《通信原理》知识点汇总
第一章 绪论
? 知识要点:通信系统的组成、系统模型及分类;通信技术的发展历史及趋势;信号、消息;信息及其度量,信息量和平均信息量;通信系统的性能度量;掌握信道数学模型; 随参信道、恒参信道。
? 重点:1. 模拟和数字通信系统模型。
2.信息量与平均信息量(信息的熵)的计算。
3.码元速率,信息速率,频带利用率,误码率,误信率的定义与计算;
4. 恒参信道特性及其对信号传输的影响;
5.随参信道的三个特点及其对信号传输的影响。 ? 难点:1.信息量与平均信息量(信息的熵)的计算
2.恒参、随参信道特性及其对信号传输的影响。 ? 教学方法:课堂讲解与讨论
第二章 信号
第一部分:确定信号分析
? 知识要点:信号的类型,(确知信号和随机信号)(功率信号和能量信号);确知信号的频域性质,时域性质(自相关函数) ? 重点:能量信号和功率信号的判断、功率信号的频谱/能量信号的频谱密度/能量谱密度/功率谱密度,自相关函数 ? 难点:频域特性的求解方法,自相关函数的计算。 第二部分 随机信号分析
? 知识要点:随机过程及白噪声的概念;平稳随机过程的数字特征(均值、方差、相关函数)的计算方法;平稳随机过程通过线性系统后的自相关、功率谱的计算方法;正态随机过程、窄带噪声的特征、分析方法;信号加窄带噪声的分析方法。 ? 重点:1.随机过程的数字特征。
2.平稳随机过程的特性—各态历经性
3.高斯过程的一维概率密度函数的特性。
4.正弦波加窄带高斯过程。
5.平稳随机过程通过线性系统的特点。
难点:1.平稳随机过程的相关函数与功率谱密度。
2.平稳随机过程通过线性系统的特点。
第三章 模拟调制系统
? 知识要点:线性调制、非线性调制、相干解调、非相干解调的概念;
? 重点:1.幅度调制的原理。
2.非线性调制的原理。
3.各种模拟调制系统的性能比较。
第四章 模拟信号的数字化
? 知识要点:抽样定理;PCM编码原理(A律13折线非线性量化编码)及量化信噪比的计算方法;增量编码调制(DM)的原理;增量编码调制的原理。
? 重点:1.PCM系统组成,PCM调制原理,13折线A率的编译码方法及PCM系统中的噪声分析
2.过载量化噪声
? 难点:1.13折线A率的编译码方法
第五章 基带数字信号的表示和传输
? 知识要点:无码间串扰系统的条件及滚降无串扰系统特性的分析方法;时域均衡的分析及计算方法;基带传输系统特性;主要传输码型差分码、AMI、HDB3的编码规则及特点;奈奎斯特定理;眼图的含义及作用。
? 重点:1.基带传输的常用码型,基带信号的频谱特性。
2.无码间干扰的基带传输特性。
3.检测系统性能的实验手段—眼 图。
? 难点:无码间干扰的基带传输特性
第六章 正弦载波数字调制系统
? 知识要点:ASK、FSK、PSK、DPSK调制、解调原理,已调信号时域表示及频谱结构;数字系统抗噪性能分析方法;理解数字载波键控概念;
? 重点:1.二进制数字调制系统的调制解调原理及各点波形图。
2. 二进制数字调制系统的性能比较
第七章 同步 知识要点:同步的分类
第八章 数字信号的最佳接收
? 知识要点:数字信号接收的统计描述,最佳接收原理;匹配滤波器的设计分析方法;
? 重点:1.关于最佳接收的准则表述。
2.确知信号最佳接收的分析。
第九章 多路复用和多址技术
? 知识要点:多路复用的概念和分类,多址技术的分类,基群 多次群
第二篇:通信原理知识点总结
Outline
2012.5
Chapter 0
l Basic elements of communication systems (p.2)
l Primary communication resources (p.3)
l The mobile radio channel (p.18)
l Block diagram of digital communication system (p.22)
l Shannon’s information capacity theorem (p.23-24)
Chapter 1
l Definition and basic concepts of random process
l Stationary and non-stationary
l Mean, correlation, and covariance functions, the mean-square value and variance
l The concept of ergodic process
l Transmission of a random process through a linear time-invariant filter
n 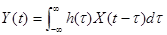
n The mean, autocorrelation function, and mean-square value of Y
l Power spectral density
n Definition (Equ. 1.38)
n Input-output relation (Equ. 1.39)
n Einstein-Wiener-Khintchine relations (Equ. 1.42, 1.43)
n Properties
l Gaussian process (Equ. 80)
l Concept of white noise
l Representation of narrowband noise
n The canonical form (Equ. 1.100)
n Properties of the in-phase and quadrature components (p. 65-66)
n Representation using envelop and phase components (Equ. 1.105-1.107)
n Basic concepts of Rayleigh distribution and Rician distribution
l Uncorrelated and statistically independent (p.58)
n Uncorrelated: Covariance is 0
n Statistically independent: defined by joint probability density function
Chapter 2
l Concepts of amplitude modulation and angle modulation (FM and PM)
l AM
n AM signal (Equ. 2.2 and Fig. 2.3), and the amplitude sensitivity ka
n Conditions of correct detection (p. 90)
n Spectrum of AM wave (Equ. 2.5 and Fig. 2.4)
n Transmission bandwidth BT = 2W
n Virtues and limitations of AM
l Linear modulation schemes
n The general form (Equ. 2.7)
n DSB
u DSB signal (Equ. 2.8 and Fig. 2.5)
u Spectrum of DSB wave (Equ. 2.9 and Fig. 2.6)
u Coherent receiver
u Basic knowledge of costas receiver
u Basic concept of quadrature-carrier multiplexing
n Basic concepts of SSB and VSB
l Concepts of mixer (Fig. 2.16)
l Concepts of FDM
l Definitions of angle modulation
l FM
n A nonlinear modulation process
n Single-tone FM modulation
u Definitions of Df, b
u Basic knowledge of narrowband and wideband FM
n Transmission bandwidth
u Carson’s rule (Equ. 2.55)
u Know the universal curve
n Demodulation
u Frequency demodulation (a direct method) (Fig. 2.30)
u Know phase-locked loop (an indirect method)
l Definitions of SNR’s
n (SNR)I, (SNR)O, and (SNR)C
n Figure of merit (Equ. 2.81)
l Comparison of figure of merits between DSB-SC (Equ. 2.88) and AM (Equ. 2.95)
l Basic concepts of threshold effect of AM (p.138) and FM systems (p.149)
Chapter 3
l Sampling
n Definitions of the sampling period and sampling rate
n Instantaneous sampling and the ideal sampled signal (Equ. 3.1-3.3, Fig. 3.2)
n Derivation of the interpolation formula (Equ. 3.4-3.9)
n The sampling theorem and definitions of Nyquist rate and Nyquist interval
n The methods of combat aliasing effect (p.187)
l PAM
n The difference between PAM and natural sampling
n The concept of “sample and hold”
n The PAM signal (Equ. 3.10-3.19)
n The aperture effect
l Know PPM and PDM
l Quantization
n Quantization noise and (SNR)O of a uniform quantizer (Equ. 3.25-3.33)
l PCM
n Basic concepts
u Discrete in both time and amplitude
u Sampling, quantizing, and encoding
n Non-uniform quantizers
u m-law and A-law
u Piecewise linear approximation to the companding circuit
n Five types of line codes and their waveforms
n Differential encoding
n Noise in PCM systems
u Know that noise including channel noise and quantization noise, and that performance is essentially limited by the quantization noise
l Concepts of TDM (Fig. 3.19)
l Know the basic concept of digital hierarchy (p.214) and that the basic rate is 64 kbps
l Concepts of DM and delta-sigma modulation
l Concepts of linear prediction and linear adaptive prediction
l DPCM and its processing gain (Equ. 3.82)
Chapter 4
l Two sources of bit errors: ISI and noise
l Matched filter
n Frequency response (Equ. 4.14) and impulse response (Equ. 4.16)
n Properties: the peak SNR dependents only on signal energy-to-noise psd ratio at the filter input
l Error rate due to noise
n Derivation of Equ. 4.35
n The complementary error function (Equ. 4.29)
n The result with equiprobable input signals (Equ. 4.38-4.40)
l The baseband data transmission system model (Fig. 4.7 and Equ. 4.44-4.48)
l Nyquist’s criterion
n The Nyquist’s criterion (p.262)
n The ideal Nyquist channel (Equ. 4.54-4.56 and Fig. 4.8, 4.9)
n Raised cosine spectrum (Equ. 4.59, Fig. 4.10)
u The definition of a and the bandwidth BT
l Correlative-level coding (partial response signaling)
n Duobinary signaling (class I partial response)
u Basic concepts (Fig. 4.11, 4.13, Equ. 4.66, 4.71)
u The concept of decision feedback
u Error-propagation and precoding
n Generalized form of correlative-level coding
l Baseband M-ary PAM transmission (Equ. 4.84)
l ADSL (Fig. 4.26)
l Optimum linear receiver
n For linear channel with both ISI and noise
n The MMSE receiver (Equ. 4.110 and Fig. 4.27)
l Adaptive equalization
n The LMS algorithm (Equ. 4.114, 4.115)
n The basic concept of decision-feedback equalization (Fig. 4.32)
Chapter 5
l Geometric representation of signals (Equ. 5.5-5.7 and Fig. 5.3)
n The vector form (Equ. 5.8) and definitions of length, Euclidean distance, and angle
n Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization procedure
l Conversion of the continuous AWGN channel into a vector channel
n Basic formulations (Equ. 5.28-5.34)
n The vector representation represents sufficient statistics for detection
l Log-likelyhood functions for AWGN channel (Equ. 5.51)
l Maximum likelihood decoding
n The concept of signal constellation
n The maximum likelihood rule (Equ. 5.55), for AWGN channel, the rule is Equ. 5.59 and 5.61
l Equivalence of correlation and matched filter sampled at time T
l Probability of error
n Know the invariance to rotation and translation
n The concept of the minimum energy signals
n Know how to use union bound to derive a upper bound (p. 332 – 335) (Equ. 5.89)
n Know that there is, in general, no unique relationships between symbol error probabilities and BER
Chapter 6
l Basic concepts of keying and ASK, FSK, and PSK
l The relationship between baseband and passband power spectral density (Equ. 6.4)
l Bandwidth efficiency (Equ. 6.5)
l The passband transmission model
l Coherent PSK
n BPSK
u Basic definitions (Equ. 6.8-6.14, Fig. 6.3)
u Error probability (Equ. 6.20)
n QPSK
u Basic definitions (Equ. 6.23-6.27)
u Error probability (Equ. 6.34, 6.38)
u Generation and detection (Fig. 6.8)
n M-PSK
u Basic definitions (Equ. 6.46)
u Bandwidth efficiency
u Know that the power spectra of M-PSK has no discrete frequency component
l M-QAM
n Basic definitions (Equ. 6.53-6.55)
n QAM square constellations (Fig. 6.17)
l Coherent FSK
n Coherent BFSK
u Basic definitions (Sunde’s FSK) (Equ. 6.86-6.91, Fig. 6.25)
u Error probability (Equ. 6.102)
u Know that the power spectra of BFSK has discrete frequency components
n MSK
u The concept of CPFSK
u The concept of MSK
u The phase trellis
u Signal-space diagram (Fig. 6.29)
u Error probability (Equ. 6.127)
n Bandwidth efficiency of M-FSK signals
l Noncoherent receivers (Fig. 6.37)
l The reason of envelop detection (Fig. 6.38)
l Error probability of noncoherent receiver (Equ. 6.163)
l Noncoherent BFSK
n Receiver structure (Fig. 6.42)
n Error probability (Equ. 6.181)
l DPSK
n Basic concepts (Fig. 6.43, 6.44)
n Error probability (Equ. 6.184)
l Comparison of digital modulation schemes
n Relationship among the error probabilities (Table 6.8 and Fig. 6.45)
n Bandwidth efficiencies of M-PSK, M-QAM, and M-FSK
