博士英语复习资料
分数组成:卷面80分+出勤10分+口试10分
卷面:一. 听力选择(放2遍):1分*10=10分
二. 给出后缀,要求写出它的意思,并以此后缀造词并写出中文意思:0.5分*10=5分
三、单复数的变化
四. 选择正确的解释并将所选选项翻译成中文(神经系统、消化系统、心血管系统、呼吸系统、药
理):本题出自各章课后习题Multiple choice部分:1分*10=10分
五. 2段英翻中(医学科普):5分*2=10分
2段中翻英(一般为中医):内容包括证、病机、症状、治则的翻译,书中以肺为例,考试中可
以变为脾等脏。详见《博士生医学英语教材》中的IX、X、XI:10分*2=20分
六. 给一段中文科普文章,翻译成80字左右的英文摘要
七. 作文:Economic Growth and Environment(80字) A4纸手写、不能从网上下,夹在卷子里:10
分
一.复数形式(教科书P42~43)
Ampulla—Ampullae 尾突(另有一意思为壶腹)
Corona—Coronae 冠状 Vertebra—Vertebrae 脊椎
Bronchus—Bronchi 支气管
Capillus—Capili 毛发
Fungus—Fungi 真菌
Omphalos—Omphali 脐
Genus—Genera 属
Stercus—Stercora 粪
Gonad—Gonades 性腺
Testis—Testes 睾丸
Diagnosis—Diagnoses 诊断
Psychosis—Psychoses 精神病
Epididymis—Epididymides 附睾
Thorax—Thoraces 胸部
Appendix—Appendices 阑尾
Pollex—Pollices 拇指
Meninx—Meninges 脑脊膜
Caries—Caries龋齿
Derma—Dermata 真皮,皮肤
Sarcoma—Sarcomata 肉瘤
Stoma—Stomata 口
Flagellum—Flagella 鞭毛
Labium—Labia 唇
Protozoon—Protozoa 原生动物
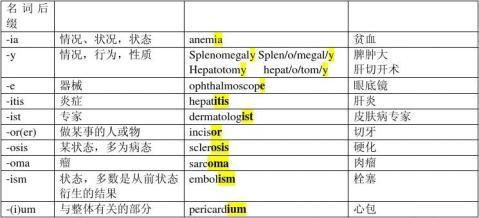

格(p17~p20)及课后练习题I的所有单词。笔者按后缀相关性顺序排列单词,旨在提供一种相对好记的方法,可结合书内表格记忆。 形容词性后缀:
心脏的(-ac: pertaining to) 支气管的 先天的 髂的 舌下的 扁桃体的 目的 HEPA 肝的 传染的 食道的 喉的 睫状的 粘液的
纤维性的(-ous: containing) 分泌脂质的(-ous: secreting)
囊样的(-oid: resembling) 腺样的
名词性后缀:
肉瘤(-oma: tumor)
脑瘤 HEPA 肝炎(-itis: inflammation) 胃炎 心包炎
喉炎 切牙(-or:refers to a doer, person or thing) ASPIRA 抽吸(-or:that which) 心包(-ium:a part related to a whole) 上腹部 贫血(-ia: condition) 恐惧症 营养不良 脾肿大 栓塞(-ism: condition, usually
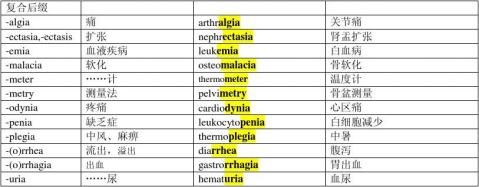
the result of a prior condition) 脓毒病(-sis:condition) 硬化(-osis: abnormal condition) 皮肤病 动脉硬化(-sclerosis: a hardening) 骨软化(-malacia: softening) 动脉狭窄(-stenosis: a narrowing) 杀菌剂(-e: that which) 解毒剂 验眼镜(-e: instrument) 验眼镜(-scope: instrument for viewing) 膀胱镜(-scopy: examination)
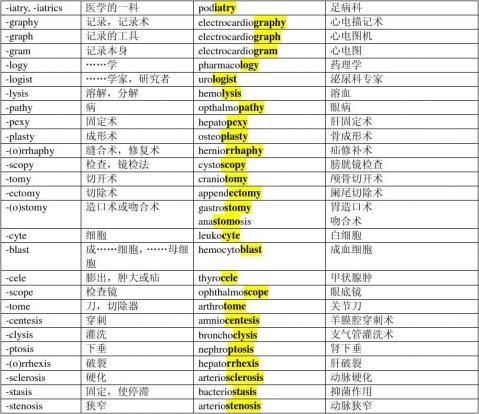
温度计(-meter: instruments for measuring) 骨盆测量(-metry: measurement) 关节刀(-tome: instrument for cutting) 关节痛(-algia: pain) 心痛 泄泻(-rrhea:flow, discharge) 胃出血(-rrhagia: excessive flow)
足医学(-iatry:branch of medicine) 老年学 眼病(-pathy: disease) 药理学(-logy: process of studying) 泌尿科医生(-logist: one who specializes in) 牙医(同上) 儿科医生 肝破裂(-rrhrxis: rupture) 疝缝合术(-rrhaphy: suturing) 肝固定术(-pexy: fixing by suturing) 骨成形术(-plasty: surgical repair)
颅骨切开术(-tomy: incision) 阑尾切除术(-ectomy: cutting off) 扁桃体切除术 胃造口术(-stomy: making an opening into or a connection between) 吻合术(同上) 白细胞(-cyte: cell) 细胞缺乏症(-penia: deficiency)
原始血细胞(-blast: a cell that is primitive) 溶血(-lysis: dissolution) 支气管灌洗术(-clysis: washing)
制菌(-stasis: halting) 肾下垂(-ptosis: a falling) 肾盂扩张(-ectasia: dilatation) -plegia: stroke) 心电图描记(-graphy:process of recording) 甲状腺肿(-cele: hernia)
羊膜穿刺术(-centesis:surgical puncture to withdraw fluid)
关于各大系统相关单词总结:本部分需结合书中题目记忆,笔者这里只做正确选项的标注翻译 The Nervous System(Exercise III、VII): 1.b dendrites树突 2.a axon轴突
3.d convergence收敛性 4.c microglia 小胶质细胞 5.b
Exercise VII:
1. c apraxia 失用 2. d apoplexy 中风 3. b embolism 栓塞 4. a coma 昏迷
5. b grand mal 癫痫大发作 6. c hydrocephalus 脑积水 7. d hypertension 高血压
8. b myasthenia gravis 重症肌无力 9. c multiple sclerosis 多发性硬化 10. b shingles 带状疱疹 11. a spina bifida 脊柱裂
12. b subdural hematoma 硬膜下血肿 13. c ischemia 缺血
14. a gliomas 神经胶质瘤 15. c metastasis 转移
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM(Exercise VI):9、10划掉 1. a heart block 心脏传导阻滞 2. c pericarditis 心包炎 3. d tachycardia 心动过速
4. b myocardial infarction 心梗 5. d hypertension高血压 6. b aneurysm 动脉瘤 7. b murmur 杂音 8. b atherosclerosis 动脉粥样硬化 9. 10.
11. a pernicious anemia 恶性贫血 12. a infectious mononucleosis 传单 13. c varicose veins 静脉曲张
14. b sickle cell anemia 镰状细胞性贫血 15. c hemophilia 血友病 16. c leukemia 白血病
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM (Exercise V): 1. b dyspnea 呼吸困难
2. c Cheyne-Stokes 潮式呼吸 3. b pertussis 百日咳
4. d hyaline membrane disease 新生儿呼吸窘迫综合
症
5. a atelectasis 肺不张 6. c tuberbulosis 肺结核 7. a silicosis 矽肺 8. c emphysema 肺气肿 9. b pleurisy 胸膜炎 10. a aspiration 抽胸水
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM (Exercise VI) 1. b cold sore 单纯性疱疹 2. d leukoplakia 粘膜白斑 3. c intussusception 肠套叠 4. b diverticula 憩室 5. a melena 黑便
6. b serum hepatitis 乙肝 7. a cirrhosis 肝硬化 8. c neoplasm 肝囊肿 9. b ascites 腹水
三.选择(注:此处为避免混淆,只记录正确答案,剩余选项忽略不计) 神经系统
1. The afferent processes of nerve cells are the: dendrites 树突 [?dendrait]
2. Those processes that conduct impulses away from neurons are the: axons 轴突 [??ks?n]
3. The transmission of impulses by many neurons to a single neuron is known as: convergence 会聚 4. Which of the following supportive nerve cells act as phagocytes: microglia 小胶质细胞
phagocyte [?f?ɡ?usait]吞噬细胞
5. Which of the following is not considered part of the central nervous system? nerves originating from the brain and the spinal cord 脑和脊髓发出的神经 6. The inability to perform certain body movements is known as: apraxia 失用症
Apraxia [??pr?ksi?] 失用; 精神性运动不能
7. The medical word for stroke is: apoplexy 脑卒中 [??p?pleksi] -plexy 发作,中
8. A blood clot that leaves its original site and blocks an artery is called: embolism 栓塞
9. An abnormal deep sleep is called: coma 昏迷 [?k?um?]
10. The more serious form of epileptic seizure is referred to as: grand mal 癫痫大发作
epileptic seizure [.epi'leptik] ['si:??] n.癫痫发作
11. The medical word for an excessive amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain is: hydrocephalus 脑积水
Cerebrospinal [.seribr?u'spain?l] adj 脑脊髓的的
12. A sympathectomy is performed to relive: hypertension 高血压
sympathectomy [?simp??θekt?mi] 交感神经阻断术 13. A general feeling of muscular weakness and fatigue resulting from a lack of acetylcholine:
myasthenia gravis 重症肌无力 myasthenia [mai?s?θi?ni?]肌无力 gravis 重的,剧烈的acetylcholine [??si?t?l?k?ulin] 乙酰胆碱
14. A condition in which the myelin coverings of the brain and spinal cord are destroyed and the gray and white matters become hard: multiple sclerosis 多发性硬化
spinal cord n.脊髓
15. A viral infection characterized by blisterlike sores on the skin: shingles [??i?g?l]带状疱疹
Blisterlike像水泡样
16. A congenital defect characterized by a protruding sac containing cerebrospinal fluid: spina bifida 脊柱裂 congenital defect 先天性缺陷protrude [pr??tru:d] vi.突出 sac [s?k] 囊 cerebrospinal fluid 脑脊液
17. A blood clot originating in one of the membranes covering the brain: subdural hematoma 硬膜下血肿 subdural n.硬膜下的 hematoma [?hi?m??t?um?] 血肿
18. The medical word indicating the obstruction of a blood vessel: ischemia 缺血
19. Malignant tumors originating from the supportive nerve cells: gliomas 神经胶质瘤[ɡlai??um?] malignant tumors 恶性肿瘤
20. The medical word indicating the spread of malignant tumors to other areas of the body: metastasis 转移
[m??t?st?sis]
心血管系统
1. The obstruction of electrical impulses moving from the atria to the ventricles is called: heart block 心传导阻滞
atria 房,前房 ventricle [?ventrikl] 脑室; 室
2. Inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart is known as: pericarditis 心包炎 [?perikɑ??daitis]
3. A type of arrhythmia: AV block, 房室传导阻滞 tachycardia 心动过速 tachy-速,快速 4. Necrosis of an area of heart tissue due to insufficient blood supply: myocardial infraction 心肌梗死 necrosis [ne?kr?usis] 坏死 myocardial [?mai?u?kɑ?di?l] 心肌的 myo-肌
5. The medical term for high blood pressure: hypertension 高血压
6. The ballooning of a blood vessel: aneurysm 动脉瘤 aneurysm [??nj?r?z(?)m] 动脉瘤
7. Abnormal heart sound resulting from incompetent heart valves: murmur 心脏杂音
heart valve 心脏瓣膜
8. Abnormal condition in which fatty plaques adhere to the walls of a blood vessel: atherosclerosis 动脉粥样硬化 fatty plaque 脂肪斑块
11. The type of anemia brought on by absence of an intrinsic factor necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12: pernicious anemia 恶性贫血 pernicious [p???ni??s] 恶性的
12. A viral infection characterized by enlarged lymph glands, sore throat, fever, and fatigue: infectious mononucleosis 传染性单核细胞增多症
enlarged lymph gland 淋巴结肿大 mononucleosis [?m?n?unju?kli??usis ]单核白细胞增多症
13. Abnormal enlarging and twisting of leg veins: varicose veins 静脉曲张 varicose [?v?rik?us]曲张的
14. A type of anemia in which the erythrocytes change their shape at low oxygen levels: sickle cell anemia 镰形红细胞贫血 erythrocyte [i?riθr?usait]红细胞; 红血细胞
15. Hereditary bleeding disease affecting only male offspring: hemophilia 血友病
hereditary [hi?redit?ri] a.遗传的,遗传性的; offspring [??f?spri?] n.子女,子孙,后代
16. A form of cancer in which there is an uncontrolled increase of white blood cells: leukemia 白血病 呼吸系统
1. Labored breathing: dyspnea 呼吸困难 -pnea 呼吸 apnea 呼吸暂停 2. Hyperpnea followed by apnea: Cheyne-Stokes 陈-施呼吸(潮式呼吸)
3. An infectious disease that produces a proximal whooping type of coughs: pertussis
pertussis [p?'t?sis] 百日咳 proximal 接近的,邻近的
4. A respiratory disease affecting the newborn in which the alveoli are covered with a thick membrane: hyaline membrane disease 肺透明膜病(新生儿呼吸窘迫综合征)
hyaline 透明的,玻璃样的
5. Collapse of lungs: atelectasis 肺不张 atel- 发育不全 -ectasis 扩张,膨胀
6. An infectious disease of the lungs in which the bacteria become encapsulated: tuberculosis 结核TB
[tju:.b?:kju'l?usis]
7. An example of a pneumoconiosis: silicosis 矽肺pneumo- 肺回戏,空气coni (单conus)圆锥,锥体-osis 病
8. A condition in which lung tissues swell and lose their elasticity: emphysema [.emfi'si:m?] 肺气肿 elasticity 弹性emphy 肺气肿 9. Inflammation of the serous membrane covering the lungs and thoracic cavity: pleurisy 胸膜炎 serous [?si?r?s]血清的 thoracic cavity 胸腔
9. Process of removing fluid from pleural cavity: aspiration 抽吸pleural cavity 胸膜腔 ['plur?] 消化系统
1. A virus, herpes simplex, causes a blister to erupt on the mucous membrane lining of the mouth: cold sore 唇疱疹
blister n.水疱, mucous membrane n.粘膜
2. Inflamed patches of mucous membrane that can become malignant: leukoplakia [lu:k?'pleiki?]粘膜白斑
3. The invagination of one portion of intestine into another: intussusceptions [.int?ss?'sep??n]肠套叠
invagination 内陷 intestine n.肠 intestinal 肠的,在肠内的
4. Pouches that form on the intestinal wall: diverticula肠憩室 pouch n.小袋
5. Bloody stools: melena [m?'li:n?] 黑便
6. A form of liver disease caused by a blood transfusion with contaminated blood: serum hepatitis 血清性肝炎 serum 血清
7. Scarred condition of the liver that results in impeded circulation of blood: cirrhosis [si'r?usis] 肝硬化 impede vt.阻碍,妨碍,阻止
8. The development of new but abnormal tissue: neoplasm 肿瘤 ['ni:?upl?z?m]
plasm 浆,原生质,形成物质
9. The buildup of excessive fluid in the peritoneal cavity: ascites 腹水[?'saitiz]
peritoneal [,perit?'ni:?l] n.腹膜的 peritoneal cavity 腹膜腔 buildup 积累,聚集,增长,增加
药理:
Antitussives are drugs that suppress coughing.[.?nti't?siv] n. 止咳药, 镇咳药adj. 镇咳的 tussive adj. 咳嗽的 Antispasmodic drugs are used to relieve bronchial spasms. [?ntisp?z'mɑdik]解痉药
spasm n.痉挛;突发一阵spasmodic 痉挛(性)的,间歇的 antispasmodic adj. 止痉挛的n. 镇痉药
中枢系统药物
Stimulants stimulant [?stimjul?nt] increase CNS activity 兴奋药 Depressants depressant [di'pres?nt] decrease CNS activity 抑制药 Analgesics analgesic [??n?l?d?i:zik] a substance that reduces pain 止痛药 Hypnotics hypnotic [hip'n?tik] drugs that produce sleep hyp-在?下 安眠药 Sedatives sedative [?sed?tiv] has a calming,tranquilizing effect 镇静药 Barbiturates barbiturates [bɑ:'bitju?rits] 巴比妥类 a powerful drug that makes you feel calm and relaxed or puts you to sleep. Anesthetics anesthetic [??nis?θetik] causes a loss of awareness and sensation麻醉药 ?Tranquilizers tranquilizer ['tr??kwilaiz?] reduce mental tension 安定药
关于中医翻译的常用词组: 急性热病 acute febrile disease 外感病 external disease 温病 warm disease 病因 cause of disease
辨证论治 syndrome differentiation and treatment IX
先天之精 innate essence 后天之精 acquired essence 水谷 foods and fluids
肾气/阴/阳 kidney qi/yin/yang 温煦作用 warming influence
运化 transportation and transformation
精主生长、生殖 jing governing/dominating growth and reproduction
助神 aiding the mind/shen 安神 anchor the shen 气生血 qi produce blood 气摄血 qi hold the blood
气为血之帅,血为气之母 qi is the commander of blood, and blood is the mother of qi 血虚 deficient blood 血滞 stagnant blood 血热 heat in the blood
行肾气 promoting kidney qi 生髓 producing marrow 耳聋 deafness 头晕 dizziness 耳鸣 tinnitus 发白 graying 衰老 senility 阳痿 impotence
腰痛 lower back pain X、XI(具体药不用记) 病例 case history
病机 mechanism of disease 累及卫分(气/营/血)wei(qi/ying/xue) system may become involved
变化快 evolves rapidly
证 syndrome(书中说的是symptom-complexes) 痰热阻肺 blockage of the lung by phlegm-heat 风邪袭肺 invasion of the lung by pathogenic wind 邪热袭肺 invasion of the lung by pathogenic heat 邪热内陷心包 penetration of pathogenic heat into the pericardium
气虚精亏 deficiency of vital energy and vital essence 亡阳 depletion of yang
痰留热恋 remaining phlegm and pathogenic heat 治则 principle of treatment
祛热毒化痰 removing toxic heat from the lung and resolving phlegm
祛痰 eliminating phlegm 清肺 clearing lung 润肺 moisten lung
清营分邪热 dispelling pathogenic heat from the ying system
醒神 resuscitating the patient
回阳救逆 restoring vital function from collapse and reinforcing vital energy
用辛凉药祛表邪 dispelling pathogenic factors from the exterior of the body with herbs pungent in flavor/taste and cool in property/nature 临表 manifestations
无汗 absence of sweating 大汗 profuse sweating 少汗 scanty sweating
动则汗出 sweating on exertion 畏寒 intolerance of cold 寒战 chill 发热 fever
中等热 moderate fever 午后潮热 afternoon fever
五心烦热 feverish sensation in the palms and soles 颧红 malar flush 乏力 lassitude
持续高热夜甚 protracted high fever that is worse at night
烦热 heat and restlessness 大渴 extreme thirst 谵语 delirium
昏迷 loss of consciousness 抽搐 convulsion 项强 stiff neck
四肢厥冷 cold limbs
面色苍白 pallid countenance 紫绀 cyanosis 哮 wheezing
气短 shortness of breath 咳嗽 cough 干咳 dry cough
咯白粘痰/脓痰/锈色痰/血丝 expectoration of white mucoid /purulent/rust-colored/blood-flecked sputum 鼻翼扇动 flaring of the nostrils 口唇干燥 dry mouth and lips
胸痛咳甚 chest pain exacerbated by coughing
胸闷或痛 suffocating or painful sensation in the chest 胸痛厉害 sharp chest pain
两胁钝痛 dull pain in the hypochondrium 食欲不振 anorexia
腹胀 abdominal distention 便秘 constipation
少尿 concentrated urine
舌边红 reddened tongue border 舌边紫 purpura at the tongue border 舌干 dry tongue 少苔 scanty tongue
苔薄白或略黄 thin white or light yellow fur 舌中剥脱苔 shedding of some fur in the middle 浮数脉 floating and rapid pulse
洪脉 gigantic pulse 滑脉 slippery pulse 细脉 thready pulse 沉脉 deep pulse 弦脉 wiry pulse 方 prescription 汤 decoction
加减 modifications 加**药 add 减**药 omit
**汤合**汤 in combination with 冲服 take with the decoction 先煎 decocted first 验方 proven recipes 主穴 main points 刺血 prick to bloodlet 泻法 reducing method 补法 reinforcing method 留/埋针 retain/embed needle
随症取穴 points according to manifestations 草药 herbal medicines 中药 Chinese pharmacy
9.4.1 Liver Blood Deficiency Syndrome
It refers to insufficient liver blood, usually caused by insufficient blood production or massive blood loss, or injury to liver blood in a chronic disease.
【Clinical Manifestations】Dizziness, pale complexion, blurred vision ,numbness of limbs, tremor of hands and feet, joint motion problem, scanty volume of menses, or even amenorrhea, pale tongue with white fur and thready pulse
9.4.3 Syndrome of Liver Qi Stagnation
It refers to emotional problems and rage that impair the liver, or other pathogenic factors, impeding smooth flow of liver qi. 【Clinical Manifestations】Distending pain or scurrying pain in the chest and lower abdomen, depression or bad temper, frequent deep sighing, thin white fur and wiry pulse, or distending pain in women’s breasts, irregular menses, dysmenorrhea , closely related to emotional changes
9.5.3 Kidney Essence Insufficiency Syndrome
It refers to the syndrome due to the decreased function in growth, development and reproduction because of kidney essence deficiency, usually caused by insufficient innate endowment, congenital defect, or improper postnatal nursing, or excessive sexual activity, or kidney essence injury in a chronic disease.
【Clinical Manifestations】Retarded development of children, short figure, feeble bones, sluggish movement, infertility , poor
sexual function, presenility of adults, tinnitus or poor hearing, amnesia and weak feet
9.6.4 Heart-Kidney Yang Deficiency Syndrome
It is caused by declined yang qi of the heart ,with the kidney involved in a chronic condition, or kidney yang deficiency, dysfunction in qi transformation, upward attack of the heart by retained water.
【Clinical Manifestations】Cold body and limbs, palpitation, weakness and cold in the lower back and knees, edema, difficult urination, purple lips and nails, pale purple tongue with white and slippery fur and faint pulse
9.6.13 Syndrome of Invasion of the lung by liver fire
It is usually caused by liver injury by rage, accumulated qi transforming into fire, or invasion of the lung by reversed rise of heat, which accumulates in the liver.
【Clinical Manifestations】Burning pain in the chest and hypochondrium, dizziness with distending pain in the head, irritability and bad temper, bloodshot eyes, bitter taste in the mouth, coughing, even spitting blood, red tongue with thin white fur, and wiry rapid pulse
6.1.2.1 Cold Syndrome
It is caused by exposure to external pathogenic cold, or excessive yin and yang deficiency, resulting in hypofunction of the body, marked by symptoms with cold and chilly characteristics. Since excessive yin and yang deficiency can cause cold syndromes, there are excess cold syndrome and deficiency cold syndrome.
【Clinical Manifestations】 Aversion to cold, preference for heat, cold limbs, huddling up with cold, cold pain, alleviated by warmth, tastelessness in the mouth, absence of thirst, clear and thin sputum, and nasal discharge, pale complexion, light pale tongue with white and moist fur and tight or slow pulse
9.6.9 The Lung-Kidney Qi Deficiency Syndrome
It is caused by chronic coughing, which involves the kidney over time, or over-work, or innate deficiency and poor health of the aged.
【Clinical Manifestations】Weak coughing and panting, long exhalation than inhalation, worse when active, profuse and thin sputum, weakness in the lower back and knees, or urine out on coughing, lassitude, feeble voice, shortness of breath, spontaneous sweating and pale tongue with weak pulse
【Focal Points in Syndrome Differentiation】Weak coughing and panting, long exhalation than inhalation, weakness in the lower back and knees and other symptoms of qi deficiency
Exercise 1.
Using aspirin , an over-the-counter pill on sale in every supermarket without a prescription, to treat serious circulatory disease may seem almost like quakery (江湖医术). But today doctors recognize the drug as a potential compound as important as antibiotics.
In its natural form as willow bark and leaves, this remarkable remedy dates back to Hippocrates. In 1829 the chemical in the willow trees that can relieve pain and reduce fever was discovered to be salicin (柳素).
Since then, aspirin and compounds containing aspirin have been taken by tens of millions of arthritis patients. As a pain killer aspirin is , according to one study, more effective than all other narcotics available for oral use. It also acts on the body’s thermostat(恒温器), turning down fever.
Exercise 4.
The major objective of biochemistry is the complete understanding of the molecular level of all of the chemical processes associated with living cells.
To achieve this objective, biochemists have sought to isolate the numerous molecules found in cells., determine their structure, and analyze their function.
A further objective of biochemistry is to attempt to understand how life began. Knowledge of this fascinating subject is still embryonic (胚胎的).
Exercise 2.
According to type, a virus may infect a particular kind of animal, plant, fungus, blue-green alga(藻), bacterium or protozoan. Some types of virus invariably cause the death and lysis (分解) of the host cell. The infection of animal cells by certain virus may lead to cell fusion (融合)or cell transformation (including tumor formation). This infection of organisms by virus may or may not give rise to symptoms of disease—depending on e.g. the type of virus involved. Diseases of viral etiology include: chickenpox, influenza, measles, mumps, poliomyelitis, rabies, rubella, smallpox and hepatitis.
Exercise 3.
Shock is a common fundamental pathologic process caused by a variety of etiologic factors.
The basic feature of shock is the failure of peripheral circulation and the vital function is depressed. In other words, shock is a condition in which the perfusion(灌注) of tissue with blood is inadequate. It consequently leads to cellular membrane dysfunction. Abnormal cellular metabolism and eventually cellular death. The clinical picture is usually described as pale face, hypotension, cold, cyanotic skin, thready rapid pulse, dull sensation, oliguria (尿少), etc. In shock many organs may be profoundly affected, in men, the lung, the kidney, the liver , the heart and the brain appear particularly susceptible to shock.. The failure of a specific organ may account for the eventual refractory (顽固的) nature of shock.
Exercise 5.
Carcinoma of the colon and rectum is the second most common malignancy occurring in the United States. It is also the second leading cause of cancer death. Carcinoma of the colon and rectum is generally a disease of older individuals with an approximately equal incidence in men and women. The etiology of the carcinoma of the colon and rectum remains unclear . However, many studies have suggested a correlation between colorectal cancer, economic status, geographic location, and dietary exposure. In industrialized countries , including the United States and those of Western Europe, a great deal of animal fat, protein, and refined carbohydrates are consumed; in these geographical areas the incidence of colorectal cancer is much higher than in the developing countries in Africa, South America, and Japan, where considerably less meat is consumed and the diet is significantly higher in vegetable fiber.
Exercise 6.
Although the incidence of tuberculosis has declined dramatically in most developed countries over the past century, tuberculosis remains a disease resulting in significant morbidity (发病率) and mortality in children of many developing countries. Children are typically infected by prolonged , close contact wih an adult who has untreated open pulmonary tuberculosis. Although the incidence of tuberculosis is low in developed countries , migrants from developing countries provide a constant source of new cases of tuberculosis. It is important that infected children are diagnosed and treated , as those untreated or inadequately treated primary infection may still become new cases of
tuberculosis if their disease reactivates during adult life.
Exercise 7.
A six-year old boy was admitted to the hospital because of recurrent abdominal pain with vomiting and weight loss.
The boy had been well until 3 months earlier, when he began to experience recurrent periumbilical pain once or twice a week, with vomiting two or three times daily for 1 to 3 days accompanied by anorexia, and reduced energy. There was no diarrhea, and the vomitus was free of blood and bile. The pain improved after emesis or a bowel movement and worsened after a meal. Three weeks before admission, abdominal and rectal examinations were normal, so was a test for occult blood in a stool examination. Two weeks before the admission, the patient began to feel feverish during the bouts (发作) of pain. One week before admission , his mother noted increasing pallor, and two days later , the pain began to radiate to the right upper abdomen.
9.4.1. 肝血虚证
肝血虚多因生血不足,或失血过多,或因久病耗伤肝血所致。
临床表现: 头晕,面色无华,视物模糊,肢体麻木,手足震颤,关节拘急不利,或妇女经量少,甚则
闭经, 舌淡苔白,脉细。
9.4.3. 肝郁气滞证
肝郁气滞多因情致不遂,郁怒伤肝,或因其他病邪阻滞,肝失疏泄调达所致。
临床表现: 胸胁或少腹胀闷,窜痛,情致郁抑或易怒, 善太息,苔薄白, 脉弦。妇女乳房胀痛,
月经不调,痛经,病情轻重与情致变化关系密切。
9.5.3.. 肾精不足证
肾精不足是指生长发育和生殖机能减退所表现的征候。 多由禀赋不足,先天发育不良,或后天
失调。 或房劳过度,或久病耗肾精所致。
临床表现: 小儿发育迟缓,身材矮小, 骨骼痿软,动作迟缓, 男子不育。 女子不孕, 性功能低
下,成人早衰,耳鸣耳聋, 健忘, 足痿无力。
9.6.4. 心肾阳虚证
心肾阳虚证多由心阳虚衰, 久病及肾, 或肾阳亏虚, 气化失权, 水气上凌心阳所致。
临床表现: 形寒肢冷, 心悸, 腰膝酸冷, 肢体浮肿,小便不利,甚则唇甲青紫, 舌淡紫, 苔白
滑,脉微。
征候分析: 心肾阳虚,形体失于温养, 则形寒肢冷,;心失温熙,则心悸
;腰膝失熙,则腰膝酸冷。 肾主水,肾阳亏虚,气化无权,水湿泛滥肌肤,则小便不利, 肢体浮肿, 心阳不振,运血无力,则唇甲青紫, 舌淡紫, 苔白滑, 脉微, 为心肾阳虚,水湿内停之证。
9.6.13 肝火犯肺证
肝火犯肺多由郁怒伤肝, 气郁化火, 或肝经蕴热, 上逆犯肺所致。
临床表现: 胸胁灼痛, 头晕头胀, 急躁易怒, 目赤, 口苦,咳嗽, 或咳血,舌红, 苔薄白, 脉
弦数。
征候分析: 肝火炽盛, 肝经热壅气滞,则胸胁灼痛, 偱经上攻头目, 则头晕头胀,目赤, 热蒸
胆气上溢, 则口苦, 肺失清肃, 则咳嗽阵作,或灼肺络, 则咳血, 舌红, 苔薄黄, 脉弦数, 为
肝经实火内炽之证。
6.1.2.1.寒证
寒证是指感受寒邪, 或阳虚阴盛,导致机体功能活动低下所表现的具有“冷”的、“凉”特点的征候。 由于阴盛可表现为寒的征候,阳虚也可以表现为寒的征候,故寒证有实寒与虚寒之分。
临床表现: 恶寒喜暖, 肢冷踡卧, 冷痛喜温, 口淡不渴, 痰、涕清稀, 小便清长, 面色苍白, 舌质浅淡, 苔白而润, 脉紧或迟等。
征候分析: 因感受寒邪, 或过服生冷寒凉所致, 起病急, 体质壮实者,多为实证, 因内伤久病, 阳气虚弱而阴寒偏盛者, 多为虚寒证。 寒邪袭于表者, 多为表寒证。体失温熙, 故见恶寒喜暖, 肢冷踡卧,冷痛喜温等症。
9.6.9.肺肾气虚证
肺肾虚证多由久病咳喘,病久及肾,或因劳损过度,先天不足,年老体弱等所致。
临床表现: 咳喘无力,呼多吸少, 动则益甚,咳痰清稀,腰膝酸软,或咳则尿出,神疲乏力,语声低下,气短自汗,舌淡,脉弱。
征候分析: 肺为气之主,肾为气之根。 肺肾气虚,则咳喘无力, 呼多吸少,动则耗气,肺气虚, 故咳痰清稀, 腰膝失养,则腰膝酸软,卫气不固,则自汗,神疲乏力,气短,语声低下,舌淡,脉弱,均为气虚之证。
辨证要点: 咳喘无力,呼多吸少,腰膝酸软与气虚。
