A guide to middle school English grammar
3. 名词所有格:直接在词后加’s,如:my brother’s hamburg. 如果东西为两个人共同拥
有则最后一词加’s.例:mary and jone’s house.(共有) 表达无生命的名词所有格通常用“of+名词”来表示,如:the gate of school,the window of the rom.
4. 主谓一致:语法形式上的一致,主语为单数,谓语动词用单数.例:The number of mistake
was surprising.
5. 就近一致(主谓一致):1)谓语动词的单复数形式与它最近的主语保持一致。如:连词
or,either…or,not only..but also,等连接的并列主语,句中谓语动词就近一致。
例:Either A or B,A or B,Neither A nor B+谓语动词(与B一致)
2)当主语后面跟有as well as等引导的介词短语或其他从属结构时,其谓语动词的单复数根据主语的单复数而定。
主语+
+名词+谓语动词与主语一致.
如:The teacher as well as the students was excited.
3)某些集体名词做主语时,如果作为一个整体看待,谓语动词用单词形式。如果就其中一个个成员而言,谓语动词用复数形式。如:
His family is going to have a long journey.
The whole family are watching TV.
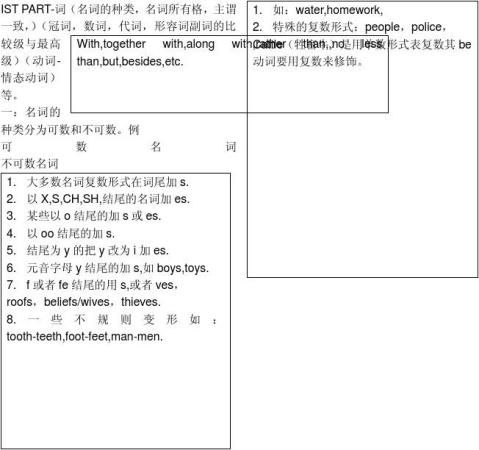
常见集体名词还有:audience,class,club,team,etc.(people,police,cattle一定用复数形式的谓语动词)
4)以ics结尾的学科名词,虽然形式上是复数但是是不可数的名词.例:physics,politics,economics,etc.
5)不定代词each,every,no修饰的名词即使用and或逗号连接多个主语其谓语动词仍用单数。Each boy each girl wants to serve the people in the future.
二.代词other或another的用法
another是三者或三者以上的另一个。
通常another是三者或三者以上的另一个the other是两者的另一个。如:
Some students like English and other students (others) like physics.
I have two pens. One is blue. The other (pen) is black.
John did better than all the other players in the sport.
This shirt is too large for me. Please show me another.
三.形容词副词比较级
1. 单音节词和少数双音节词
(1)一般情况在原级词尾加-er构成比较级,加-est构成最高级。
如:high→higher→highest.
(2)一些词本身没有比较级和最高级形式,如:right, wrong, full, empty, round, complete, wooden, dead, daily等。
形容词比较级的用法
1. 两者比较时用形容词比较级,其结构为“... 比较级 + than ...”。如:Actions speak louder than words.
2. 在两者之间选择“哪一个更……”时,用句型 “Which / Who is +比较级, ... or ...?”。 如:Which sweater is cheaper, the red one or the yellow one?
3. 表示“两者之间最……的一个”时,用“the + 比较级”。如:Lucy is the taller of the twins.
4. 表示“越……,越……”时,用“the + 比较级,the + 比较级”。如:The more you eat, the fatter you will become.
5. 表示“越来越……”时,用“比较级 + and + 比较级”,多音节词和部分双音节词用“more and more + 形容词原级”。如:We should make our country more and more beautiful.
6. 形容词比较级前可以用下列词修饰:much, a little, far, a bit, a few, a lot, even, still, rather等。如:It's much colder today than .
四.被动语态
表示主语是动作的承受者,即行为动作的对象。巧记为:被动、被动、主被动。例如:English is spoken by many people.主语English是动词speak的承受者。 一般现在时:am/is/are+taught 一般过去时:was/were+taught
:will/shall be+taught:am/is/are being+taught
过去进行时:have/has been+taught现在完成时:have/has been+taught Some new computers were stolen last night.
一些新电脑在昨晚被盗了。(不知道电脑是谁偷的)
This book was published in 1981.这本书出版于19xx年。
例如:the window was broken by Mike.窗户是迈克打破的。
This book was written by him.这本书是他写的。
五.情态动词
助动词(auxiliary)主要有两类:基本助动词和情态助动词。基本助动词有三个:do, have和be;情态助动词有十三个:may, might; can, could; will, would; shall, should; must, need, dare, used to, ought to。
1) can和could的用法1.表示能力或客观可能性,还可以表示请求和允许。如: Can you finish this work tonight?
— Can I go now? — Yes, you can.
注意:①could也可表示请求,预期委婉,主要用于疑问句,不可用于肯定句,答语应用can(即could不能用于现在时态的简略答语中)。如:
Could I come to see you tomorrow?-Yes, you can. (否定答语可用No, I’m afraid not.)②can表示能力时,还可用be able to代替。如:I’ll not be able to come this afternoon.
2) may和might的用法
1. 表示许可表示请求、允许时,might比many的语气更委婉一些,否定回答时要用mustn’t表示“不可以”、“禁止”、“阻止”之意。如:You may drive the car.
— Might I use your pen? — No, you mustn’t.
must和have to的用法
1. 表示必须、必要。如:You must come in time.
回答must引出的问句时,如果是否定的回答,不能用mustn’t,而要用needn’t或don’t have to。— Must we hand in our exercise books today?
— Yes, you must. (No, you don’t have to.)
2. “must be + 表语”的结构表示推测,它的否定或疑问式用can代替must。
This must be your pen.
3. “must + have + 过去分词”的结构常用在肯定句中,表示对过去发生的行为的推测。它的否定或疑问式用can代替must。He must have been to Shanghai.
4. have to的含义与must相似,两者往往可以互换使用,但have to有各种形式,随have的变化而定。must与have to有下列几点不同:
① must表示的是说话人的主观看法,而have to则往往强调客观需要。如:
The play is not interesting. I really must go now.
I had to work when I was your age.
② must一般只表现在,have则有更多的时态形式。
③ 二者的否定意义不大相同。如:
You mustn’t go. 你可不要去。You don’t have to go. 你不必去。
④ 询问对方的意愿时应用must。如:Must I clean all the room?
dare和need的用法
1. need表示“需要”或“必须”,作情态动词时,仅用于否定句或疑问句中,在肯定句中一般用must, have to, ought to,或should代替。如:You needn’t come so early.
— Need I finish the work today?— Yes, you must.
注意:needn’t + 不定式的完成式“表示本来不必做某事而实际上做了某事”。如:
You needn’t have waited for me.
2. Dare作情态动词时,主要用于疑问句、否定句和条件从句中,一般不用在肯定句中。如:How dare you say I’m unfair.
He daren’t speak English before such a crowd, dare he?
Should表示劝告、建议、命令,其同义词是ought to;在疑问句中,通常用should代替ought to。如:You should go to class right away.Should I open the window?
Should的含义较多,用法较活,现介绍三种其特殊用法:
① I should think it would be better to try it again. 我倒是认为最好再试一试。 ② You are mistaken, I should say. 依我看,你是搞错了。
③ I should advise you not to do that. 我倒是劝你别这样做。
④ This is something I should have liked to ask you. 这是我本来想问你的。
此外,Why(or How) + should结构表示说话人对某事不能理解,感到意外、惊异等意思。意为“竟会”。如:Why should you be so late today? 你几天怎么来得这么晚?Where is Betty living? — 贝蒂住在哪里?How should I know? — 我怎么会知道呢?I don’t know why you should think that I did it. 我真不知道你凭什么认为这件事是我干的。
六.状语从句
状语从句在句中作状语,修饰主语中的动词,形容词副词等。状语从句分为九大类:时间,目的,原因,条件,让步,方式,地点,比较,结果状语。
1.引导的连词
主要有when, while, as, by the time, before, after, since, till/until, as soon as等。其中whenwhile和as都可表示"当……时候",但用法有区别:
①when意为"在……时;当……时",可表示某一个时间点,突然发生的事。 从句谓语可以是终止性动词,也可以是延续性动词。例如:When I got home, he was having supper.
②as意为"边……边……"或"与……同时",强调同一个时间内两个相继发生或变化的情况,或者两个动作一前一后发生。例如:
As he was eating lunch,he heard the doorbell ring.(强调同一时间)
As I was going out,it began to rain.(强调两个动作先后发生)
As the spring warms the earth,all flowers begin to boom.(as有随着的含义)
③while只可表示"段时间",从句谓语只限于延续性动词。例如:
While I was sleeping, my father came in.
while还可以表示“然而,但是”如:Tom is very shy,while Jack is brave.
Before表示“在…之前”如:I started my meal before he arrived.
Till/until表示动作延续,如live,last,stand,stay,wait,work.表示主句的动作延续到从句所要表达的动作发生为止:“一直到….时”如:He worked until it was dark.
He didn’t got up until his mother came in.
2.引导的连词 原因状语从句一般由because(因为), since(既然), as(由于), for(因为)引导注意as,because,since和for的区别:①如果原因是构成句子的最主要部分,一般用because。because引导的从句一般不放在句子的开头。例如:I missed the train because I got up late.注:对于以why开头的问句,一般只能用because引导的从句来回答。
②如果原因已为人们所知,或不如句子的其余部分重要,就用as或since、since比as稍微正式一些。as和since引导的从句一般放在句子的开头。例如:
As he was not well,I decided to go there without him.
Since this method doesn't work, let's try another.
③for表示所说的理由是一种补充说明,因此,for引导的从句可以放在括号里,而且for引导的从句一般不放在句子的开头。例如:
I decided to stop and have lunch, for I was feeling quite hungry.
3.引导的连词 主要有so/such…that…,so that等。
1) so...that结构在某种情况下可以与enough to和too...to结构相互转换。例如:
She is so short that she can't reach the of the lift. =She is too short to reach the of the lift.
2)so that也可以引导结果状语从句,意为"结果是;以致于"。例如:
They missed the bus so that they were late for class.
七.定语从句 根据定语从句与先行词的关系,定语从句可分为限制性定语从句及非限制性定语从句。限制性定语从句紧跟先行词,主句与从句不用逗号分开,从句不可省去,非限制性定语从句主句与从句之间有逗号分开,起补充说明作用,如省去,意思仍完整。
1. that 既可以用于指人,也可以用于指物。在从句中作主语或宾语,作主语时不可省略,作宾语可省略。例如:
Mary likes music that is quiet and gentle.玛丽喜欢轻柔的音乐。(that作主语)
The coat I put on the desk is blue.我放在桌子上的那件外套是蓝色的. 2.which用于指物,在句中作主语或宾语,作主语不可省略,作宾语可省略。例如:
The building which stands near the train station is a supermarket.
位于火车站附近的那座大楼是一家超市。(作主语)
The film (which) we saw last night was wonderful. 我们昨天晚上看的那部电影很好看。(作宾语)
3.who, whom用于指人,who 用作主语,whom用作宾语。例如:
The girl who often helps me with my English is from England.经常在英语方面帮助我的那个女孩是英国人。(作主语)
Who is the teacher (whom) Li Ming is talking to?正在与李明谈话的老师是谁?(作宾语)注意:(1)当定语从句中含有介词,介词放在句末时,who, that, which可省略,但介词在关系代词前时,只能用“介词+which/whom”结构。例如: This is the house in which we lived last year.这是我们去年居住的房子。
Please tell me from whom you borrowed the English novel.请告诉我你从谁那借的这本英文小说。
(2)含有介词的固定动词词组中,介词不可前置,只能放在原来的位置上。例如: This is the person whom you are looking for. 这就是你要找的那个人。
(3)关系词只能用that的情况:
a. 先行词被序数词或形容词最高级所修饰,或本身是序数词、基数词、形容词最高级时,只能用that,而不用which.例如:
He was the first person that passed the exam. 他是第一个通过考试的人。
b.被修饰的先行词为all, any, much, many, everything, anything, none, the one等不定代词时,只能用that,而不用which.
