Edison (1847—1931) ________ the world-leading inventor for sixty years.
A. would be B. has beenC. had been D. was
15. —You were out when I dropped in at your house.
—Oh, I ________ for a friend from England at the airport.
A. was waiting B. had waitedC. am waiting D. has waited
第二部分
1. She has set a new record, that is, the sales of her latest book ________ 50 million.
A. have reached B. has reached C. are reaching D. had reached
2. He kept looking at her, wondering whether he ________ her somewhere.
A. saw B. has seenC. sees D. had seen
3. The crazy fans ________ patiently for two hours and they would wait till the movie star arrived.
A. were waiting B. had been waiting
C. had waited D. would wait
4. She ________ her hairstyle in her hometown before she came to Chongqing for a better job.
A. would change B. has changed
C. changed D. was changing
5. The first use of atomic weapons was in 1945, and their power ________ increased enormously ever since.
11
A. is B. was C. has been D. had been
6. —You haven’t said a word about my new coat, Brenda. Do you like it?
—I’m sorry I ________ anything about it sooner. I certainly think it’s pretty on you.
A. wasn’t saying B. don’t say C. won’t say D. didn’t say
7. All morning as she waited for the medical report from the doctor, her nervousness ________.
A. has grown B. is growing C. grew D. had grown
8. Why don’t you put the meat in the fridge? It will ________ fresh for several days.
A. be stayed B. stay C. be staying D. have stayed
9. How can you possibly miss the news? It ________ on TV all day long.
A. has been B. had been C. was D. will be
10. -Sorry to have interrupted you. Please go on.
-Where was I?
-You ________ you didn’t like your father’s job.
A. had said B. said C. were saying D. had been saying
11. I arrived late; I ________ the road to be so icy.
A. wouldn’t expect B. haven’t expected
C. hadn’t expected D. wasn’t expecting
12. I ________ while reading the English textbook. Luckily, my roommate woke me up in time!
A. had fallen asleep B. have fallen asleep
C. fell asleep D. fall asleep
13. Although he has lived with us for years, he _______ us much impression.
A. hadn’t left B. didn’t leave C. doesn’t leave D. hasn’t left
14. I ________ ping-pong quite well, but I haven’t had time to play since the new year.
A. will play B. have played C. played D. play
15. I wonder why Jenny ________ us recently. We should have heard from her by now.
A. hasn’t written B. doesn’t write C. won’t write D. hadn’t written
第三部分
1. A short time before she ________ , the old lady ________ a will, leaving all her money to her brother.
A. died; has written B. has died; wrote
C. had died; wrote D. died; had written
2. — Kate doesn’t look very well. What’s wrong with her?
— She has a headache because she ________ too long; she ought to stop work.
A. has been reading B. had read C. is reading D. was reading
12
3. As time ________ on, Sally began to wonder if Bruce ________ Bilks’new poem called Tabled’Hute.
A. has gone; had read B. went; has read
C. goes; has read D. went; had read
4. —Mike, do you know who wanted me on the phone?
—Sorry. I don’t know. I ________ a bath in the bathroom.
A. have had B. was having C. had D. am having
5. —Could you tell me how your father usually goes to work?
—Yes. If it is fine, he ________ to his office.
A. will walk B. will go on foot C. walks D. would go on foot
6. — I called you at ten, but there was no reply.
—Oh, that was probably when I ________ a shower.
A. am taking B. took C. were to take D. was taking
7. — Have you ever worked with a tape recorder?
— I ________ it a lot when I was studying French in school.
A. used B. was used C. have used D. had used
8. —You must have met him the other day. —Oh, no, I ________ .
A. hadn’t B. mustn’t C. haven’t D. didn’t
9. —Which flight ________ ? —I want to catch the 13:00.
A. you are to catch B. are you catching
C. do you catch D. have you caught
10. —Excuse me, sir. Would you do me a favor?
—Of course. What is it?
—I ________ if you could tell me how to fill out this form.
A. had wondered B. was wondering
C. would wonder D. did wonder
11. How can I ever concentrate (集中精力) if you ________ continually ________ me with silly questions?
A. have…interrupted B. had interrupted
C. are…interrupting D. were…interrupting
12. —I bought this shirt for 35 yuan yesterday.
—It’s on sale today for only 29. You should have waited.
—Oh, really? But how ________ I know?
A. would B. can C. did D. do
13. —Will you go now?
—Not until I ________ my experiments.
A. will finish B. have finished
C. will have finished D. had finished
14. —Look! Someone has spilt coffee on the carpet.
—Well, it ________ me.
A. isn’t B. hasn’t been C. hadn’t been D. wasn’t
15. —Did you enjoy your holiday?
—Yes, it’s the best holiday I ________ these years.
A. had B. have had C. had had D. would have
13
第四部分
1. I don’t understand how you got a ticket. I always ________ you ________ a careful driver.
A. think; are B. am thinking; are C. thought; were D. think; were
2. I really ought to go on a diet。I ________ on so much weight since I gave up jogging.
A. put B. am putting C. have put D. had put
3. We ________ to go skiing tomorrow,but there’s no snow,so we’ll just stay home instead。
A. are going B. were going C. will go D. would go
4. At the time of the earthquake Jeff was still in his office. He ________ to finish a project before he left for the day.
A. has tried B. had tried C. has been trying D. had been trying
5. The student didn’t pay any attention to the lecture; he ________ of something else.
A. thought B. had thought C. would think D. was thinking
6. —Such a mistake could have been avoided.
—Unfortunately, he ________ the mistake again and again.
A. repeated B. would repeat C. had repeated D. would have repeated
7. —Did you find the missing couple in the mountain yesterday? —No, but we ________ to get in touch with them ever since.
A. have tried B. have been trying
C. had tried D. had been trying
8. I would have come sooner but I ________ that they were waiting.
A. haven’t known B. hadn’t known
C. don’t know D. didn’t know
9. -Oh, it’s you, Steve! I ________ you.
-No surprising. I’ve just had my hair cut.
A. don’t recognize B. haven’t recognized
C. didn’t recognize D. hadn’t recognized
10. I’m glad to see that you ________ a lot of progress since I ________ you last.
A. will make; have met B. have been making; met
C. had made; met D. have made; meeting
11. -Have you finished your composition already?
-Yes. I ________ it in twenty minutes.
A. have finished B. finished C. will finish D. had finished
12. Once a programme ________ put into a computer, it ________ accordingly.
A. is; acts B. is being; is acting
14
C. has been; will act D. will be; acts
13. —What place is it?
—Haven’t you seen that we ________ back where we ________ ?
A. were;had been B. are;were
C. were;have been D. are;had been
14. —Didn’t the guard see him breaking into the bank?
—No, he ________ in the other direction.
A. was looking B. had looked C. looked D. is looking
15. —Have you persuaded him?
—Yes. After some hours of discussion, I ________ to reason him in accepting the new plan.
A. had managed B. would manage C. have managed D. managed
16. —I suppose the young beautiful actress is about 20 years old.
— ________ ! She is still a college student.
A. You guess it B. You guessed it
C. You have it guessed D. You’re guessing it
17. -The enemy spy was found at last. -Really? Where ________ himself?
A. had he hidden B. did he hide C. has he hidden D. was he hidden
第五部分
1. —Your phone number again? I _______ quite catch it.
—It’s 9568442.
A. didn’t B. couldn’t C. don’t D. can’t
2. —Can I help you, sir?
—Yes. I bought this radio here yesterday, but it _______.
A. didn’t work B. won’t work C. can’t work D. doesn’t work
3. Helen _______ her keys in the office so she had to wait until her husband _______ home.
A. has left; comes B. left; had come
C. had left; came D. had left; would come
4. —_______ my glasses?
—Yes, I saw them on your bed a minute ago.
A. Do you see B. Had you see
C. Would you see D. Have you seen
5. I first met Lisa three years ago. She _______ at a radio shop at that time.
A. has worked B. was working
C. had been working D. had worked
6. —Is this raincoat yours?
—No, mine _______ there behind the door.
A. is hanging B. has hung C. hangs D. hung
7. —Alice, why didn’t you come yesterday?
—I _______, but I had an unexpected visitor.
15
A. had B. would C. was going to D. did
8. —Who is Jerry Cooper?
—_______? I saw you shaking hands with him at the meeting.
A. Don’t you meet him yet B. Hadn’t you met him yet
C. Didn’t you meet him yet D. Haven’t you met him yet
9. —Hi, Tracy, you look tired.
—I am tired. I _______ the living room all day.
A. painted B. had painted
C. have been painting D. have painted
10. —Nancy is not coming tonight.
—But she _______!
A. promises B. promised C. will promise D. had promised
11. Shirley _______ a book about China last year but I don’t know whether she has finished it.
A. has written B. wrote C. had written D. was writing
12. —Hey, look where you are going!
—Oh, I’m terribly sorry. _______.
A. I’m not noticing B. I wasn’t noticing
C. I haven’t noticed D. I don’t notice
13. The price _______ but I doubt whether it will remain so.
A. went down B. will go down
C. has gone down D. was going down
14. The reporter said that the UFO _______ east to west when he saw it.
A. was traveling B. traveled
C. had been traveling D. was to travel
15. —You’ve left the light on.
—Oh, so I have. _______ and turn it off.
A. I’ll go B. I’ve gone C. I go D. I’m going
第六部分
1. Selecting a mobile phone for personal use is no easy task because technology _______ so rapidly.
A. is changing B. has changed C. will have changed D. will change
2. I _______ ping-pong quite well, but I haven’t had time to play since the new year.
A. will play B. have played C. played D. play
3. I wonder why Jenny _______ us recently. We should have heard from her by now.
A. hasn’t written B. doesn’t write C. won’t write D. hadn’t written
4. —You haven’t said a word about my new coat, Brenda. Do you like it?
—I’m sorry I _______ anything about it sooner. I certainly think it’s pretty on you.
16
A. wasn’t saying B. don’t say C. won’t say D. didn’t say
5. All morning as she waited for the medical report from the doctor, her nervousness _______.
A. has grown B. is growing C. grew D. had grown
6. I thought Jim would say something about his school report, but he _______ it.
A. doesn’t mention B. hadn’t mentioned
C. didn’t mention D. hasn’t mentioned
7. —You’re drinking too much.
—Only at home. No one _______ me but you.
A. is seeing B. had seen C. sees D. saw
8. I’ve won a holiday for two weeks to Florida. I _______ my mum.
A. am taking B. have taken C. take D. will have taken
9. The little girl _______ her heart out because she _______ her toy bear and believed she wasn’t going to find it.
A. had cried; lost B. cried; had lost
C. has cried; has lost D. cries; has lost
10. John and I _______ friends for eight years. We first got to know each other at a Christmas party. But we _______ each other a couple of times before that.
A. had been; has seen B. have been; have seen
C. had been; had seen D. have been; had seen
11. It _______ long before we _______ the result of the experiment.
A. will not be; will know B. is; will know
C. will not be; know D. is; know
12. —How long _______ David and Vicky _______ married?
—For about four years.
A. were; being B. have; got C. have; been D. did; get
13. How can you possibly miss the news? It _______ on TV all day long.
A. has been B. had been C. was D. will be
14.-Sorry to have interrupted you. Please go on.
-Where was I?
-You ______ you didn't like your father's job.
A. had said B. said C. were saying D. had been saying
15. I arrived late; I _____ the road to be so icy.
A. wouldn't expect B. haven't expected
C. hadn't expected D. wasn't expecting
第七部分
1. Dear me! Just _____ at the time! I _____ no idea it was so late.
A. look, have B. looking, had
C. look, had D. looking, have
2. “What’s his name?” “I _____.”
A. forget B. forgot
17
C. had forgotten D. am forgetting
3. Your mother _____, however, say that to us that day.
A. does B. did C. is doing D. was doing
4. New medicines and instruments ______ every day to extend life.
A. develop B. are being developed
C. are developing D. have developed
5. I _____ your last point — could you say it again?
A. didn’t quite catch B. don’t quite catch
C. hadn’t quite caught D. can’t quite catch
6. I feel sure I _____ her before somewhere.
A. was to meet B. have met C. had met D. would meet
7. They haven’t arrived yet but we _____ them at any moment.
A. are expected B. have expected
C. are expecting D. will expect
8. “I suppose you _____ that report yet?” “I finished it yesterday, as a matter of fact.”
A. didn’t finish B. haven’t finished
C. hadn’t finished D. wasn’t finishing
9. “When he _____ is not known yet.” “But when he ____, he will be warmly welcomed.”
A. comes, comes B. will come, will come
C. comes, will come D. will come, comes
10. The bridge, which _____ 1688, needs repairing.
A. is dated from B. was dated from C. dates from D. dated from
11. I had hoped to see her off at the station, but I _____ too busy.
A. was B. had been C. would be D. would have been
12. You _____ your turn so you’ll have to wait.
A. will miss B. have missed C. are missing D. had missed
13. I left my pen on the desk and now it’s gone; who _____ it?
A. took B. has taken C. will take D. had taken
14. You’ll never guess who I met today — my old teacher! We _____ for 20 years.
A. don’t meet B. haven’t met C. hadn’t met D. couldn’t meet
15. I think you must be mistaken about seeing him at the theatre; I’m sure he _____ abroad all week.
A. is B. was C. has been D. had been
16. —Don’t put the waste on the ground.
—Oh, I’m very sorry. I _____the dustbin there.
A. don’t see B. isn’t seeing C. didn’t see D. haven’t see
17. —How is the weather in your country this summer?
—It _____as much as it does now for a long time.
A. hasn’t rained B. doesn’t rain C. wasn’t raining D. didn’t rain
18. —Does Liu Hui serve in the army?
—No, but he _____in the army for three years.
18
A. served B. has served C. is serving D. would serve
19. —Sorry. I _____to post the letter for you.
—Never mind. _____it myself after school.
A. forget; I’d rather post B. forgot; I’ll post
C. forgot; I’m going to post D. forget; I’d better post
20. Unfortunately, when I dropped in, Professor Smith _____, so we only had time for a few words.
A. has just left B. had just left C. just left D. was just leaving
21. —What were you doing when I phoned you last night?
—I _____my painting and was starting to take a bath.
A. have already finished B. was finishing
C. had just finished D. was going to finish
22. You _____television. Why not do something more active?
A. always watch B. are always watching
C. have always watched D. have always been watching
23. I have been studying computer for several years and I still _____.
A. have B. do C. have been D. am
24. Jane was disappointed that most of the guests________ when she ________at the party.
A. left; had arrived B. left; arrived
C. had left; had arrived D. had left; arrived
25. The pen I ________ I ________ is on my desk, right under my nose.
A. think; lost B. thought; had lost
C. think; had lost D. thought; have lost
第八部分
1. We ________ to move but are still considering where to go to.
A. are deciding B. decided C. have decided D. had decided
2. I left my pen on the desk and now it’s gone; who ________ it?
A. took B. has taken C. will take D. had taken
3. They won’t buy any new clothes because they ________ money to buy a new car.
A. save B. were saving C. have saved D. are saving
4. I ________ your last point — could you say it again?
A. didn’t quite catch B. don’t quite catch
C. hadn’t quite catch D. can’t quite catch
5. —Are you a teacher?
—I ________, but now I am working in a company.
A. is B. am C. was D. had
6. I feel sure I ________ her somewhere before.
A. was to meet B. have met C. had met D. would meet
7. —Does Liu Hui serve in the army?
19
—No, but he ________ in the army for three years.
A. served B. has served C. is serving D. would serve
8. —Tom came back home yesterday.
—Really? Where ________ at all?
A. had he been B. has he been C. had he gone D. has he gone
9. Unfortunately, when I dropped in, Professor Smith ________, so we only had time for a few words.
A. has just left B. had just left C. just left D. was just leaving
10. —I’m sorry; I shouldn’t have been so rude to you.
—You ________ your temper but that’s OK.
A. have lost B. had lost C. did lose D. were losing
11. —You must have met him the other day.
—Oh, no, I ________.
A. hadn’t B. mustn’t C. haven’t D. didn’t
12. —Will you go to the park now?
—Not until I ________ my physics exercises.
A. will finish B. have finished C. will have finished D. had finished
13. —Did you enjoy the film?
—Yes, it’s the best one I ________ these years.
A. had B. have had C. had had D. would have
14. —Did Alan enjoy seeing his old friends yesterday?
—Yes, he did. He ________ his old friends for a long time.
A. didn’t see B. wouldn’t see C. hasn’t seen D. hadn’t seen
15. When I called you this morning, nobody answered the phone. Where ________?
A. did you go B. have you gone C. were you D. had you been
16. She ought to stop working; she has a headache because she ________ too long.
A. has been reading B. had read C. is reading D. read
17. —Why do you look worried?
—Fred left the company half an hour ago. His work ________ unfinished since.
A. left B. was left C. has left D. has been left
18. —You could have asked Mr Johnson for help. He is kind-hearted. —I ________ that. A whole day ________.
A. forget; wastes B. forgot; was wasted
C. forgot; had wasted D. forget; was wasted
19. You’d better not phone the manager between 7 and 8 tomorrow evening; he ________ an important meeting then.
A. will have B. would have C. will be having D. will have had
20. —I’m sorry, but the boss isn’t here yet. Shall I have him call you when he comes back?
—No, I’ll call him back. If I call again in half an hour, do you think she ________ ?
A. had arrived B. has arrived C. will arrive D. will have arrived
20
21. —What’s wrong with your coat? —Just now when I wanted to get off the bus, the man next to me ________on it. A. sat B. had sat C. had been sitting D. was sitting 22. —Why weren’t you at the meeting? —I ________ for a long-distance call from my aunt in America. A. waited B. was waiting C. had been waiting D. had waited 23.—Will you attend the meeting this evening? —But I ________ told anything about it. A. wasn’t B. am not C. haven’t been D. won’t be 24. — What did you think of Act I of the play last night? — I’m sorry. The play ________ when I got there. A. had been started B. had been on for half an hour C. was to start D. had begun for half an hour 25. —Why did you come by bus? —My car broke down yesterday evening and I ________ it repaired. A. didn’t have B. don’t have C. won’t have D. haven’t had
时态复习题答案
一
1. B. when引导的是一个非限制性定语从句,when指20世纪90年代初,当然用一般过去时。
2. A. 这是“祈使句+and +陈述句”句型,祈使句相当于一个条件状语从句,and后的陈述句的谓语用一般将来时,这是一个较为固定的句型。
3. D. 因为Jane已经度假去了,“离开”此地就当然是在此之前的过去某个时间了,所以用一般过去时,选D。另外,when通常都不与完成时连用,排除B和C,A也与语境不符。
4. D. 过去进行时在此表示过去准备要做的事。句意为:(Tony给我打电话时)我刚好做完工作,准备去冲凉。
5. A. 由now可知前句的意思是:我曾经叫你不要搬动我的词典的 (你偏不听)。“叫”是在过去发生的动作,用一般过去时。
6. C. 根据句意“我不知道Sam现在是否已经做完了作业,(但是我知道)他今天早上一直在做作业”,可知要用过去进行时。
7. B. 由What’s=What is可知,现在在出声音;进而知道“邻居们正在为一个晚会作准备”,所以用现在进行时态。再说,已经准备好了或者将作准备,我们不可能听得到声音,问句也就不成立了,排除A和D。
8. B. 根据but she hasn’t decided yet (尚未决定) 可知,从开始失业时起一直在考虑再去上学,现在还在考虑。表示从过去某一时刻开始一直到现在,并且现在依然在发生的动作,用现在完成进行时,现在完成进行时由“have/has been doing”构成,所以选B。
9. A. 由when the earthquake struck可知,要用一般过去时,排除C和D;又因为主语是单数the teacher,所以只有A正确。
10. D. 由when?was brought in可知,come也是过去发生的事,用一般过去时。句意是:当引入一个有趣的话题时,那场讨论又变得活跃起来。
11. C. 由all the T-shirts are sold at half price可知,这家商店还没有关闭,但准备将要关
21
闭,所以选C,用现在进行时表示最近的打算。
12. A. “祈使句+or+陈述句”句型中,陈述句的谓语用“will+动词原形”,几乎是固定的。句意是:让我们扣住主题吧,否则,我们就作不了决定。
13. D. 因为was saying表明“他说”发生在过去,“没听到”应该是“他说”的时候没听到,所以miss也是发生在过去,而miss作“未听见、未理解”解时,一般没有进行时,因此,只有D正确。句意是:我的注意力当时并没有集中在他所说的内容上,所以恐怕有一半我都没听到。
14. D. 根据括号内的1847—1931可知,此处应填过去时态;另外,由于没有另一个过去的时间或动作与之比较,故不能用过去完成时,即只能选D。
15. A. 句意是:(你来我家时) 我正在机场等候一位从England来的朋友。表示在过去某一时刻或在过去某一段时间内正在发生的事,用过去进行时,所以选A。
二
1. A. 因为that is意为“换句话说,即 (=in other words, which means)”,而前句中的谓语has set是现在完成时,后一句的谓语动词也应用现在完成时,排除C和D;又因主语the sales是复数,选出正确答案A。
2. D. 因为由语境可知,see应当发生在kept looking之前,即过去的过去,所以用过去完成时,只有D正确。
3. B. 因为would wait是过去将来时,可见此事发生在过去,再结合for two hours可知,wait这个动作是从过去某一时刻开始一直延续到另一个过去时刻,并且还在等,一直要等到那位影星到来,所以用过去完成进行时:had been doing,因此选B。
4. C. 由came可知,她已来重庆了,而改变发型是在来重庆之前,即过去的过去,按理要用过去完成时,但before已经表明紧接着发生的先后两个动作,所以也可用一般过去时,所以选C。
5. C. 句中的since为副词,表示“从过去某时起一直到现在”,它通常要与现在完成时连用。
6. D。由句中的sooner(意为“早点儿”)可知用一般过去时。句意为“对不起,我没有早点儿说。我确实认为你穿很好看”。
7. C。her nervousness(紧张)伴随waited(等)的过程而产生,因此grow与waited同时发生,时态一致,都用一般过去时。
8. B。stay是系动词不能用被动语态,故排除A;系动词一般不用于进行时(feel除外),故排除C;stay为非延续性动词,不能与表示一段时间的状语连用,故排除D。句意为“你为什么不把肉放在冰箱里呢?那样会保质好几天”。
9. A。根据句中all day long来判断,此句是强调播放新闻对现在的影响,故用现在完成时。意为“你怎么可能没看到新闻?整天都在播放”。
10. C。用过去进行时态表示过去某一特定时刻正在进行的动作。此处是指“我”的话在被打断前正在谈论的情况。句意为“对不起打断你的话,请继续”。“我说哪儿了?”“你在说你不喜欢你父亲的工作”。
11. C。由I arrived late可知是过去的情况。I haddn’t expected表示过去没有料到。句意为“我迟到了。我没料到路面结冰”。
12. C。while 从句用过去进行时,主句用过去时,表示在某个动作的持续过程中,发生过某事。句意为“我在读英语课本时睡着了。幸亏我的室友及时叫醒了我”。
22
13. C。句意为“尽管他和我们生活了好多年,但没给我们留下多少印象”。根据前句中的现在完成时可知,下句是强调的现在的状态,因此用一般现在时。
14. D。“我的乒乓球打得好”是现在具有的技能,故用一般现在时。下句“但自新年以来还一直没有时间去打”。与前句谓语动词的时态无关。
15. A。由句中的recently和by now两个提示可知此句用现在完成时。
三
1. D. “死”与“写(遗书)”都发生在过去,显然“写”应发生在“死”之前,即:过去的过去。因此,die用一般过去时,write用过去完成时。
2. A. 根据后文可知,“她现在依然在工作”,表示从过去某一时刻开始,一直延续到现在,并且现在仍然在进行的动作或存在的状态,就用现在完成进行时,即:have been doing
3. D. 从began是一般过去时可知,go也用一般过去时,read应发生在began to wonder之前,所以要用过去完成时。
4. B. 从wanted是过去式,可知打电话发生在过去,“我”现在不知道,因为当有人打电话来时,“我”正在冲凉。表示在过去某一时刻正在发生的动作,当然用过去进行时。
5. C. 从问句中usually goes to work来看,是问通常的情况,其回答也应该是指通常的情况,因此要用一般现在时,即:“如果天气好,他通常是步行上班的”。注意:千万不要认为条件句中的谓语动词用一般现在时,而主句中的谓语动词就用一般将来时,而错选A或C。
6. D. 意为:“你打电话来时,我可能正在洗淋浴”。指在过去某个时候正在发生的动作,用过去进行时。
7. A. 句意为:“我在学校学法语期间,经常使用录音机”。指过去经常发生的动作,当然用3一般过去时。
8. D. 问句是对过去情况猜测,答句I didn’t的完整句子是I didn’t meet him the other day. (几天前我没有见到他。)
9. B. 从语境来看,显然指将来:“你打算坐哪趟班机?”表示最近打算或安排要做的事,可以用进行式或“be to do”来表示,因此,可选出A和B,而答案A的语序不对,所以只有B对(from )。
10. B. 表示刚才想叫你帮忙,就是“我在想你可不可以帮我填这个表格”,所以用过去进行时。
11. C. 因为从can和句意可知,是指目前正在发生的事。句意是“如果你 (象现在这样) 不断地用一些无聊问题来妨碍我,我又怎能集中精力呢?”
12. C. 因为意思是“我当时 (昨天) 怎么知道呢?”。
13. B. 因为在时间状语从句中要用一般现在时代替一般将来时;若强调从句动作发生在主句动作之前时,用现在完成时代替将来完成时,本题属后一种情况。
14. D. 从上文可知,已经将coffee溅在地毯上了,spilt已经在过去发生了,所以用一般过去时,wasn’t。
15. B. 因为these years是包括现在在内的,通常与现在完成时连用。
四
1. C. 因为指you got a ticket之前,“我原来一直认为你是位非常小心的司机”,所以用过去时。
2. C. 因为与表示“自?以来”的since从句或短语连用的通常是现在完成时态;再说前
23
面的“我应当节食了”,也说明现在“我已经增肥”了。
3. B. were going to do sth. 指“原打算做?”。
4. D. 指从发生地震之前的某一时候开始到发生地震时一直在努力完成一项计划,并且在发生地震时依然在办公室努力完成这一计划,所以要用过去完成进行时。
5. D. 指这位学生在没有注意听课的同时“正在想着别的事情”。
6. A. 因为could have done是对过去发生的事表示遗憾,所以答语也应该是指他在过去一再犯这样的错误。
7. B. 因为ever since是“自那以后(直到现在)”之意,常与完成时连用,又根据but 可知,现在也还在设法与他们取得联系,所以用现在完成进行时。
8. D. 因为would have come是表示与过去事实相反的虚拟语态,所以是“我当时不知道他们在等”。
9. C. 因为说话时已经认出来了,指在说话之前“刚才我没有认出你来”,所以用一般过去时。
10. B. 因为是“上次见你”,所以since从句的谓语动词用一般过去时,排除A和D;又表示从上次见你以来一直到现在并且现在依然在不断取得进步,所以用现在完成进行时。
11. B. 由答语Yes可知,现在已经做完了,后文强调的是完成的时间,要用一般过去时。
12. C. 因为时间状语从句或者条件状语从句中用一般现在时或现在完成时,主句用一般将来时。
13. B. 句意是“难道你没有看到我们现在又回到了我们原来所在的地方吗?”
14. A. 指他闯入银行那个时候,the guard正在朝别的方向看。
15. D. 由Yes知道已经劝服,After短语是说明劝服的时间,所以用一般过去时。此题与26题类似。
16. B. 意思是你刚才猜对了,所以用一般过去时。
17. A. 因为hide是指在被找到之前,即过去的过去,所以用过去完成时。
五
1. A。句意为“我刚才没有听清楚”。
2. D。“昨天在这买的收音机,现在坏了。”work 指机器设备的运作。
3. C。leave 应发生在 had to wait 这个过去动作之前,“过去的过去”用过去完成时;后一空用一般过去时表示过去将来。
4. D。现在完成时表示过去发生的动作对现在的影响:问话人的目的是想知道眼镜在哪里。
5. B。在三年前见到她时,她当时正在一家 radio shop 工作。
6. A。hang 表示某物“悬挂”在某处,是不及物动词;is hanging 正悬挂在。
7. C。was going to do 表示未完成的意愿:本打算做(但却没有做成)。would 无此用法。
8. D。由 I saw...可知 meet 发生在过去,且强调对现在的影响:你不是已经和他见过面了吗?
9. C。表示从过去某个时间开始一直延续到现在的动作,要用现在完成进行时。all day 是关键词。
10. B。“但她曾经答应要来的”,过去的许诺,故用一般过去时。
11. D。由“我不知道她是否已经写完了”推知,她去年“正在写”。
12. B。你提醒之前我没注意,即“我刚才没有注意”。
13. C。后文(will remain so)暗示物价已经降下来了。
24
14. A。过去进行时表示报告人当时所看到的情景。
15. A。从语境很容易判断用将来时。表示临时的决定只能用 will;再说,going 也不能与 turn 并列。
六
1. A。选择移动电话不容易,因为科学技术正在迅速发展。
2. D。“我的乒乓球是打得相当好的,但自新年以来还一直没有时间去打。”球打得好是现在已有的技能,故用一般现在时。
3. A。由 recently 和 by now 可知用现在完成时。
4. D。用一般过去时是指“我刚才没急于说”。
5. C。紧张伴随等的过程而产生,应同时发生,waited 是一般过去时,grow 也用一般过去时。
6. C。只描述过去所发生的情况,但没有强调对现在的影响,用一般过去时。
7. C。由 only at home 可知“我”只在家里喝得多,除你之外,没有人看见。谈的是现在一般性情况,故用一般现在时。
8. A。现在进行时表示按计划或安排将要发生的动作。
9. B。由 believed 知 cry 和 lose 都发生在过去;显然先丢后哭,丢是过去的过去。另外,cried 与 believed 为并列谓语,同为过去式。
10. D。到目前为止成为朋友八年,用现在完成时;在那次晚会相识成为朋友之前已经见过几次面,用过去完成时。
11. C。句意为:不久之后我们就会知道实验结果。在句型 It is not long before?不久之后就?)中,before 引导的是时间状语从句,用一般现在时表将来。
12. C。由 For about four years 可知,要用现在完成时,排除 A 和 D;与时间段连用,不可用 get married, 要用 be married。
13. A。信息句为一般现在时,根据后句中all day long判断,这显然是强调播放新闻对现在的影响,故选现在完成时。
14. C。此处指“我”的话在被打断前正在谈论的情况。表示过去某一特定的时刻在进行的动作用过去进行时态。
15. C。“迟到”用的是过去时,“没想到路面结冰”应是过去的过去。
七
1. C。第一空填 look, 因为这是祈使句的谓语;第二空填 had,因为前一句说“看看时间吧”,这一看当然知道了现在很迟的情形,“不知道这么迟了”显然应是“过去”的事,故应用一般过去时态。
2. A。从语境上看,“忘记”的时间应是现在,即指现在不记得了。
3. B。其中的 did 为强调用法。
4. B。从语境上看,develop 不仅要用被动语态,而且要用进行时态。
5. A。从下文的语境看,既然现在叫对方重复一遍,说明“没听清对方的最后一点”应发生在过去(即说此话之前)。
6. B。before 用作副词时不与具体时间连用,泛指“以前”,通常与一般过去时或现在完成时连用。
25
7. C。表示目前的一种状态。
8. B,注意下文语境:事实上,我昨天就做完了。从该回答的语气上推测,填空处应填现在完成时态。
9. D。第一个 when 引导的是主语从句,用一般将来时表示将来;第二个 when引导的是时间状语从句,用一般现在时表示将来。
10. C。因为 date from 的意思是“自某时起存在至今”(=have existed since),它通常用于一般现在时,而不用过去时态(尽管其后接的总是表示过去的时间),除非所谈论的东西现在已不复存在,如:The church, which dated from the 13th century, was destroyed in an earthquake two years ago (那座教堂是13世纪建成的,两年前在一次地震中被毁了)。(注:与 date from 同义的 date back to 也有类似用法。)
11. A。前一句谓语用had hoped,表示的是过去未曾实现的想法或打算,可以译为“本想”,而后一句说“我太忙”,这是陈述过去的一个事实,所以要用一般过去时。
12. B。用现在完成时表示结果,即你已经错过了机会,其结果是:你只能等。
13. B。用现在完成时表示影响或结果,即现在笔不见了,是由于某人已经把它拿走了的结果。
14. B,用现在完成时表示从过去持续到现在的一段时间。
15. C,用现在完成时表示影响或结果,即他整个星期都在国外,所以你说你在剧院见过他,你一定是搞错了。
16. C。指刚才对方提醒之前没看到垃圾箱,用过去式。
17. A。由now和for a long time可知“很长时间都没有像现在这样下雨这么多”,用现在完成时。
18. A。由no是对前句的否定可知现在不在部队服役,是以前“服过役”,故用一般过去时。
19. B。从语境看“忘记”应为过去;“放学后自己去记”是临时的决定,不能用表示计划或打算的be going to。
20. D。从“我们只谈了几句话”可知,当我们去拜访时,Professor Smith“正要”离开了,D是过去进行时表示过去将来时。
21. C。由“我正要去洗澡”可知昨天你打电话时“我刚刚画完”,“画完”在“打电话前”之前,即过去的过去,故用过去完成时。
22. B。always有时可与进行时态连用,但含有某些感情色彩,如报怨、厌恶、赞美等。此句表示的是报怨。
23. D。句意为“我已学电脑几年了,我现在还在学。”am后省略了studying。
24. D. 在她arrived之前就已离开;即过去的过去,用had left.
25. B. 语境为:原以为(thought)丢了的(had lost)确在鼻子底下。
八
1. C。用现在完成时表示影响,即指现在已经作出决定。
2. B。用现在完成时表示影响或结果,即现在笔不见了,是由于某人已经把它拿走了的结果。
3. D。用现在进行时表示现在正在进行的动作。
4. A。从下文的语境看,既然现在叫对方重复一遍,说明“没听清对方的最后一点”应发生在过去(即说此话之前)。
5. C。这时用一般过去时表示过去曾经是老师,但现在不是了。
26
6. B。before 用作副词时不与具体时间连用,泛指“以前”,通常与一般过去时或现在完成时连用。
7. A。由no是对前句的否定可知现在不在部队服役,是以前“服过役”,故用一般过去时。
8. A。have been to?去过某地(已回来),have gone to?到某地去了(没回来);又因为问的是Tom回来之前到去过某地,故用过去完成时态。
9. D。从“我们只谈了几句话”可知,当我们去拜访时,Professor Smith“正要”离开了,D是过去进行时表示过去将来意义。
10. C。上句“我本不该对你那么无礼”是对过去情况的自责,答语“你当时的确很生气”,用一般过去时,did 在 lose 前表示强调。
11. D。问句是对过去情况的猜测,所以答句用一般过去时。I didn’t是I didn’t meet him the other day 的省略。
12. B。因为在时间状语从句中要用一般现在时代替一般将来时。若强调从句动作发生在主句动作之前时,用现在完成时代替将来完成时,本题属后一种情况。
13. B。因为 these years 是包括现在在内的,故用现在完成时。
14. D。由于见朋友发生在过去(即昨天),而很久没有见到朋友自然是昨天的见面之前,即属于过去的过去,故用过去完成时。
15. C。句子的前半句说上午打电话时没有人接电话,而后半句问对方当时在什么地方。显然,句子前后两部分的时间应一致,即用一般过去时。
16. A。从第一句话She ought to stop working 可知“他仍然在学习”,故后面用现在完成进行时态。
17. D。受前一句left的影响,易误选B。题干中的since说明此处应用现在完成时态。从问句中也可看出来,此处强调动作对现在的影响,故要用现在完成时的被动式。
18. B。说话之前“忘了”,故用一般过去时态;第二空应用一般过去时的被动语态形式。
19. C。指将来某时或某段时间正发生的事用将来进行时。
20. D。一般将来时表示将要发生的动作,而将来完成时表示将来某个时间之前已经发生或完成的动作。根据语境可知是强调将来的结果,应用将来完成时。
21. C。意思是:刚才我想下公共汽车时,(我才发现)靠近我坐的那个人一直坐在我的外衣上。表示从过去某一时刻开始一直延续到另一过去时间仍在进行的动作或状态用过去完成进行时。
22. B。该题考查根据语境选用正确时态题。上句说“你为什么没去参加会议”,据此回答“我当时正在等我姑姑从美国打来的长途电话”,说的是“你们开会时”我正在等一个电话。
23. C。指到目前为止还没有人把这件事通知我。相当于在后面省略了so far。
24. B。句意:戏剧在我到达之前就已上演了半小时,即表示“过去的过去”,且短暂性动词不与持续性时间连用,故须将 start→be on 才可与持续性时间连用。
25. D。从昨天坏了一直到今天来时还没有修好,表示从过去某一时刻开始一直延缓到现在的动作或状态要作现在完成时态。
27
