DE5G 35: Financial Reporting and Analysis Assessment 3
1. Four additional ratios and investment ratios (40 points)
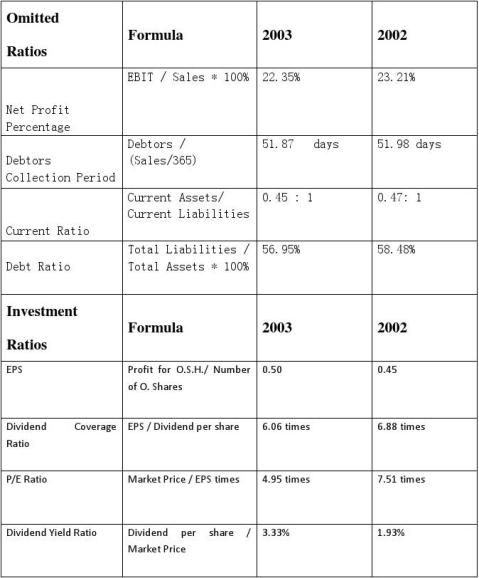
2. Analysis on the four additional ratios (12 points)
?. Net Profit Percentage
DE5G 35: Financial Reporting and Analysis Assessment 3
From the profit and loss account, we can calculate that the net profit percentage is 23.21% in 2002 and 22.35% in 2003 which indicates the decrease trend and this is not a good sign. The reason we can know from the profit and loss account is that there is a significant increase in distribution costs which rise by 36.92%, however the sales just rise by 22.35%. This ration is proportional to net profit and is inversely proportional to sales revenue. Enterprises should ensure the increase of both the amount of sales revenue and net profit, and then make the sales margin remained unchanged or increased. By analyzing the change of net profit margin, enterprises can expand sales, at the same time they can pay attention to management and profitability improvement.
?. Debtors’ collection period
A. Debtors collection period maintains at approximately 52 days, which is due to a 43.21% increase in sales and an almost same increase of 42.90% in debtors.
B. Debtors collection period indicates the length of time customers are taking to pay for the received goods or services, a long collection period suggests that there may be problems with credit control. There exists no improvement on Debtors collection period, so a few possible reasons are as follows:
a. Poor customers’ credibility investigation;
b. Poor invoicing system, Poor reminding system;
c. Poor credit sales policy, such as no incentives for early payment, no discount for cash sales, focusing on sales revenue rather than cash inflows;
d. Poor economic conditions.
?.Current Ratio
A. The current ratio has illustrated a slight decline by 4.26% (0.47:1 in 2002, 0.45:1 in 2003) over the year. The decrease is due to a 31.49% increase in current assets and a higher growth of 37.14% in current liabilities.
B. The current ratio is used to measure the ability of an organization to meet its short term liabilities, and the ideal range of this ratio will be between 1 and 3. The company’s current ratio is below 1 (0.45:1) indicating that for each 1 pound of current liabilities, there is only 0.45 pound of current assets, the company has difficulty to pay its debts falling due within one year. Further investigation on the components of current liabilities tells us that the bank overdraft has grown by 99.92% from 1192 pound in 2002 to 2,383 pound in 2003. Therefore, for the management, actions have to be taken to reduce the overdrafts.
?.Debt ratio
From the Balance Sheet, we can calculate that the Bebt ratios are 58.48% and 56.95% in 2002 and 2003 respectively. There is a significant increase in tangible fixed assets from 2002 to 2003, which is the same to creditors and deferred taxation. However the range of increase is smaller than the assets, resulting in the decrease in Debt ratio from 2002 to 2003.
The higher the ratio, the greater risk will be associated with the firm's operation. In addition, high debt to assets ratio may indicate low borrowing capacity of a firm, which in turn will lower the firm's financial flexibility. Like all financial ratios, a company's debt ratio should be compared with their industry average or other
DE5G 35: Financial Reporting and Analysis Assessment 3
competing firms.
Total liabilities divided by total assets. The debt/asset ratio shows the proportion of a company's assets which are financed through debt. If the ratio is less than 0.5, most of the company's assets are financed through equity. If the ratio is greater than 0.5, most of the company's assets are financed through debt. Companies with high debt/asset ratios are said to be "highly leveraged," not highly liquid as stated above. A company with a high debt ratio (highly leveraged) could be in danger if creditors start to demand repayment of debt.
3. Analysis on investment ratios (20 points)
?. EPS
There is a slight increase in EPS from 2002 to 2003. The reason is the company issued more 150000 ordinary shares in 2003 and the preference shares in still 70. The key reason for the increase is net profit after tax. It is one of the important indicators to monitor the value of equity investments and is a basic indicator to analyze the value of per share. Besides, it is an important indicator to comprehensive reflect the company’s profitability and is the ratio between the company net profit and the number of shares during a period. This ratio reflects the profit after tax per share created, the higher the ratio, and the more profits created. If the company only has ordinary shares, the earning is profit after tax and the number of shares issued is outside of the ordinary shares. If the company still has preference shares, it should deduct the interests allocated to preference shareholders from profit.
?. Dividend Coverage Ratio
Increase the EPS,the company put more percentage of EPS distributes as dividends. It is the ratio of company earnings to net dividends paid to stockholders. This tells investors whether the company can actually afford to pay a dividend. It is found by dividing earnings per share by dividends per share. If the ratio is low, the company is likely to cut its dividend payment, which can decrease the value of the organization
?. P/E Ratio
The investors are willing to pay £5 for£1 in EPS. The price decrease from £3.4 in 2002 to £2.5 in 2003.The EPS increase from 0.45 in 2002 to 0.5 in 2003. It means that the investors are less confidence in the future growth in 2003.
The P/E ratio of a stock is a measure of the price paid for a share relative to the annual net income or profit earned by the firm per share. Unlike EV/EBITDA multiple, P/E reflects the capital structure of company in question. P/E is a financial ratio used for valuation: a higher P/E ratio means that investors are paying more for each unit of net income, so the stock is more expensive compared to one with lower P/E ratio.
?. Dividend Yield Ratio
DE5G 35: Financial Reporting and Analysis Assessment 3
Dividend Yield Ratio is used for measure the return on investment from dividend receivable. It is only a part in the whole retain on investment increase. When the price decrease and the dividend increase resulting in the Dividend Yield Ratio has increased from 1.93% in 2002 to 3.33% in 2003.
This ratio simply tells you how much dividends a stock is paying off for the price of the stock. Certain companies and ETFs pay off good dividends because it helps their tax situation. That can actually help the individual investor. In fact some studies suggest that dividends pay off as much as 97% of the profit the average investor can expect to make in the market.
4. Relationships between ratios or ratio categories(20 points)
ROE = Net Profit/Owner’s Equity
= (Net Profit/Sales)*(Sales/Owner’s Equity)
= (Net Profit/Sales)*(Sales/Total Assets)*(Total Assets/Owner’s Equity) ROE = Net Profit Percentage * Total Assets Turnover * Equity Multiplier
= 22.35%*0.6*2.32 = 31.38%
The goal of management is to maximize return on owner’s equity (ROE), it is affected by three things which are operating efficiency (as measured by profit margin), asset use efficiency (as measured by total asset turnover) and financial leverage (as measured by the equity multiplier).
Weakness in either operating or asset use efficiency (or both) will show up in a diminished return on assets, which will translate into a lower ROE. A firm could leverage up its ROE by increasing its amount of debt. It turns out this will only happen if the firm’s ROA exceeds the interest rate on the debt.
5. Possible sources of long-term finance for the company (8 points) The ordinary share capital in 2003 is 4800k and in 2002 is about 3800k. 10% Preference share capital (700k), and 10% Debentures (1,500k).
Sources of possible long-term finance includes following four sections.
The first, the current market price (2.5) is lower than the price (3.4) in previous year, the dividend yield ratio is only 3.33%, in addition, a decrease of 34% in P/E ratio indicates that investors may become pessimistic (not optimistic) about the future of the company, such that it is not a good time for raising money by issuing more ordinary shares.
Second, the company is currently paying preferred dividend at a rate of 10% which is very attractive to investors compared with the current interest rates, therefore the company may choose to finance by issuing additional preferred shares, and this option is good if the expected interest rates grow in the future.
Third, although the company may be regarded high geared due to the 57% in debt ratio, the interest coverage ratio is considerable high at 40 times in 2003, the company may choose to issue additional debenture to finance its future profitable project to
DE5G 35: Financial Reporting and Analysis Assessment 3
develop the performance of company as long as a positive financial leverage holds. Fourth, the company may consider finance by long-term loan from either a bank or a finance company, but the management needs to watch its interest coverage ratio and capital structure to ensure interest payments and to repay the loan over its term. In addition, the company has a bank overdraft balance of 2,383k in 2003, banks may wish to convert some (or all) of the overdrafts into a medium to long-term loan, which would make it easier to manage and would be in the interests of both the company and the bank.
