功能说明:
一个简易的图片上传展示程序,后台可以新建,修改,删除图片.前台是图片列表,最近一周上传的图片会有"new"标记.
任务说明:
1. 一周之内模仿以下图中的项目,做一个同样功能及相似外关的项目,具体要求如下:
1.在自己机器上搭建服务器,程序语言为PHP,数据库不限制。
2.例子项目中的所有功能由自己观察得出,模仿过程以功能为主,外观为次,功能外观能全部一样更好。
3.所做的程序最好可以很好的展示程序员的水平,如技术高度,编码风格,执行效率等。
4.每天把下班前一小时,需要把工作日志发到邮箱 bobhero.chen@gmail.com,格式自定,工作日志至少应包括计划,进度,问题。(可不做)
2.一周之内有除硬件环境问题,其它问题(包括但不限于 环境配置,各种软件的使用)尽量自行解决,如解决不了可以找陈作星。(仅限到公司实训人员)
登录
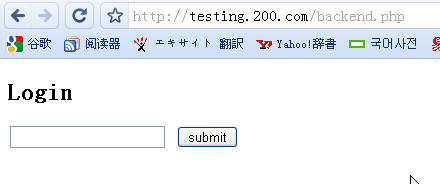
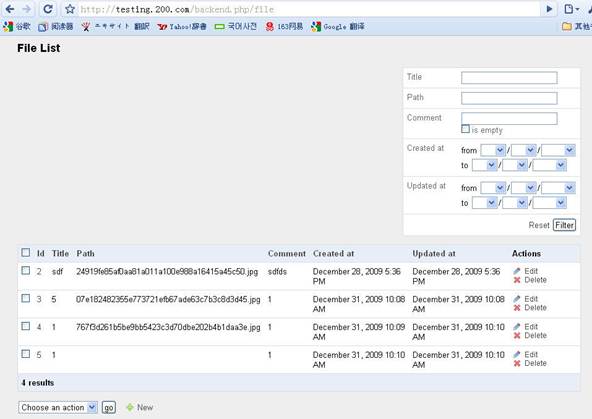
后台显示列表
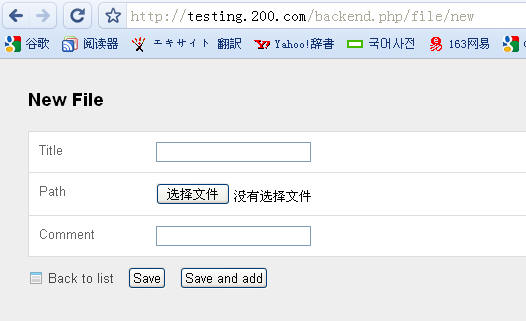
后台新建
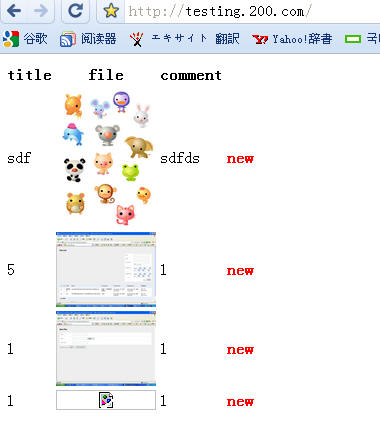
前台显示
第二篇:培训PHP
PHP Syntax
You cannot view the PHP source code by selecting "View source" in the browser - you will only see the output from the PHP file, which is plain HTML. This is because the scripts are executed on the server before the result is sent back to the browser.
Basic PHP Syntax
A PHP scripting block always starts with <?php and ends with ?>. A PHP scripting block can be placed anywhere in the document.
On servers with shorthand support enabled you can start a scripting block with <? and end with ?>. However, for maximum compatibility, we recommend that you use the standard form (<?php) rather than the shorthand form. <?php
?>
A PHP file normally contains HTML tags, just like an HTML file, and some PHP scripting code. Below, we have an example of a simple PHP script which sends the text "Hello World" to the browser: <html>
<body>
<?php
echo "Hello World";
?> </body> </html>
Each code line in PHP must end with a semicolon. The semicolon is a separator and is used to distinguish one set of instructions from another.
There are two basic statements to output text with PHP: echo and print. In the example above we have used the echo statement to output the text "Hello World".
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
Comments in PHP
In PHP, we use // to make a single-line comment or /* and */ to make a large comment block. <html> <body>
<?php //This is a comment
/* This is
a comment
block
*/
?>
</body> </html>
PHP Variables
Variables are used for storing values, such as numbers, strings or function results, so that they can be used many times in a script.
Variables in PHP
Variables are used for storing a values, like text strings, numbers or arrays.
When a variable is set it can be used over and over again in your script
All variables in PHP start with a $ sign symbol.
The correct way of setting a variable in PHP:
$var_name = value;
New PHP programmers often forget the $ sign at the beginning of the variable. In that case it will not work.
Let's try creating a variable with a string, and a variable with a number:
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
<?php $txt = "Hello World!";
$number = 16; ?>
PHP is a Loosely Typed Language In PHP a variable does not need to be declared before being set.
In the example above, you see that you do not have to tell PHP which data type the variable is. PHP automatically converts the variable to the correct data type, depending on how they are set. In a strongly typed programming language, you have to declare (define) the type and name of the variable before using it.
In PHP the variable is declared automatically when you use it.
Variable Naming Rules
?
?
? A variable name must start with a letter or an underscore "_" A variable name can only contain alpha-numeric characters and underscores (a-Z, 0-9, and _ ) A variable name should not contain spaces. If a variable name is more than one word, it
should be separated with underscore ($my_string), or with capitalization ($myString)
PHP String
A string variable is used to store and manipulate a piece of text.
Strings in PHP
String variables are used for values that contains character strings.
In this tutorial we are going to look at some of the most common functions and operators used to manipulate strings in PHP.
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
After we create a string we can manipulate it. A string can be used directly in a function or it can be stored in a variable.
Below, the PHP script assigns the string "Hello World" to a string variable called $txt: <?php
$txt="Hello World";
echo $txt; ?>
The output of the code above will be:
Hello World
Now, lets try to use some different functions and operators to manipulate our string.
The Concatenation Operator
There is only one string operator in PHP.
The concatenation operator (.) is used to put two string values together.
To concatenate two variables together, use the dot (.) operator: <?php
$txt1="Hello World";
$txt2="1234";
echo $txt1 . " " . $txt2; ?> The output of the code above will be: Hello World 1234
If we look at the code above you see that we used the concatenation operator two times. This is because we had to insert a third string.
Between the two string variables we added a string with a single character, an empty space, to separate the two variables.
Using the strlen() function
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
The strlen() function is used to find the length of a string.
Let's find the length of our string "Hello world!": <?php
echo strlen("Hello world!"); ?>
The output of the code above will be: 12
The length of a string is often used in loops or other functions, when it is important to know when the string ends. (i.e. in a loop, we would want to stop the loop after the last character in the string)
Using the strpos() function
The strpos() function is used to search for a string or character within a string.
If a match is found in the string, this function will return the position of the first match. If no match is found, it will return FALSE.
Let's see if we can find the string "world" in our string: <?php
echo strpos("Hello world!","world"); ?>
The output of the code above will be: 6
As you see the position of the string "world" in our string is position 6. The reason that it is 6, and not 7, is that the first position in the string is 0, and not 1.
Complete PHP String Reference
For a complete reference of all string functions, go to our . The reference contains a brief description and examples of use for each function!
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
PHP Operators
Operators are used to operate on values.
PHP Operators
This section lists the different operators used in PHP. Arithmetic Operators Operator +
Description Addition
Example x=2 x+2
-
Subtraction
x=2 5-x
*
Multiplication
x=4 x*5
/
Division
15/5 5/2
%
Modulus (division remainder)
5%2 10%8 10%2
++
Increment
x=5 x++
--
Decrement
x=5 x--
x=4 3 2.5 1 2 0 x=6 20 3 Result 4
Assignment Operators Operator = += -= *= /= .= %=
Example x=y x+=y x-=y x*=y x/=y x.=y x%=y
Is The Same As x=y x=x+y x=x-y x=x*y x=x/y x=x.y x=x%y
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
Comparison Operators Operator == != > < >= <=
Description is equal to is not equal is greater than is less than
is greater than or equal to is less than or equal to
Example
5==8 returns false 5!=8 returns true 5>8 returns false 5<8 returns true 5>=8 returns false 5<=8 returns true
Logical Operators Operator &&
Description and
Example x=6 y=3
(x < 10 && y > 1) returns true
||
or
x=6 y=3
(x==5 || y==5) returns false
!
not
x=6 y=3
!(x==y) returns true
PHP If...Else Statements
The if, elseif and else statements in PHP are used to perform different actions based on different conditions.
Conditional Statements
Very often when you write code, you want to perform different actions for different decisions. You can use conditional statements in your code to do this.
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
?
? if...else statement - use this statement if you want to execute a set of code when a condition is true and another if the condition is not true elseif statement - is used with the if...else statement to execute a set of code if one of
several condition are true
The If...Else Statement
If you want to execute some code if a condition is true and another code if a condition is false, use the if....else statement.
Syntax if (condition)
code to be executed if condition is true;
else
code to be executed if condition is false;
Example
The following example will output "Have a nice weekend!" if the current day is Friday, otherwise it will output "Have a nice day!": <html>
<body>
<?php
$d=date("D");
if ($d=="Fri")
echo "Have a nice weekend!";
else
echo "Have a nice day!";
?>
</body> </html>
If more than one line should be executed if a condition is true/false, the lines should be enclosed within curly braces:
<html>
<body>
<?php
$d=date("D");
if ($d=="Fri")
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
{
echo "Hello!<br />";
echo "Have a nice weekend!";
echo "See you on Monday!";
}
?>
</body>
</html>
The ElseIf Statement
If you want to execute some code if one of several conditions are true use the elseif statement Syntax if (condition)
code to be executed if condition is true;
elseif (condition)
code to be executed if condition is true;
else
code to be executed if condition is false;
Example
The following example will output "Have a nice weekend!" if the current day is Friday, and "Have a nice Sunday!" if the current day is Sunday. Otherwise it will output "Have a nice day!": <html> <body>
<?php
$d=date("D");
if ($d=="Fri")
echo "Have a nice weekend!";
elseif ($d=="Sun")
echo "Have a nice Sunday!";
else
echo "Have a nice day!";
?>
</body>
</html>
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
PHP Switch Statement
The Switch statement in PHP is used to perform one of several different actions based on one of several different conditions.
The Switch Statement
If you want to select one of many blocks of code to be executed, use the Switch statement. The switch statement is used to avoid long blocks of if..elseif..else code.
Syntax switch (expression)
{
case label1:
code to be executed if expression = label1;
break;
case label2:
code to be executed if expression = label2;
break;
default:
code to be executed
if expression is different
from both label1 and label2; }
Example
This is how it works:
?
?
?
?
? A single expression (most often a variable) is evaluated once The value of the expression is compared with the values for each case in the structure If there is a match, the code associated with that case is executed After a code is executed, break is used to stop the code from running into the next case The default statement is used if none of the cases are true
<html>
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
<body> <?php
switch ($x) { case 1: echo "Number 1"; break; case 2: echo "Number 2"; break; case 3: echo "Number 3"; break; default:
echo "No number between 1 and 3"; }
?>
</body>
</html>
PHP Arrays
An array can store one or more values in a single variable name.
What is an array?
When working with PHP, sooner or later, you might want to create many similar variables. Instead of having many similar variables, you can store the data as elements in an array. Each element in the array has its own ID so that it can be easily accessed.
There are three different kind of arrays:
?
?
? Numeric array - An array with a numeric ID key Associative array - An array where each ID key is associated with a value Multidimensional array - An array containing one or more arrays
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
Numeric Arrays
A numeric array stores each element with a numeric ID key.
There are different ways to create a numeric array.
Example 1
In this example the ID key is automatically assigned: $names = array("Peter","Quagmire","Joe");
Example 2
In this example we assign the ID key manually: $names[0] = "Peter";
$names[1] = "Quagmire";
$names[2] = "Joe";
The ID keys can be used in a script: <?php
$names[0] = "Peter";
$names[1] = "Quagmire";
$names[2] = "Joe";
echo $names[1] . " and " . $names[2] .
" are ". $names[0] . "'s neighbors"; ?>
The code above will output: Quagmire and Joe are Peter's neighbors
Associative Arrays
An associative array, each ID key is associated with a value.
When storing data about specific named values, a numerical array is not always the best way to do it.
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
With associative arrays we can use the values as keys and assign values to them.
Example 1
In this example we use an array to assign ages to the different persons: $ages = array("Peter"=>32, "Quagmire"=>30, "Joe"=>34);
Example 2
This example is the same as example 1, but shows a different way of creating the array: $ages['Peter'] = "32";
$ages['Quagmire'] = "30";
$ages['Joe'] = "34";
The ID keys can be used in a script: <?php
$ages['Peter'] = "32";
$ages['Quagmire'] = "30";
$ages['Joe'] = "34";
echo "Peter is " . $ages['Peter'] . " years old."; ?>
The code above will output:
Peter is 32 years old.
Multidimensional Arrays
In a multidimensional array, each element in the main array can also be an array. And each element in the sub-array can be an array, and so on.
Example
In this example we create a multidimensional array, with automatically assigned ID keys: $families = array (
"Griffin"=>array
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
(
"Peter",
"Lois",
"Megan"
),
"Quagmire"=>array
(
"Glenn"
),
"Brown"=>array
(
"Cleveland",
"Loretta",
"Junior"
)
);
The array above would look like this if written to the output: Array
(
[Griffin] => Array
(
[0] => Peter
[1] => Lois
[2] => Megan
)
[Quagmire] => Array
(
[0] => Glenn
)
[Brown] => Array
( [0] => Cleveland
[1] => Loretta
[2] => Junior
)
)
Example 2
Lets try displaying a single value from the array above: echo "Is " . $families['Griffin'][2] .
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
" a part of the Griffin family?";
The code above will output: Is Megan a part of the Griffin family?
PHP Looping
Looping statements in PHP are used to execute the same block of code a specified number of times.
Looping
Very often when you write code, you want the same block of code to run a number of times. You can use looping statements in your code to perform this.
In PHP we have the following looping statements:
?
?
?
? while - loops through a block of code if and as long as a specified condition is true do...while - loops through a block of code once, and then repeats the loop as long as a special condition is true for - loops through a block of code a specified number of times foreach - loops through a block of code for each element in an array
The while Statement
The while statement will execute a block of code if and as long as a condition is true. Syntax while (condition)
code to be executed;
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
Example
The following example demonstrates a loop that will continue to run as long as the variable i is less than, or equal to 5. i will increase by 1 each time the loop runs: <html> <body>
<?php
$i=1;
while($i<=5)
{
echo "The number is " . $i . "<br />";
$i++;
}
?>
</body>
</html>
The do...while Statement
The do...while statement will execute a block of code at least once - it then will repeat the loop as long as a condition is true.
Syntax
do
{
code to be executed;
}
while (condition);
Example
The following example will increment the value of i at least once, and it will continue incrementing the variable i as long as it has a value of less than 5:
<html>
<body>
<?php
$i=0;
do
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
{ $i++;
echo "The number is " . $i . "<br />";
}
while ($i<5);
?>
</body>
</html>
The for Statement
The for statement is used when you know how many times you want to execute a statement or a list of statements.
Syntax for (initialization; condition; increment)
{
code to be executed;
}
Note: The for statement has three parameters. The first parameter initializes variables, the second parameter holds the condition, and the third parameter contains the increments required to implement the loop. If more than one variable is included in the initialization or the increment parameter, they should be separated by commas. The condition must evaluate to true or false. Example
The following example prints the text "Hello World!" five times: <html> <body>
<?php
for ($i=1; $i<=5; $i++)
{
echo "Hello World!<br />"; }
?>
</body>
</html>
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
The foreach Statement
The foreach statement is used to loop through arrays.
For every loop, the value of the current array element is assigned to $value (and the array pointer is moved by one) - so on the next loop, you'll be looking at the next element.
Syntax foreach (array as value)
{
code to be executed;
}
Example
The following example demonstrates a loop that will print the values of the given array: <html> <body>
<?php $arr=array("one", "two", "three"); foreach ($arr as $value) { echo "Value: " . $value . "<br />"; } ?> </body> </html>
PHP Functions
The real power of PHP comes from its functions.
In PHP - there are more than 700 built-in functions available.
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
PHP Functions
In this tutorial we will show you how to create your own functions.
For a reference and examples of the built-in functions, please visit our
Create a PHP Function
A function is a block of code that can be executed whenever we need it.
Creating PHP functions:
?
?
?
?
? All functions start with the word "function()" Name the function - It should be possible to understand what the function does by its name. The name can start with a letter or underscore (not a number) Add a "{" - The function code starts after the opening curly brace Insert the function code Add a "}" - The function is finished by a closing curly brace
Example
A simple function that writes my name when it is called: <html> <body>
<?php
function writeMyName()
{
echo "Kai Jim Refsnes";
}
writeMyName();
?>
</body> </html>
Use a PHP Function
Now we will use the function in a PHP script:
<html>
<body>
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
<?php
function writeMyName()
{
echo "Kai Jim Refsnes";
}
echo "Hello world!<br />";
echo "My name is ";
writeMyName();
echo ".<br />That's right, ";
writeMyName();
echo " is my name.";
?>
</body> </html>
The output of the code above will be:
Hello world!
My name is Kai Jim Refsnes.
That's right, Kai Jim Refsnes is my name.
PHP Functions - Adding parameters
Our first function (writeMyName()) is a very simple function. It only writes a static string.
To add more functionality to a function, we can add parameters. A parameter is just like a variable. You may have noticed the parentheses after the function name, like: writeMyName(). The parameters are specified inside the parentheses.
Example 1 The following example will write different first names, but the same last name:
<html>
<body>
<?php
function writeMyName($fname)
{
echo $fname . " Refsnes.<br />";
}
echo "My name is ";
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
writeMyName("Kai Jim");
echo "My name is ";
writeMyName("Hege");
echo "My name is ";
writeMyName("Stale");
?>
</body> </html>
The output of the code above will be:
My name is Kai Jim Refsnes.
My name is Hege Refsnes.
My name is Stale Refsnes.
Example 2
The following function has two parameters: <html>
<body>
<?php
function writeMyName($fname,$punctuation)
{
echo $fname . " Refsnes" . $punctuation . "<br />"; }
echo "My name is ";
writeMyName("Kai Jim",".");
echo "My name is ";
writeMyName("Hege","!");
echo "My name is ";
writeMyName("St?le","...");
?>
</body> </html>
The output of the code above will be:
My name is Kai Jim Refsnes.
My name is Hege Refsnes!
My name is St?le Refsnes...
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
PHP Functions - Return values
Functions can also be used to return values.
Example <html>
<body>
<?php
function add($x,$y)
{
$total = $x + $y;
return $total;
}
echo "1 + 16 = " . add(1,16);
?>
</body> </html> The output of the code above will be: 1 + 16 = 17
PHP Forms and User Input
The PHP $_GET and $_POST variables are used to retrieve information from forms, like user input.
PHP Form Handling
The most important thing to notice when dealing with HTML forms and PHP is that any form element in an HTML page will automatically be available to your PHP scripts.
Form example:
<html>
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
<body>
<form action="welcome.php" method="post">
Name: <input type="text" name="name" />
Age: <input type="text" name="age" />
<input type="submit" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
The example HTML page above contains two input fields and a submit button. When the user fills in this form and click on the submit button, the form data is sent to the "welcome.php" file. The "welcome.php" file looks like this:
<html>
<body>
Welcome <?php echo $_POST["name"]; ?>.<br />
You are <?php echo $_POST["age"]; ?> years old.
</body> </html>
A sample output of the above script may be:
Welcome John. You are 28 years old.
The PHP $_GET and $_POST variables will be explained in the next chapters.
Form Validation
User input should be validated whenever possible. Client side validation is faster, and will reduce server load.
However, any site that gets enough traffic to worry about server resources, may also need to worry about site security. You should always use server side validation if the form accesses a database.
A good way to validate a form on the server is to post the form to itself, instead of jumping to a different page. The user will then get the error messages on the same page as the form. This makes it easier to discover the error.
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
PHP $_GET
The $_GET variable is used to collect values from a form with method="get".
The $_GET Variable
The $_GET variable is an array of variable names and values sent by the HTTP GET method. The $_GET variable is used to collect values from a form with method="get". Information sent from a form with the GET method is visible to everyone (it will be displayed in the browser's address bar) and it has limits on the amount of information to send (max. 100 characters).
Example <form action="welcome.php" method="get">
Name: <input type="text" name="name" />
Age: <input type="text" name="age" />
<input type="submit" />

</form>
When the user clicks the "Submit" button, the URL sent could look something like this: The "welcome.php" file can now use the $_GET variable to catch the form data (notice that the names of the form fields will automatically be the ID keys in the $_GET array):
Welcome <?php echo $_GET["name"]; ?>.<br /> You are <?php echo $_GET["age"]; ?> years old!
Why use $_GET?
Note: When using the $_GET variable all variable names and values are displayed in the URL. So this method should not be used when sending passwords or other sensitive information! However, because the variables are displayed in the URL, it is possible to bookmark the page. This can be useful in some cases.
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
Note: The HTTP GET method is not suitable on large variable values; the value cannot exceed 100 characters.
The $_REQUEST Variable
The PHP $_REQUEST variable contains the contents of both $_GET, $_POST, and $_COOKIE.
The PHP $_REQUEST variable can be used to get the result from form data sent with both the GET and POST methods.
Example Welcome <?php echo $_REQUEST["name"]; ?>.<br /> You are <?php echo $_REQUEST["age"]; ?> years old!
PHP $_POST
The $_POST variable is used to collect values from a form with method="post".
The $_POST Variable
The $_POST variable is an array of variable names and values sent by the HTTP POST method. The $_POST variable is used to collect values from a form with method="post". Information sent from a form with the POST method is invisible to others and has no limits on the amount of information to send.
Example <form action="welcome.php" method="post">
Enter your name: <input type="text" name="name" />
Enter your age: <input type="text" name="age" />
<input type="submit" /> </form>
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
When the user clicks the "Submit" button, the URL will not contain any form data, and will look something like this:

The "welcome.php" file can now use the $_POST variable to catch the form data (notice that the names of the form fields will automatically be the ID keys in the $_POST array): Welcome <?php echo $_POST["name"]; ?>.<br /> You are <?php echo $_POST["age"]; ?> years old!
Why use $_POST?
?
? Variables sent with HTTP POST are not shown in the URL Variables have no length limit
However, because the variables are not displayed in the URL, it is not possible to bookmark the page.
The $_REQUEST Variable
The PHP $_REQUEST variable contains the contents of both $_GET, $_POST, and $_COOKIE.
The PHP $_REQUEST variable can be used to get the result from form data sent with both the GET and POST methods.
Example Welcome <?php echo $_REQUEST["name"]; ?>.<br /> You are <?php echo $_REQUEST["age"]; ?> years old!
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建
