Unit 1 the Correct Word
Focus
Denotation and Connotation
1. Denotation refers to the literal and primary meaning of a word-the definition you find in a dictionary.
2. Connotation refers to the implied or suggested meaning of a word.
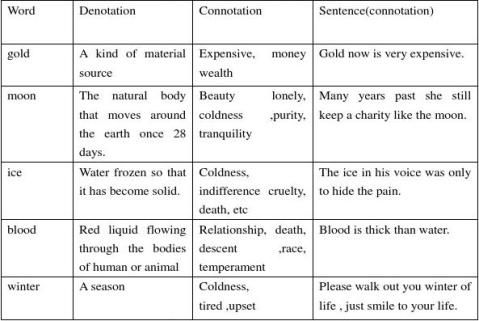
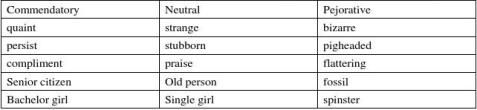
Attitude: when we write in English, we have to be careful with some emotionally loaded words-i.e. words that can reveal the writer’s attitude.
We can divide the words attitude into three parts: 1commendatory\positive 2neutral 3derogatory\pejorative
Collocation: fixed combination of words
There are several types of collocation: 1.V+N(follow the fashion) 2. A+N(a brilliant success)
3.V+AD(think alike) 4.PREP+N(the answer to a question) 5. V+PREP(think of an idea)
False Friends
Advise(v) vs. advice(n) angel (天使)vs. angle(角度)capital(首都,资金)vs. capitol(国会大厦)
Complement(补充) vs. compliment (称赞)credible(可信的,确实的) vs. credulous(轻信的,易受骗的) get knowledge(t) vs. learn knowledge(f)
Grammar
Subject-Verb agreement
1when the subject is compound
Work and play are equally important.
Ham and eggs is my favorite breakfast.
(1)由and或both…and连接的并列结构作主语时,如果意义为复数,谓语动词用复数;如果作主语的并列结构不是指两个或两个以上的人或物,而是表示单数,则动词用单数;and与each等限定词时,随后动词用单数。
(2)由neither…nor not only…but also连接的并列结构作主语,随后动词形式常遵循就近原则。
(3)主语后用along with, together with引导等词组,动词形式根据主语形式而定。 2When the subject expresses quantity
(1)有many a等限定词,其后动词形式为单数
(2)a pair, heap of 后动词多接单数形式
3when the subject is a relative pronoun, a what-clause, or in the there-be structure
(1)以nominal clause 作主语,随后动词通常用单数
(2)relative clause 中谓语动词单复数形式通常以关系代词先行项的形式而定
(3)there be 谓语动词单复数形式取决于所后的
Unit2 The Appropriate Word
Focus
Style: in English, words can be, roughly, formal , general, colloquial, and slang in terms of style. Formal and general
Formal words are not as common as general words, which form the basis of the vocabulary and
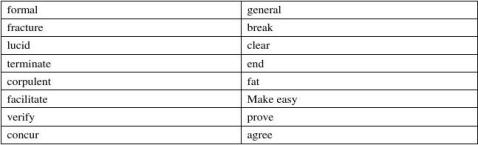
Notice: a common belief among students is that formality is a virtue, but the best policy is to use general words in most cases and formal words in specific, formal contexts .
Colloquial and slang
Well, now, you know, I’d like to say, oh, may god, I think….which can be used in colloquial, and contraction and abbreviation also can be used. But in some formal constitution we’d better not use it.
Notice : the colloquial style takes a less prominent role, therefore, for most writing tasks, it may not be ideal. Too much slang can make a passage loose and unserious; some may even sound odd. Style and audience
The formal style is characterized by extensive vocabulary, frequent use of formal and abstract words, absence of slang and almost no contraction or clipped words.
The informal style is characterized by vocabularies ranging from formal to colloquial but mostly general, and occasional and clipped words.
Different style are used to address different audiences and on different occasions.
Chinglish: it refers to the unidiomatic use of English by Chinese speaker
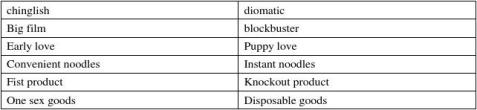
请帮我们(宣传)一下这个新产品。
Please help us to propagate this new product.
Propagate should be replaced by promote
他遇事总是先想着自己,真是太个人主义了
He is self-concerned and individualistic。 Individualistic should be replaced by selfishness Grammar
Pronouns
1Subjective vs. objective
Subjective: I she you he it who whom they
Objective: me her you his whom whose them its
2Singular vs. plural
3Point of view is used to describe the perspective in writing.
Unit 3 the Better Word
Focus
Conciseness (Brevity is the soul of wit. )
Tip: 1 eliminate or expression rewrite that repeat the same point
2cut out unnecessary intensifiers
3avoid overusing the noun forms of verbs
4change phrase into single words
5 change unnecessary “that, who and which” clause into phrases.
Notice: redundancy is not always easy to spot. the best way is to proofread your writing carefully and try to find words, phrases or even sentence that are not essential.
Preciseness:The concreteness of expression
General words convey inexact intangible and often abstract concepts whereas specific words provide precise, sensory or concrete details.
For example: it was fine last weekend, so we went to the countryside and had a good time. We saw many things and people there. And we had a wonderful time.
Improved: It was a wonderful and relaxed weekend, we drive our private and spacious car to the countryside, there we were a enjoyable and relax time. We saw so many people who wearied plain and simple clothes and there are so much interesting tings like assembly and folk dance. We’re welcomed by passionate villager and had delicious dinner with them. That was really a memorable and wonderful time.
Effectiveness
Sentence Base Unit 4
Focus
The sentence base, which is like the trunk of a tree, consists of at least one subject and one verb.
Subject: to choose a good subject is the first crucial step in sentence writing, tell us who or what is responsible for an action, feelings, and state or process.
Position of the subject: The subject is usually, through not always ,put at the beginning of a sentence.
The subject of a declarative sentence- a sentence that makes a statement – usually precedes the verb .but in one situation , it follows the verb,( In the center of the painting stands a lady in white. )
Voice: the voice of a verb depends on the relation between the verb and its subject. when the subject acts, the verb is in the active voice; when the subject is acted upon, the verb is in the passive voice.
1Choosing the active voice
The active voice stresses the activity of the subject and helps to make a sentence direct, concise, and vigorous.
2Choosing the passive voice
Though the active voice is more commonly used in writing, the passive voice may be more suitable for the following:
1when the agent is followed by a long modifier, we use the passive voice to avoid suspension of the verb
2the passive also used to keep the focus of two sentences
Grammar
Tense
1The simple present: a表示现在的状态,b表经常或习惯性动作,c表主语具备的性格和功能 d普遍真理和自然规律e表示将来和过去时间
2Sequence of tenses: simple present, simple past, present progressive, past progressive, present perfective, past perfective, present perfective progressive, past perfective progressive
Mood: the indicative mood, the imperative mood, the subjunctive mood
The subjunctive mood: In grammar, the subjunctive mood (abbreviated sjv or sbjv) is a verb mood typically used in subordinate clauses to express various states of unreality such as wish, emotion, possibility, judgment, opinion, necessity, or action that has not yet occurred. It is sometimes referred to as the conjunctive mood, as it often follows a conjunction
Unit 5 Expanded Sentence Base
Focus
Attributes: words or phrases used to narrow down or describe nouns are called attributes. What can be used as attribute?
A Determiners: refers to words that are used to define the referential meaning of a noun or a nominal phrase.
It included articles, possessive and demonstrative pronouns, and cardinal and ordinal numerals.
B adjectives are the most common attributes.
For example: hairy animals, a red rose
C nouns: most of them indicate the feature of the noun modified.
For example: Her boy friend is a fashion designer.
D-ing forms : to describe the function ,feature ,or to indicate the present state of the noun. We all like her smiling face.
E –ed forms
He only drinks imported wine.
F infinitives: now it must be placed after the noun.
Do you have a friend to talk to.
G prepositional phrases: it is placed after the noun it modifiers.
I can’t stand that silly ad for dog food, can you?
Relative Clauses
Why use relative clause: to make the nouns either more exact or more vivid; we can direct readers’ attention to the main clause
My son liked the toy car very much which I bought for his birthday.
The toy car was liked by my son very much which I bought for my son.
Writing correct relative clauses
RULE1 where the antecedent refers to a thing
For example A+ that\which +clause\
RULE2 where the antecedent refers to a person
For example A+ that\who +clause\
RULE3 where the antecedent is used as possessive in the clause
For example A +whose +clause
RULE4 where the antecedent refers to a time
For example A+ when + clause
RULE5 where the antecedent refers to a place
For example A+ where\ (in\at+ which) + clause
RULE6 where the antecedent refers to a cause
For example A+ why + clause
RULE7 where the antecedent refers to a manner
For example A+ in which + clause
RULE8 where the antecedent refers to the main clause as a whole
Foe example preceding sentence+ which +clause
Rule 9 where the relative clause has no relative word
If the relative is used as object, it can be omitted.
Rule 10 where the relative begins with a preposition
For example antecedent+ prep+ which+ clause
Rule 11 where the antecedent and the relative clause are separated by a comma
For example: a non-restrictive clause (The boy, who have played truant to watch the football match, will have to copy the text.)
Grammar
Incomplete Sentence
A Phrase fragment: inexperienced writers may write a phrase as if it were a sentence because they borrow the phrase directly from the spoken language.
I’ll meet you in the library. At four in the afternoon.. ( I’ll meet you in the library at four in the afternoon.)
B fragment without a subject
She stood by the window. And looked at the street below. ( She stood by the window and looked at the street below.)
C fragment without a auxiliary verb: fragments often contain verb-like particles or infinitives which cause the writer to think a verb has been include.
D fragment of dependent clauses: when a dependent clause are fairl long, a writer might mispuctuate it as a sentence.
Word Order
Determiners: 名词前的限定词顺序为前位-中位-后位,同时一个名词中心词前不能同时用两个中位限定词或两个前位限定词。
Adjectives
形容词修饰名词的顺序为:限定词-数词-描绘词-(大小,长短,形状,新旧,颜色)出处-材料性质类别-名词。
Unit 6 Expanded Sentence Base
Focus
Participle
Getting to know participle: there are two kinds of participle, one ending with –ing, and the other ending with –ed which forms to use depends on the relationship between the verb and the noun described.
1The trembling old man stood by the broken window.
2Frightened by a strange noise downstairs he went down slowly ,holding his gun in his hand Complex participle phrase
A present participle in different modes and aspects
B Participle with conjunction
Time: we use while when to emphasize that the participle action and the predicate action take place at the same place. We also use words like before ,after to show the sequence of the two action
While chasing the cat, the dog hurt its feet.
Concession: we use words like though ,although ,even if , etc. to show concession.
She doesn’t plan to go to the party, even though invited.
Condition: we use if when or unless before a participle to indicate that this is just a condition , instead of a fact.
When hearted, this material will give off a very bad smell.
Getting to know participle’s function
A creating concise sentence
B producing more detailed sentence
1The old man held the receiver in his hand, shocked at what he was told, not uttering a single word.
2Shocked at what he was told, not uttering a single word, the old man held the receiver in his hand.
(Better)
C establishing clearer logic
I’ll have to stay in bed for a couple of days, hurt in a accident.
Hurt in a accident, I’ll have to stay in bed for a couple of days.
Absolutes
Getting to know absolutes
Using absolute with purpose
A adding descriptive details to make sentence much more vivid.
The manager sat quietly in his office, his eye closed.
The manager sat quietly in his office, a cigarette burning in his hand.(better)
B indicating cause-effect relationships
He glared at his boss, smile disappeared.
The girl was enjoying her favorite song, laughed loudly.
Grammar
Comma-split sentence: use a coma to connect two separate ideas, or two independent sentence We can use some conjunction to combine the sentence.
Fused sentence
We should know the base structure of sentence, like SVC, SV, SVO, SVOC….
Unit 7 Joining Sentence Together
FOCUS
Coordination: is a common syntactic pattern formed by grouping together two or more categories of the same type with the help of a conjunction such as and, but , or.
Coordinate structures
A basic coordinate formula
Coordination= item A+ and\but+ item B (a red and yellow curtain)
B coordination a different grammatical levels
1 hard but rewarding (word level )
2 a five-thousand-Yuan salary and a two-month paid holiday (phrase level)
3 who is old enough to provide knowledgeable lessons about life and who is young enough to treat students as friends. (clause level)
4Leaders work with mind, and laborers work with hand.. (sentence level)
C coordination with different types of coordinators
1. Single coordinators: and, but, or
2. Paired coordinators: both…and…, either…or…, neither…nor…
3. Serial coordination
Coordination in series= item A+ item B+ item C…,+Coordinator+ last item
D using conjunctive adverbs (sentence connectors)
1indicate contrast: however, instead, on the other hand, nevertheless, otherwise, in contrast… 2 indicate cause and effect: therefore, thus, hence, consequently, as a result, for this reason 3inndicate a similar idea follows: besides, moreover, furthermore, in addition, similarly 4indicate emphasis and illustration: indeed, in fact, in particular, for example, for instance 5 indicate time: then, meanwhile, at the same time, afterward, later
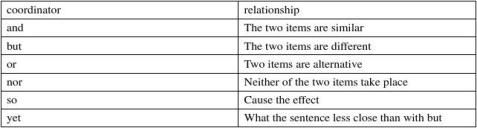
Function of coordinate sentences: to clarity the relationship between clauses and assigns equal weight to the ideas
Advanced usages of coordinate sentence
A repetition or absence of coordinators
B semicolons: a it quittance the pace of the sentence ; b slowly the sentence down, so the reader will pun date over the ideas.
C interrupted coordination: the phrase inserted adds more information to the original sentence. B Making the sentence pasterns more varied.
Joining Sentence Together Unit 8
Focus
Subordination The clause that can be used independently is called independent clause ; the clause that cannot be used alone is called dependent clause ,and the word used to connect them and indicated relationship is called subordinator.
Subordination vs. coordination
Similarity: they both combine two clause into one sentence
Difference: The two clauses in coordinate sentence can be used indecently, because their
meanings are complete; while in subordinate only one sentence is complete meanings and can be used indigently.
Coordination: Tony is very gifted in music ,but he chose to major in accounting.
Subordination: Although Tony is very gifted in music, he chose to major in accounting. Types of subordination
A nominal clause: a nominal clause is a dependent clause functioning as a noun.
Why your father comes here is a mystery to me.
B relative clauses: I like the dog that\which is chasing a cat
C adverbial clauses
Functions of subordination
A more information
B emphasis: to sum up, subordination can add more information to a sentence, and more importantly, it can give special emphasis to part of the sentence.
Effective use of subordination
A position of the subordinate clause
B simplified subordination
Unit 9 Sentence Variety
Ways to achieve sentence variety
1By varying the length
A short sentence: emphatic, suitable for the presentation of important facts and ideas.
B long sentence: capable of expressing complex ideas with precision ; suitable for the explanation of views and theories, or the description of things with many details.
2 By varying the pattern: by sentence patterns, we mean sentence of different functions and structures
A Avoid strings of brief and simple sentence
B Avoid too many compound sentence.
Sentence function: declarative .interrogative imperative exclamatory
Grammatical structure; simple, compound, complex, compound-complex
3By varying the emphasis
The first strategy for emphasis
Natural emphasis position in English sentence
1 The end of a sentence is the most emphasis position; the beginning the second ; the middle the last.
2 When we shift the order, we create a certain emphatic effect , other elements such as attributes and adverbials are usually placed close to what they modify.
The second strategy; by using emphatic patterns, like what…is…, it is…that…, there be… who\that…, do\verb, passive voice
4 By varying the beginner
A subject: besides nouns and pronouns ,numerals, infinitives, ing participle and clause can also be used as subject .by using different kinds of subjects to begin sentences, we can also achieve sentence variety.
B adverbial: besides beginning sentence with subject , we may also put adverb ,-ly at the beginning and “to” beginners, prepositional phrase beginner, adj\adv phrase can all be used as subjects . this can also improve sentence variety.
Unit 10 Punctuation
Common punctuation marks: the comma (,), the period (.), the semicolon (;), the colon (:), the question marks (?), the dash (-), quotation marks (“”), the exclamation mark (!), parentheses (()), the slash(\), italics underling(_)
Period: 1 use a period to show the end of sentence. 2 use a period after certain abbreviations. Comma: 1 Join short and closely related parallel sentence
2 in a compound sentence before the conjunction or connective
3 after an adverbials clause or phrase before the subject of the sentence
4nonerestrictive clauses and phrase are set off by commas
5 commas set off parenthetical elements
6 use a comma with quotation marks to show what someone has said directly 7 in the date, in the order
Semicolons
1 use a semicolon between independent clause not joined by coordinating conjunction
His mother won’t let him; she is afraid he might get hurt.
2 the semicolon is used to separate a series of items which contain
For example, professor Zhao, Dean of the Normal College; Mr., Han, editor in-chief of the local evening paper.
3有些其联系作用的副词,如however, thus, otherwise, hence, nevertheless, besides, consequently 等等,不应该用作连词来联系并列句,他们之间应该用分号而不用逗号,此后用逗号。
The invention brought him fame; moreover, it brought him money.
Colon
1 uses a colon to introduce an explanation, a summary, an appositive, or a list of things. 2 it is used after a complete statement when introducing a list.
常用错误,在英语中例如一类的词后常用逗号代替冒号。
Quotation
1 the period and the comma always come inside the quotation marks.
2 the semicolon and the colon always come outside the quotation marks.
3use it to enclose the titles of essays, articles, short stores, short poems, chapters…
