20##年《电子商务》知识点总结
第一章:
1、电子商务的狭义和广义概念;电子商务的类型。
l 狭义的电子商务定义(EC):单纯地从商品或服务的交易角度定义电子商务,指借助互联网及相关通讯技术从事信息、产品和服务的买卖和交换的过程。
l 广义的电子商务定义(EB):从整个供应链角度定义电子商务,是指企业从原料供应到生产、分销、零售等全部经营过程与经营活动的信息化、网络化,公司内部部门之间以及公司与供应商、分销商、零售商直至客户之间的协同和信息共享是EB的主要特征,如Dell(dell.com)、IBM(ibm.com)。
l Fivegenerale-commercecategories:Business-to-consumer(B2C)
n Business-to-business(B2B)
n Businessprocessesthatsupportbuyingandsellingactivities(B2E)
n Business-to-government(B2G)
n Consumer-to-consumer(C2C)
n Consumer-to-Business(C2B)
2、电子商务的商业模式及其六要素
1. Direct sales (直销)
?Intermediary (中介)
Content provider (内容提供商)
?Full-service provider (服务提供商)
?Shared public infrastructure (公共基础设施)
?Software supplier (软件提供商)
?Virtual community (虚拟社区)
?Consolidator of service(综合服务商)
l Six elements of a business model include:
A. Customers to be served and the company’s relationships with these customers including customers’ value proposition.
B. All products and services the business will offer
C. The business process required to make and deliver the products and services
D. The resources required and the identification of which ones are available, which will be developed in house, and which will need to be acquired
E. The organization’s supply chain, including suppliers and other business partners
F. The revenues expected (revenue model),anticipated costs, sources of financing, and estimated profitability (financial viability)
3、电子商务的盈利模式与商业模式的区别及联系
l Business Model: how a company operates its business processes and generates its core competition.
l Revenue model: Description of how the company or an EC project will earn revenue ?
l The major revenue models are:
A. Sales
B. Transaction fees
C. Subscription fees
D. Advertising fees
E. Affiliate fees
F. Other revenue source
4、网络外部性Network externalities
When the value of a technology, product, or service depends upon the number of other entities using it, the phenomenon is called network externality.
5、梅奥法则
l Metcalfe's law(梅特卡夫定律)states that the value of a telecommunications network is proportional to the square of the number of connected users of the system (n2).
l Metcalfe's Law is related to the fact that the number of unique connections in a network of a number of nodes (n) can be expressed mathematically as n(n?1), which is proportional to n2 asymptotically.
6、电子商务如何降低了企业的交易成本?
Businesses and individuals can use electronic commerce to reduce transaction costs by:
l Improving the flow of information
l Increasing coordination of actions
7、波特的价值链模型
l 把企业内外价值增加的活动分为基本活动和支持性活动,基本活动涉及企业生产、销售、进料后勤、发货后勤、售后服务。支持性活动涉及人事、财务、计划、研究与开发、采购等,基本活动和支持性活动构成了企业的价值链。
8、与传统企业相比,电子商务具有怎样的优势和劣势?
l 优点:1、快捷方便,大大缩短了时间和空间。很能适应现代都市人快的生活节奏。可谓企业、白领购物洽谈的首选。2、经营成本低,隐蔽性强,容易偷税漏税。
l 缺点:1、少了人与人之间的沟通与关爱。很没有乐趣,完全是为了生意而做。2、很难与顾客建立长久稳定的关系。
9、电子商务企业适合哪些行业?不同行业如何应用电子商务活动以促进其生产经营活动?
10、Dell案例分析
第二章:
1、分组交换网络的基本原则是什么Packet-Switched Networks—basic principle
Ø Packets switch----包交换(分组交换) --The files are broken into many packets with control information.
Ø Storage-forward---存储转发 --Routing tables decide the path of packets.
2、What is IP Protocol? How does it operate?
l Specifies addressing details for each packet, labeling each with the information formats of packet’s origination and destination address.
3、What is TCP Protocol? How does it operate?
l Controls disassembly of a message or a file into packets before transmission over the Internet
l Controls reassembly of packets into their original formats when they reach their destinations
4、一个房间里的两台计算机需要联机,有哪些方式?
5、接入互联网都有哪些方式?
6、什么是中介免除化?请举例。
l Disintermediation(中介免除化)
– Removal of an intermediary from a value chain
7、什么是中介再生化?请举例。
l Reintermediation(中介再生化)
– Introduction of a new intermediary to a value chain
8、互联网价值网络(Internet Value Networks)是什么?包括哪些部分,用结构图表示?请举例说明每部分的代表性企业。
l Internet value network:
Ø Associated with each of the components of the Internet is an industry or group of firms that market similar or related products.
Ø In the broadest sense, all the components and their interrelations create value for the end users, the customers, and organizations that actually use the network.
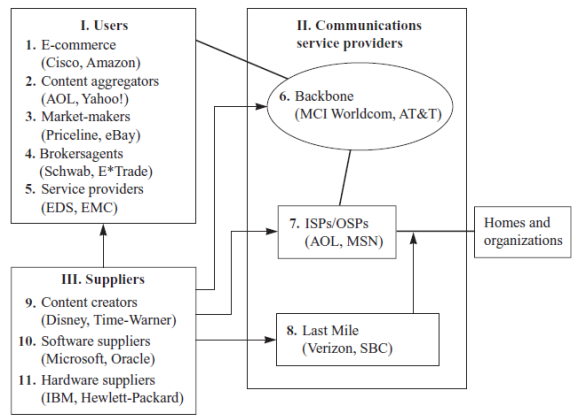
9、如何理解在线业务与离线业务的渠道冲突、渠道合作以及战略联盟,请分别举例。
2. Channel conflict
Ø Occurs whenever sales activities on a company’s Web site interfere with existing sales outlets
Ø Levis Strauss&Company
Ø Stop directly sell online
Ø
第三章:
1、所有企业的电子商务活动都是为了盈利吗?还有其它什么用途?
Not all electronic commerce initiatives have the goal of providing revenue; some are undertaken to reduce cost or improve customer service
2、电子商务活动的盈利模式有哪些类型?有何特征?请分别说明代表性企业。
I. Revenue models
A. Commission(佣金模式)-A commission is a fee that is levied on a transaction by a third party (usually an intermediary).
a. E*Trade、券商
b. eBay
c. Travelocity、携程
II. Advertising(广告模式)
A. In the advertising-based model, the owner of a website provides to end users subsidized or free content, services, or even products that attract end-user visitors.
B. – Examples: www.sohu.com,www.sina.com,www.163.com , my.yahoo.com
III. Markup(销售增值模式)
A. Markup(销售增值) refers to value added in sales rather than in production.
B. Markup-based model is one in which firms’ primary source of revenues is via markup.
1. This model has been traditionally used by wholesalers and retailers.
2. The most famous example is Amazon.com.
C. The key here is clearly the size of the markup.
IV. Production(生产模式)
A. In the production model, or manufacturing model, manufacturers try to reach customers or end users directly through the Internet.
1. Manufacturer-direct, manufacturers sell directly to end-user customers (e.g., Dell Apple, Dell, Gateway).
2. Content producer, in which firms produce entertainment, information, art, or other content and sell the content (e.g., Sony Entertainment).
3. E-procurement, companies tender and procure goods and services over the Web, increasing the choice of suppliers and keeping costs down (e.g., Ford Motor Company’s increasing use of electronic procurement in purchasing parts from suppliers).
V. Referral(转介费模式)
A. In the referral-based model, firms rely on fees for steering visitors to another company.
B. This referral fee is often a percentage of the revenues of the eventual sale but can also be a flat fee.
C. In this model, a merchant has affiliates whose websites have click-throughto the merchant.
D. Each time a visitor to an affiliate’s site clicks through to the merchant’s site and buys something, the affiliate is paid a referral fee.
1. Example: Amozon, 蘑菇街等
VI. Subscription(内容订阅模式)
A. In the subscription-based model a company charges a flat rate on a periodic basis (such as a month) that qualifies the user for a certain amount of service.
B. The user pays this subscription fee whether or not the service is actually used.
1. ISPs/OSPs (Internet access providers), which provide Internet access and sometimes additional content.
2. Last Mile operators, which provide local loop and end-user access points and telecommunications service.
3. Content creators (content providers), in which information and entertainment are offered to end-user consumers (e.g. 优酷,Disney,news).
VII. Fee-forservice(服务费模式)
A. In the fee-for-service model, firms pay as they go. Activities are metered and users pay for the services that they consume.
B. In this model, customers pay for only the service that they actually use.
1. Service provider, in which firms make money by selling services rather than products to end users.
2. B2B service provider, which supports businesses by selling services to other businesses (e.g.,alibab.com).
3. Application service provider, “rents” software applications to businesses (e.g., SAP).
4. Application service provider, “rents” software applications to businesses (e.g., SAP).顺丰
3、优酷等视频类网站未来的盈利模式可能有哪些?
4、微博等社区网站未来的盈利模式可能有哪些?
5、在线杂志类网站未来的盈利模式可能有哪些?
第四章:
9、点击流Clickstream data:Data generated in the Web environment and provide a trail of a user’s activities (the user’s click stream behavior) in a web site.
10、点击流技术如何协助电子商务企业经营活动?
点击流数据仓库将网络与数据仓库技术结合起来,它的数据来源与一般数据仓库不同,来自点击流数据,通过收集、整理、转换这些数据,建立针对Web点击信息的各种维度,进而分析网站用户的行为并最终探索导致这些行为的内在原因是点击流数据仓库的建设初衷。通过点击流数据仓库将描述用户行为,的数据转为决策者可以利用的有效信息,为网站经营者提供决策支持。通过分析包含在点击流仓库中的用户行为模式,商务人员能够拓展他们的市场,改善客户关系,降低成本,使操作流水化,有效地辅助他们改进商业策略。
11、搜索引擎包括哪几部分要素?如何工作?Search Engine
I. 搜索引擎一般由搜索器、索引器、检索器和用户接口四个部分组成;
A. 搜索器:其功能是在互联网中漫游,发现和搜集信息;
B. 索引器:其功能是理解搜索器所搜索到的信息,从中抽取出索引项,用于表示文档以及生成文档库的索引表;
C. 检索器:其功能是根据用户的查询在索引库中快速检索文档,进行相关度评价,对将要输出的结果排序,并能按用户的查询需求合理反馈信息;
D. 用户接口:其作用是接纳用户查询、显示查询结果、提供个性化查询项。
II. 工作原理
A. 第一步:爬行
搜索引擎是通过一种特定规律的软件跟踪网页的链接,从一个链接爬到另外一个链接,像蜘蛛在蜘蛛网上爬行一样,所以被称为“蜘蛛”也被称为“机器人”。搜索引擎蜘蛛的爬行是被输入了一定的规则的,它需要遵从一些命令或文件的内容。
B. 第二步:抓取存储
搜索引擎是通过蜘蛛跟踪链接爬行到网页,并将爬行的数据存入原始页面数据库。其中的页面数据与用户浏览器得到的HTML是完全一样的。搜索引擎蜘蛛在抓取页面时,也做一定的重复内容检测,一旦遇到权重很低的网站上有大量抄袭、采集或者复制的内容,很可能就不再爬行。
C. 第三步:预处理
1. 搜索引擎将蜘蛛抓取回来的页面,进行各种步骤的预处理。⒈提取文字⒉中文分词⒊去停止词 ⒋消除噪音(搜索引擎需要识别并消除这些噪声,比如版权声明文字、导航条、广告等……)5.正向索引6.倒排索引7.链接关系计算8.特殊文件处理
2. 除了HTML 文件外,搜索引擎通常还能抓取和索引以文字为基础的多种文件类型,如 PDF、Word、WPS、XLS、PPT、TXT 文件等。我们在搜索结果中也经常会看到这些文件类型。 但搜索引擎还不能处理图片、视频、Flash 这类非文字内容,也不能执行脚本和程序。
D. 第四步:排名
用户在搜索框输入关键词后,排名程序调用索引库数据,计算排名显示给用户,排名过程与用户直接互动的。但是,由于搜索引擎的数据量庞大,虽然能达到每日都有小的更新,但是一般情况搜索引擎的排名规则都是根据日、周、月阶段性不同幅度的更新。
12、搜索引擎优化及排名:
l 搜索引擎优化(Search Engine Optimization,简称SEO)是一种利用搜索引擎的搜索规则来提高目的网站在有关搜索引擎内的排名的方式。深刻理解是:通过SEO这样一套基于搜索引擎的营销思路,为网站提供生态式的自我营销解决方案,让网站在行业内占据领先地位,从而获得品牌收益。
l 搜索引擎排名指搜索引擎派出一个能够在网上发现新网页并抓取文件的程序,这个程序通常被称为蜘蛛(spider)或者机器人(robot)。搜索引擎蜘蛛从数据库中已知的网页开始出发,就像正常用户的浏览器一样访问这些网页并抓取文件。对搜索词进行处理后,搜索引擎排序程序开始工作,从索引数据库中找出所有包含搜索词的网页,并根据排名算法计算出哪些网页应该排在前面,然后按一定的格式返回“搜索”页面。然后进行排序过程只须一两秒之内就能完成并返回用户所要的搜索结果。
第五章
1、MRO产品的特点是什么?电子商务活动可以如何便利MRO产品的采购?
Ø MRO (Maintenance、Repair and Operations)
l 指工厂或企业对其生产和工作设施、设备进行保养、维修,保证其运行所需要的非生产性物料,这些物料可能是用于设备保养、维修的备品备件,也可能是保证企业正常运行的相关设备,耗材等物资。
Ø Characteristic of Indirect materials:
ü low value
ü harder to predict demand
ü less important to production
ü most are commodities where price is the only criterion
ü numerous so that it is hard to control
Ø 如何便利MRO采购
ü – Implementing purchasing cards in buyer organizations
ü – Implementing web catalogue selling
ü Purchasing cards
– Special-purpose payment cards issued to a company’s employees to be used solely for purchasing non-strategic materials and services up to a preset dollar limit.
n centralized purchase;
n business trip;
n daily small-amount administrative office utilities consumption.
2、货物跟踪系统(Web-enabled tracking systems)
Ø 货物跟踪系统(Web-enabled tracking systems) :
l 指物流运输企业利用物流条形码和EDI技术及时获取有关货物运输状态的信息(如货物品种、数量、货物在途情况、交货期间、发货地和到达地、货物的货主、送货责任车辆和人员等),提高物流运输服务的方法。
Ø 步骤:
l 物流运输企业的工作人员分别在向货主取货时、在物流中心重新集装运输时、在向顾客配送交货时;
l 利用扫描仪自动读取货物包装或者货物发票上的物流条形码等货物信息;
l 通过公共通讯线路、专用通讯线路或卫星通讯线路把货物的信息传送到总部的中心计算机进行汇总整理,这样所有被运送的货物的信息都集中在中心计算机里。
3、EDI是什么?工作原理是怎样的?What is EDI and how does it works?
l Electronic Data Interchange (EDI):EDI
n A computer-to-computer transfer of business information between two businesses.
n a standard format of some kind.
n taking use of computer communication networks to exchange data.
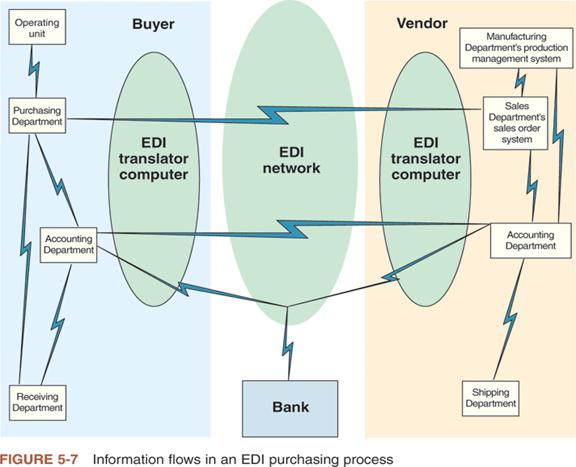




4、间接EDI的优点及缺点(Advantages of Using a VAN)
优点
l Users: Support only the VAN’s one communications protocol (what?)
l The VAN:
n Records message activity in an audit log
n Can provide translation between different transaction sets used by trading partners
n Can perform automatic compliance checking
缺点
l Cost:
n Using a single VAN:Using VANs can become cumbersome and expensive for companies that want to do business with a number of trading partners, each using different VAN.
n Using Multi-VAN:Most VANs require an enrollment fee, a monthly maintenance fee, and a transaction fee.
5、基于Internet的EDI的优势及阻碍(EDI on the Internet:roadblocks)
l 优势:比传统封闭式EDI节省投资和运营成本
n 以国际互联网为基础的EDI比在增值网络上运行的EDI要节省投资和运营成本。
n 增值网络服务商是按照每一笔生意或每千字节来收取费用,而国际互联网的联接一般则只需每月付固定的费用。
l Roadblock
n 安全问题
u 由于国际互联网是开放性的信息传输网络,因此,企业交易信息虽然被加密,但技术仍然不是很成熟或者实施成本较高, 企业对于互联网安全问题的担心还没有完全消除。
u 对于许多大公司来讲,一般解决的方案之一是在接入国际互联网时设立网络安全屏障,也就是俗你的“防火墙”。另外,公司还要有一套网络接入的权限限制。
u 对于中小企业,仅需要EDI,而不需联接国际互联网,就要考虑投资的大小了,或许传统的EDI投资更合算。
n 网络运营的可靠性
u 互联网的传输可靠性较差。由于互联网的传输的节点众多, 受链路以及流量的影响很大。网络运营中传输出现故障或信息丢失的可能性不时会发生。
u 相对于专用网络,公共网络不会提供完善的服务保证。
n 第三方认证问题
u 电子商务要求交易的所有参与者有效保留传递的交易信息,在必要时要求提供有力的证据来证实信息传递者的身份、传递的内容、传输方式和传输时间。
u 目前提供EDI服务的专营网络商往往都相应提供第三方认证的服务,即以第三方(公正方)的名义证实信息传递者的身份及其信息传递的有效性。
u 不能为信息传输提供运行记录和第三方验证,不能很好地解决不可否认问题。
6、中国电子口岸的特点
Ø 完全基于公网,系统开放性好,提供全天候、全方位服务。
Ø 入网成本低。
Ø 加密与数字签名的安全防护措施使系统安全可靠。
Ø 一个公共数据中心,集中存放电子底帐,信息资源共享。
Ø 一个系统入口,一站式服务。
7、无限射频技术的特点及运行原理radio frequency identification (RFID)
l 射频技术 相对于传统的磁卡及IC卡技术具有非接触、阅读速度快、无磨损等特点。 无线射频技术在阅读器和射频卡之间进行非接触双向数据传输,以达到目标识别和数据交换的目的。与传统的条型码、磁卡及IC卡相比,射频卡具有非接触、阅读速度快、无磨损、不受环境影响、寿命长、便于使用的特点和具有防冲突功能,能同时处理多张卡片。
l 工作原理:
n 一套完整的RFID系统, 是由阅读器(Reader)与电子标签(TAG)即应答器(Transponder)及应用软件系统三个部份所组成
n 其工作原理是Reader发射一特定频率的无线电波能量给Transponder,用以驱动Transponder电路将内部的数据送出,此时Reader便依序接收解读数据, 送给应用程序做相应的处理。
8、利用IT技术进行供应链管理的优势。Supply Chain Management with IT
l The collaborative use of technology to improve the operations of supply chain activities as well as the management of supply chains.
l Clear communications and quick responses
l Technologies, especially the technologies of the Internet and the Web, can be very effective communication enhances
9、什么是横向电子市场及纵向电子市场?请举例说明。
横向电子市场是指一个连接了很多行业买方和卖方的电子化市场,主要是MRO*物料的交易。此外,MRO物料包括范围很广泛的产品和服务,比如办公室、旅游、运输以及一些金融服务等。
纵向电子市场是指一个连接特点行业的买方和卖方的电子市场(比如石油和天然气、纺织品以及零售业)
10、电子市场及门户包括哪些类型,请举例说明。Electronic Marketplaces and Portals
A. 电子市场分类:Direct products – Vertical EMs/Vertical portal
Indirect products – Horizontal EMs
B. Vertical portals
a. Offer a doorway (or portal) to the Internet for industry members
b. Vertically integrated
第六章
1、拍卖的类型
Ø Types of Auctions
n English Auctions (Yankee Auctions) and Dutch Auctions
n First-Price and Second-Price Sealed-Bid Auction
n Open-Outcry and Sealed-Bid Double Auctions
n Reverse (Seller-Bid) Auctions
Ø Online Auctions
n B2C/C2C Auctions
n B2B Auctions
n Auction Related Services
2、eBay英式拍卖机制设计 English auction
n Left bids system(离拍系统)
n Allows a seller to set a reserve price
n Bidders are listed and set a WTP price
n Allows sellers to specify that an auction be made private
3、eBay多数量物品拍卖机制设计。
I. 如果卖家有多件相同的物品要出售,那么他在一个登录物品中提供相同物品两件以上的竞拍卖法称为多数量竞拍。
II. 与普通的易趣竞拍不同的是:多数量竞标会有多个得标者。
III. 拍卖机制
A. 当竞买多数量物品时,只需指定要购买的物品数量和愿意为物品支付的单件最高价格。最高出价金额对其他买家和卖家是保密的。易趣的代理出价系统会将出价与其他买家的出价进行比较。
B. 其加价幅度正好能让买家保持在最高出价者或能赢得物品的地位。该系统代理出价功能最多会将出价提高到买家所输入的最高出价金额为止。
C. 系统按照买家的单件物品出价金额和顺序选择出价。如果物品有两个买家出了相同的单件价格,则较早出价的买家优先。
D. 如果其他买家为剩余数量的物品出的价格比最高出价高,出价将被超出。
E. 如果其他买家为剩余可购数量的物品出的最高出价都比出价低,就可能赢得物品。可能只需要支付比最高出价低得多的金额!
F. 多数量竞标都支付同一价格,该价格是买家们在竞标中的最低成功出价;最高出价者得到其所购数量,次高出价者得到剩余数量,依次类推;遇到出相同价格者,则先出价者优先。

4、Lock-in Effect(锁定效应),并举例说明。Yahoo! Auction(2): the first online auction in Japan
Ø Lock-in Effect(锁定效应)
n Market become more efficient (yielding fairer prices to both buyers and sellers) as the number of buyers and sellers increase
n New auction participants are inclined to patronize established marketplaces.
n Thus, existing auction sites, such as eBay, are inherently more valuable to customers than new auction sites.
n That is, the task of creating other successful general consumer Web auction sites even more difficult in the future.
5、eBay.com,Yahoo.com,Amazon.com,Taobao.com各网站机制设计的特点。
l eBay.com:
A. eBay auction(1): English Auction—英式拍卖
B. The first major Web auction for consumers
C. Provide assurance that the privacy policies of the Web sites meet certain standards verified by the third party
D. Proxy bid(委托出价)
E. Mainly use email 、Many of them apply Skype
F. paypal :Direct to the sellers or receivers!
G. Risks:
1. For sellers :Buyers who use stolen credit card numbers、Buyers who place the winning bid but never contact the seller to conclude the transaction.
2. For buyers :Sellers who never deliver、Sellers who misrepresent their merchandise(货物不符)
H. Promotion Activities
1. Advertise widely
2. Spend more than $800 million each year to market and promote its Web site.
3. Depend on traditional mass media outlets, such as television advertising.
4. People who have a hobby or a very specific interest in items that are not locally available.
I. eBay stores
1. Integrated into the auction site
2. With a very low cost, sellers can establish eBay stores
3. Show items for sales as well as items being auctioned.
l Yahoo.com
A. Offered its auction service to sellers at no charge at first.
B. Yahoo! Auction(2): the first online auction in Japan
l Amazon.com
A. Amazon auction(1):Auction Guarantee(拍卖担保)
B. Third-party escrow service
C. Joint venture with Sotheby’s----the famous British auction house.
D. zShop platform
1. In lower end of market, Amazon integrated its zShops platform with its auction operation.
2. Gives small sellers a combined selling space that eBay offers.
3. Search results pages for customers who are shopping in any part of the Amazon site.
l Taobao.com
A. 1. 单件拍卖
发布要求:认证会员;参与拍卖的商品件数为1;可使用系统代理加价幅度。
B. 2. 荷兰式拍卖
发布要求:卖家信用的分数须大于等于11分;参与拍卖的商品件数必须大于1; 可使用系统代理加价幅度。
C. Taobao auction(2): Aliwangwang(阿里旺旺)
D. Taobao auction(3): Alipay(支付宝)
E. Taobao auction(3): credit system(评价体系)
6、大公司和小公司如何利用电子商务形式对其剩余库存进行拍卖?
l Specific existing needs: distribute excess inventory
A. For large companies:
1. Have liquidation specialists (清算专家) who find buyers or these inventory items
2. Online auction: create their own auction site that sells their own excess inventory
B. For smaller businesses:
1. liquidation brokers(清算经纪人)
----Firms that find buyers for unusable inventory items.
2. A third party Web auction
----Takes the place of the liquidation broker.
----Auction excess inventory listed on the site by a number of smaller sellers.
7、企业供应链B2B采购采用反向拍卖适应于及不适应哪些情况?
ü The need for trust and long-term strategic relationships with suppliers makes reverse auctions less attractive in some industries
ü The use of reverse auctions replaces trusting relationships with a bidding activity that pits suppliers against each other
案例分析:
三个案例的相关问题。
可以思考的问题:
生鲜食品网站的问题
电子商务网站免费与收费之间的均衡
移动APP的盈利问题
余额宝等网上理财产品的相关问题
O2O平台的优势与瓶颈
……
