实训报告
学生姓名: 李佳奇 学 号: 33
专业班级: 网络091
课程名称: 个性教育
学年学期: 2 0 1 2 —2 01 3 学年第1学期
指导教师: 齐林
2 0 1 2 年 12 月
实训成绩评定表
目 录
一、实训背景及目的要求......................................................................................... 1
1.1背景简介.............................................................................................................. 1
1.2实训目的及要求................................................................................................... 1
二、设计思路.............................................................................................................. 2
2.1设计题目.............................................................................................................. 2
2.2功能分析.............................................................................................................. 2
2.3模块划分.............................................................................................................. 2
三、设计实现及代码分析......................................................................................... 2
3.1第一个Activity...................................................................................................... 2
3.1.1布局文件:main.xml:................................................................................ 2
3.1.2源代码文件:MainActivity.java..................................................................... 5
3.2第二个Activity...................................................................................................... 7
3.2.1布局文件:result.xml.................................................................................. 7
3.2.2源代码文件:ResultActivity.java................................................................... 8
3.3字符串资源文件:strings.xml.............................................................................. 10
3.4程序清单文件:AndroidManifest.xml.................................................................... 11
四、程序功能测试及截图....................................................................................... 12
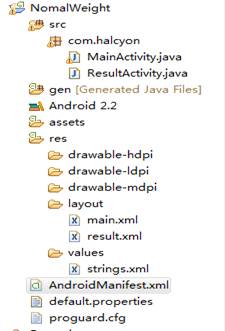
4.1工程项目目录..................................................................................................... 12
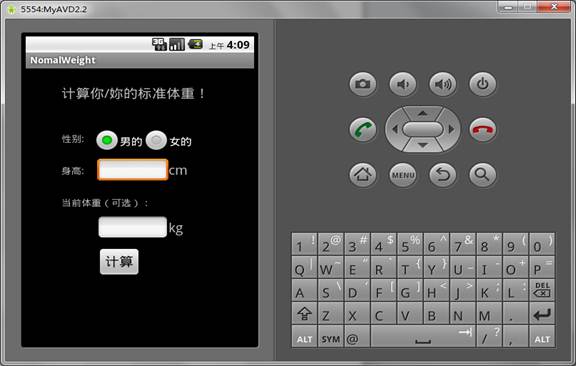
4.2程序运行界面:.................................................................................................. 13
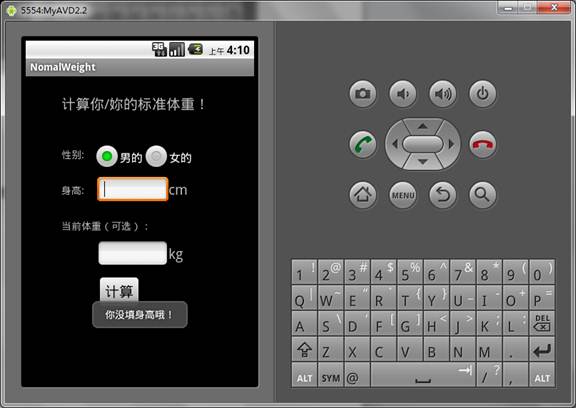
4.3未填身高提示:.................................................................................................. 13
4.4计算示例:......................................................................................................... 14
4.5拓展:................................................................................................................ 14
五、实训总结............................................................................................................ 21
一、实训背景及目的要求
1.1背景简介
Android(读音:['ændr?id])是一种以Linux为基础的开放源码操作系统,主要使用于便携设备,目前尚未有统一中文名称,中国大陆地区较多人使用安卓或安致。Android操作系统最初由Andy Rubin创办[5],最初只支持手机。20##年由Google收购注资,并拉拢多家制造商组成开放手机联盟(Open Handset Alliance)开发改良,逐渐扩展到到平板电脑及其他领域上[6]。 20##年末数据显示,仅正式推出两年的操作系统的Android已经超越称霸十年的诺基亚Symbian系统,跃居全球最受欢迎的智慧手机平台。采用Android系统手机厂商包括HTC、Samsung、Motorola、Lenovo、LG、Sony Ericsson等。
1.2实训目的及要求
Android以Linux为核心的Android行动平台,使用Java作为编程语言。本实训是在学习java语言程序设计的基础上进行的一次综合实践。通过综合训练,要求学生掌握java语言程序设计的基本技能和Android编程的应用,并较系统地掌握JAVA语言程序设计开发方法以及帮助文件的使用等,使学生通过本次实训,能够进行独立的Android应用程序开发,能够在实际操作中得到进一步的提高,为以后的学习和工作打下良好的基础。
目的:
1、培养学生运用所学课程Java语言程序设计的理论知识和技能,分析解决计算机实际应用中的问题的能力。
2、培养学生在Java语言程序设计的基础上,开发Android应用程序的思想和方法。
3、培养学生调查研究、查阅技术文献、资料、手册以及编写技术文献的能力。
通过课程设计,要求学生在指导教师的指导下,独立完成课程设计的全部内容,包括:
1、确定开发的程序,收集和调查有关技术资料。
2、按软件工程步骤进行程序设计。
3、对完成的程序进行测试和完善。
4、完成课程设计报告。
二、设计思路
2.1设计题目
以Android系统的UI界面开发为基础,设计一个可以简单计算标准体重的应用程序,要求以2个Acitivity实现,第一个Activity作为输入界面,第二个Activity作为结果输出界面,具体实现细节自行设计。
2.2功能分析
该设计题目要求实现可计算输出标准体重功能的应用程序。通过查阅资料可知,按照世界卫生组织推荐的计算标准体重的方法,需要获知的输入信息有性别、身高。故可在第一屏设置有单选框以确定性别,输入框以获取身高。另,为了增加程序的实用性,可再设一可选输入框,用来得到实际体重,与标准体重对比,给出用户一些健康提议。第二屏设置有结果输出显示区域与健康提示显示区域。
2.3模块划分
通过程序功能分析,可将程序划分为2个模块,即2个Activity:
第一个Activity:两个单选框(RadioButton)获取性别,一个输入框(EditText)获取身高,一个可选输入框(EditText)获取实际体重,一个按钮(Button)及一些提示文本。
第二个Activity:一个文本显示区(TextViw)显示计算结果,一个可选文本显示区(TextView)显示提示信息。
三、设计实现及代码分析
3.1第一个Activity
3.1.1布局文件:main.xml:
采用绝对布局,以实现控件精准显示;
RadioGroup包含两个RadioButton,以实现性别男女选择;
两个供输入的EditText限定了输入类型为numberDecimal,以确保只接收数字型数据。
main.xml完整代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<AbsoluteLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/tv1_t"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_x="50px"
android:layout_y="25px"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/tv_sex"
android:layout_x="50px"
android:layout_y="100px"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/tv_tall"
android:layout_x="50px"
android:layout_y="150px"
/>
<RadioGroup
android:id="@+id/rg"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_x="95px"
android:layout_y="90px"
>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rb_male"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/male"
/>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rb_female"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/female"
/>
</RadioGroup>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_tall"
android:layout_width="100px"
android:layout_height="40px"
android:layout_x="100px"
android:layout_y="140px"
android:inputType="numberDecimal"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="200px"
android:layout_y="145px"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="cm"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="50px"
android:layout_y="200px"
android:text="@string/tv_real"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_real"
android:layout_width="100px"
android:layout_height="40px"
android:layout_x="100px"
android:layout_y="230px"
android:inputType="numberDecimal"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="200px"
android:layout_y="235px"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="kg"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/compute"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="100px"
android:layout_y="280px"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="@string/compute"
/>
</AbsoluteLayout>
3.1.2源代码文件:MainActivity.java
使用main.xml布局文件,为计算按钮(Button)注册事件监听,添加事件响应代码;
实现未填身高提示:
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, R.string.tall_hint, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
实现Activity之间跳转设置:
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, ResultActivity.class);
实现Activity之间数据封装传输:
bundle.putDouble("height", height);
bundle.putString("sex", sex);
bundle.putString("real", real);
intent.putExtras(bundle);
MainActivity.java完整代码如下:
package com.halcyon;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.RadioButton;
import android.widget.Toast;
publicclass MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private RadioButton rb1 = null;
private RadioButton rb2 = null;
private EditText et = null;
private EditText et_real = null;
private Button bt = null;
publicvoid onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
rb1 = (RadioButton)findViewById(R.id.rb_male);
rb2 = (RadioButton)findViewById(R.id.rb_female);
rb1.setChecked(true); //默认为男性选中
et = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.et_tall);
et_real = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.et_real);
bt = (Button)findViewById(R.id.compute);
bt.setOnClickListener(this); //注册点击事件监听
}
@Override
publicvoid onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
/**事件响应代码,获取性别、身高,判断是否输入了实际体重
* 新建Intent对象用于Activity之间跳转,及传输输入的数据
* **/
if(et.getText().toString().length()==0){ //身高未填提示
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, R.string.tall_hint, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
else {
double height = Double.parseDouble(et.getText().toString());
String real = et_real.getText().toString();
String sex = "";
if(rb1.isChecked()){
sex = "M";
}
else{
sex = "F";
}
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, ResultActivity.class);
Bundle bundle = new Bundle(); //存放数据,以封装传输
bundle.putDouble("height", height);
bundle.putString("sex", sex);
bundle.putString("real", real);
intent.putExtras(bundle);
this.startActivity(intent);
}
}
}
3.2第二个Activity
3.2.1布局文件:result.xml
绝对布局,三个TextView,内容用紫色显示,提示标号用绿色显示,以达到较醒目的感觉。
result.xml完整代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<AbsoluteLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_margin="10px">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="20px"
android:layout_y="100px"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textColor="#8855ff"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="20px"
android:layout_y="200px"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textColor="#00ff00"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="20px"
android:layout_y="240px"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textColor="#8855ff"
/>
</AbsoluteLayout>
3.2.2源代码文件:ResultActivity.java
使用result.xml布局文件,获取intent,取得传入的数据信息,以
男性:(身高cm-80)×70﹪=标准体重
女性:(身高cm-70)×60﹪=标准体重
的标准来计算标准体重,方法
private String getWeight(double height, String sex)
实现此功能;
可根据用户是否输入了实际体重,来选择是否显示健康提示信息,方法
private void healthHint(double weight)
实现此功能;
方法private String form(double d)实现数据格式化。
ResultActivity.java完整代码如下:
package com.halcyon;
import java.text.NumberFormat;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
publicclass ResultActivity extends Activity{
private TextView tv_1 = null;
private TextView tv_2 = null;
private TextView tv_3= null;
private Intent intent = null;
private Bundle bundle = null;
privatedouble height = 0;
private String sex = "";
publicvoid onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.result);
tv_1 = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv_1);
tv_2 = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv_2);
tv_3 = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv_3);
intent = this.getIntent();
bundle = intent.getExtras();
height = bundle.getDouble("height");
sex = bundle.getString("sex");
tv_1.setText(this.getWeight(height,sex));
}
/**男性:(身高cm-80)¡Á70﹪=标准体重
* 女性:(身高cm-70)¡Á60﹪=标准体重
* **/
private String getWeight(double height, String sex) {
double weight = 0;
String result = "";
if(sex.equals("M")){
weight = (height-80)*0.7;
result = "这位先生,\n你的标准体重为"+form(weight)+"公斤。\n";
}
else {
weight = (height-70)*0.6;
result = "这位女士,\n妳的标准体重为"+form(weight)+"公斤。\n";
}
healthHint(weight);
return result;
}
privatevoid healthHint(double weight) {
/*根据用户是否输入了实际体重来判断是否添加显示提示信息
* 如果输入了实际体重,按以下原则给用户以健康提示
* 标准体重正负10﹪为正常体重
* 标准体重正负10﹪~ 20﹪为体重过重或过轻
* 标准体重正负20﹪以上为肥胖或体重不足
* */
String result = "";
String real = bundle.getString("real");
if(real.equals("")){
result = "";
}
else {
double r = Double.parseDouble(real);
double rate = (r-weight)/weight;
if(rate>0.2){ //过胖
result = this.getString(R.string.very_fat);
}
elseif(rate>=0.1&&rate<=0.2){ //胖
result = this.getString(R.string.fat);
}
elseif(rate>-0.1&&rate<0.1){ //正常
result = this.getString(R.string.normal);
}
elseif(rate>=-0.2&&rate<=-0.1){ //瘦
result = this.getString(R.string.thin);
}
elseif(rate<-0.2){ //过瘦
result = this.getString(R.string.very_thin);
}
tv_2.setText(getString(R.string.hint));
}
tv_3.setText(result);
}
private String form(double d){ //格式化数据输出
String str = NumberFormat.getInstance().format(d);
return str;
}
}
3.3字符串资源文件:strings.xml
在一个Android工程中,我们可能会使用到大量的字符串作为提示信息。这些字符串都可以作为字符串资源声明在配置文件中,从而实现程序的可配置性。
在代码中我们使用Context.getString()方法,通过传递资源ID参数来得到该字符串,也可以在其他资源文件中引用字符串资源,引用格式为:"@string/字符串资源名称。
本程序所引用的strings.xml内容为:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="app_name">NomalWeight</string>
<string name="result_name">计算结果</string>
<string name="tv1_t">计算你/妳的标准体重!</string>
<string name="tv_sex">性别:</string>
<string name="tv_tall">身高:</string>
<string name="tv_real">当前体重(可选):</string>
<string name="male">男的</string>
<string name="female">女的</string>
<string name="compute">计算</string>
<string name="tall_hint">你没填身高哦!</string>
<string name="hint">温馨提示:</string>
<string name="normal">体重适中,要保持哟!</string>
<string name="thin">"有点偏瘦哦,应该再多吃些东西啊!"</string>
<string name="very_thin">"一定是受谁的虐待了,要好好补补身体的,身体要强壮才行滴!"</string>
<string name="fat">"有点胖哦,要多锻炼啊!"</string>
<string name="very_fat">"不能太胖啊,要为自己制作运动减肥表了!"</string>
</resources>
3.4程序清单文件:AndroidManifest.xml
每一个Android项目都包含一个清单(Manifest)文件--AndroidManifest.xml,它存储在项目层次中的最底层。清单可以定义应用程序及其组件的结构和元数据。
它包含了组成应用程序的每一个组件(活动、服务、内容提供器和广播接收器)的节点,并使用Intent过滤器和权限来确定这些组件之间以及这些组件和其他应用程序是如何交互的。
因本程序使用了2个Activity,故对AndroidManifest.xml有一定的修改,内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.halcyon"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0">
<application
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity android:name=".ResultActivity"
android:label="@string/result_name">
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
四、程序功能测试及截图
4.1工程项目目录
4.2程序运行界面:
4.3未填身高提示:
4.4计算示例:

4.5拓展:
增加屏幕旋转:
在 Android的 Settings->Sound and Display中有 Orientation这一设置项。当选中时,反转手机,手机屏幕会随之旋转,一般只可以旋转90度。
这一 settings设置是在文件 SoundAndDisplaySettings.java中,该项对应的键字符串为:
1. private static final String KEY_ACCELEROMETER = "accelerometer" ;
其默认值保存在 xml文件中,默认是 Enable。 UI程序初始化时会根据其值是否在复选框中打勾(代码在 onCreate函数中):
1. protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
2. …
3. mAccelerometer = (CheckBoxPreference) findPreference(KEY_ACCELEROMETER);
4. mAccelerometer.setPersistent(false );
5. …
6. }
当用户改变了该值时,会保存起来:
1. public boolean onPreferenceTreeClick(PreferenceScreen preferenceScreen, Preference preference) {
2. …
3. } else if (preference == mAccelerometer) {
4. Settings.System.putInt(getContentResolver(),
5. Settings.System.ACCELEROMETER_ROTATION,
6. mAccelerometer.isChecked() ? 1 : 0 );
7. …
8. }
文件 frameworks/policies/base/phone/com/android/internal/policy/impl/PhoneWindowManager.java中的 SettingsServer会随时监控其值,对用户设置做出反应:
1. public void update() {
2. ContentResolver resolver = mContext.getContentResolver();
3. boolean updateRotation = false ;
4. synchronized (mLock) {
5. …
6. int accelerometerDefault = Settings.System.getInt(resolver,
7. Settings.System.ACCELEROMETER_ROTATION, DEFAULT_ACCELEROMETER_ROTATION);
8. if (mAccelerometerDefault != accelerometerDefault) {
9. mAccelerometerDefault = accelerometerDefault;
10. updateOrientationListenerLp();
11. }
12. …
13. }
14.
上述是设置生效流程。当 Orientation设置 Enable时,会发生什么呢?
在 PhoneWindowManager.java有个 Listener,它会根据 Sensor判别出的旋转方向,调用 WindowManager.setRotation让屏幕进行旋转。另外,当应用程序显示禁止屏幕旋转时则不会旋转,见函数 needSensorRunningLp()。
1. class MyOrientationListener extends WindowOrientationListener {
2. MyOrientationListener(Context context) {
3. super (context);
4. }
5.
6. @Override
7. public void onOrientationChanged( int rotation) {
8. // Send updates based on orientation value
9. if ( true ) Log.i(TAG, "onOrientationChanged, rotation changed to " +rotation);
10. try {
11. mWindowManager.setRotation(rotation, false ,
12. mFancyRotationAnimation);
13. } catch (RemoteException e) {
14. // Ignore
15. }
16. }
17. }
18. MyOrientationListener mOrientationListener;
19. boolean useSensorForOrientationLp( int appOrientation) {
20. if (appOrientation == ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_SENSOR) {
21. return true ;
22. }
23. if (mAccelerometerDefault != 0 && (
24. appOrientation == ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_USER ||
25. appOrientation == ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_UNSPECIFIED)) {
26. return true ;
27. }
28. return false ;
29. }
30.
31. /*
32. * We always let the sensor be switched on by default except when
33. * the user has explicitly disabled sensor based rotation or when the
34. * screen is switched off.
35. */
36. boolean needSensorRunningLp() {
37. if (mCurrentAppOrientation == ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_SENSOR) {
38. // If the application has explicitly requested to follow the
39. // orientation, then we need to turn the sensor or.
40. return true ;
41. }
42. if (mAccelerometerDefault == 0 ) {
43. // If the setting for using the sensor by default is enabled, then
44. // we will always leave it on. Note that the user could go to
45. // a window that forces an orientation that does not use the
46. // sensor and in theory we could turn it off... however, when next
47. // turning it on we won't have a good value for the current
48. // orientation for a little bit, which can cause orientation
49. // changes to lag, so we'd like to keep it always on. (It will
50. // still be turned off when the screen is off.)
51. return false ;
52. }
53. return true ;
54. }
在 WindowOrientationListener(见文件 javaframeworks/base/core/java/android/view/WindowOrientationListener.java)中会监听Sensor的值,对旋转方向进行判断,然后调用抽象方法 onOrientationChanged,因此,只要在子类 Listener中重新实现这个函数即可对四个不同方向做出响应(见上面让屏幕旋转即是一例)。
遗憾的是在 Donut和 Éclair中,对旋转方向的识别只给出了 90度旋转,在 Froyo中增加了一个 270度旋转,不支持 180度即倒立的操作。
可以在修改下面代码,判断来自于 Gsensor的值,识别出旋转方向:
1. public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent event) {
2. float [] values = event.values;
3. float X = values[_DATA_X];
4. float Y = values[_DATA_Y];
5. float Z = values[_DATA_Z];
6. float OneEightyOverPi = 57 .29577957855f;
7. float gravity = ( float ) Math.sqrt(X*X+Y*Y+Z*Z);
8. float zyangle = ( float )Math.asin(Z/gravity)*OneEightyOverPi;
9. int rotation = - 1 ;
10. if ((zyangle <= PIVOT_UPPER) && (zyangle >= PIVOT_LOWER)) {
11. // Check orientation only if the phone is flat enough
12. // Don't trust the angle if the magnitude is small compared to the y value
13. float angle = ( float )Math.atan2(Y, -X) * OneEightyOverPi;
14. int orientation = 90 - ( int )Math.round(angle);
15. // normalize to 0 - 359 range
16. while (orientation >= 360 ) {
17. orientation -= 360 ;
18. }
19. while (orientation < 0 ) {
20. orientation += 360 ;
21. }
22. // Orientation values between LANDSCAPE_LOWER and PL_LOWER
23. // are considered landscape.
24. // Ignore orientation values between 0 and LANDSCAPE_LOWER
25. // For orientation values between LP_UPPER and PL_LOWER,
26. // the threshold gets set linearly around PIVOT.
27. if ((orientation >= PL_LOWER) && (orientation <= LP_UPPER)) {
28. float threshold;
29. float delta = zyangle - PIVOT;
30. if (mSensorRotation == Surface.ROTATION_90) {
31. if (delta < 0 ) {
32. // Delta is negative
33. threshold = LP_LOWER - (LP_LF_LOWER * delta);
34. } else {
35. threshold = LP_LOWER + (LP_LF_UPPER * delta);
36. }
37. rotation = (orientation >= threshold) ? Surface.ROTATION_0 : Surface.ROTATION_90;
38. } else {
39. if (delta < 0 ) {
40. // Delta is negative
41. threshold = PL_UPPER+(PL_LF_LOWER * delta);
42. } else {
43. threshold = PL_UPPER-(PL_LF_UPPER * delta);
44. }
45. rotation = (orientation <= threshold) ? Surface.ROTATION_90: Surface.ROTATION_0;
46. }
47. } else if ((orientation >= LANDSCAPE_LOWER) && (orientation < LP_LOWER)) {
48. rotation = Surface.ROTATION_90;
49. } else if ((orientation >= PL_UPPER) || (orientation <= PORTRAIT_LOWER)) {
50. rotation = Surface.ROTATION_0;
51. }
52. if ((rotation != - 1 ) && (rotation != mSensorRotation)) {
53. mSensorRotation = rotation;
54. onOrientationChanged(mSensorRotation);
55. }
56. }
57. }
在Froyo中,对上述算法进行了修改,让其报出270度的旋转方向。
Android Sensor 屏幕360度旋转实现
修改下面函数
1. void android.view.WindowOrientationListener SensorEventListenerImp.onSensorChanged(android.hardware.SensorEvent event)
2. float[] values = event.values;
3.
4. float X = values[_DATA_X];
5. float Y = values[_DATA_Y];
6. float Z = values[_DATA_Z];
7. //For fixing the problem of Sensor change the window orientation error but the sensor game is no problem.
8. float OneEightyOverPi = 57.29577957855f;
9. float gravity = (float) Math.sqrt(X*X+Y*Y+Z*Z);
10. float zyangle = (float)Math.asin(Z/gravity)*OneEightyOverPi;
11. int rotation = -1;
12. if ((zyangle <= PIVOT_UPPER) && (zyangle >= PIVOT_LOWER)) {
13. // Check orientation only if the phone is flat enough
14. // Don't trust the angle if the magnitude is small compared to the y value
15. float angle = (float)Math.atan2(Y, -X) * OneEightyOverPi;
16. int orientation = 90 - (int)Math.round(angle);
17. // normalize to 0 - 359 range
18. while (orientation >= 360) {
19. orientation -= 360;
20. }
21. while (orientation < 0) {
22. orientation += 360;
23. }
24. Log.i("Tiger","orientation="+orientation);
25. //确定由角度与屏幕方向的对应范围
26. if(orientation > 325 || orientation <= 45){
27. rotation = Surface.ROTATION_0;
28. }else if(orientation > 45 && orientation <= 135){
29. rotation = Surface.ROTATION_270;
30. }else if(orientation > 135 && orientation < 225){
31. rotation = Surface.ROTATION_180;
32. }else {
33. rotation = Surface.ROTATION_90;
34. }
35.
36. Log.i("Tiger","mSensorRotation="+mSensorRotation+" , rotation="+rotation);
37. if ((rotation != -1) && (rotation != mSensorRotation)) {
38. mSensorRotation = rotation;
39. onOrientationChanged(mSensorRotation);
40. }
41. }
使用动画,需要在“res\anim\”目录下创建xml文件,示例代码如下:
1. <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2. <rotate xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
3. android:duration="1500"
4. android:fromDegrees="0.0"
5. android:interpolator="@android:anim/linear_interpolator"
6. android:pivotX="50.0%"
7. android:pivotY="50.0%"
8. android:toDegrees="360.0" />
2.使用Matrix矩阵旋转,示例代码如下:
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
matrix.setRotate(float degrees, float px, float py);
canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap, matrix, null);
五、实训总结
刚开始接触Android感觉到它很有意思,在界面开发上和web也可以形成了相通的架构,更加方便,视觉上也是非常的酷,在前期我通过的大量的Android SDK开发范例大全中的例子以及Android提供的APIDEMOS进行学习,尽管例子之间的连接比较零散,不过通过这些例子的学习我可以学习到了很多和以前java上相通的思想。 我在为期半个月的实习中学到了很多在课堂上根本就学不到的知识,收益非浅.现在我对这半个月的实习做一个工作小结。
1通过半个月的android实习,基本掌握了Android应用程序开发的一般流程。对常用控件基本掌握其用法,对其事件的监听方法也基本掌握。学习Android不仅是对前沿开发技术的了解,也是对编程知识的一次提升。
2通过学习Android的控件、布局、Activity、Service等一系列基础知识,对整个Android的开发有了大致的了解。例如: 要的布局(或者控件) ,在学习界面中,我发现Android为我们提供了很好的类似反射机制,通过Layout文件夹下的配置文件,可以快速的形成界面,在配置文件可以设置属性或者样式都是很快捷方便。对比较特殊的界面也可以通过处理嵌入到指定的界面,同样你可以通过java代码直接创建View进行添加,不过这种方式比较复杂。对一些点击、选中、按键等处理的事件,界面之间的 跳转Intent管理,通过Bundle对数据在界面之间进行传输。
3在手机交互式通信服务中,学习了Android手机之间进行短信发送、广播、对广播的监听、服务等,在Service类中没有context,可以通过Handler来每秒反复运行,自动送出系统广播信息,同时在这里我们也知道可以设计一个常用的变量类,设计一个当前的CurrentActivity这个变量进行控制,进行处理。
在Android编程过程中巩固熟悉了Java的编程。由于Android应用程序的开发离不开Java的支持,所以基础的Java知识是必须的。Android系统是基于Linux的手机操作系统平台,要深入系统的学习Android,不仅仅是有Java和Android应用开发,必须要具备Linux,C/C++高级编程才能深入的涉及Android Framework和Android内核开发。成为Android开发的高素质人才。所以,在后续对Android的学习中可能会看一些较底层的书籍。
由于这次实习时间较短,对于Android应用程序的高级编程讲的很少,是这次实习中的不足。要想开发一些好的应用程序,还需要更多的知识支持。在做实习最后的项目时,遇到了很多平时没有遇到或者没有特别关注的问题,如常见的Activity忘记注册,对SD卡存取需要权限,在写SQL语句时细微的错误就可能导致程序运行错误。这些问题只有自己在实际开发中才能体会到并且解决,并且在解决后可以长时间的记住。
通过Android的实习,我们在大四毕业前,我们又掌握了一项新的前沿的开发技能,也有了更多的发展方向,这在以后的找工作的过程中无疑为我们增加了砝码,也可以成为我们的一项兴趣爱好,可以根据我们自己的需要设计一些小的程序。总之,在这次实习中,我获得了很多东西,提高了自己的编程技巧和编程方法,并且认识了Android应用程序的开发,以及加深了对Java的认识。
最后,通过实习,我收获了很多东西,特别是编程方面的,这对即将毕业的我们来说,这次实习是一次较为珍贵的充电。
