
本科生毕业设计
开题报告书
题 目 许昌空港新城项目施工组织设计
姓 名
学 号
学 院 土木建筑工程学院
专 业 工程管理
指导教师
2014年 4 月 2 日

第二篇:苏通大桥B1标30m跨——基础工程及下部构造施工组织设计相关材料(毕业设计任务书.开题报告.文献综述.翻译)
目 录
第一部分: 毕业设计任务书
第二部分: 开 题 报 告
第三部分: 文 献 综 述
第四部分: 外 文 翻 译

注:1. 此任务书应由指导教师填写。
2. 此任务书最迟必须在毕业设计开始前一周下达给学生。
学生完成毕业设计(论文)工作进度计划表
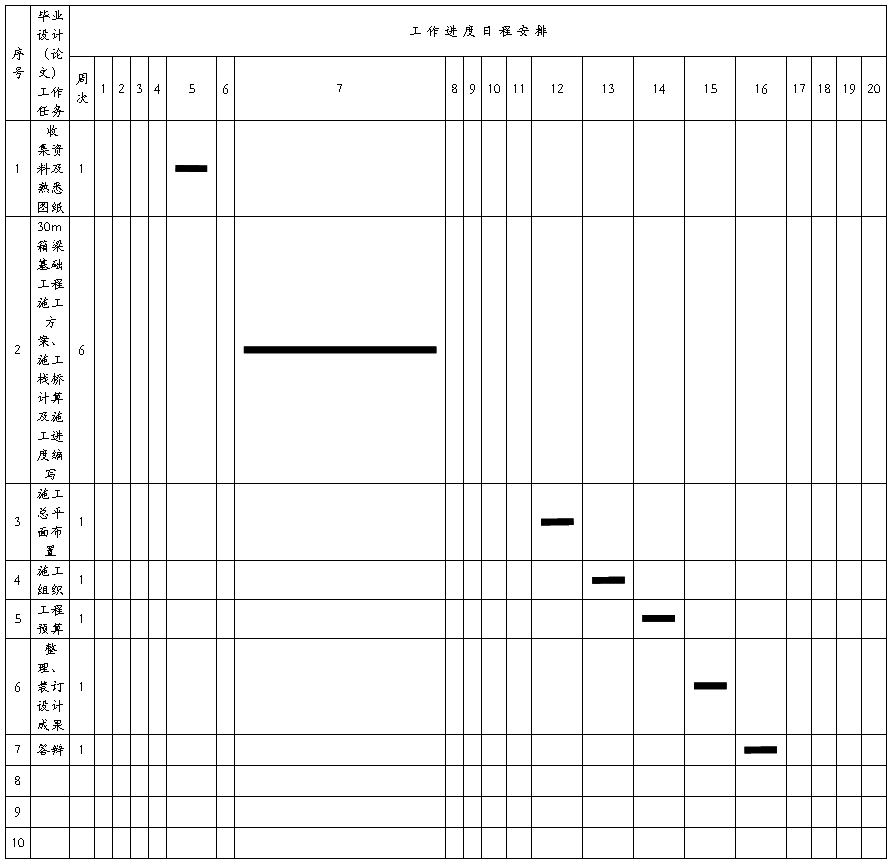
注:1. 此表由指导教师填写。
2. 此表每个学生一份,作为毕业设计(论文)检查工作进度之依据;
3. 进度安排请用“—”在相应位置画出。
毕业设计(论文)阶段工作情况检查表

注:1. 此表应由教师认真填写;
2. “组织纪律”一栏根据学生具体执行情况如实填写;
3. “完成任务情况”一栏按学生是否按进度保质保量完成任务的情况填写;
4. 对违纪和不能按时完成任务者,指导教师可根据情节轻重对该生提出警告或不能参加答辩的建议。
一、选题目的的理论价值和现实意义
作为一名工科毕业的大学生,施工技术专业知识是必不可少的,同时,施工组织与管理知识也同样很重要。通过毕业设计,进一步巩固和提高已学过的基本理论和专业知识,增强运用已学知识解决实际问题的能力;进一步掌握施工组织的基本步骤,懂得如何对实际工程进行施工组织设计和掌握具体的施工技术;初步掌握施工计划网络图的绘制方法及时性其优化原理;初步掌握工种预算的理论和方法;培养毕业生独立解决问题的能力,尽快适应以后所从事的工作,为将来走上工作岗位奠定坚实的基础。
苏通大桥位是我国建桥史上工程规模最大、综合建设条件最复杂的特大型桥梁工程。建设苏通大桥对完善国家和江苏省干线公路网、促进区域均衡发展以及沿江整体开发,改善长江安全航运条件、缓解过江交通压力、保证航运安全等具有十分重要的意义。
二、本课题在国内外的研究状况及发展趋势
苏通大桥前期工作开始于1991年,经历了规划、预可、工可、初设和施工图设计等阶段。从1991年进行规划研究,至20##年6月开工,历时12年。1998年江苏省上报了苏通大桥项目建议书,1999年4月,交通部组织专家对苏通大桥项目建议书进行了行业评审;1999年9月,国家计委组织专家对项目建议书进行了评估;20##年6月,国家计委以“计基础[2001]1089号”文批准苏通大桥项目建议书;20##年12月,江苏省和交通部联合在南京主持召开了苏通大桥国际技术研讨会。20##年2月,受国家计委委托,中国国际工程咨询公司组织专家对工可报告进行了评估。20##年4月,评估报告上报国家计委。20##年11月,交通部分别组织有关专家对苏通大桥基础设计资料、结构设计参数、设计方案等进行了现场调研和审查;20##年3月,交通部以“交公路发[2003]95号”文批复了苏通大桥初步设计;20##年6月,经交通部同意,同时江苏省发展计划委员会以“苏计投资函(2003)123号”转达国家发展和改革委员会意见,同意苏通大桥控制工程先行开工建设。
苏通大桥不仅规模宏大,在斜拉桥几何尺度方面创造四项世界第一,而且在技术方面极具挑战性,难度非常大,是从设计到施工、科研和管理等全方位的超越。可以说,它比国内以往任何一座桥梁遇到的难题更多、建设更复杂,因此它代表了目前中国乃至世界建桥技术的最前沿。
三、研究重点
作为本次设计的B1标段属于北引桥部分,由陆地和水上两部分组成。主要施工项目有陆上钻孔灌注桩、承台、墩台、箱梁,水上钻孔灌注桩、钢套箱、钢吊箱以及钢栈桥和施工平台的施工。30m跨段全部在陆上,相对来说施工比较容易,因此,本设计的重点和难点就在于钻孔灌注桩和箱梁的施工。在施工中分别采用了回旋钻机泥浆护壁水下灌注混凝土和支架现浇箱梁的施工方法。承台和墩台均采用模板现浇的施工方法。在施工中需要注意的是成孔的质量,以及大体积混凝土浇注时的温度控制。
四、主要参考文献
[1] 《公路桥涵施工技术规范》(JTJ041-2000)。
[2] 周永兴,《路桥施工计算手册》[M],北京:人民交通出版社,2001。
[3] 丛培经,《工程项目管理》[M],北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2003。
[4] 范立础,《桥梁工程》[M],北京:人民交通出版社,2001。
[5] 黄绳武,《桥梁施工及组织管理》[M],北京:人民交通出版社,2000。
五、指导教师意见
指导教师:
六、学院毕业设计(论文)指导小组意见
负责人:
文献综述
苏通大桥主要由北岸接线工程、跨江大桥工程和南岸接线工程三部分组成。作为本次设计的B1合同段属于北岸接线工程,位于北岸浅滩区,30m跨段位于陆上,50跨段位于水深较浅的岸边。因此施工的重点也是难点就在于钻孔灌注桩以及现浇预应力混凝土箱梁的施工。
钻孔灌注桩目前在沿海地基处理中应用十分广泛,但因属隐蔽工程,成桩后质量检查比较困难,且由于软土的特殊性质,经常会出现一些质量问题。在查阅了大量文献及期刊论文后,现对其在施工过程中经常遇到的问题和相应的防治措施做简要阐述。
钻孔灌注桩施工过程:平整场地→泥浆制备→埋设护筒→铺设工作平台→安装钻机并定位→钻进成孔→清孔并检查成孔质量→下放钢筋笼→灌注水下混凝土→拔出护筒→检查质量。
在施工中经常遇到的问题和相应的防治措施:
缩颈:
产生的原因 :(1)清孔不彻底,泥浆中含泥块较多,再加上终灌拔管过快,引起桩顶周边夹泥,导致保护层厚度不足。
(2)孔中水头下降,对孔壁的静水压力减小,导致局部孔壁土层失稳坍落,造成砼桩身夹泥或缩颈。孔壁坍落部分留下的窟窿,成桩后形成护颈。
防治措施:预防缩径的关键是控制泥浆比重,确保泥浆能保持孔壁平衡。
(1)使用直径合适的钻头成孔,根据地层变化配以不同的泥浆。
(2)成孔施工时应重视清孔,在清孔时要做到清渣而不清泥,预防清孔后的在浇筑砼的过程中局部坍塌,导致缩径的产生。
断桩
产生的原因 :(1)砼拌和物发生离析使桩身中断。
(2)灌注中,发生堵塞导管又未能处理好;或灌注中发生导管卡挂钢筋笼,埋导管,严重坍孔,而处理不良时,都会演变为桩身严重夹泥,砼桩身中断的严重事故。
(3)灌注时间过长,首批砼已初凝,而后灌注的砼冲破顶层与泥浆相混;或导管进水,未及时作良好处理,均会在两层砼中产生部分夹有泥浆渣土的截面。
防治措施:(1)导管要有足够的抗拉强度,能承受其自重和盛满砼的重量;内径应一致,其误差应小于±2毫米,内壁须光滑无阻,组拼后须用球塞、检查锤作通过试验;导管最下端一节导管长度要长一些,一般为4米,其底端不得带法兰盘。
(2)导管在浇灌前要进行试拼,并做好水密性试验。
(3)严格控制导管埋深与拔管速度,导管不宜埋入砼过深,也不可过浅。及时测量砼浇灌深度,严防导管拔空。
(4)经常检测砼拌和物,确保其符合要求。
桩顶局部冒水、桩身孔洞
产生的原因 :(1)水下砼灌注过程中,导管埋深过大,导管内外砼新鲜程度不同,再加上灌注过程中上下活动导管过于频繁,致使导管活动部位的砼离析,保水性能差而泌出大量的水,这些水沿着导管部位最后灌入的、最为新鲜的砼往上冒,形成通道(即桩身孔洞) 。
(2)水下砼灌注过程中,砼倾倒入导管速度过快过猛,把空气闷在导管中,在桩内形成高压气包。高压气包在其自身浮力或导管起拔等外力的作用下,在砼内不断上升,当上升到桩顶附近时,气包浮力与上升阻力接近,在没有外力的作用下,气包便滞留在桩身内,最终形成桩身孔洞。另外,有一些桩在余桩截后,桩身内残余的高压气体,因通道打开而顺桩身的细小缝隙释放出来。这时,常会携带部分遗留在气包内的水往上冒,出现“桩顶冒气泡”的怪现象。
(3)水下砼灌注时间过长,最早灌入孔内的砼坍落度损失过大,流动性变差,终灌导管起拔后会留下难以愈合的孔洞。
防治措施 :(1) 控制导管的埋深,灌注过程中做到导管勤提勤拔。
(2) 砼倾入导管的速度应根据砼在管内的深度控制,管内深度越深,砼倾入速度越应放慢。在可能的情况下,应始终保持导管内满管砼,以防止桩身形成高压气包。实际施工中,往往因为导管每次起拔后管内都会形成空管,再次灌注时,桩身形成高压气包就很难避免。因此,应在灌注过程中适当上下活动导管,把已形成的高压气包引出桩身。
(3)加适当缓凝剂,确保砼在初凝前完成水下灌注。
钢筋笼上浮
产生的原因:砼由漏斗顺导管向下灌注时,产生一种顶托力,使钢筋笼上浮。
防治措施 :(1)钢筋骨架上端在孔口处与护筒相接固定。
(2)灌注中,当砼表面接近钢筋笼底时,应放慢砼灌注速度,并应使导管保持较大埋深,使导管底口与钢筋笼底端间保持较大距离,以便减小对钢筋笼的冲击。
(3)砼液面进入钢筋笼一定深度后,应适当提导管,使钢筋笼在导管下口有一定埋深。但注意导管埋入砼表面应不小于2 m,不大于10m。如果钢筋笼因为导管埋深过大而上浮时,现场操作人员应及时补救,补救的办法是马上起拔拆除部分导管;导管拆除一部分后, 可适当上下活动导管;这时可以看到,每上提一次导管,钢筋笼在导管的抽吸作用下,会自然回落一点;坚持多上下活动几次导管,直到上浮的钢筋笼全部回落为止。当然,如果钢筋笼严重上浮,那么这一补救措施也不一定会十分奏效。
“烂桩头”
产生的原因 :(1)清孔不彻底,桩顶浮浆过浓过厚,影响水下砼灌注时测量桩顶位置的精度。
(2)导管起拔速度过快,尤其是桩头直径过大时,如未经插捣,直接起拔导管,桩头很容易出现砼中间高、四周低的“烂桩头”。
(3)浇筑速度过快,导致孔壁局部坍塌,影响测量结果。
防治措施 :(1)认真做好清孔工作,确保清孔完成后孔口没有泥块返出;在空孔较长的桩内测量砼上升面时,应控制好测量重锤的质量。通常认为使用5~40mm碎石砼时,重锤的质量可以控制在1.5kg 左右;使用5~25mm 碎石砼时,重锤的质量可以控制在1kg 左右。在设计桩顶与地面距离<4 m时,通常认为使用竹竿通过手感测量砼面更直观,精度更高。
(2)砼终灌拔管前,应使用导管适当地插捣砼,把桩身可能存在的气包尽量排出桩外后,以便精确测量砼面。也可通过导管插捣使桩顶砼摊平。
参考文献:
[1] 《公路桥涵施工技术规范》(JTJ041-2000)。
[2] 周永兴,《路桥施工计算手册》[M],北京:人民交通出版社,2001。
[3] 丛培经,《工程项目管理》[M],北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2003。
[4] 范立础,《桥梁工程》[M],北京:人民交通出版社,2001。
[5] 黄绳武,《桥梁施工及组织管理》[M],北京:人民交通出版社,2000。
20##年
桥梁工程中大体积混凝土裂缝的产生与预防
说明:从大尺度结构的钢筋混凝土桥梁施工的基础上,从设计,施工的角度,分析了造成该结构的大桥大量混凝土裂缝产生的原因及如何防止和处理大体积混凝土裂缝的主要技术措施。
关键词:桥梁工程 大体积混凝土裂缝的预防检查过程控制
随着国家建设项目投资的发展和市政工程的投入进一步增加和桥梁在各种市政工程中的日益普及,大体积混凝土桥梁结构应用越来越多。但是,相应的问题暴露的也越来越多,其中,大体积混凝土裂缝尤为突出。普通混凝土配合比设计规范中这样定义:混凝土结构实体尺寸最小值不小于1 m 即被称作大体积混凝土。
目前,机械荷载引起的裂纹问题在国内外有更深入的研究。但导致裂缝产生的温度荷载研究的并不是很多。我们应该更多的注意避免裂缝对结构产生伤害。由于大体积混凝土温度控制应力和裂缝多集中在水坝、高层建筑的深基坑底板,所以桥梁大体积混凝土裂缝在研究中并没有得到足够的重视。在本文中,主要分析探讨裂缝产生的原因及控制措施。
1 大体积混凝土裂缝产生的原因
大体积混凝土结构通常有以下几个特性:混凝土是脆性材料,抗拉强度只有1/10%。因为水泥的水化热和以后在相当大的应力条件下的慢慢冷却过程的影响,混凝土内部的温度将会很快上升;在大体积混凝土结构表面通常只有很少的钢筋布置。因此,来自混凝土本身的张拉应力由它本身承受。
1.1水泥水化热的影响
水泥水化过程中释放出大量的热量,其中主要集中在浇筑后7天内。一般每克水泥可产生约500焦耳的能量。如果水泥用量为350kg/m3至550 kg/m3,每立方米混凝土将被释放17500kj ? 27500kj的热量,从而增加了内部的混凝土的温度。(最多大约70 ° C,甚至更高)。特别是对大体积混凝土来说,这种现象更为严重。因为混凝土内部与表面的冷却条件不同,在内部产生压应力,而在表面产生拉应力,从而形成温度梯度,当拉应力超过混凝土的极限抗拉强度时,在混凝土表面将会形成裂缝。
1.2混凝土收缩
混凝土在空气中体积减少硬化现象,叫做混凝土收缩。混凝土在不受外力情况下,外部约束(边界条件,模板等)条件同样会使混凝土产生自发变形,在混凝土表面产生拉应力使混凝土开裂。混凝土裂缝的主要原因是塑性收缩、干缩变形和温度收缩。在早期硬化中主要集中在水泥水化凝固过程中的体积变化,晚期主要是内部水分蒸发所造成的收缩和变形。
1.3室外温度和湿度变化的影响
大体积混凝土结构施工期间,室外温度的变化对防止大体积混凝土裂缝的产生有巨大的影响。混凝土内部温度是由浇筑温度,水泥水化热保温温度和结构的冷却温度叠加组成。浇注温度和外面的温度有直接关系,外界温度越高,混凝土浇筑温度会越高。如果外界温度较低时会大量增加混凝土内外温度梯度。如果外界气温下降过快,这将造成很大的温度应力,很容易导致混凝土开裂。此外,外界湿度对混凝土裂缝的产生也有很大的影响,湿度越低会加速混凝土收缩,导致混凝土开裂。
2大体积混凝土裂缝控制
2.1大体积混凝土的水泥种类和数量
理论研究表明,大体积混凝土产生裂缝的一个主要原因是水泥在水化的过程中释放出大量的热量。所以,我们建造大体积混凝土桥梁时应选择中低热量的水泥。水泥温度和释放热量的规模和速度取决于水泥中所含的不同的矿物成分。水泥中矿物质加热速度最快的是铝酸三钙(C3A),其他成分含量分别为硅酸三钙(C3S) ,硅酸二钙(C2S的)和铁铝酸四钙 (C4AF)。此外,细水泥发热快,但并不影响最后的热量。因此,在大体积混凝土施工时应充分利用矿渣水泥和火山灰水泥。我们应充分利用混凝土后期强度,以减少水泥用量。大体积混凝土,因为建筑期限长, 在28d龄期的混凝土上施加设计荷载是不可能的,因此将试验混凝土强度标准推至56d或90d是合理的。基于这一点,许多专家在国内外也提出了类似的建议。充分利用这一后期强度每立方米混凝土可降低水泥用量40 - 70公斤,混凝土内部温度降低4℃至7℃
2.2加入额外的材料及添加剂
大体积混凝土拌和一定量的粉煤灰,可以增加混凝土的密度、提高抗渗性。为了减少大体积混凝土由于水泥水化热引起的内部温度升高,以防止裂缝,在结构中利用粉煤灰作混凝土掺合料是最有效的方法。
2.3大体积混凝土粗骨料控制
在骨料的选择应选定的高强度,且各种粒径分布比较均匀的。这可以减小孔隙度和比表面积,从而同时减少水泥用量,降低水化热,减少收缩,减少混凝土裂缝。
2.4优化大体积混凝土设计
大体积钢筋混凝土表面并不是一块布一样平整,我们仍然能够很容易找到裂缝易发区,如孔洞和靠近角落处,在这些地方布置一些斜筋,这样斜筋就可以帮助混凝土承担拉应力,可以有效控制裂缝的发展。为了避免出现裂缝,在设计时应充分利用水泥混凝土后期强度。结构工程的设计,要特别注意下部结构的制约。钢筋混凝土保护层的厚度应尽量取较小值,保护层厚度较大较容易形成裂缝。
2.5大体积混凝土施工
混凝土施工,包括混凝土生产,运输,安置与表面保护,为了避免出现大量的裂缝,在混凝土中温度控制是关键。主要的控制手段就是控制混凝土内外温度差异ΔT:
ΔT=Tp+Tr-Tf:
这里:Tp:开始浇注温度;Tr:水泥水化温度;Tf:天然或人工冷却后,浇注后稳定温度。
在较高的温度下施工,我们要高度重视降低混凝土浇筑温度。在施工现场,露天堆放应盖上沙子以减少阳光辐射量,同时对砂石降温。在混凝土搅拌过程中加入冰水。通过这些措施,能够有效地减少混凝土内部的温度。混凝土内部水冷却循环一个周期的保温养护以加快混凝土内部的热量散发。混凝土表面应覆盖一些织物以保温保湿养护,它不仅可以降低混凝土内外温度差异,防止表面裂缝,而且可以防止因骤冷产生的混凝土裂缝,也使水泥水化热均匀散发。如果是冬季施工,应防止混凝土早期冻结。要求混凝土浇筑应该有更高的浇注温度。但另一方面,正因为天气寒冷,混凝土温度很低,往往超出允许的温度,不能达到防止裂缝要求。因此,在冬季施工混凝土浇注温度一般5℃至10℃。混凝土浇筑前也应用蒸气对原料进行偏高或偏低的温度加热。暖气石应避免过热和过度干燥,最高温度不应超过75℃。此外,我们需要运输保温,浇注过程中,以减少损失,保温和养护。
2.6大体积混凝土裂缝的检查及治理
混凝土裂缝的预防,需要经过详细的设计,施工。不过,由于目前使用的防止裂缝的安全系数小,但实际情况是复杂多变的,因此,实际的项目是无可避免的出现一些裂痕。大体积混凝土裂缝分为三种:表面裂缝、深裂缝和贯穿裂缝。表面裂缝,因为它对上部结构,耐用性和安全性没有任何影响,一般不会处理。深裂纹和贯穿裂缝,可采取凿开裂缝,可采用气压回升,风钻或人工凿除,然后进行混凝土浇筑。若裂缝遇钢筋,混凝土充分冷却后,在裂缝内铺设2层钢筋后继续浇筑新的混凝土。对于较为严重的裂缝,可采取水泥灌浆和化学灌浆。水泥灌浆适用于裂缝宽度为0.5毫米;化学灌浆适用于裂缝宽度小于0.5毫米,化学灌浆材料用环氧糠醛,丙酮等。
三,结束语
总之,虽然大体积混凝土容易产生裂缝。但很多科学的研究以及成功的项目都作为案例告诉我们:只要我们在设计,施工,材料选择和后期的养护过程中能充分考虑各种因素的影响,完全是可以避免裂缝的产生。
摘自《土木工程》20##年第三期
Bridge Engineering massive concrete cracks and prevention
Description : Based on the large-scale structure of reinforced concrete bridge construction site, from design, construction perspective, Analysis of the structure of the bridge caused massive concrete cracks causes and how to prevent it inspection and processing massive concrete cracks of the main technical measures.
Keywords : bridge engineering massive concrete cracks prevention check processing control
With national construction investment development and municipal engineering inputs increase further, bridges in various municipal projects of the increasingly widespread, massive concrete bridge structure in the application of more and more it is mainly used by the main force, however, the corresponding exposed more and more poblems, which, Massive concrete cracks, it is particularly prominent. My normal concrete mix design specifications : Concrete structures Entity minimum size is not less than 1 m were used in the concrete namely, mass concrete.
Currently, the mechanical load at home and abroad caused the cracking problems in a more thorough study. And the right temperature loads caused cracks in the study is not sufficient. We should pay attention to prevent harm to the structure cracks. As regards the massive concrete temperature control stress and cracks are more concentrated in the dam water, high-rise building of deep foundation slab. For Bridges massive concrete cracks in the study did not receive enough attention. In this paper, this analysis to explore the causes of cracks and control measures.
1. Massive concrete reasons for the cracks
Massive concrete structure usually has the following characteristics : Concrete is brittle materials, tensile strength of only 1 / 10%. Massive concrete section of a larger size, because of the heat of hydration of cement concrete internal temperature will rise sharply; and the subsequent cooling process, in a certain constraint conditions under considerable stress of Rafah. Massive concrete structure on the surface is usually only a small amount of the allocation of steel or reinforced seat. Therefore, the tensile stress from the concrete itself to bear.
1.1 the impact of Cement hydration heat
Cement hydration process release a lot of heat, which is mainly concentrated in the pouring about 7 d, General per gram of cement can produce about 500 J of energy. If the amount of cement Kg/m3 ~ 350 to 550 Kg/m3, per m3 of concrete will be released 17500KJ ~ 27500KJ heat, thereby increasing internal concrete. (Up to about 70 ° C, or even higher). Especially for large volume concrete terms, this phenomenon is even more serious. Because concrete and the internal surface of the cooling conditions are different, concrete high temperatures, This will form the temperature gradient within the concrete compressive stress, surface tensile stress, When the tensile stress over the ultimate tensile strength of concrete at the concrete surface will result in cracks.
1.2 Concrete contraction
Concrete in the air when the volume was reduced sclerosis phenomenon called concrete shrinkage. Concrete without outside circumstances such spontaneous deformation, when external constraints (boundary conditions, bar, etc.) will be produced in the concrete tensile stress, makes concrete cracking. Concrete cracks caused mainly plastic shrinkage and drying shrinkage and shrinkage temperature. In the early hardening mainly in the cement hydration Hard solidification process the volume change, Concrete is mainly late free internal moisture evaporation caused by shrinkage and deformation.
1.3 the impact of Outside temperature and humidity changes
Massive concrete structure during construction, changes in the outside temperature to prevent massive concrete cracks have played a huge influence. Concrete internal temperature by pouring temperature, cement hydration heat insulation temperature and the structure of the cooling temperature superposition's various temperature and composition. Pouring temperature and the outside temperature is directly related to the outside temperature, the higher the concrete pouring temperature will be higher. If the outside temperature is lower will increase the mass of concrete and outside temperature gradient. If the outside temperature dropped too rapidly, it will cause great temperature stress, very easily lead to the cracking concrete. Also outside the humidity of concrete cracks had a great impact outside the lower humidity will accelerate the shrinkage of the concrete, will lead to concrete cracks.
2 Massive concrete cracks control
2.1 Massive concrete cement type and quantity
The theoretical study shows that the massive concrete cracks in cement hydration is a major reason why the process of the release of a large number of calories. So, we have a bridge for the massive concrete should choose low heat or hot in the middle of cement. Cement temperature and the release of the size and speed depends on the cement of different mineral composition. Cement minerals heating rate and the fastest heat is the biggest three calcium aluminate (C3A), other ingredients were three calcium silicate (C3S), the two calcium silicate (C2S) and calcium aluminum acid 4 (C4AF). In addition, the finer the cement fever faster, but does not influence the final heat. Therefore, we in mass concrete construction should make full use of slag cement and pozzolana cement. We should make full use of concrete in the late strength, in order to reduce the amount of cement. Massive concrete because the long duration of the construction, it is impossible to 28 d impose concrete design load, So will test the strength of concrete standards to push off the age to 56 or 90 d d is reasonable [3]. This is based on this point, many experts at home and abroad have made similar suggestions. Take full advantage of this late strength can be reduced per m3 concrete cement 40 Kg-70 Kg% Concrete internal temperature lower 4 ° C to 7 ° C
2.2 Adding additional materials and additives
The massive concrete mixing a certain amount of fly ash, can increase the density of concrete and improve the impermeability. To reduce the large volume of concrete cement hydration heat caused the internal temperature to prevent cracks in the temperature structure, the use of fly ash for concrete admixture is the most effective method.
2.3 Massive concrete aggregate control
In aggregate the choice should be selected senior high intensity particle size distribution aggregate good. This can smaller porosity and surface area, thereby reducing the amount of cement, lower heat of hydration and reduce shrinkage. reduce the concrete cracks at the same time.
2.4 Optimization of mass concrete design
While the volume of reinforced concrete layout is not a cloth or less tendons, We can still crack-prone area such as holes around corners, layout and some oblique tendons, and so that instead of reinforced concrete commitment tensile stress, which can help to effectively control the development of cracks. To avoid cracks appear in the design and utilization of low-intensity end of the full use of cement concrete in the late intensity. The structural design of the project should pay special attention to the lower structure of the constraint. For reinforced concrete thickness of the protective layer should be as far as possible from the smaller value as a protective layer thickness of the larger more prone to fracture.
2.5 Massive concrete construction
Concrete construction, including concrete production, transportation, placement and temperature and surface protection, is to protect the large volume of cracks in concrete temperature is key. And the thermal stress the main means of control is to control the concrete temperature difference between inside and outside △ T :
△ T = Tp + Tr - Tf
Where : Tp-start pouring temperature; Tr - temperature cement hydration; Tf-natural or artificial cooling block after pouring temperature stability.
In the higher temperature under construction, we must pay attention to the concrete pouring to reduce the temperature. Be at the construction site of the heap in the open, covered with sand, sun to reduce its radioactivity, Meanwhile on the gravel before pouring cold cooling. Stir in the process of adding concrete to ice water. These measures can effectively reduce the income scale concrete temperature. Concrete in an internal water-cooling cycle, a cycle Insulation Conservation Act, in order to expedite the concrete internal heat distribution. Concrete surface should cover some fabric insulation and moist conservation, it will not only lower the temperature difference between inside and outside concrete, prevent surface cracks can prevent sudden cooling produce concrete cracks, and also enable the smooth cement hydration. If it is winter, construction, concrete to prevent early freeze. requiring concrete pouring should have higher pouring temperature. But on the other hand, precisely because of the cold weather, the concrete will lower temperature, often exceeding the permitted temperature, not prevent cracks in concrete demands. Therefore, the concrete-pouring temperature in winter construction generally 5 ° C to 10 ℃. pouring concrete in the past should also be based on contacts and new concrete wall with the cold steam preheating, on raw materials should be considered high or low temperature for heating. Heating stone should avoid overheating and excessive drying, the maximum temperature should not exceed 75 ℃. Furthermore, we need to transport the insulation, pouring process to reduce the loss of heat insulation and conservation.
2.6 Massive concrete cracks examination and treatment
For concrete cracks, should be prevention, and this need careful design, construction, However, as currently used to prevent cracks in the safety factor is small, but the actual situation is complicated and changeable, Therefore, the actual project is inevitably some cracks. Massive concrete cracks are divided into three types : surface cracks and deep cracks run through cracks. For surface cracks because of its stress on the structure, durability and safety of no effect, and are generally not addressed. Deep cracks and the cracks can be taken in addition to the hammer cracks can be Pneumatic Pick Housing, pneumatic drill or artificial cracks will be in addition to the hammer, to see cracks, the fluting of trapezoidal cross-section of the above then pouring concrete. Limited cracked reinforced, deep in the cracks, the concrete is usually full after cooling, Cracks on the laying of a two-layer reinforced continue after pouring new concrete. For the more serious cracks could take cement grouting and chemical grouting. Cement grouting applicable to the crack width of 0.5 mm, for the crack width of less than 0.5 mm chemical grouting to be taken. Chemical grouting material using epoxy-furfural acetone, etc.
3 Concluding remarks
In summary, although the massive concrete cracks easily. But a lot of scientific research, as well as examples of successful projects have shown : as long as we design, construction technology, material selection and the late conservation process that can take full account of the influence of various factors. completely avoidable harm structure of the cracks.
From 《Civil Engineering》
