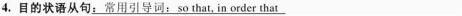状语从句
什么是状语?
状语修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子。
1. Naturally, our grandparents were pleased to get our phone call.
2. We worked hard, from sunrise to sunset.
3. To help my disabled aunt, I spend an hour working in her house every day 4. Seen from a distance, the farmhouse looked deserted.
5. I know how to light a camp fire because I had done it before. 状语的位置比较灵活,可以位于句首、句末或句中。
什么是状语从句?
状语从句指句子用作状语时,起副词作用的句子。它可以修饰谓语、非谓语动词、定语、状语或整个句子。状语从句一般由连词(从属连词)引导,也可以由词组引起。 根据其作用状语从句可分为:
1.时间状语从句
2.地点状语从句
3.原因状语从句
4.条件状语从句
5.目的状语从句
6.让步状语从句
7.比较状语从句
8.方式状语从句
9.结果状语从句
状语从句的时态特点
一般情况下,时间和条件状语从句的谓语动词一般用“一般现在时”表示“一般将来时”,用“现在完成时”表示“将来完成时”。
I will call you as soon as I arrive in Beijing.
As soon as I have finished this work, I will go home.
If he comes back, please let me know.
1. 时间状语从句
常用引导词:when, as, while, as soon as, before, after, since , till, until
…… …… 余下全文